Bacterial Growth and Metabolism Overview
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
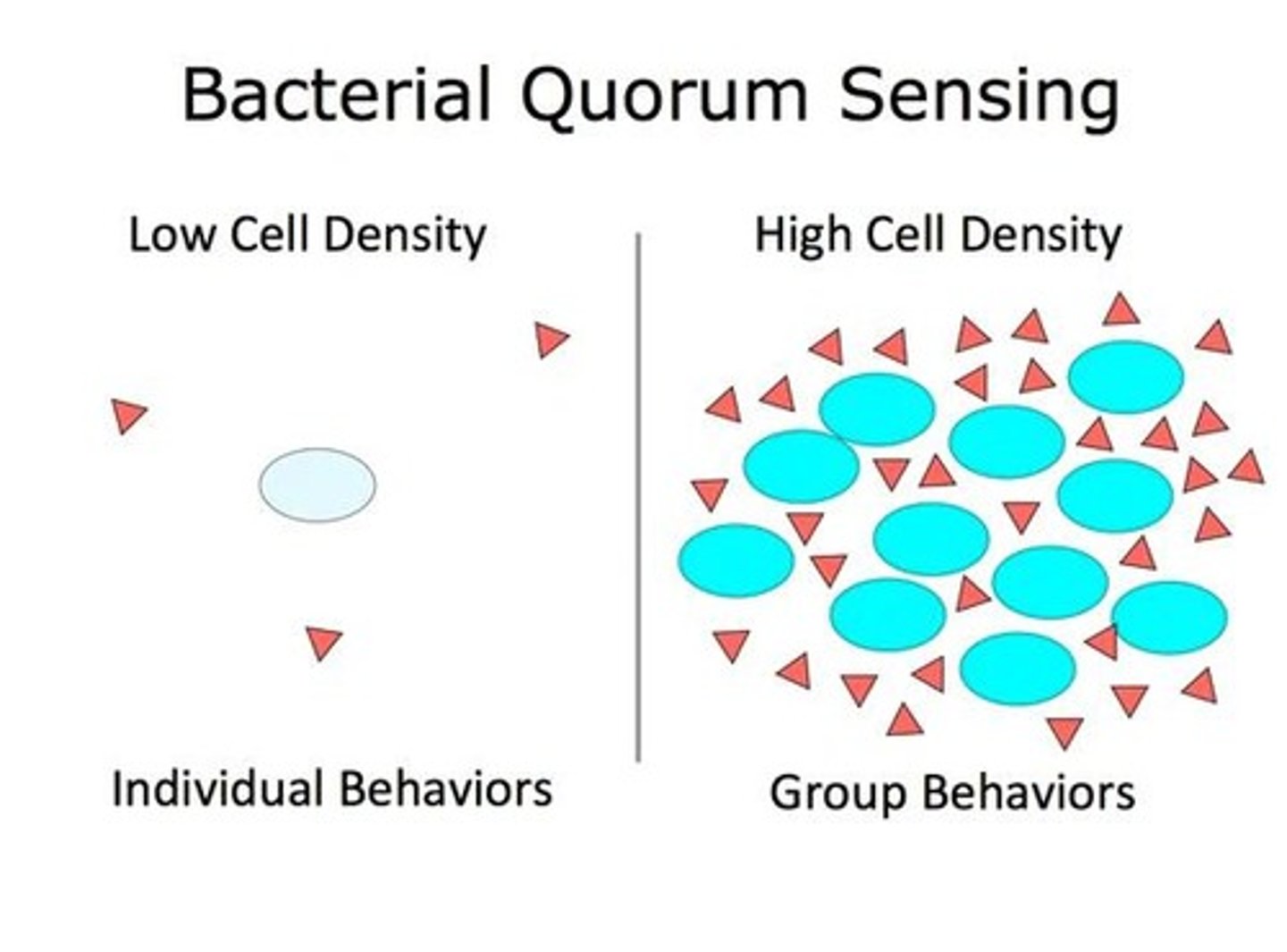
Quorum sensing
Regulatory system controlling bacterial community behaviors.
Lag phase
Initial growth stage with no cell division.
Log phase
Rapid cell division and exponential growth.
Stationary phase
Growth rate equals death rate, stable population.
Decline phase
Cell death exceeds growth, population decreases.
Biofilms
Structured communities of bacteria adhering to surfaces.
Sporulation
Process of forming spores for survival.
Catabolism
Breakdown of molecules to release energy.
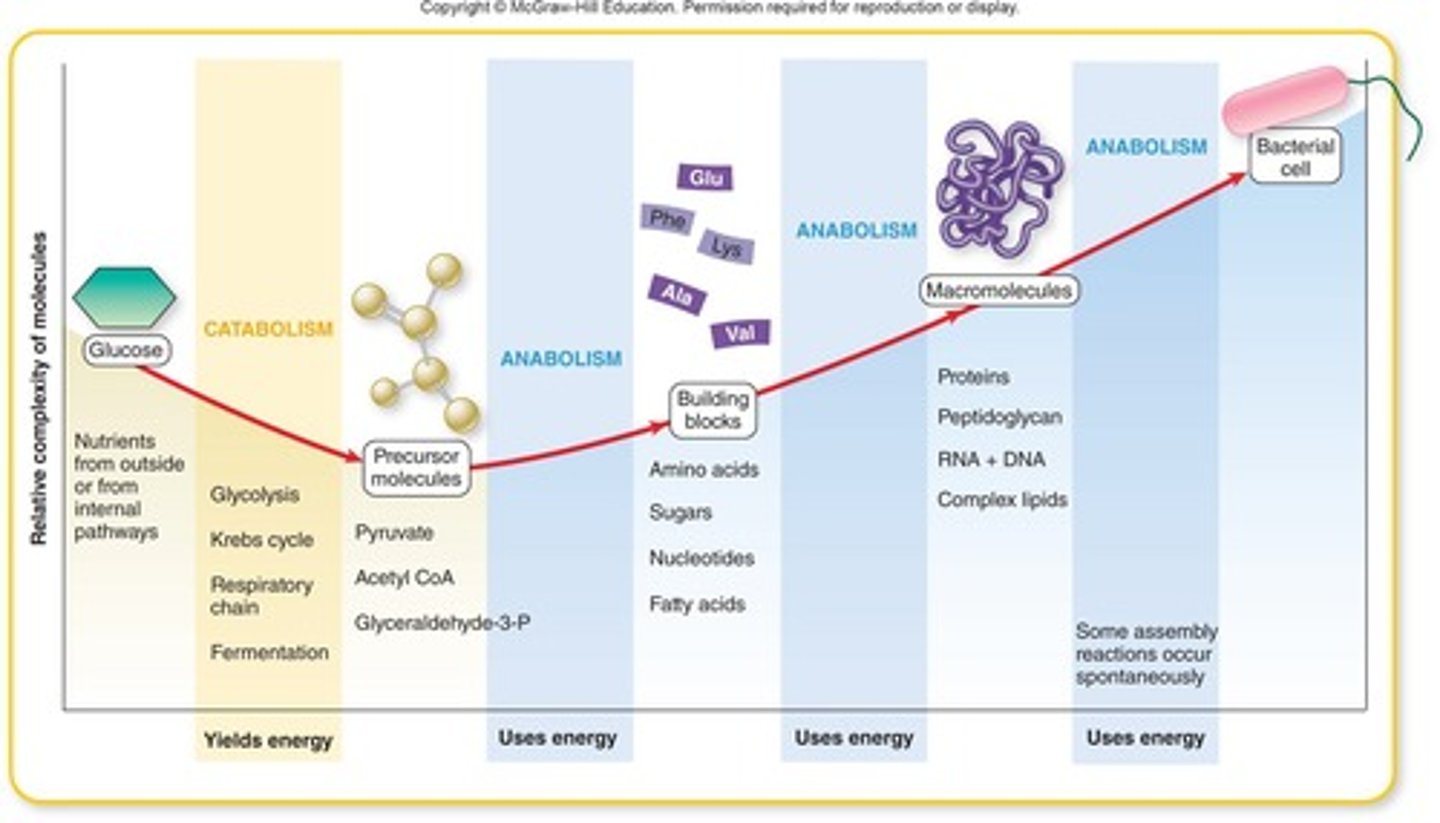
Anabolism
Synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones.
Exergonic reactions
Reactions that release energy during progress.
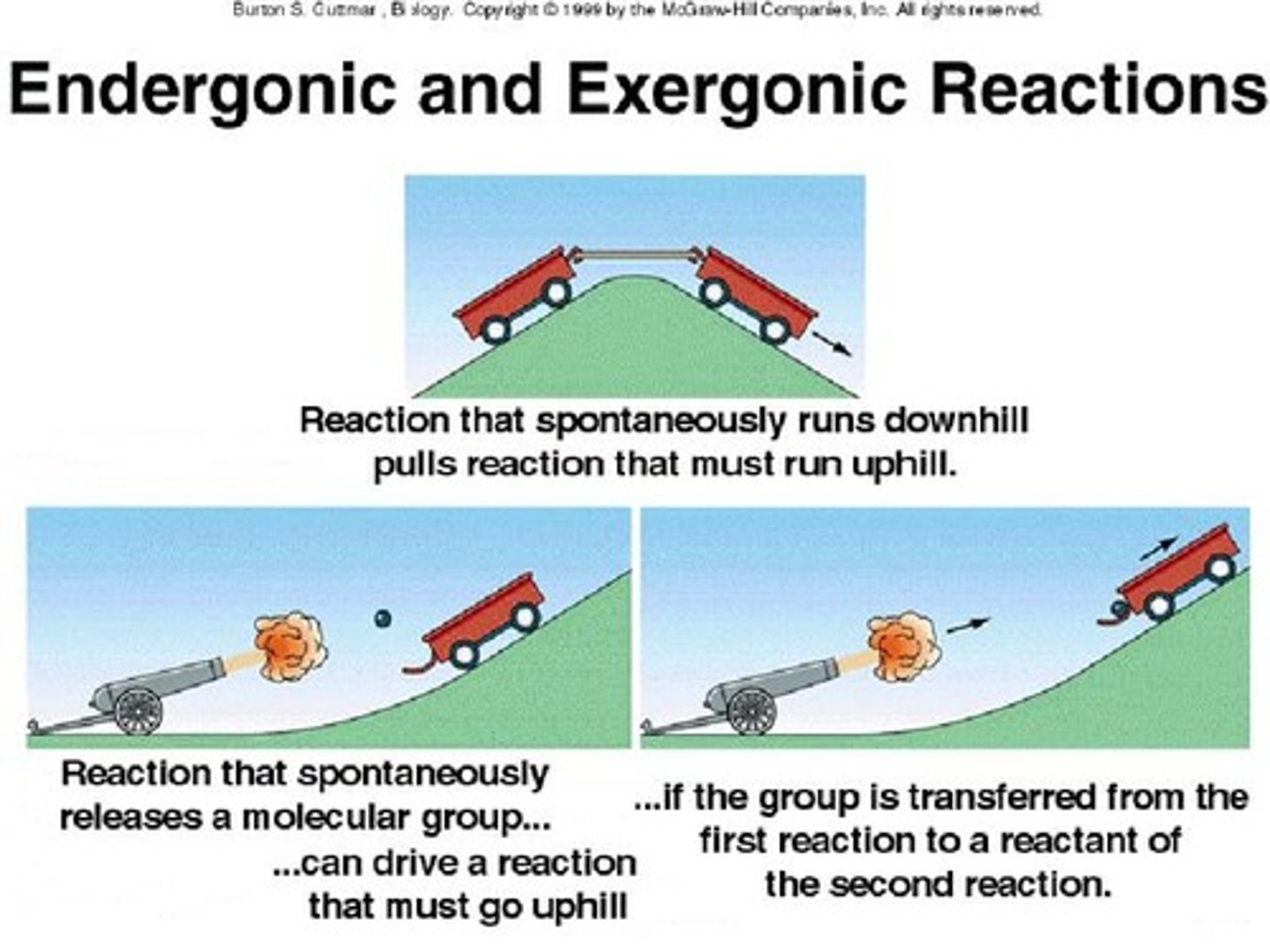
Endergonic reactions
Reactions requiring energy input to proceed.
Phototrophy
Energy capture through light in biochemical reactions.
Chemotrophy
Energy yield from chemical bond reactions.
Organotrophy
Metabolism using organic molecules as food.
Lithotrophy
Metabolism using inorganic molecules as food.
Aerobic organotrophy
Organic molecule metabolism with oxygen present.
Anaerobic organotrophy
Organic molecule metabolism without oxygen.
Aerobic lithotrophy
Inorganic molecule metabolism with oxygen present.
Anaerobic lithotrophy
Inorganic molecule metabolism without oxygen.
Biochemical pathways
Series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in cells.
Entropy
Measure of disorder, relates to energy use.
Metabolism
All chemical reactions within a living organism.
ATP
Primary energy currency of cells.
Reducing power
Electrons stored in NADH, FADH2, NADPH.
Precursor metabolites
Building blocks for macromolecules.
Catabolites
Intermediates produced during catabolism.
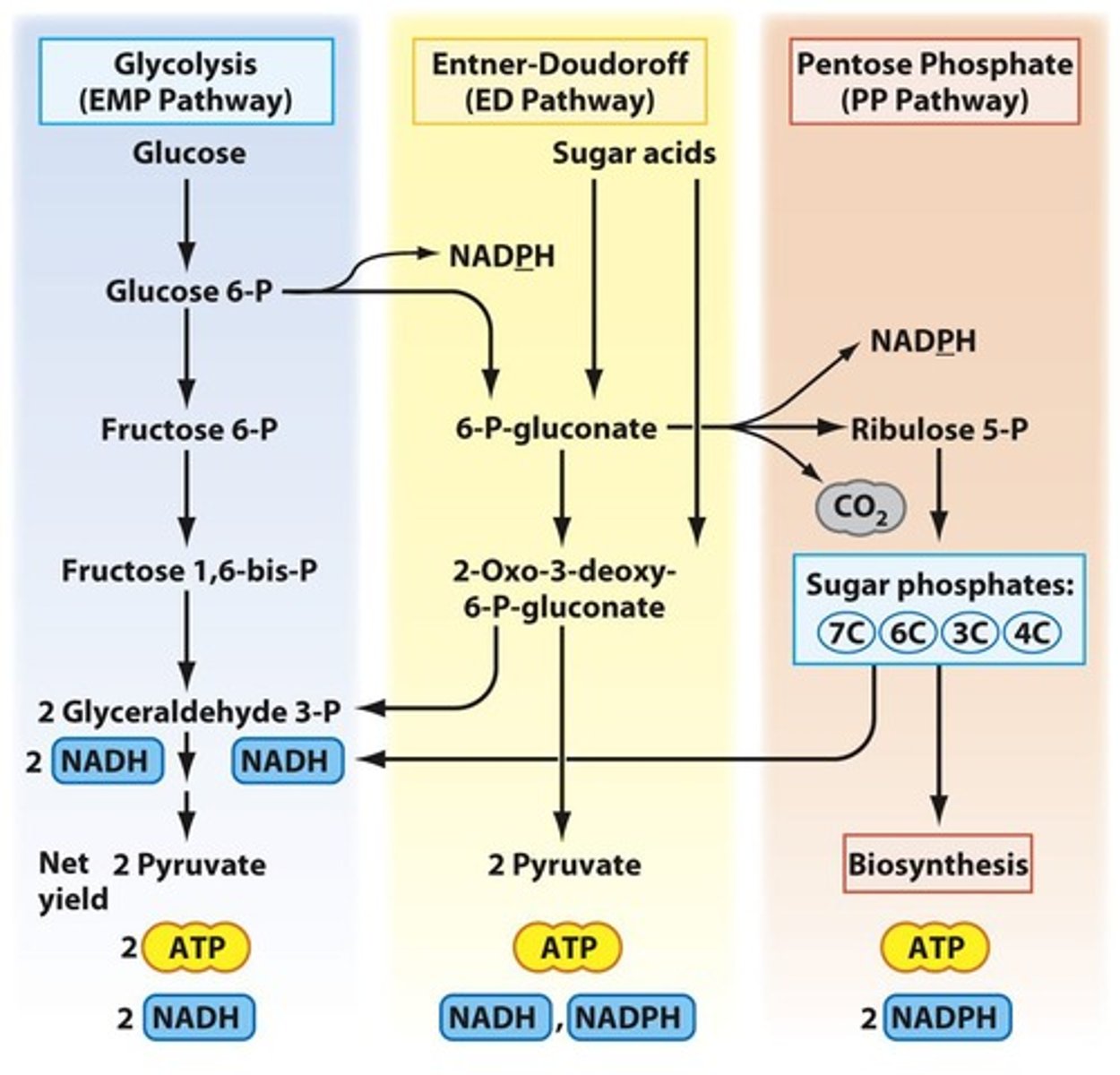
Glycolysis
Main glucose catabolism pathway in bacteria.
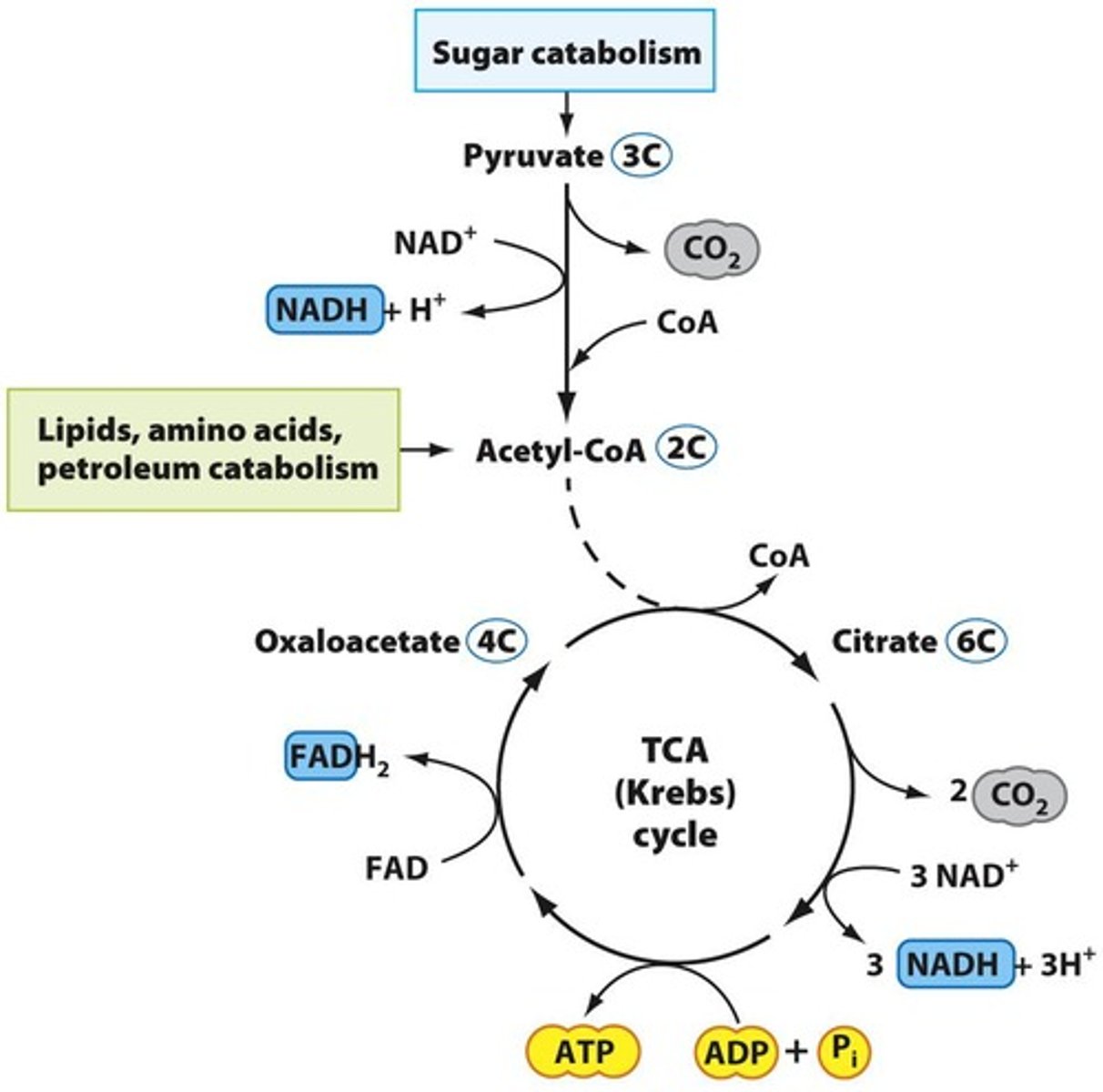
TCA cycle
Tricarboxylic acid cycle for energy release.
Energy-yielding reactions
Reactions that release energy during metabolism.
Enzymes
Catalysts that speed up metabolic reactions.
Activation energy
Energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
Exergonic reaction
Chemical reaction that releases energy.
Endergonic reaction
Chemical reaction that requires energy input.
Common energy carriers
Molecules like ATP and NADH used in metabolism.
NADH
Electron carrier used to produce ATP.
ATP formation
Requires energy input (+ΔG) for synthesis.
ATP breakdown
Releases energy when ATP is hydrolyzed (-ΔG).
Glycolysis stages
Stage 1 consumes 2 ATP; Stage 2 yields 2 ATP.
Pyruvate
End product of glycolysis, central metabolite.
Fermentation
Anaerobic process for energy production.
Respiration
Aerobic process for energy production.
Carbon skeletons
Frameworks for building macromolecules from metabolites.
Bacterial caloric intake
15% of calories from digestive tract bacteria.
Specificity of enzymes
Each enzyme catalyzes a specific reaction.
Anaerobic
Occurs without oxygen consumption during fermentation.
Lactic Acid
Common waste product of lactic acid fermentation.
Ethanol
Alcohol produced during alcoholic fermentation.
Microbial Wastes
Byproducts that inhibit further microbial growth.
Food Preservation
Using fermentation to extend food shelf life.
Diagnostic Media
Growth media containing indicators for acid production.
Phenol Red Dye
pH indicator that changes color with acidity.
Krebs Cycle
Also known as TCA cycle, breaks down pyruvate.
Acetyl CoA
Product formed from pyruvate before entering Krebs Cycle.
FADH2
Electron carrier produced in the Krebs Cycle.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ATP formation driven by proton gradient.
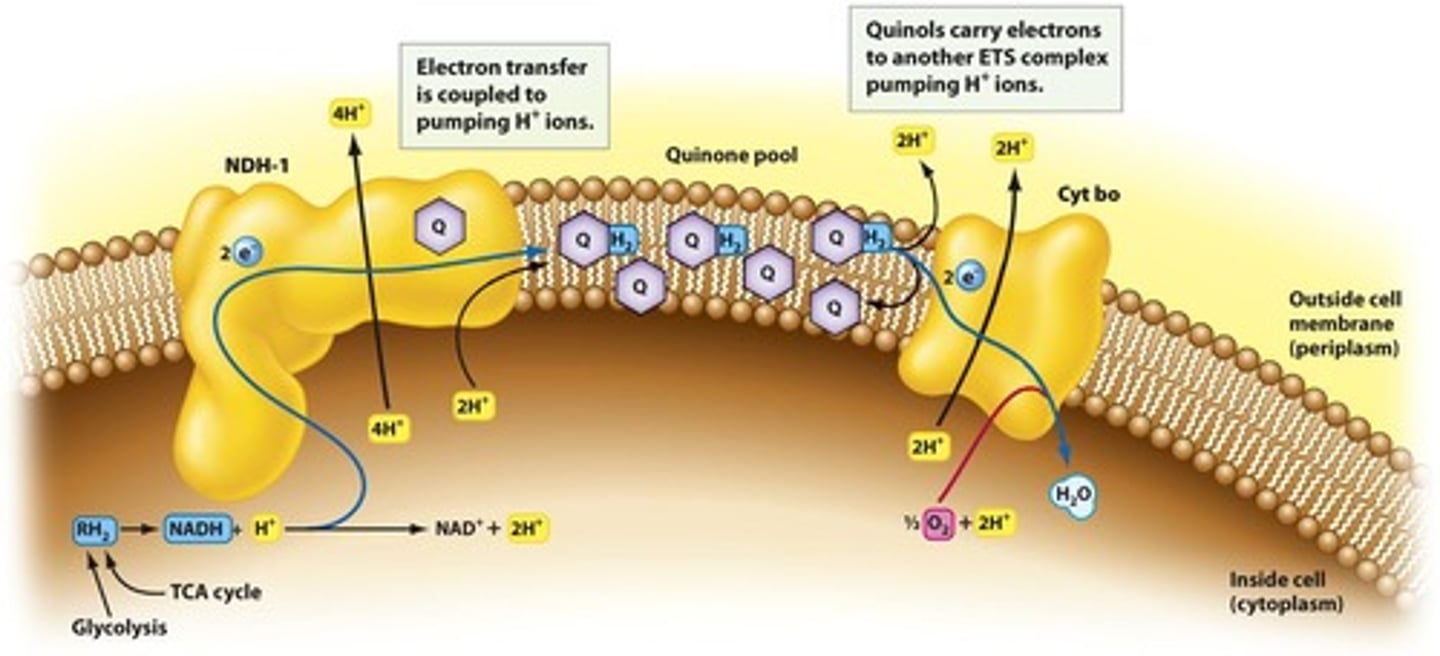
Electron Transport System (ETS)
Pathway for electron transfer to oxygen.
Proton Motive Force
Energy generated by H+ ion gradient.
ATP Synthase
Enzyme synthesizing ATP using proton flow.
Glucose Respiration Equation
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O.
ATP Yield
Respiration generates more ATP than fermentation.
Mitochondria vs. Bacteria
Mitochondria produce more ATP than bacteria.
PMF
Proton motive force; energy for cellular processes.
Anaerobic Respiration
Respiration without oxygen; uses alternative electron acceptors.
Electron Acceptors
Substances that receive electrons during respiration.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Bacteria using nitrate in anaerobic conditions.
Autotrophy
Carbon fixation; converting CO2 into organic compounds.
Photosynthesis
Process converting light energy into chemical energy.
Oxygenic Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis that produces oxygen from water splitting.
Photolysis of Water
Splitting water to release oxygen during photosynthesis.
Carbon Fixation
Transformation of CO2 into glucose and metabolites.
Lithotrophic Carbon Fixation
CO2 fixation from mineral oxidation by lithotrophs.
Reverse TCA Cycle
Pathway for CO2 fixation in some lithotrophs.
Calvin Cycle
Pathway for CO2 fixation in phototrophs.
Biosynthesis
Building cell parts; requires energy and nutrients.
Energy Yielding Metabolism
Reactions that release energy for cellular functions.
NADPH
Electron carrier used in biosynthetic reactions.
ATP Hydrolysis
Process releasing energy for cellular activities.
Essential Elements
Nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus needed for biosynthesis.
Facultative Anaerobes
Organisms that can switch between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.