sociology 101 exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:01 PM on 6/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
Social stratification
the division of nations as well as the layering of groups of people within a nation
* system divides group into layers due to their relative property, power, and prestige
* applies to nations, people in a nation, and society
* every society stratifies its members
* system divides group into layers due to their relative property, power, and prestige
* applies to nations, people in a nation, and society
* every society stratifies its members
2
New cards
Systems of Stratification
* slavery
* a form of social stratification when people own each other
* was caused based on debt, crime and war
* in some places slavery was temporary, slavery was not inheritable, slaves were not powerless or poor
* caste
* a form of social stratification in which birth determines peoples statuses which are life long
* race as a caste
* when slavery ended in US it was replaced by racial caste system
* race is marked for everyone at birth
* class
* social mobility
* movement up class ladder
* a class system allows the movement of social mobility
* an individual can change their class by what they achieve
* a form of social stratification when people own each other
* was caused based on debt, crime and war
* in some places slavery was temporary, slavery was not inheritable, slaves were not powerless or poor
* caste
* a form of social stratification in which birth determines peoples statuses which are life long
* race as a caste
* when slavery ended in US it was replaced by racial caste system
* race is marked for everyone at birth
* class
* social mobility
* movement up class ladder
* a class system allows the movement of social mobility
* an individual can change their class by what they achieve
3
New cards
Marx vs Weber in what determines social class
* Marx
* believed that social class depends on a single factor: peoples realationship to the means of production (the tools, factories, and and investment capital used to produce wealth)
* recognized other groups (farmers and peasants, lumpenproletariat, and middle class) but did not consider these groups social classes because they lacked class consciousness (a shared identity based on their relationship to the means of production)
* Weber
* believed social class has three components: property, power, and persige
* Property (wealth): is significant in determining a persons standing in society (agreed with Marx) also believed ownership is not the only significant aspect of property
* Power: the ability to control others even over their objections (agreed with MArx when said property is a major source of power) weber added that its not the only source
* Prestige: derived from property and power; property can bring prestige and vice verse
* believed that social class depends on a single factor: peoples realationship to the means of production (the tools, factories, and and investment capital used to produce wealth)
* recognized other groups (farmers and peasants, lumpenproletariat, and middle class) but did not consider these groups social classes because they lacked class consciousness (a shared identity based on their relationship to the means of production)
* Weber
* believed social class has three components: property, power, and persige
* Property (wealth): is significant in determining a persons standing in society (agreed with Marx) also believed ownership is not the only significant aspect of property
* Power: the ability to control others even over their objections (agreed with MArx when said property is a major source of power) weber added that its not the only source
* Prestige: derived from property and power; property can bring prestige and vice verse
4
New cards
Functionalism
* social darwinism
* Davis and Moore hypothesis and its critiques
* Believed stratification of society is inevitable because:
* 1. For society to function, its positions must be filled
* 2.Some positions are more important than others
* 3. The important positions must be filled by the more qualified people
* 4. To motivate the more qualified people to fill these positions, they must offer greater rewards
* Tumins critque to davis and moore
* believed davis and moore did not attempt to justify social inequality
* question why people know that the positions that offer higher rewards are more important
* also said that if davis and moores stratification worked then society will be meritocracy (positions awarded based on merit)
* also said that if social stratification was funcitional then it would benifit everyone but it doesnt
* Davis and Moore hypothesis and its critiques
* Believed stratification of society is inevitable because:
* 1. For society to function, its positions must be filled
* 2.Some positions are more important than others
* 3. The important positions must be filled by the more qualified people
* 4. To motivate the more qualified people to fill these positions, they must offer greater rewards
* Tumins critque to davis and moore
* believed davis and moore did not attempt to justify social inequality
* question why people know that the positions that offer higher rewards are more important
* also said that if davis and moores stratification worked then society will be meritocracy (positions awarded based on merit)
* also said that if social stratification was funcitional then it would benifit everyone but it doesnt
5
New cards
Conflict theoretical explanations of universal stratification
Mosca
* argued that every society will be stratified by power
* 3 ideas:
* no society can exist unless its organized, requires leadership to coordinate peoples actions
* leadership requires inequalities of power, people lead while others follow
* human nature is self-centered, people in power will use their positions to seize greater rewards for themselves
Marx
* believed people who are in power are not in power because of superior traits
* predict workers will revolt
Lenski
* suggested surplus is key
* said functionalist are right when it comes to groups that dont accumulate a surplus ( these societies share their resources to those who take on important tasks)
* believed whenever groups gain power, it uses that power to extract what it can from groups beneath it
* argued that every society will be stratified by power
* 3 ideas:
* no society can exist unless its organized, requires leadership to coordinate peoples actions
* leadership requires inequalities of power, people lead while others follow
* human nature is self-centered, people in power will use their positions to seize greater rewards for themselves
Marx
* believed people who are in power are not in power because of superior traits
* predict workers will revolt
Lenski
* suggested surplus is key
* said functionalist are right when it comes to groups that dont accumulate a surplus ( these societies share their resources to those who take on important tasks)
* believed whenever groups gain power, it uses that power to extract what it can from groups beneath it
6
New cards
Social hegemony
consent of being dominated by other groups
7
New cards
Labor Surplus, unemployment
* functionalist interpretation
* conflict interpretation
* conflict interpretation
8
New cards
Maintenance of stratification
* Ideology vs force
9
New cards
Stratification in the US, GReat Britiam and the former soviet union
* US
* similar to GB
* GB
* has a class system that can be divided in lower, middle and upper
* population is evenly divided between middle and lower
* makes class idstinctions based on material goods
* education displays generational class system
* Soviet Union
* basis of stratification was membership to communist party
* socialism
* captialism
* similar to GB
* GB
* has a class system that can be divided in lower, middle and upper
* population is evenly divided between middle and lower
* makes class idstinctions based on material goods
* education displays generational class system
* Soviet Union
* basis of stratification was membership to communist party
* socialism
* captialism
10
New cards
Global Stratification
* most industerlized
* examples: USa, Canada, GB, France, Germany, Swiss, Japan, etc.
* \
* industerlizing
* 20 percent of earths land and 16 percent of its people
* people have lower incomes
* ex: former soviet union
* least industerlized
* 68% of worlds people and 49% of earths land
* poverty
* Colonialism
* the process in which one nation takes over another nation making a colony of it to exploit labor and natural recourses usually
* purpose was to establish economic colonies
* World systems theory
* a theory of how economic an political connections develop among nations
* this theory led to 4 nations:
* core nations: countries that were industrialized first (Britian, france, etc)
* semiperiphery: Mediterranean countries depended on trade with core nations
* fringe nations: eastern European countries which sold cash crops to core nations
* external area: these nations were left of the development of capitalism
* dependency theory
* neocolonialism
* the economic and political dominance of the least industerlized mations by the most industerlized nations
* examples: USa, Canada, GB, France, Germany, Swiss, Japan, etc.
* \
* industerlizing
* 20 percent of earths land and 16 percent of its people
* people have lower incomes
* ex: former soviet union
* least industerlized
* 68% of worlds people and 49% of earths land
* poverty
* Colonialism
* the process in which one nation takes over another nation making a colony of it to exploit labor and natural recourses usually
* purpose was to establish economic colonies
* World systems theory
* a theory of how economic an political connections develop among nations
* this theory led to 4 nations:
* core nations: countries that were industrialized first (Britian, france, etc)
* semiperiphery: Mediterranean countries depended on trade with core nations
* fringe nations: eastern European countries which sold cash crops to core nations
* external area: these nations were left of the development of capitalism
* dependency theory
* neocolonialism
* the economic and political dominance of the least industerlized mations by the most industerlized nations
11
New cards
The culture of poverty and arguments against it
* the assumptions that the values and behaviors of the poor make them fundamentally different from other people, that these factors are largely responsible for their poverty and that parents perpetuate provery across generations by passing these characteristics to their children
12
New cards
The role of multinational corporations
* companies that operate across many national; boundaries to help maintain that global dominance of Most Industralized Nations
13
New cards
Social Class
* wealth
* the total value of everything someone owns minus the debts
* power
* the ability to carry out your will, even over the resistance of others
* prestige
* respect or regard
* status inconsistency
* ranking high or low on all three dimensions of social class
* the total value of everything someone owns minus the debts
* power
* the ability to carry out your will, even over the resistance of others
* prestige
* respect or regard
* status inconsistency
* ranking high or low on all three dimensions of social class
14
New cards
contradictory class locations
erik wrights term for a position in the class structure that generates contradictory interest
15
New cards
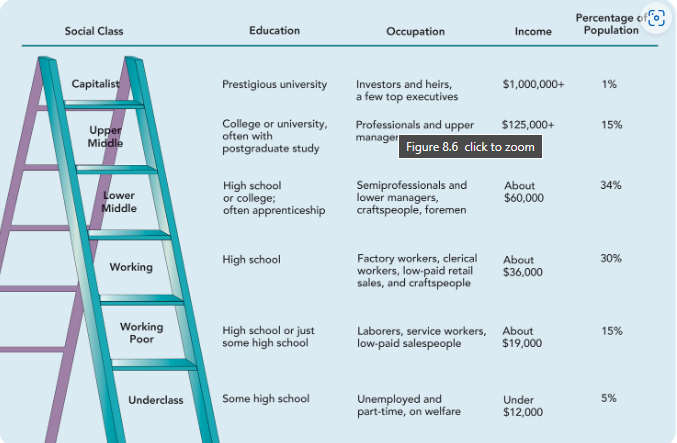
Six class model - Weber
* top of class has more property, power and prestige and vise versa; education is also a primary measure of class
16
New cards
Consequences of social class
* politics
* upper class are most likely to vote republican
* lower class are most likely to vote democrat
* religion
* Episcopalians are most likely to attract middle and upper class while baptist attract the lower class
* health
* higher social class= improved health
* lower class experience with drugs and alcohol and life is hard on poor and have the worst mental health
* family life
* upper class place emphasis on family tradition
* lower class emphasises chilfres to follow rules and obeyt authority
* upper class are most likely to vote republican
* lower class are most likely to vote democrat
* religion
* Episcopalians are most likely to attract middle and upper class while baptist attract the lower class
* health
* higher social class= improved health
* lower class experience with drugs and alcohol and life is hard on poor and have the worst mental health
* family life
* upper class place emphasis on family tradition
* lower class emphasises chilfres to follow rules and obeyt authority
17
New cards
Structal social mobility
* movement up or down a social ladder that is due more to changes in the structure of society than actions of individuals (social mobility)
* intergenerational mobility
* the change that family members make in social class from one generation to the next
* upward social mobility
* movement up a social ladder
* downward social mobility
* movement down a social ladder
* intergenerational mobility
* the change that family members make in social class from one generation to the next
* upward social mobility
* movement up a social ladder
* downward social mobility
* movement down a social ladder
18
New cards
Poverty
* Poverty line
* the official measure of poverty; calculated to include incomes that are less than 3 times a low-cost food budget
* feminization of poverty
* women only average 74% of what men earn
* a condition of US poverty in which most poor families are headed by women
* the official measure of poverty; calculated to include incomes that are less than 3 times a low-cost food budget
* feminization of poverty
* women only average 74% of what men earn
* a condition of US poverty in which most poor families are headed by women
19
New cards
myths about poor and welfare
* the belief that due to limitless possibilities anyone can get ahead if tried hard enough
20
New cards
Ethnicity vs race
* ethnicity
* having distinctive cultural characteristics
* race
* a group whose inherited physical characteristics distinguish it from other groups
* having distinctive cultural characteristics
* race
* a group whose inherited physical characteristics distinguish it from other groups
21
New cards
minorities groups vs dominant groups
* minority
* people who are singled out for unequal treatment and who regard themselves as objects of collective discrimination
* dominant
* the group with the most power, high social status and greatest privileges
* people who are singled out for unequal treatment and who regard themselves as objects of collective discrimination
* dominant
* the group with the most power, high social status and greatest privileges
22
New cards
Racism
prejudice and discrimination on the basis of race
23
New cards
prejudice
an attitude or prejudging usually in a negative way
24
New cards
discrimination
* individual
* an act of unfair treatment directed agianst an individual or a group, personal
* institutional
* negative treatment of minority group that is built into a societys institutions; systemic discrimination
* an act of unfair treatment directed agianst an individual or a group, personal
* institutional
* negative treatment of minority group that is built into a societys institutions; systemic discrimination
25
New cards
Theories of prejudice
* scapegoat
* an individual or group unfairly blamed for someone else’s troubles
* authoritarian personality
* adorns’s term for people who are prejudiced and raked high on scales of conformity, intolerance, insecurity, respect for authority, and submissiveness to superiors
* cognitive theory
* social learning theory
* an individual or group unfairly blamed for someone else’s troubles
* authoritarian personality
* adorns’s term for people who are prejudiced and raked high on scales of conformity, intolerance, insecurity, respect for authority, and submissiveness to superiors
* cognitive theory
* social learning theory
26
New cards
Functionalism
* three functions of discrimination
* ethnocentrism of subordinate group
* ethnocentrism of subordinate group
27
New cards
conflict theory
* surplus labor
* split labor market
* group interests
* Marxist perspective
* split labor market
* group interests
* Marxist perspective
28
New cards
Symbolic interactionlism
* selective perception
* sterotypes and self fuffiling propecies
* sterotypes and self fuffiling propecies
29
New cards
Global patterns of intergroups
* genocide
* \
* population transfer
* the forced transfer of a minority group
* internal colonialism
* the policy of exploiting minority groups for economic gain
* segregation
* the policy of keeping racial-ethnic groups apart
* assimilation
* the process of being absorbed into the mainstream culture
* multi-culturalism
* a policy that permits or encourages ethnic differences
* \
* population transfer
* the forced transfer of a minority group
* internal colonialism
* the policy of exploiting minority groups for economic gain
* segregation
* the policy of keeping racial-ethnic groups apart
* assimilation
* the process of being absorbed into the mainstream culture
* multi-culturalism
* a policy that permits or encourages ethnic differences
30
New cards
Race and ethnicity in US
* White Europeans
* white immigrants to the US whose cultures differ from WASP culture
* African Americans
* rising expectation
* the sense that better conditions are soon to follow, which, if unfiffiled, increases frustration
* continued gains
* 11% of AA in the US is in the HOR
* current losses
* only 3 AA sentors
* race vs class
* wilson debate
* Latinos
* umbrella terms that lumps spanish speaking cultures together
* largest ethnic group in US
* Asian Americans
* financial success
* Native Americans
* the invisble minority
* casinos
* white immigrants to the US whose cultures differ from WASP culture
* African Americans
* rising expectation
* the sense that better conditions are soon to follow, which, if unfiffiled, increases frustration
* continued gains
* 11% of AA in the US is in the HOR
* current losses
* only 3 AA sentors
* race vs class
* wilson debate
* Latinos
* umbrella terms that lumps spanish speaking cultures together
* largest ethnic group in US
* Asian Americans
* financial success
* Native Americans
* the invisble minority
* casinos
31
New cards
Sex vs gender
* sex
* biological charecristics that distinguish females and males
* gender
* the behaviors ad attitudes that a society considers proper for its males and females
* biological charecristics that distinguish females and males
* gender
* the behaviors ad attitudes that a society considers proper for its males and females
32
New cards
biology vs culture
* biology
* nature
* culture
* nurture
* nature
* culture
* nurture
33
New cards
orgins of patriarcy
* men as a group dominatinf women as a group; authority is vested in males
* women became caretakers which made them “inferior”
* women became caretakers which made them “inferior”
34
New cards
feminism
* the philosophy that men and women should be politically, economically, and socially equal’ organized activities on behalf of this principlr
35
New cards
gender inequality
* education
* more women attend college than men
* health care
* doctors are less serious towards women than men
* workplace
* pay gap
* women getting less pay then men
* glass ceiling
* the mostly invisible barrier that keeps women from advancing to the top levels at work
* glass escalators
* more women attend college than men
* health care
* doctors are less serious towards women than men
* workplace
* pay gap
* women getting less pay then men
* glass ceiling
* the mostly invisible barrier that keeps women from advancing to the top levels at work
* glass escalators
36
New cards
Inequalities of aging
* social Contruction of aging
* in US elders are forec to retire at 65, other cultures respect elders
* graying of America
* life expectancy rate increaded in US; growing age population
* ageism
* discrimination based on age
* functionalism vs conflict theory
\
* in US elders are forec to retire at 65, other cultures respect elders
* graying of America
* life expectancy rate increaded in US; growing age population
* ageism
* discrimination based on age
* functionalism vs conflict theory
\