Module 2 Dynamics (Part Two)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Kinetic Energy Formula
½mv2

Gravitational Potential Energy Formula
mgh

Mechanical Energy Formula
KE + GPE
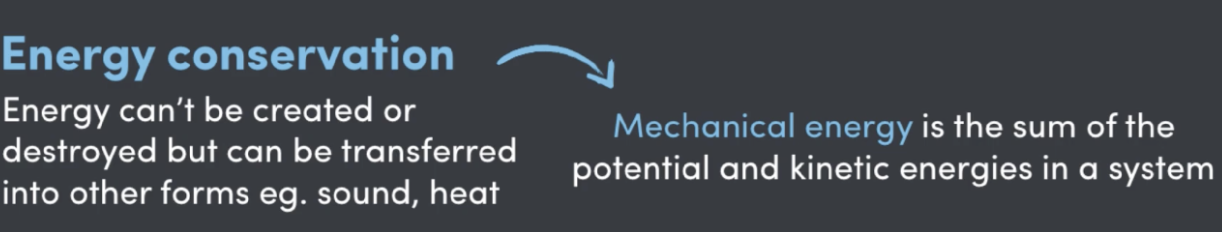
What to remember for KE, GPE and ME?
Measured in joules
When height is zero, GPE = 0
When velocity is zero, KE = 0
Use the law of conservation to your advantage in questions
Change in KE or change in GPE
1/2mv2 - 1/2mu2
Power Definition
Amount of energy consumed per unit time.
Power is change in energy over time.
Power is measured in watts.
Power Formula
Work/Time
or
(Force x Displacement)/Time
Therefore meaning Power = Force x Velocity
What does work equal when lifting an object.
W = mgh
Power is change in energy over time, therefore…
½mv2 / t
or
mgh / t
or
KE + GPE / t
If not given time use…
P = FV
You can assume what due to gravity?
Acceleration
What is ‘p’?
Momentum
p = ?
mv
What units is momentum measured in?
Momentum in (kg m/s ) units = mass (kg) units x velocity (m/s ) units.
In a closed system, mv before an interaction such as a collision = ?
mv after the interaction.
What is also conserved?
In an elastic collision, kinetic energy is also conserved, so 1/2mv2 before =1/2mv2 after.
If momentum = 0 before…
It will equal zero after. For e.g two ice skaters start off still.
For objects that collide and combine…
m1v1 (before) + m2v2 (before) = mv (after)
What must you always do?
Consider direction.
For objects that collide and separate…
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
For explosions…
mv (before) = m1v1 (after) + m2v2 (after)
When do you need to resolve vectors in collisions?
When collision occurs in 2 dimensions. (Not just in a straight line.)
Impulse = ?
Force x Time
Unit for Impulse?
Newton Seconds (Ns).
Impulse is also…
Change in momentum.
Change in momentum formula?
m(v-u)
In force time graph…
Area under curve = impulse.
This means…
Change in momentum = Force x Time
and
Time = Change In Momentum / Force
and
Force = Change In Momentum / Time
In terms of Impulse…
Force = Impulse / Time
and
Time = Impulse / Force
In inelastic collisions?
Objects colliding have less kinetic energy after the collision. You can easily tell if a collision is elastic or inelastic by seeing whether kinetic energy has been conserved. If it has, it is elastic and if it has not, then it is inelastic.