PSY101
1/96
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environmen
our sensation of the world
sensation, perception
sensation
our sense organs' detection of and responses to external stimulus energy
Perception
the way sensory information is organized, interpreted, and consciously experienced. which includes how an individual recognizes and interpreter sensory information
sensation without perception
-Blindsight -Asomatognosia
perception without sensation
-hallucinations -phantom limbs
If brain activity is responsible for consciousness, what happens when the brain dies?
-coma -consciousness
What is sleep?
period of rest/ natual loss of consciousness
How many stages of sleep are there?
5 stages
Stage 1 sleep
-Light sleep -The brain emits theta waves--> consistent with a relaxed state of wakefulness
Stage 2 of sleep cycle
small bursts of activities spindles, nonrem sleep
stage 3 and 4 of sleep cycle
Delta waves, deep sleep, night terrors, sleep walking, and talking
Stage 5 of sleep
REM sleep
function of sleep
energy conservation,
body restoration,
memory consolidation
Function of REM sleep
-give brain opportunity to analyze day's events and work through emotional events or problems(threat rehearsal)
Activation synthesis : explains why humans have dreams
biological rhythms
periodic physiological fluctuations-- circadian rhythm
factors in the environment; sleep and wakefulness, body temperature, hormone secretion, and more.
how do drugs affect behaviour
interfere with the way neurons send, receive, and process signals via neurotransmitters
Mechanism of drug action
drugs can be agonists and antagonists
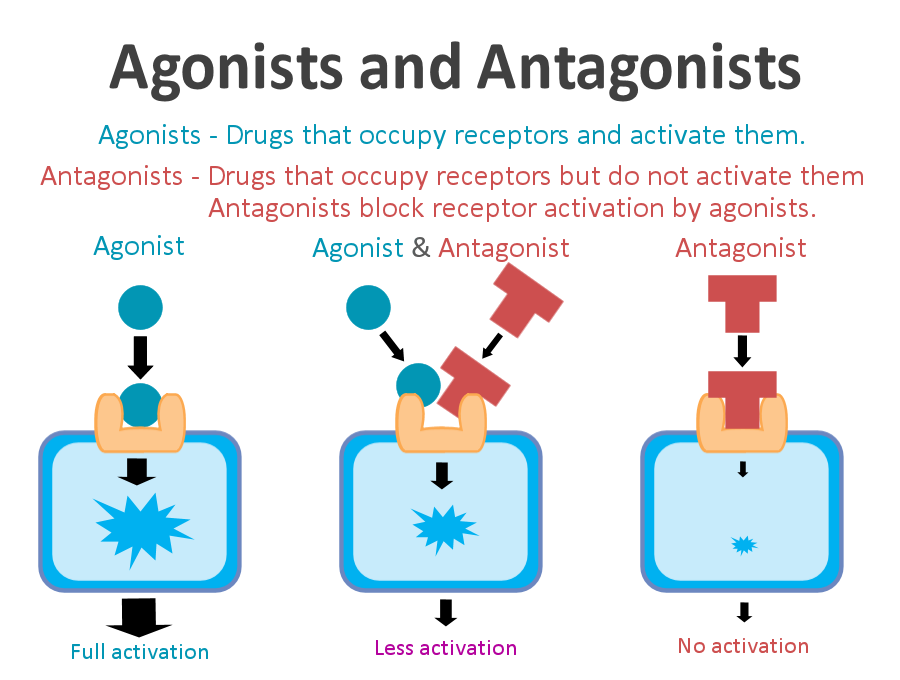
Drugs can be agonists
activates certain receptors in the brain.
mimic actions of neurotransmitters
ex: heroin, oxycodone, methadone, block reuptake of transmitters
drugs can be: antagonists
stop neural firing
block or decrease the action of neurotransmitters
ex: block reception, speed up metabolism
catergories of psychoactive drugs
drugs that change your mental state
depressants -stimulants -opioids -hallucinogens
depressants
drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
stimulants
increase neural activity and speed up body functions
agonist for various transmitters
Hallucinogens
Drugs that alter moods, thoughts, and sense perceptions including vision, hearing, smell, and touch
factors that influence effect
context, past experiences with drug, user physical and psychological state
why do we have sensory system processing
-processing sensory information
All sensory systems are related to a long history of previous adaptations to environmental conditions.
steps of sensory system
5 steps
step 1 sensory system
stimulus
step 2 sensory system
sensation
step 3 sensory system
transmission
APs travel to the primary cortical area for poressing
step 4 sensory system
translation
step 5 sensory system
perception and attention
chemical senses
taste (gustation) and smell (olfaction)
How do we taste things?
food particles dissolve in liquid (saliva, ingested)
enter taste pores (central pore surrounded by sensory neurons)
bind to receptor, causes depolarization
allows us to differentiate between the tastes
How do we smell things?
We breathe in the chemicals in the air, the chemicals dissolve in our mucus, the stimulate the smell receptors that produce messages and the messages are sent to our brains to give us the scent of the object(perception)
Proprioception
The ability to tell where one's body is in space.
our sense of body position
Somatosensation
The body senses, including body position, touch, skin temperature, and pain. -association with proprioception and interoception
vestibular sense
the sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance
sensation of pain
Means by which body is made urgently aware of the presence of tissue damage
how do we experience touch
Sensations begin as signals generated by touch receptors in your skin.
They travel along sensory nerves made up of bundled fibers that connect to neurons in the spinal cord.
Then signals move to the thalamus, which relays information to the rest of the brain
Pain receptors are called
Fast fibres register sharp, fast pain - Slow fibres register duller, more diffuse pain
auditory system
Responsible for hearing, balance, equilibrium, and communication skills
sensory organs
receive impulses from environment and relay impulses to brain including skin, tongue, nose, eyes, and ears
pitch perception
the aspect of hearing that allows us to tell how high or low a given tone is by its sound wavelength
2 theories of pitch perception
place theory and frequency theory
place theory of pitch perception
different portions of the basilar membrane are sensitive to sounds of different frequencies
frequency theory of pitch perception
nerve impulses sent to the brain match the frequency of the sound wave
visual system
Includes photoreceptors -light/dark and colors stem from different parts of the eye
the part of the central nervous system that is required for visual perception - receiving, processing and interpreting visual information to build a representation of the visual environment.
cones
color vision and fine detail
Rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray; necessary for peripheral and twilight vision, when cones don't respond
bottom-up processing
the analysis of the smaller features to build up to a complete perception
top-down processing
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
uses models, ideas to interpret sensory information
Gestalt
an organized whole. Gestalt psychologists emphasized our tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes.
Examples of Gestalt Principles
proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, symmetry, figure-ground
Paredolia
tendency to perceive meaningful images in meaningless/random visual pattern
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, understanding, remembering, and communicating
role of attention
involves focusing awareness on a narrowed range of stimuli or events depending on our goals, past experience and areas of interes
role perception
an individual's view of how he or she is supposed to act in a given situation before the mind takes action
selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus at one time
Authomaticity
fast, effortless processing requiring little to no information
pre-attentive processing
the non conscious processing of stimuli in peripheral vision before the conscious mind starts to pay attention to any specific objects
attentive process
one that requires searching through the items in series
auditory attention
being able to focus on a single sound in the presence of many other sounds
3 types of learning
non associative, associative, observational
associative learning
learning that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning).
two types of associative learning
classical conditioning and operant conditioning
Two types of nonassociative learning
habituation and sensitization
nonassociative learning
responding after repeated exposure to a single stimulus, or event
Habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation.
Sentization
increase in behavioural response after repeated exposure to a stimulus
observational learning
learning by observing others
contiguity
the tendency to perceive two things that happen close together in time as being related
contingency
a predictive relationship between two events such that the occurrence of one event predicts the probable occurrence of the other
stimulus generalization
the tendency to respond to a stimulus that is only similar to the original conditioned stimulus with the conditioned response
ability to behave in a new situation in a way that has been learned in other similar situations.
stimulus discrimination
a learned ability to differentiate among similar products
both classical and operant conditioning
shaping (operant conditioning)
The reinforcement of closer and closer approximations of a desired response.
Chaining (operant conditioning)
reinforcing combinations of learned behaviors that are the paired together form a complex behavior.
An easy task for a normally intelligent individual but a complex, multi-step task for someone of below-average intelligence.
Malaptive Behavior
actions that prevent people from adapting, adjusting, or participating in different aspects of life
examples of malaptive behaviour
Objects / "habits"
Food (both approach and avoidance)
Exercise regimes
Hoarding
Gambling
Sex
drug addiction
the uncontrollable use of a drug to a point where it affect your brain and behaviour
motivated behavior
appetitive phrase; consummatory phrase
appetitive phase
-Characterized by person's interest in sexual activity
nonspecific
consummatory phase
direct interaction with the motivational stimulus
behavior pattern that occurs in response to a stimulus and that achieves the satisfaction of a specific drive -specifc
Wanting in the brain
The subjective experience of needing or desiring something
"Liking" in the Brain
the subjective experience of a sensation as pleasurable
endogenous opioid and oxytocin
how do we measure wanting?
operant conditioning
more dopamine in the synapse = change of behaviour
single injection of d-amphetamine
increase release of dopamine
Blocks reuptake of dopamine
when stimulated repeatedly, the DA system become sensitized
... so does behaviour
Why don't all durg encounters lead to repeated use?
Conditioned control of wanting and drug taking behaviour
post surgical pain
veteran
casual experimentation -bar smokers
what happens when animals are given drugs in a specific place
Increased initial response to the drug
Enhanced sensitization to the drug
strong , long lasting conditioned responses to that environment
Why do people relapse?
-Exposure to the environment of previous drug use -Taking the drug again (same or another) -Stress
Spontaneous Recovery
the reappearance of a learned response after extinction has occurred
observational study
-social learning
modelling
lmitating
Modelling
the process of observing and imitating a specific behavior
vicrarious learning
way of learning that allows individuals to learn from the experience of others; rewarded or punished for performing an action
how do we measure the effects of context?
classical conditioning