EARLY MEDIEVAL ART in the West - OTTONIAN EMPIRE
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Otto I Presenting Magdeburg Cathedral to Christ,

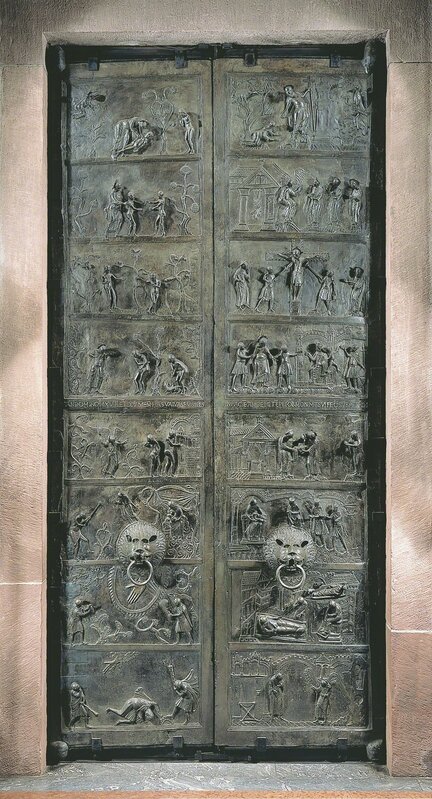
Bishop Bernward, Bronze doors, St. Michael’s Church,

Church of St. Cyriakus, Genrode

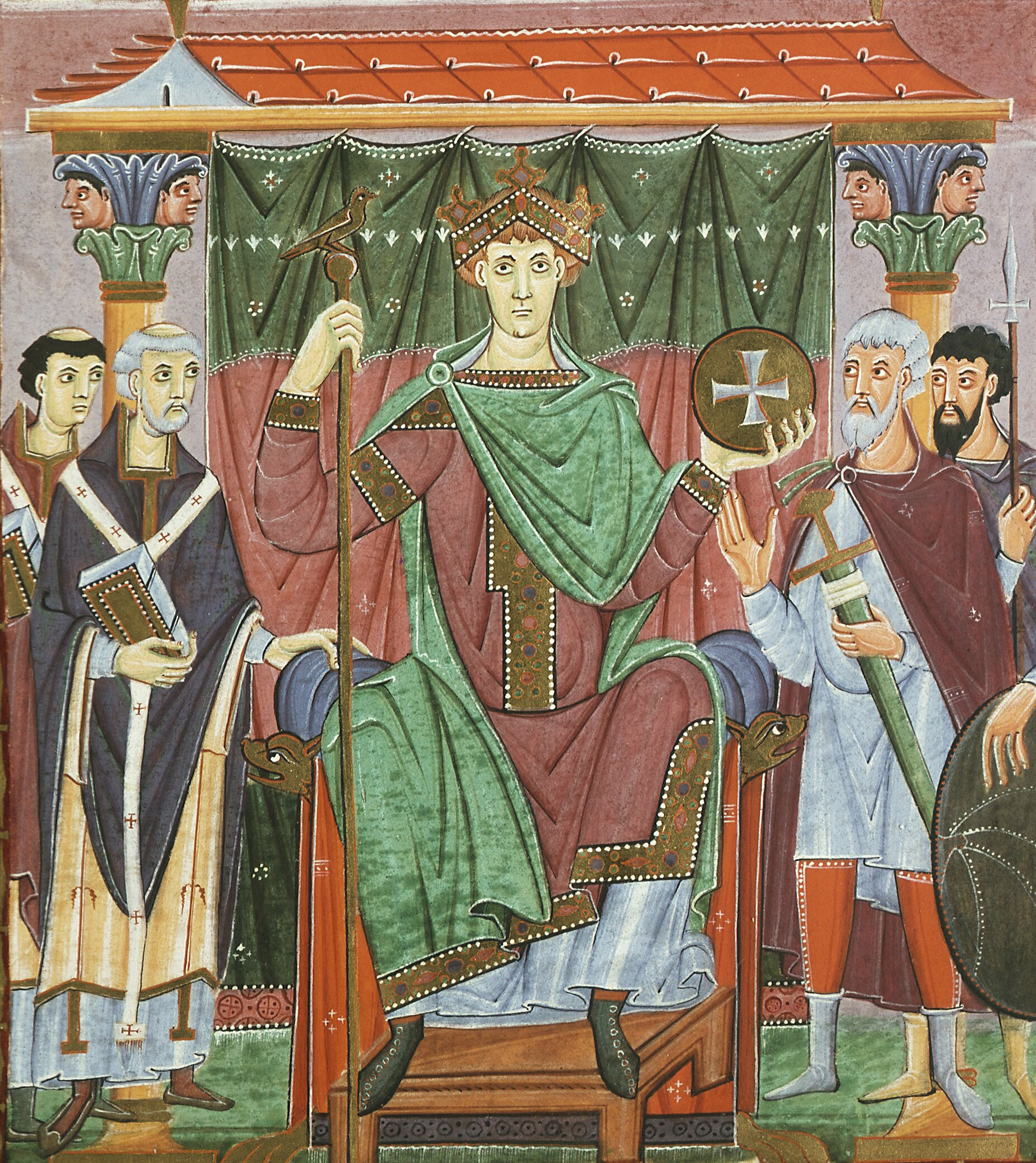
Page with Otto III Enthroned, Liuthar Gospels

Page with Christ Washing the Feet of his Disciples, Aachen Gospel Book of Otto III

Cover of the Aachen Gospel Book of Otto III

illuminated manuscripts
hand-written books with painted decoration that generally includes precious metals such as gold or silver
codex
A codex is a written manuscript bound together, typically on parchment or papyrus. Codices were the preferred format for longer writings in the 3rd and 4th centuries A.D., replacing scrolls and wax tablets. Codices allowed for writing on both sides of a page, made it easier to find specific passages, and could contain lengthy works.
parchment /vellum
archment is a general term for an animal skin which has been prepared for writing or printing. Parchment has been made for centuries, and is usually calf, goat, or sheep skin. The term vellum from the French veau refers to a parchment made from calf
carpet page
A carpet page is a full page in an illuminated manuscript containing intricate, non-figurative, patterned designs.[1] They are a characteristic feature of Insular manuscripts, and typically placed at the beginning of a Gospel Book. Carpet pages are characterised by mainly geometrical ornamentation which may include repeated animal forms.
cloisonné
Cloisonné is the technique of creating designs on metal vessels with colored-glass paste placed within enclosures made of copper or bronze wires, which have been bent or hammered into the desired pattern
interlace
Interlace is a decorative element found in medieval art. In interlace, bands or portions of other motifs are looped, braided, and knotted in complex geometric shapes. metalwork such as brooches and belt buckles

Sutton Hoo, England
Sutton Hoo is the site of two Anglo-Saxon cemeteries, Archaeologists have been excavating the area since 1938
Staffordshire Hoard
The Staffordshire Hoard is the largest hoard of Anglo-Saxon gold and silver metalwork. It consists of almost 4,600 items and metal fragments, amounting to a total of 5.1 kg of gold, 1.4 kg of silver and some 3,500 pieces of garnet cloisonné jewelry
decorated initial / inhabited initial
Inhabited Initial: An initial letter that contains human or animal figures that are decorative only and bear no relation to the text.

Four evangelists (Matthew, Mark, Luke, John)
monasteries

a building or buildings occupied by a community of monks living under religious vows.
scriptorium (scriptoria)

A scriptorium was a room in a medieval monastery where scribes copied and illuminated manuscripts
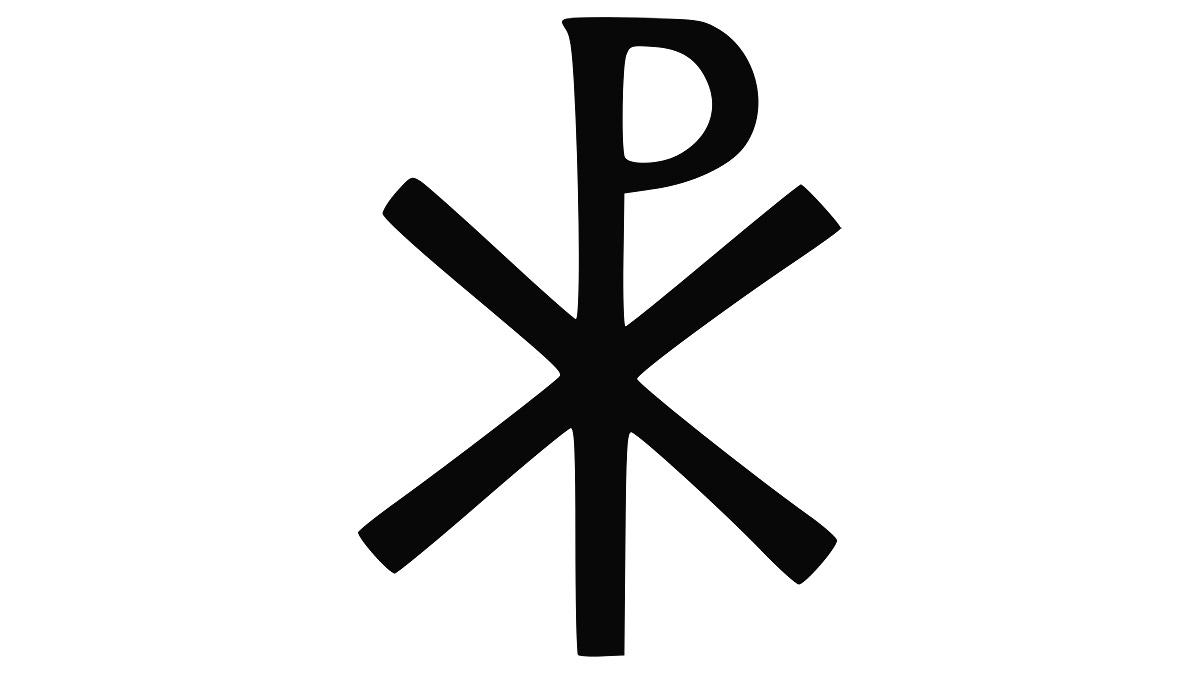
chi rho
Christian art is the Chi-Rho. It is created by superimposing the first two letters (XP) of the Greek word for Christ, ΧΡΙΣΤΟΣ. The monogram, also called a “christogram”. Jesus Christ, but is also considered to be a common representation of the crucifixion scene
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was the ruler of the Carolingian Empire. He is important for ushering in the Carolingian Renaissance, spreading Christianity, and creating the concept of the "Divine Right of Kings."
Aachen
It was a royal residence of the emperor Charlemagne, and it served as the principal coronation site of Holy Roman emperors and of German kings from the Middle Ages to the Reformation. 1 Holy Roman Emperors were crowned Kings of the Germans from 936 to 1531
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages and lasted for almost a thousand years until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars
Otto I (the Great)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ottothegreatHultonArchiveStringer-5c68669546e0fb0001f93419.jpg)
The first ruler of the Holy Roman Empire, the medieval forerunner of the modern state of Germany
westwork
A westwork is usually broader than the width of the nave and aisles. It is sometimes used synonymously with narthex

gold leaf

gospels

The gospels are the first four books of the New Testament in the Bible, which tell the story of Jesus Christ's life and death