Special Senses Comparative Anatomy & Physiology
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
General senses
House receptors throughout body (pain, touch, pressure, etc)
Special senses
Have receptors concentrated within specific structures (taste, smell, vision, balance)
Thermoreceptors
Temperature receptors; located in dermis, skeletal muscles, liver, and hypothalamus (and more)
Mechanoreceptors
Sensitive to any stimuli that cause a physical reaction (touch); Located in epidermis, internal organs tendons, and skeletal muscles (& more)
Nocireceptors
Free nerve endings that generate the sensation of pain; Found in the dermis, within joints, covering the bones, and along the walls of blood vessels
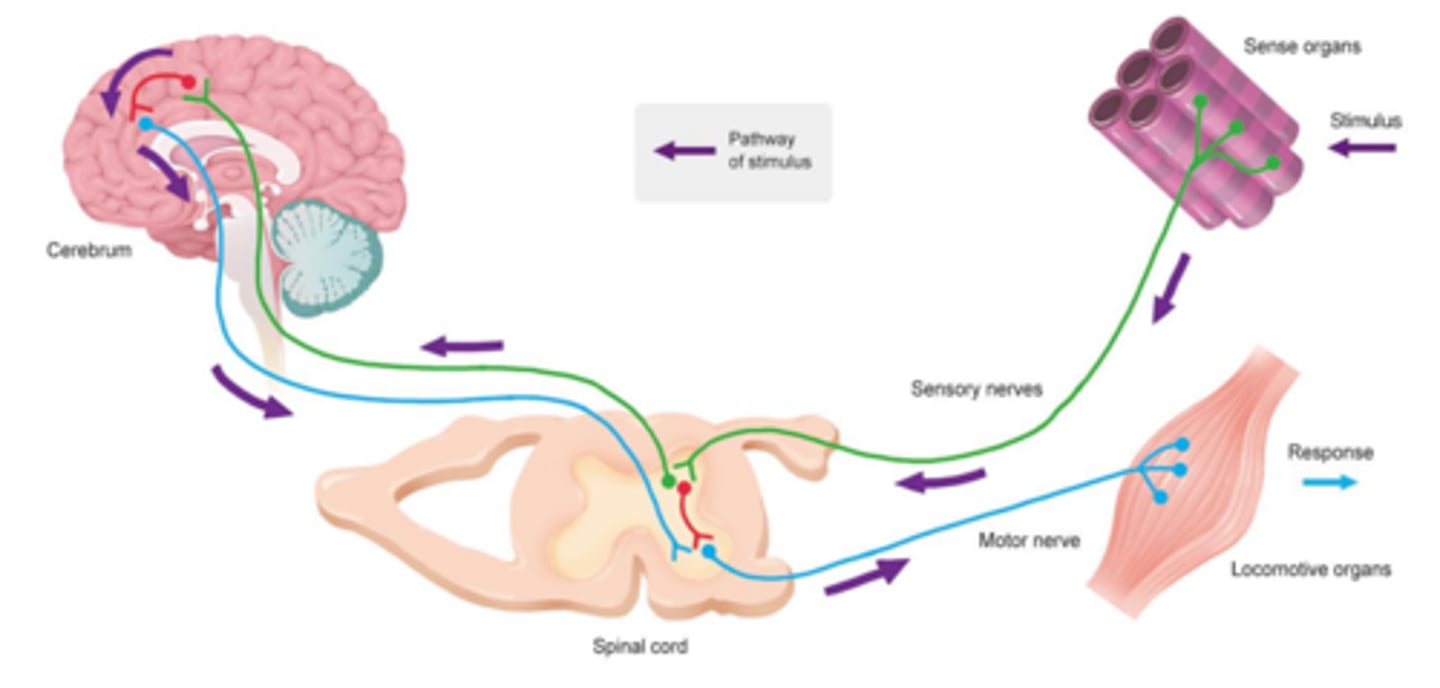
Sensory stimulus pathway
Sensory neuron -> Somatic sensory pathway -> Nerve -> Spinal cord segment -> CNS pathway -> Medulla oblongata -> sensory cortex
Eye
A special sense organ that detects visible light waves; several accessory structures help to maintain & protect it
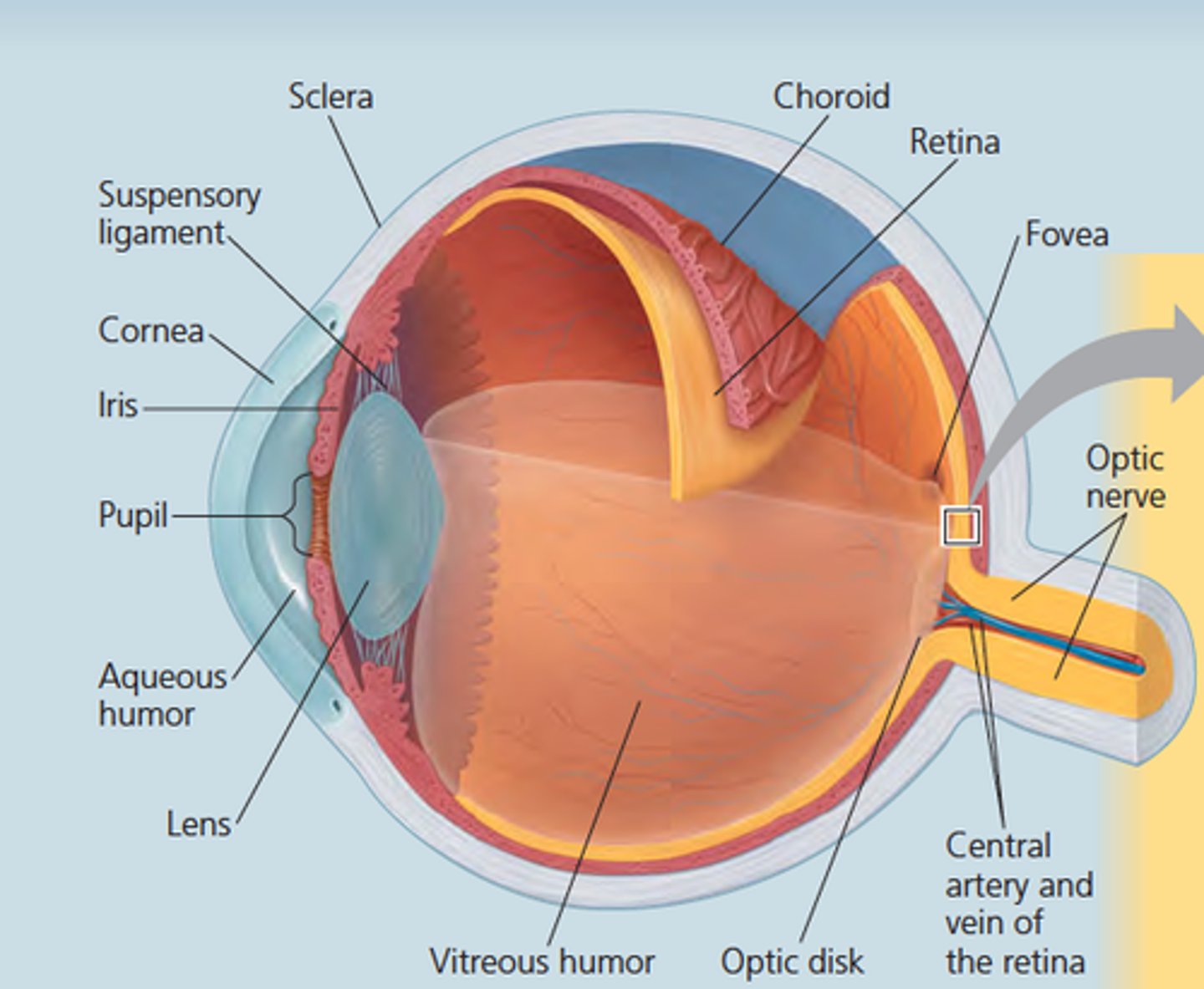
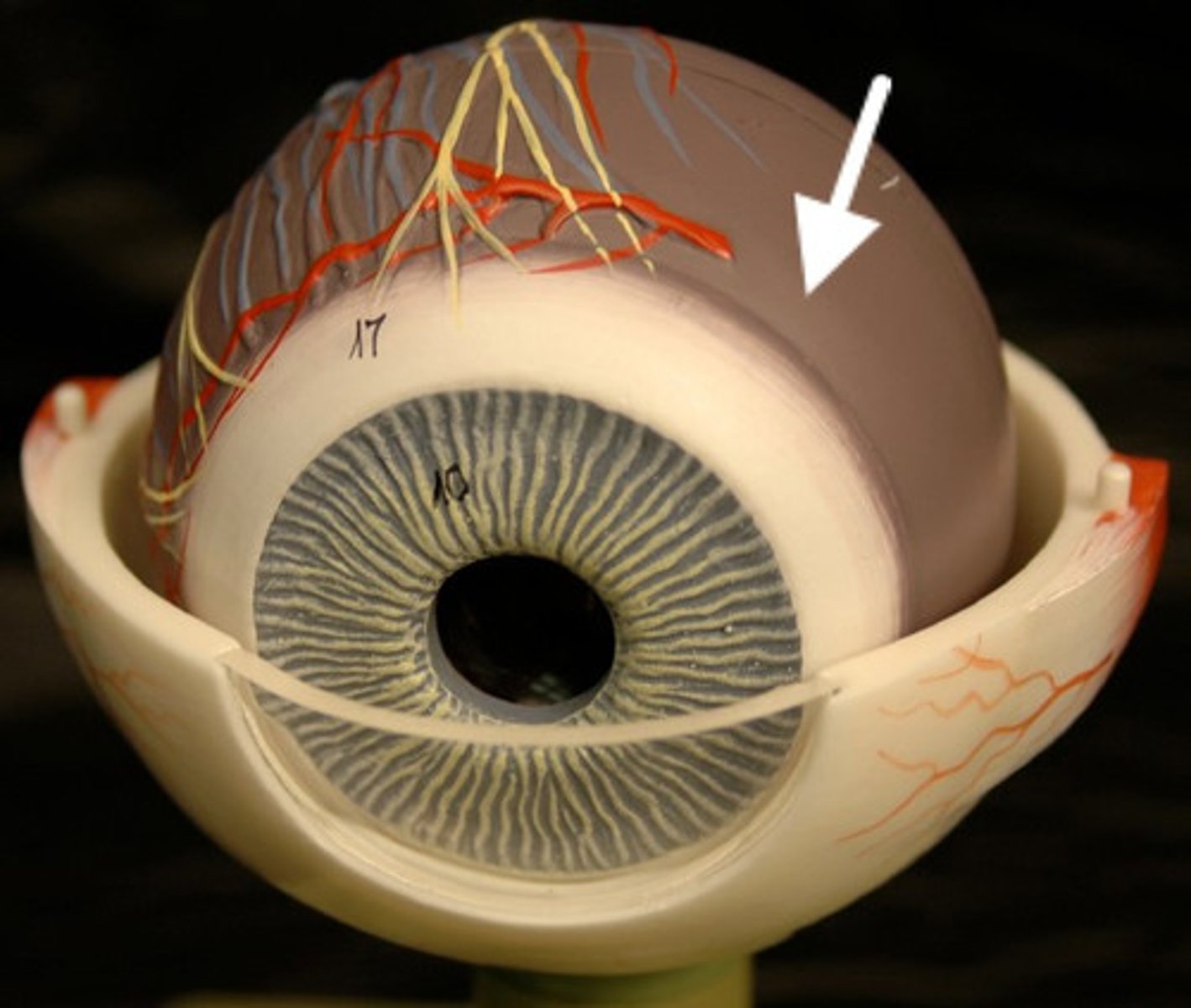
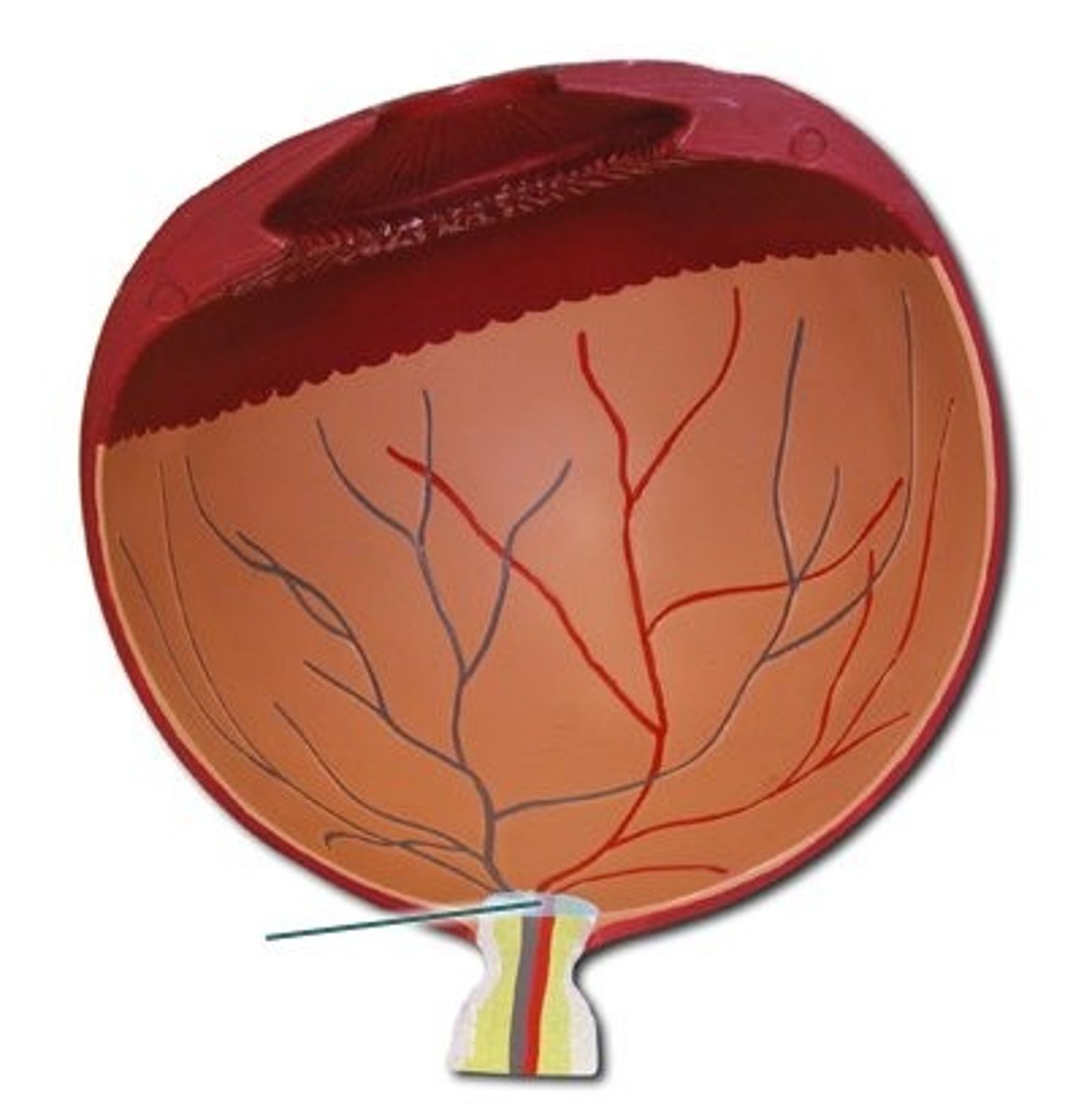
Sclera
Made of dense protective tissue and protects entire eyeball except the front; (white of eye)

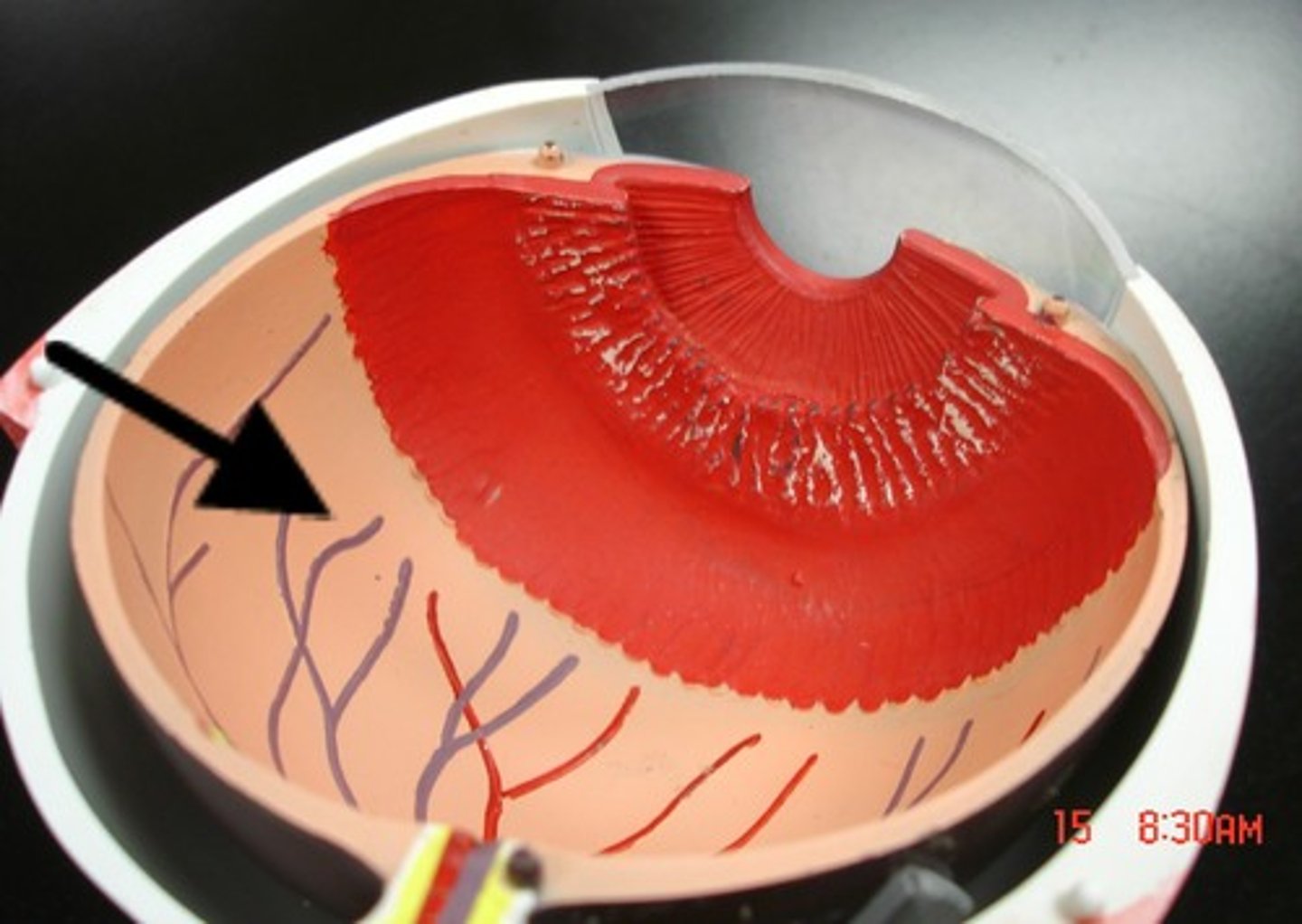
Choroid
Contains many of the blood vessels that supply the eye with oxygen and nutrients (red eye effect in photos)
Retina
Contains the photoreceptors that respond to light and any supporting cells and blood vessels
Tapetum lucidum
Shiny coating located on top of choroid in animals which reflects light and amplifies night vision (humans do not have)
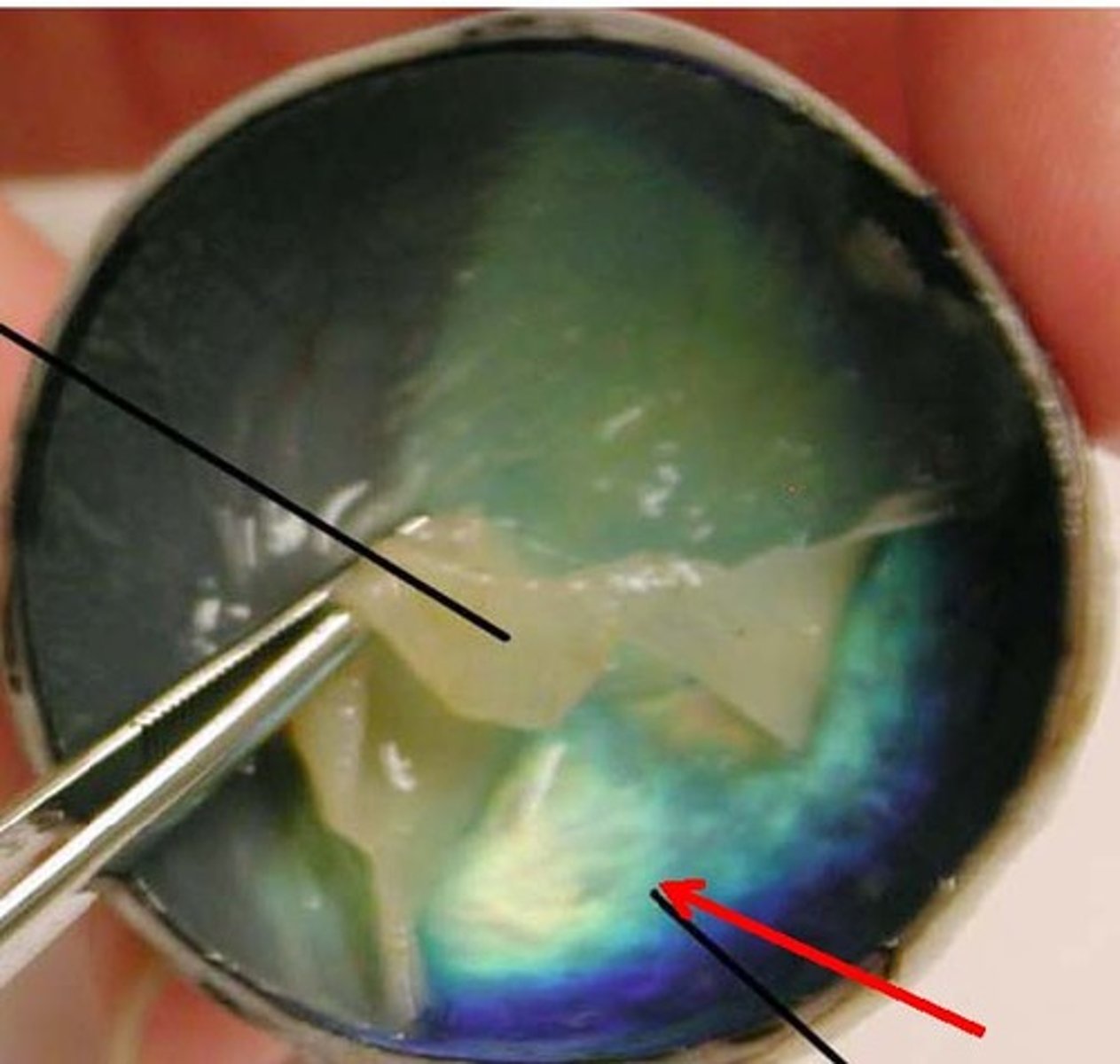
Cornea
Transparent ventral surface of the sclera; only organ that can be transplanted without rejection due to lack of blood vessels
Iris
Colored ventral surface of the choroid; can expand and contract, controlling the pupil
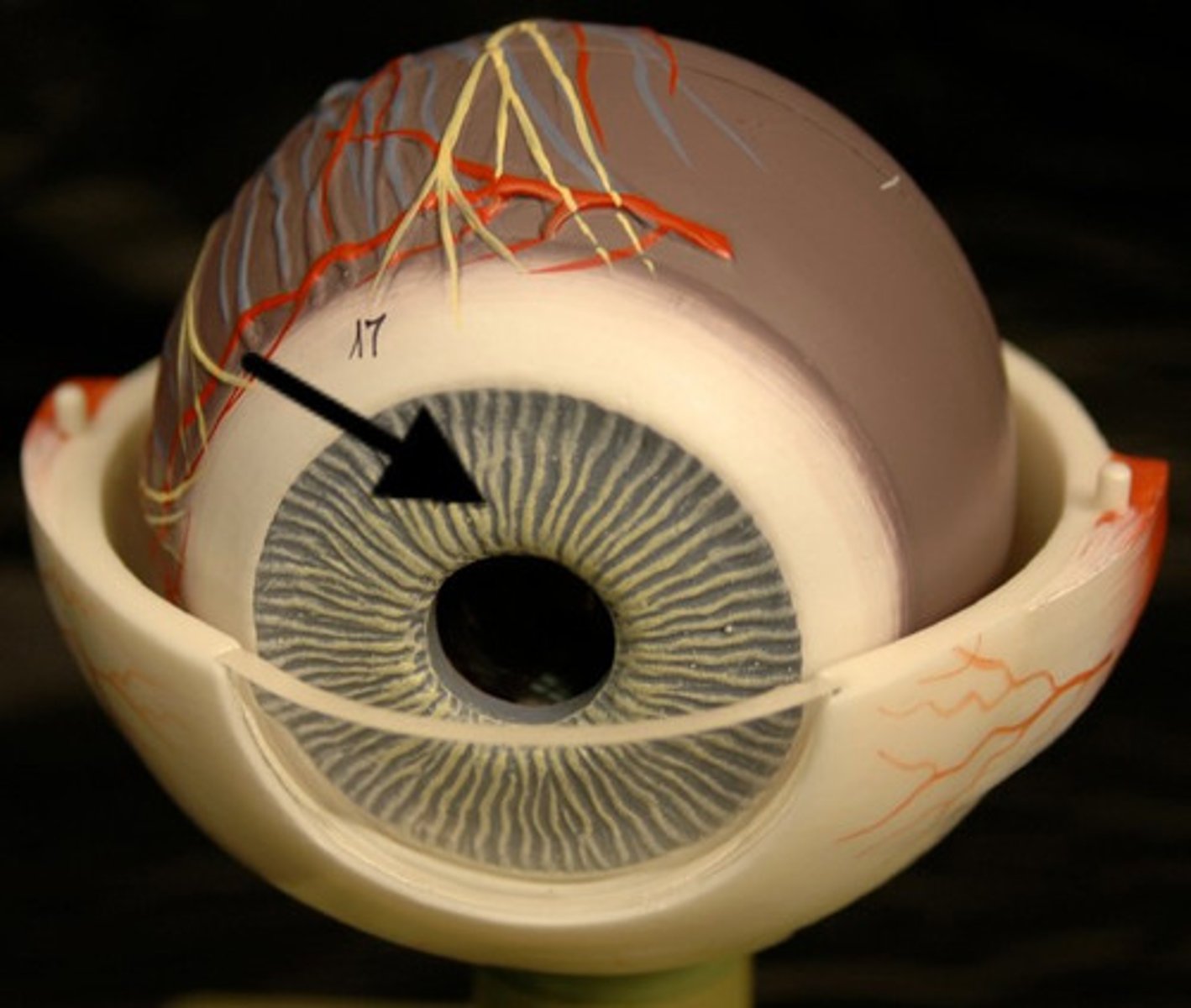
Pupil
The hole in the middle of the iris that lets light into the eye
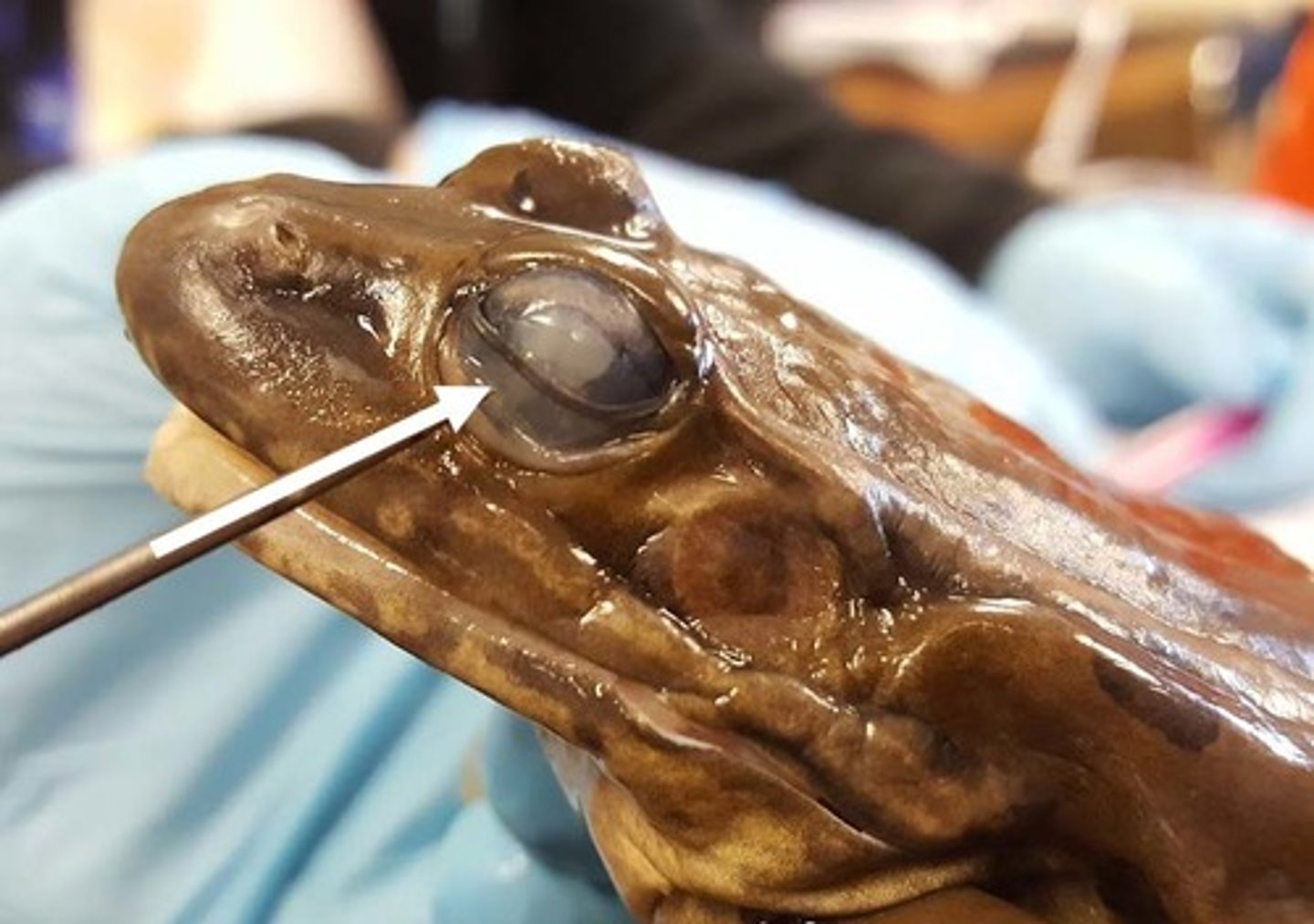
Nictitating membrane
Inner (extra) eyelid that provides an extra layer of protection as well as moistens the eye (Humans do not have; seen especially in lizards & amphibians due to terrestrial and water habitats (need more protection))
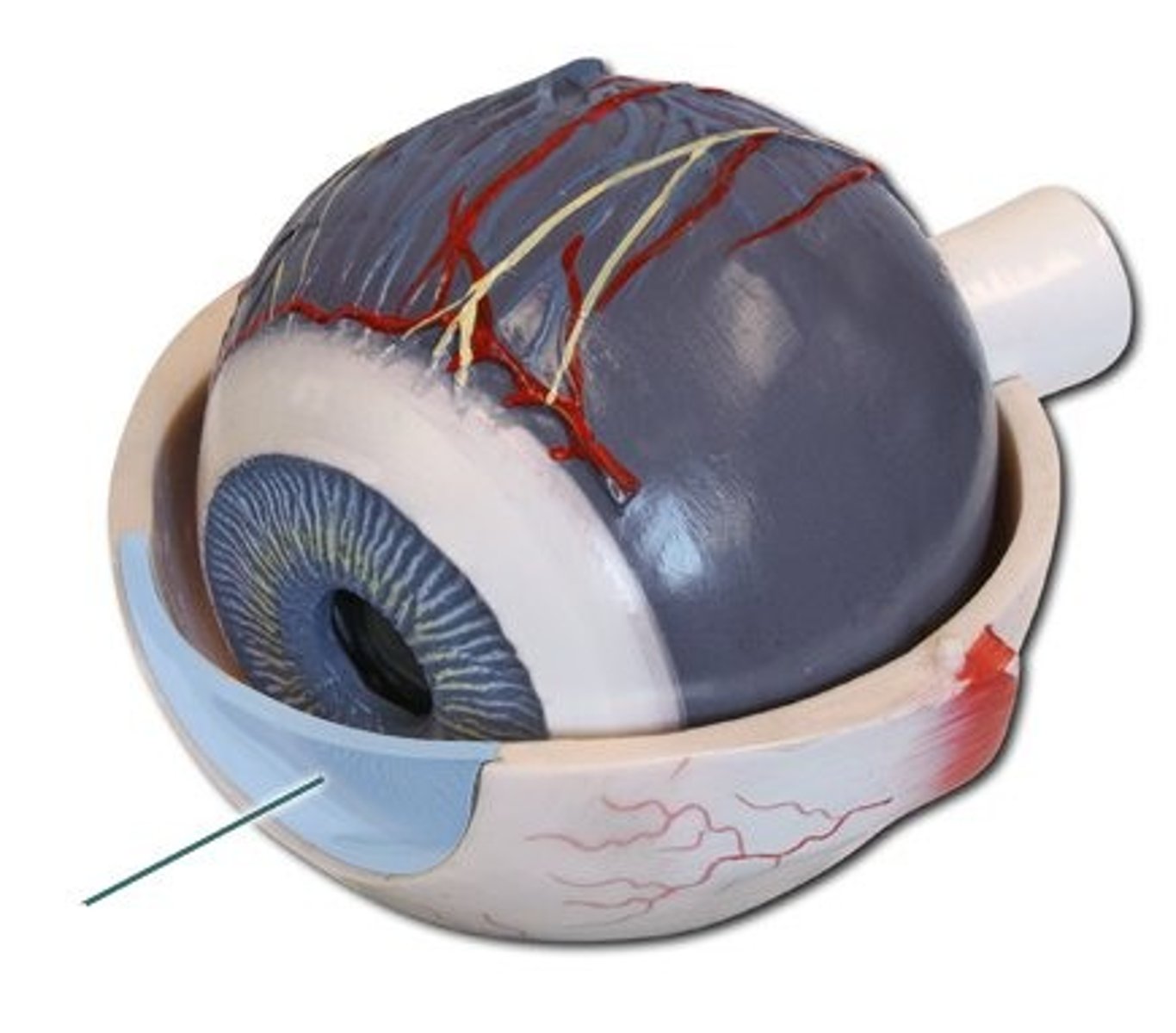
Lacrimal glands
Produce tears that moisten the eyes and clear foreign material
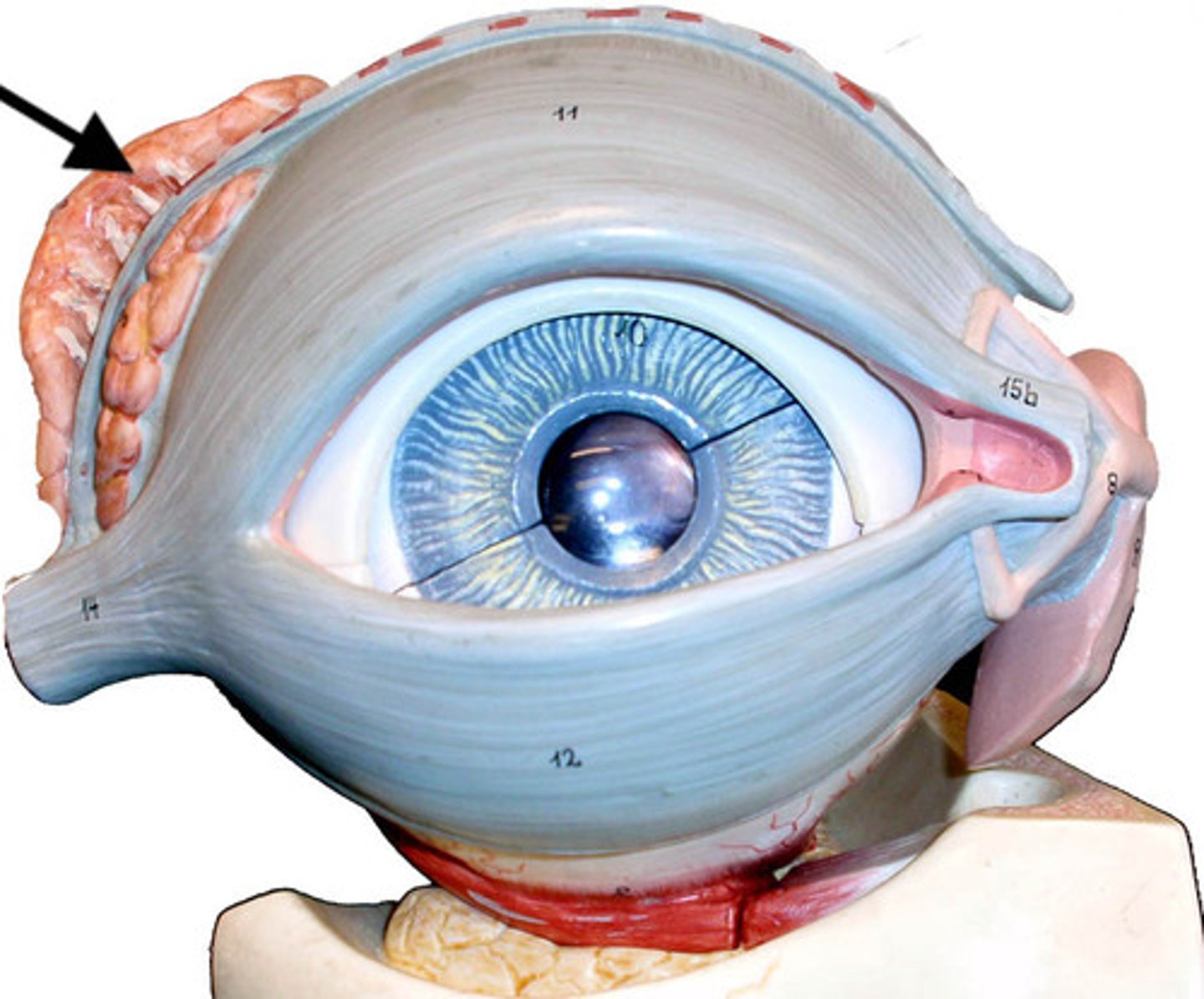
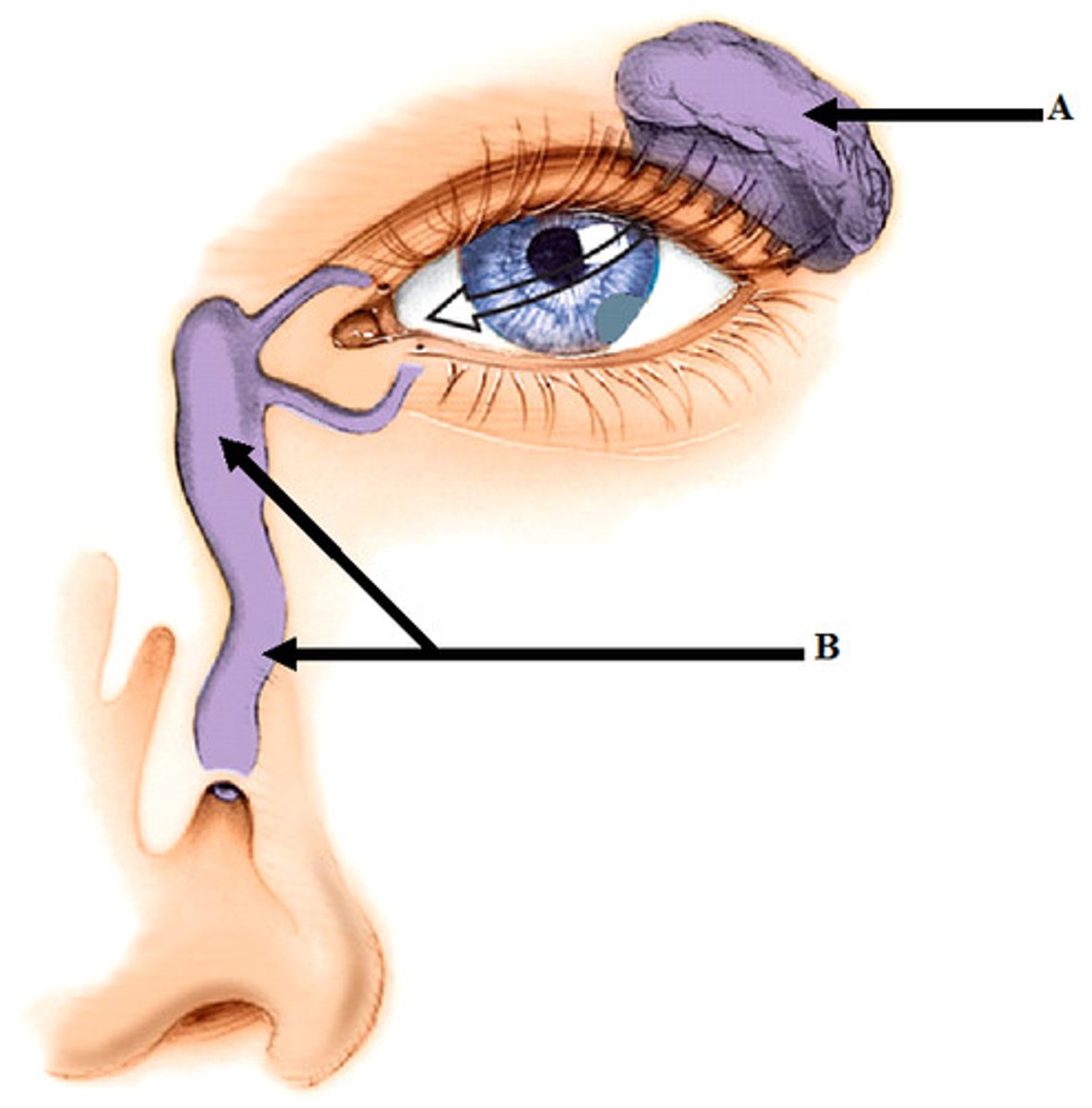
Lacrimal pores and canals
Drains tears out of eye
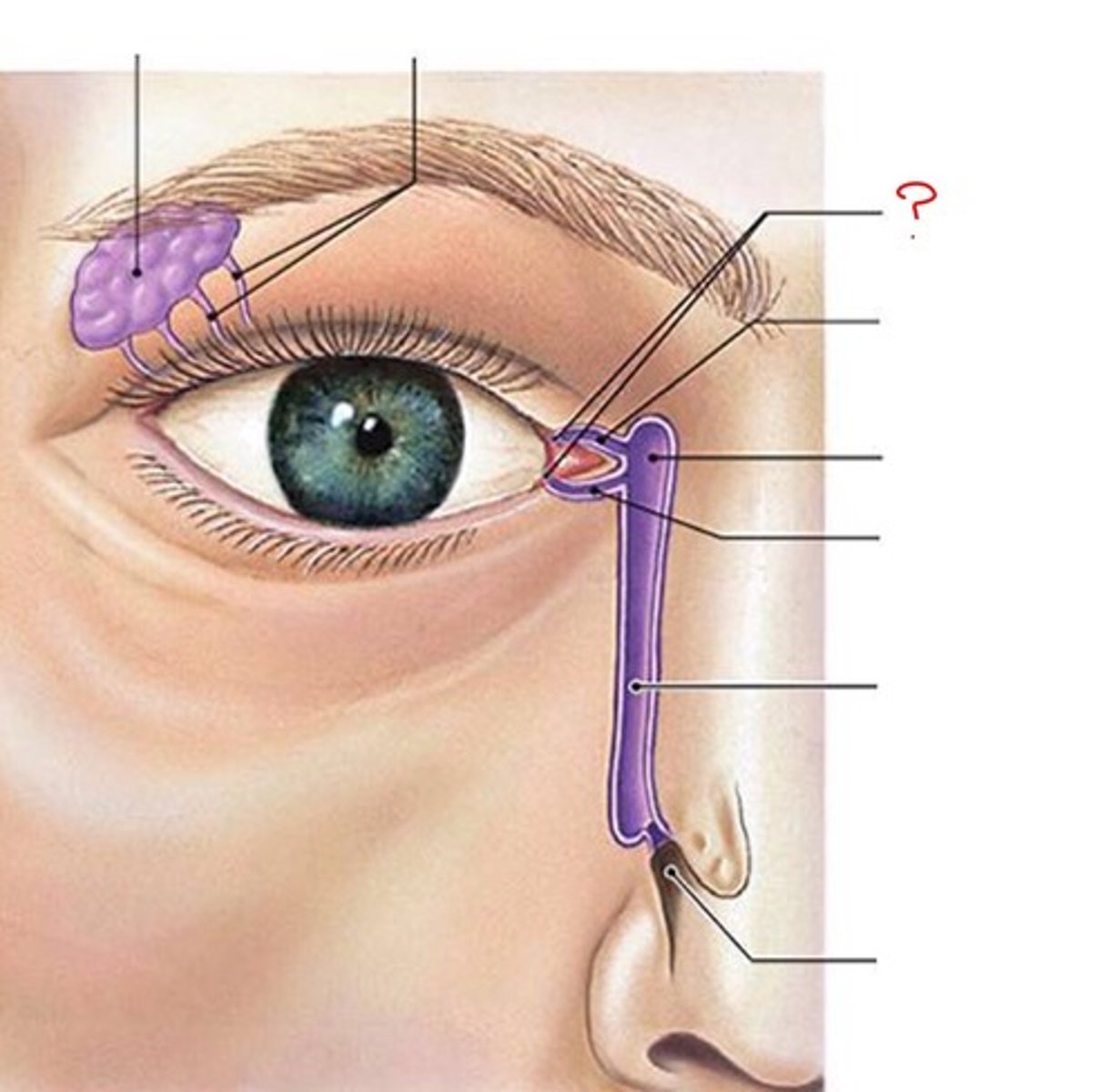
Nasolacrimal duct
Conducts tears to the nose, where they are eliminated (B)
Abducens, oculomotor, trochlear
Three cranial nerves that control the eye muscles
Lateral & medial rectus
Move eye side-to-side
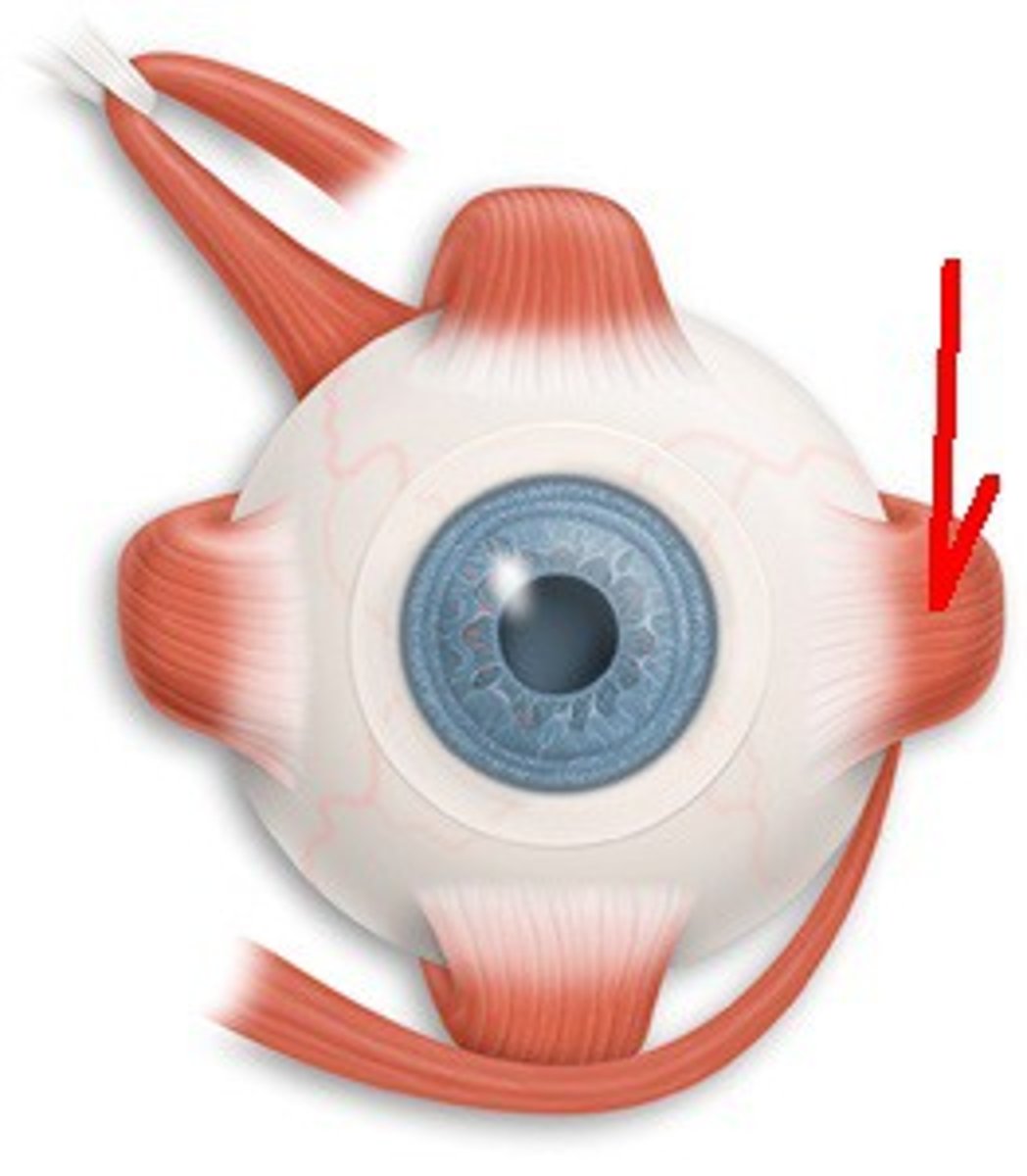
Superior and inferior rectus
Raise and lower the eye vertically
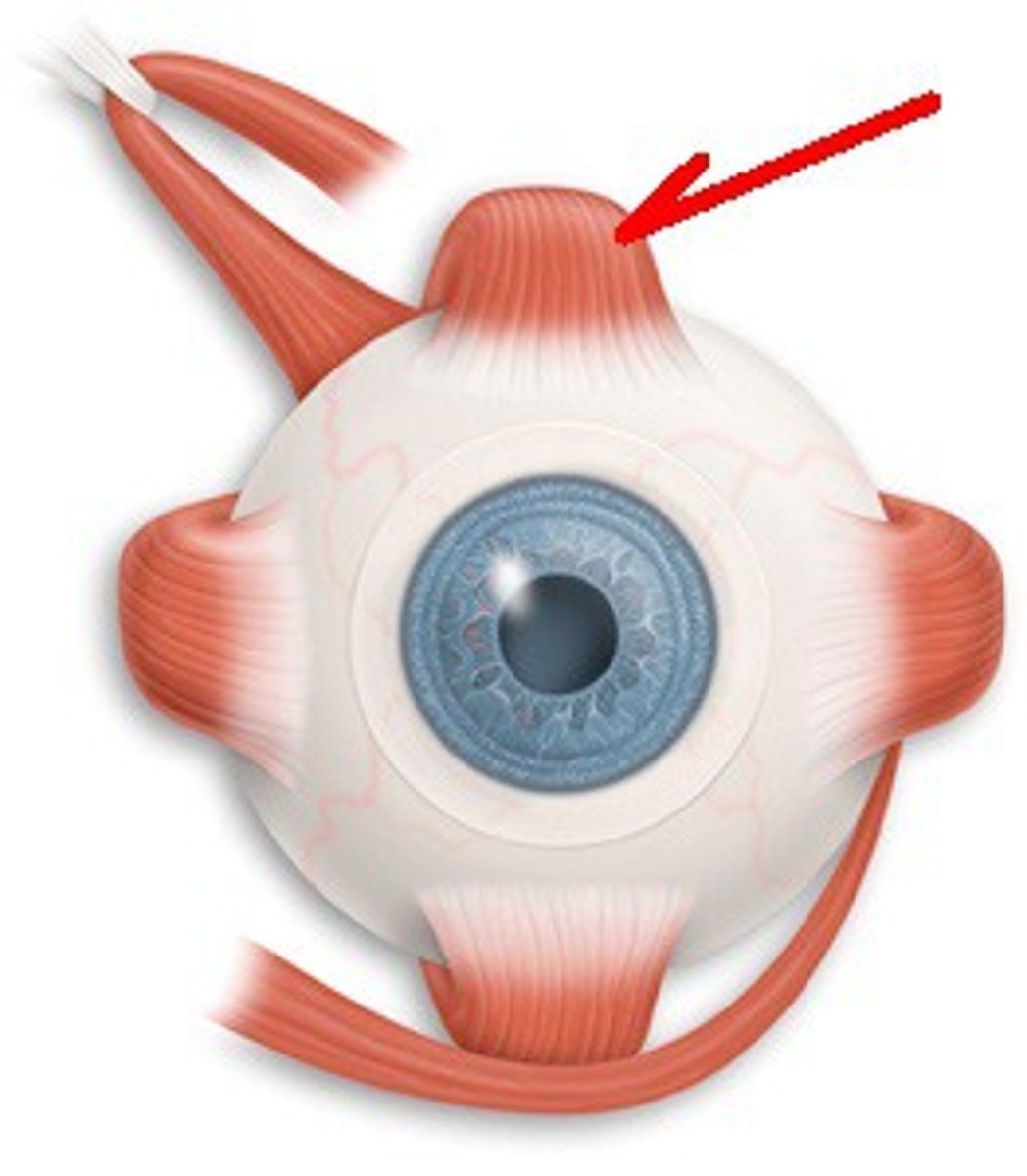
Oblique muscles
Work with rectus muscles to roll the eyes in angled directions (pictured one + bottom one in U shape)
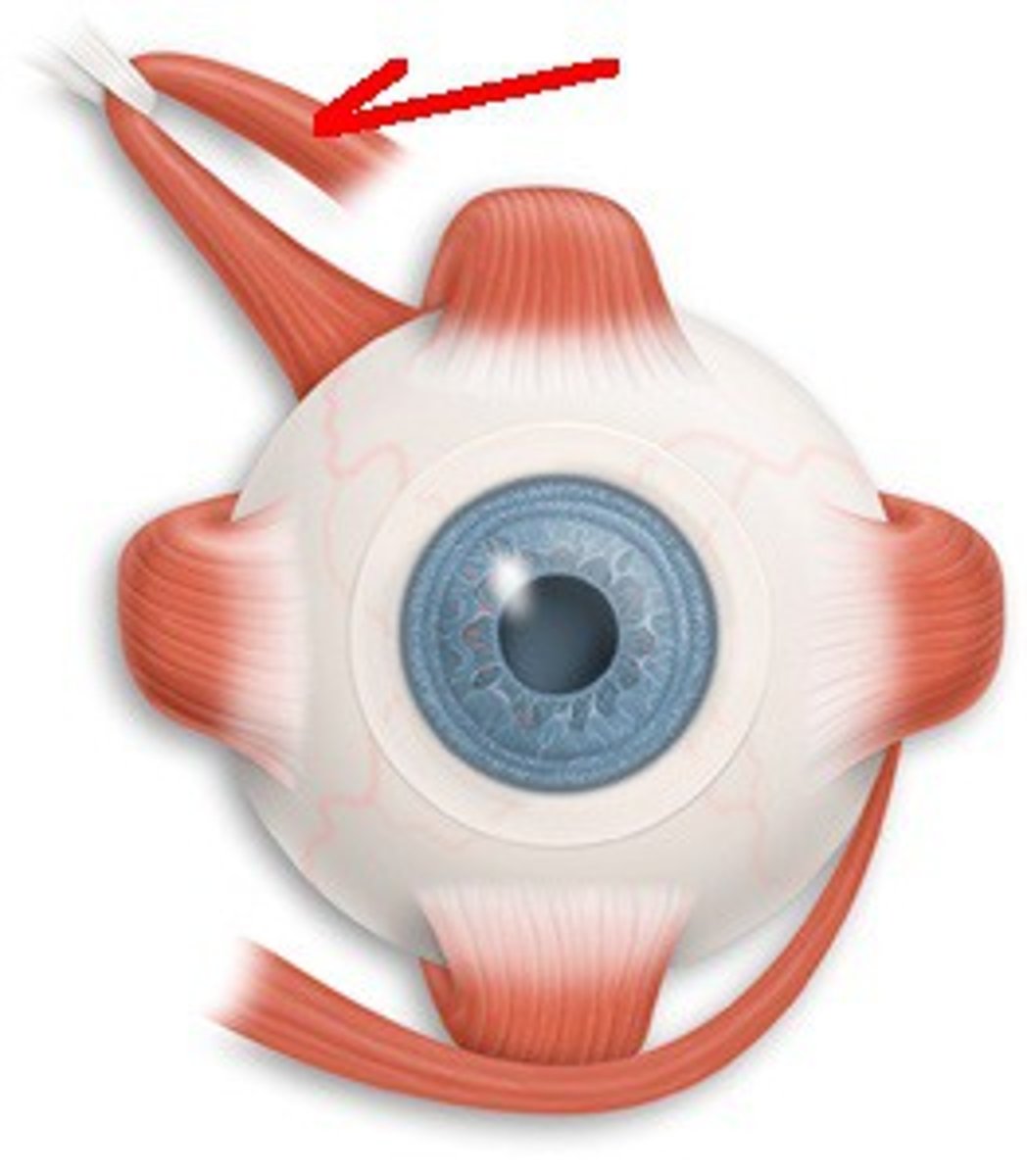
Lens
Transparent structure that refracts (bends) light towards the retina; The shape can be adjusted by a muscle called the ciliary body
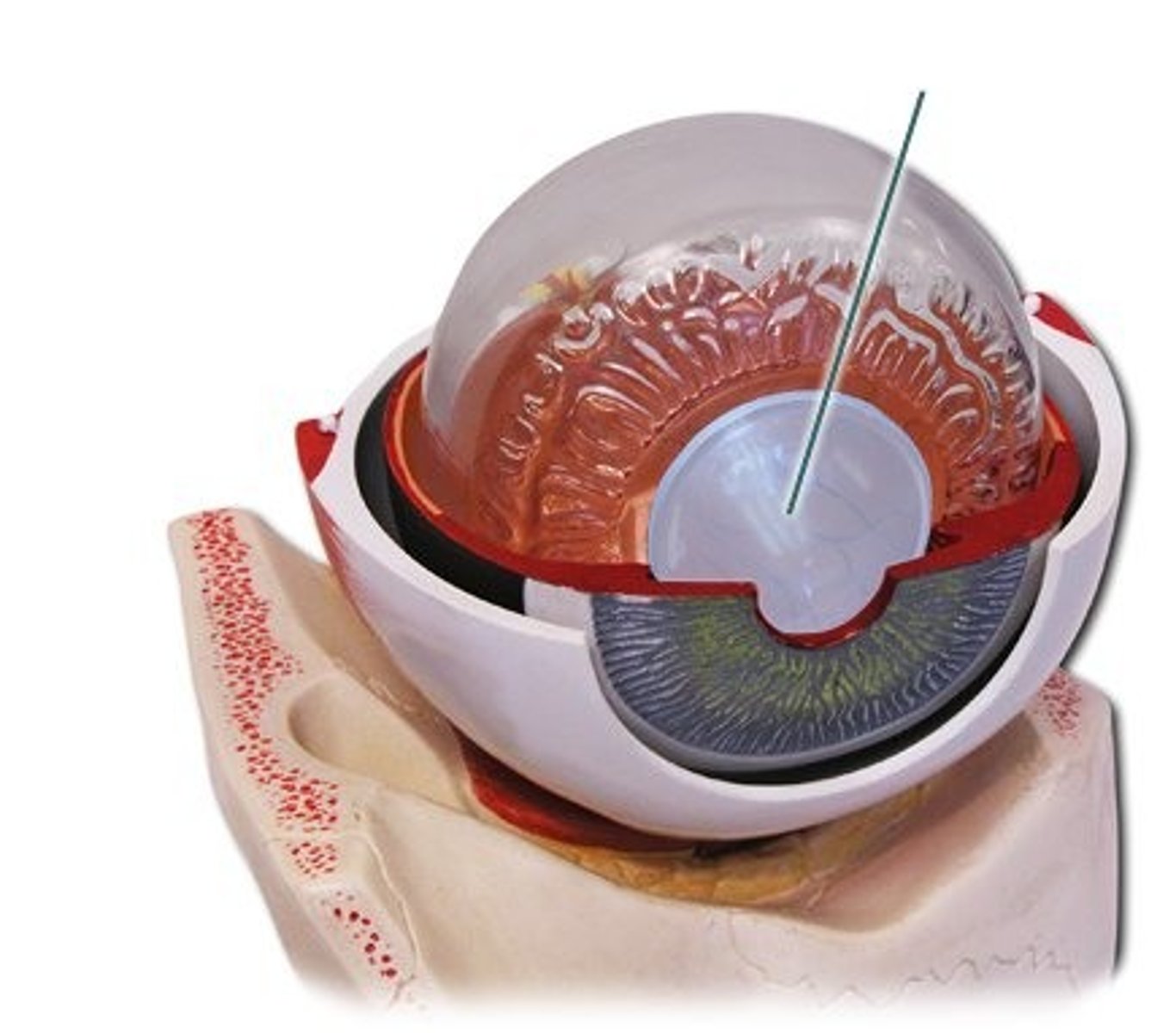
Aqueous humor
A watery solution found between the cornea and lens; provides nutrients to cornea
Vitreous humor
Gel-like solution found between the lens and retina; Gives eye its shape
Pathway of vision
Light rays from the image refract as they pass through the cornea, lens, and vitreous humor. Brain sees image as upside down & inverted due to refraction; adjusts it so we see the correct way
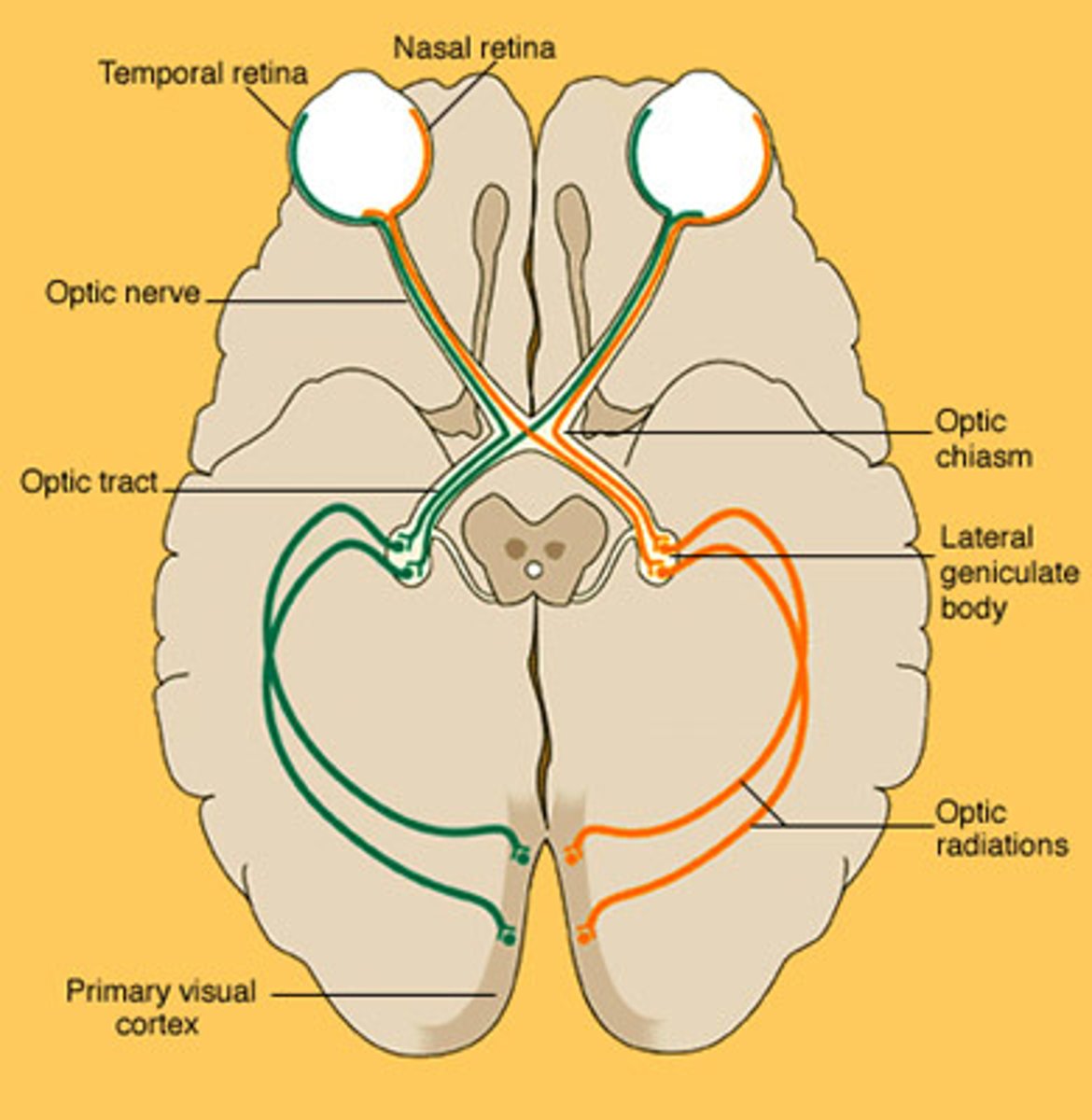
Optic disc
A blind spot is created if the image projects on the optic nerve itself (no rods or cones)
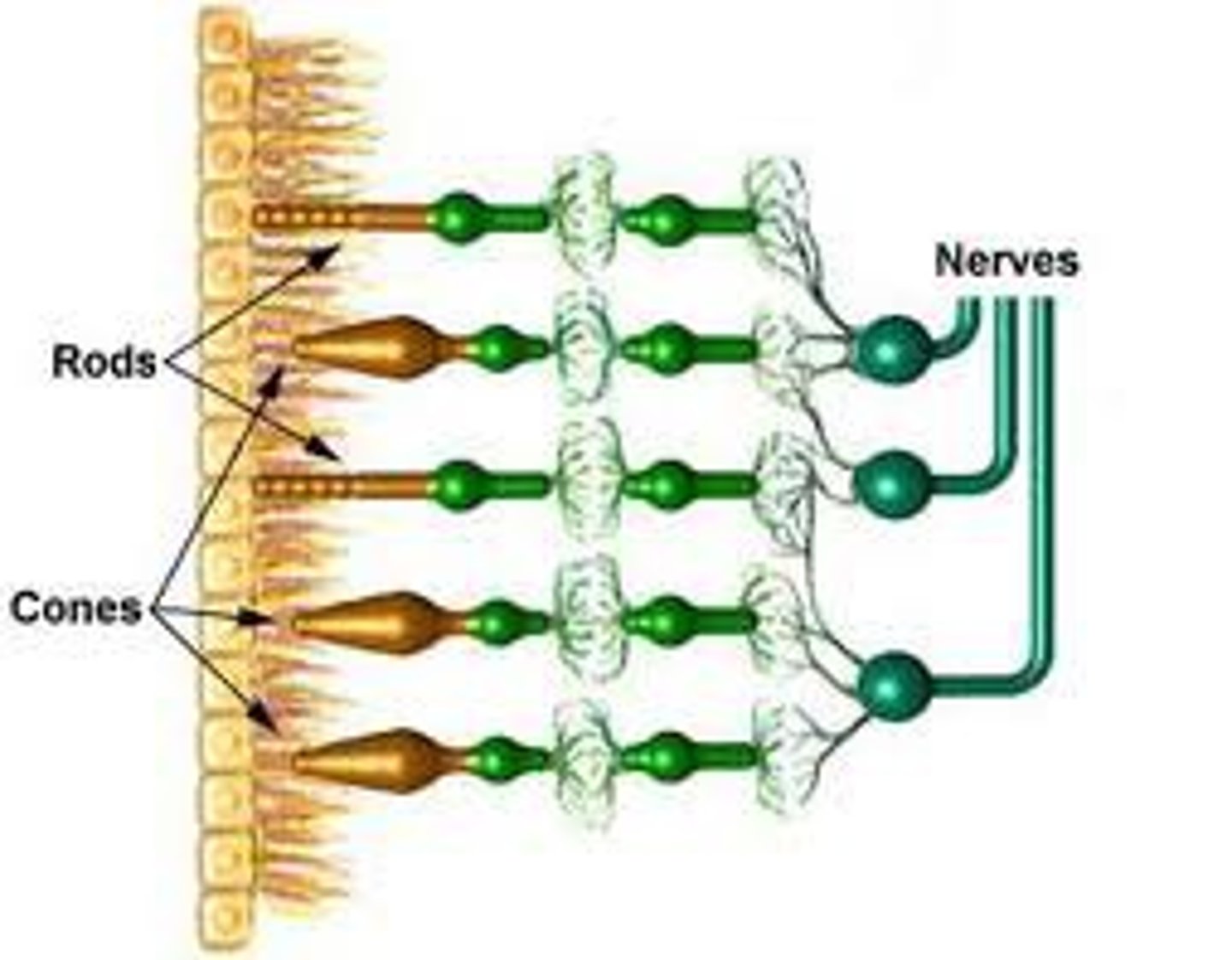
Rods
Specialized neurons which are responsible for vision at low-light levels
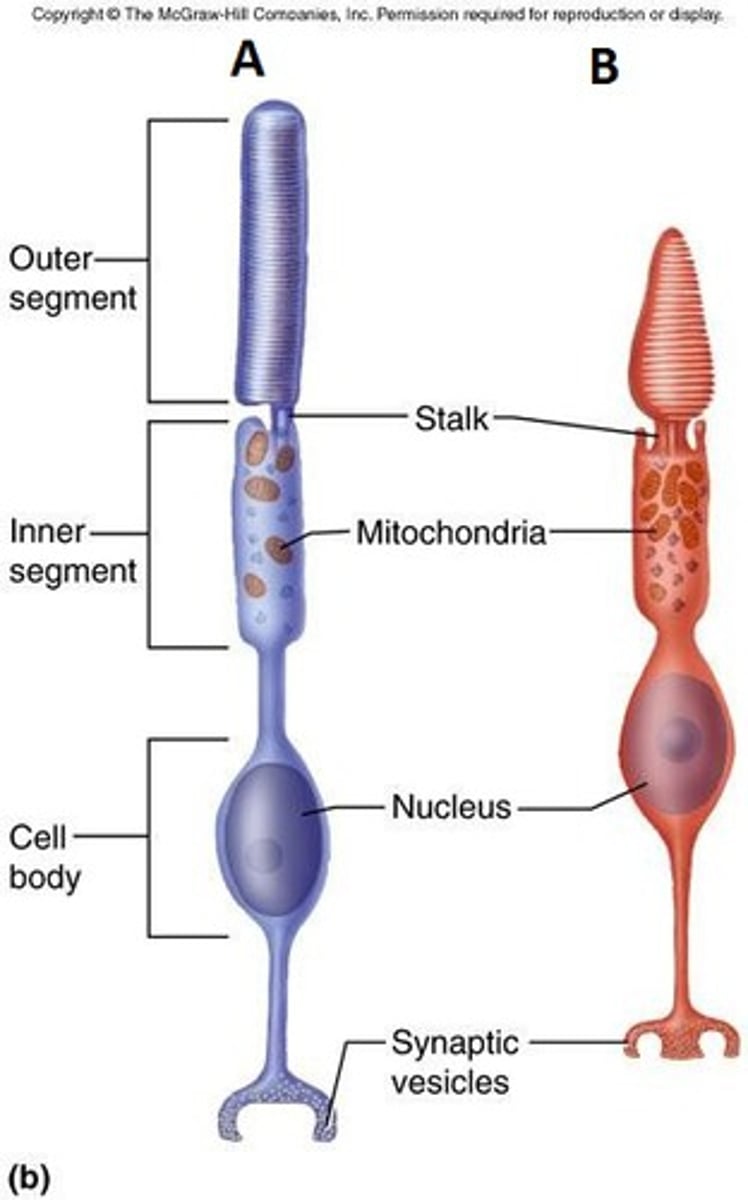
Cones
Neurons that allow color vision in brighter light; each type sensitive to different wavelength of light
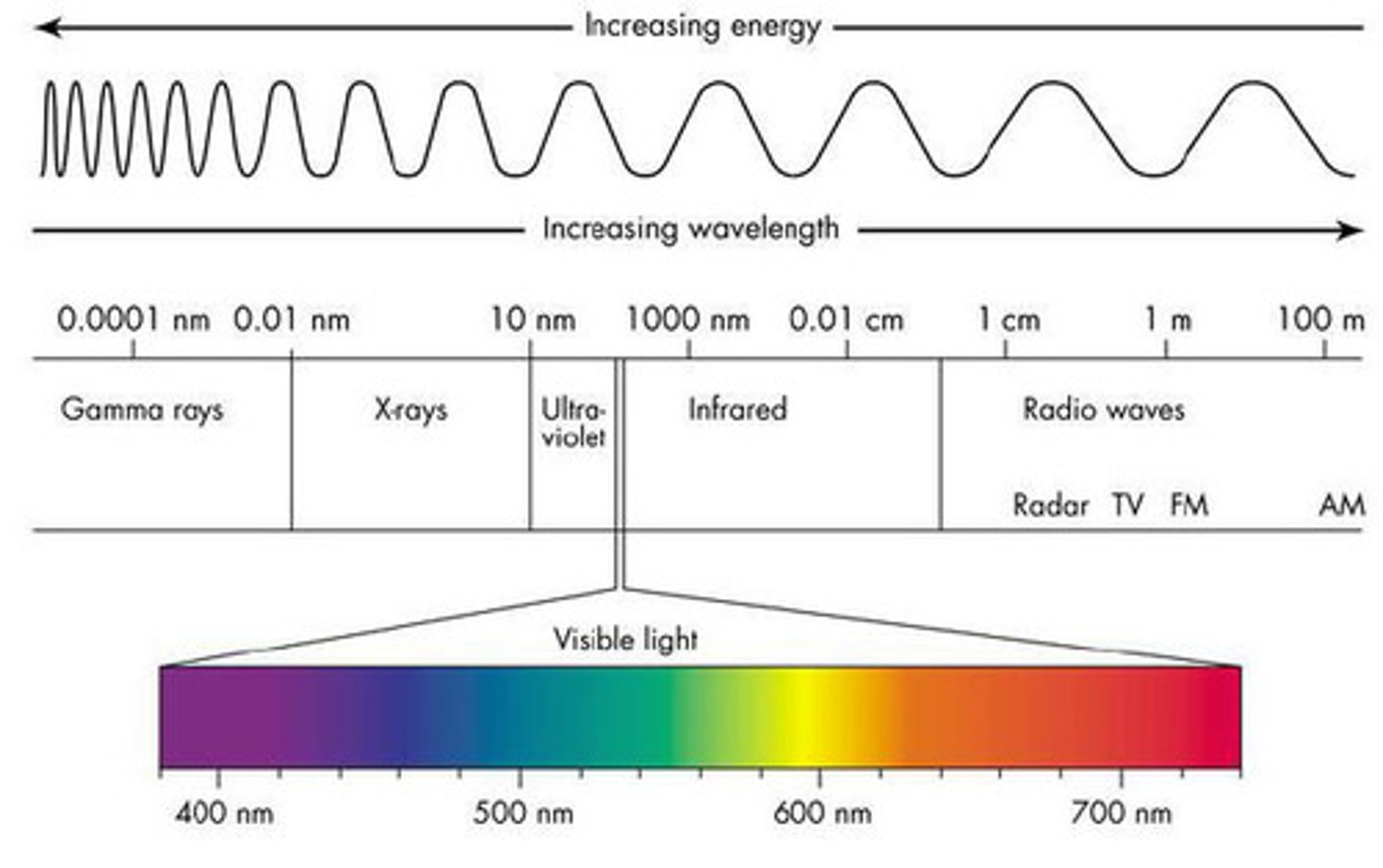
Light wavelengths
Shorter = more blue cones, longer = more green then red cones
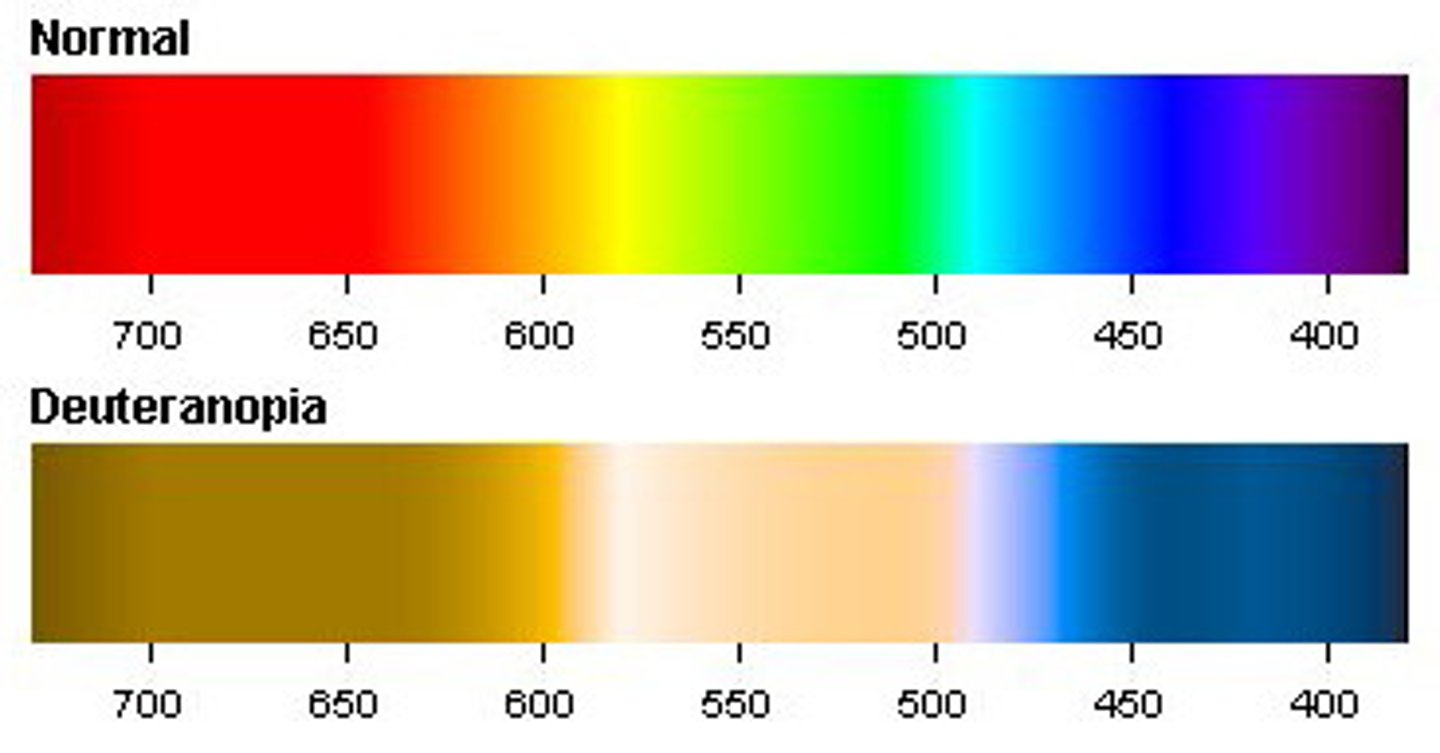
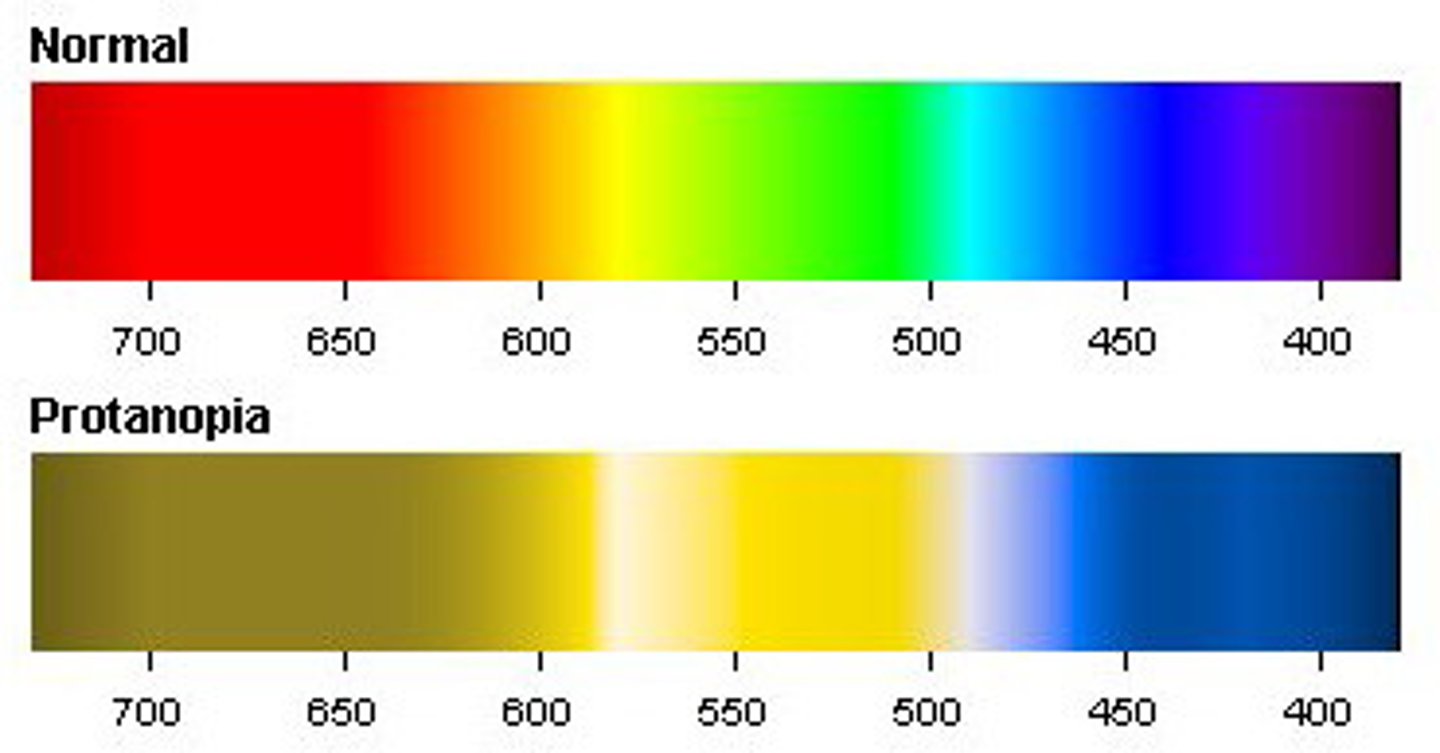
Color Blindness
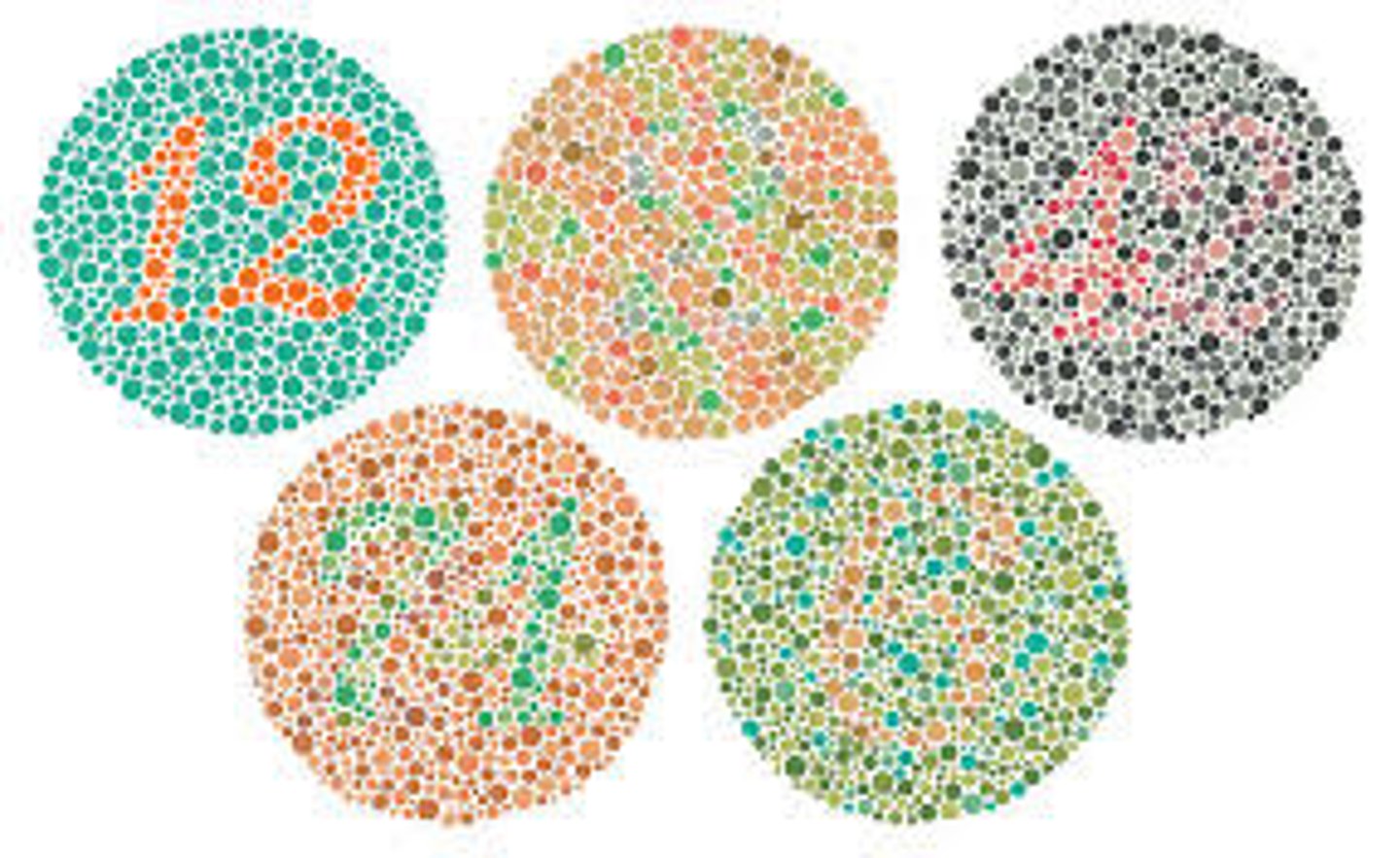
An inability to see certain colors due to a lack of one or more types of cones; Caused by recessive gene on x-chromosome (more common in males). Tested by presenting patient with a pattern of colored circles, most common type is red-green

Deuteranopia
Red-weakness colorblindness
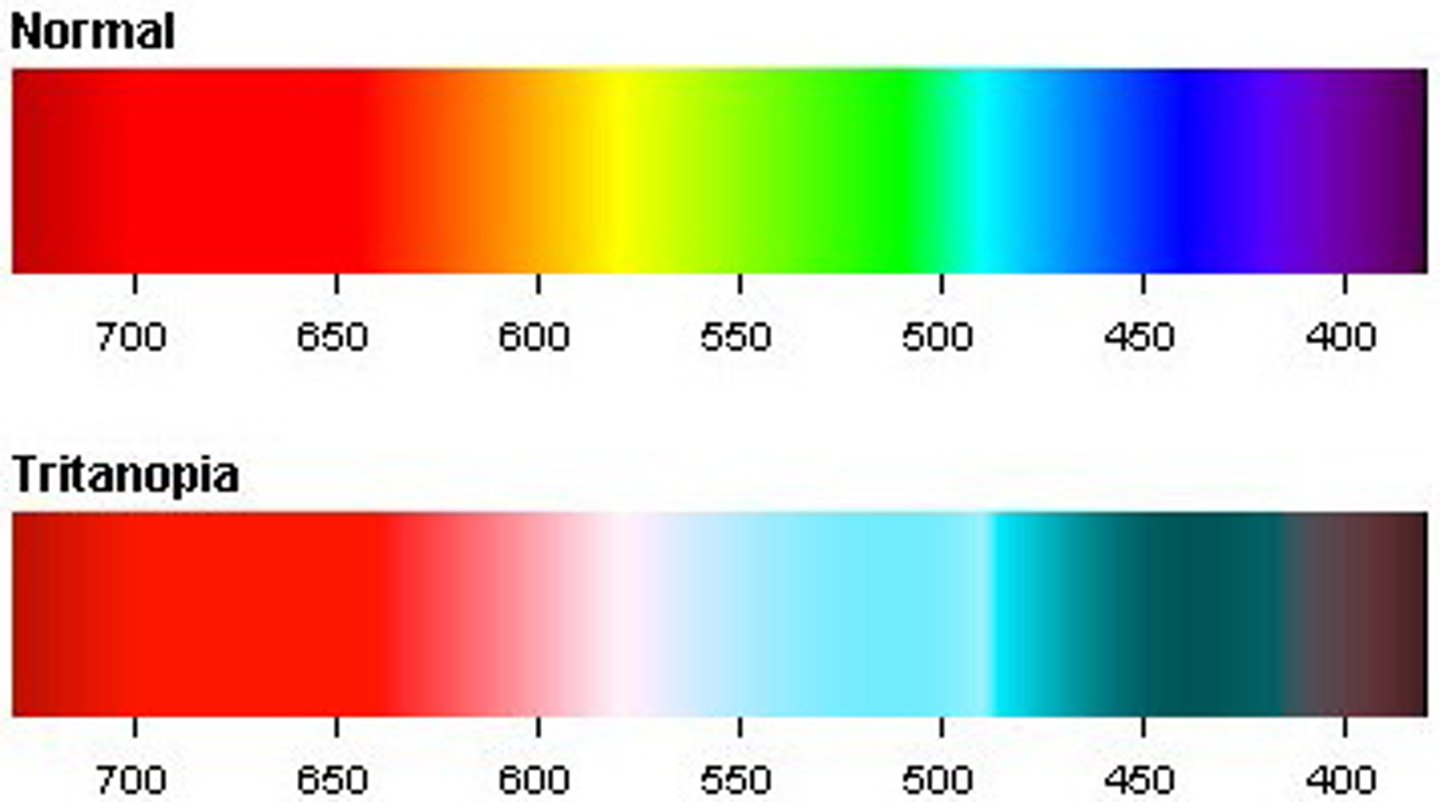
Tritanopia
Blue-weakness colorblindness

Protanopia
Green-weakness colorblindness
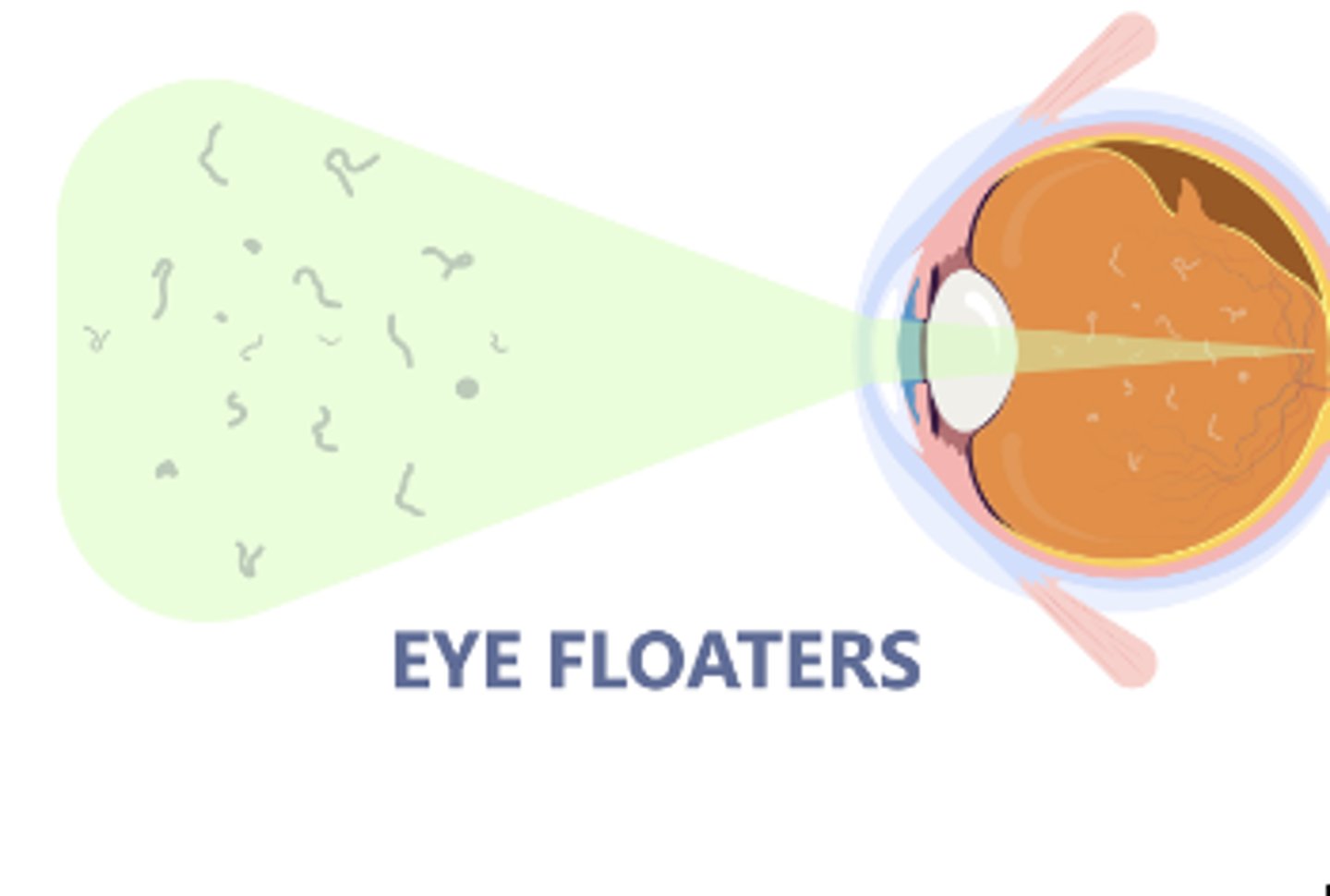
Floaters
Clumping of protein fibers in vitreous humor which usually comes with age
Path of sensory input of smell
Sensory input is sent through the olfactory nerve to the thalamus of the brain, then to the temporal lobe of the cerebrum
Olfactory nerve receptors
Located at the roof of the nasal cavity

Nose blindness
Caused by being used to a smell (constant exposure). Ex: House, clothes, body odor
Papillae
Raised projections that covers tongue that contain the sensory neurons for taste
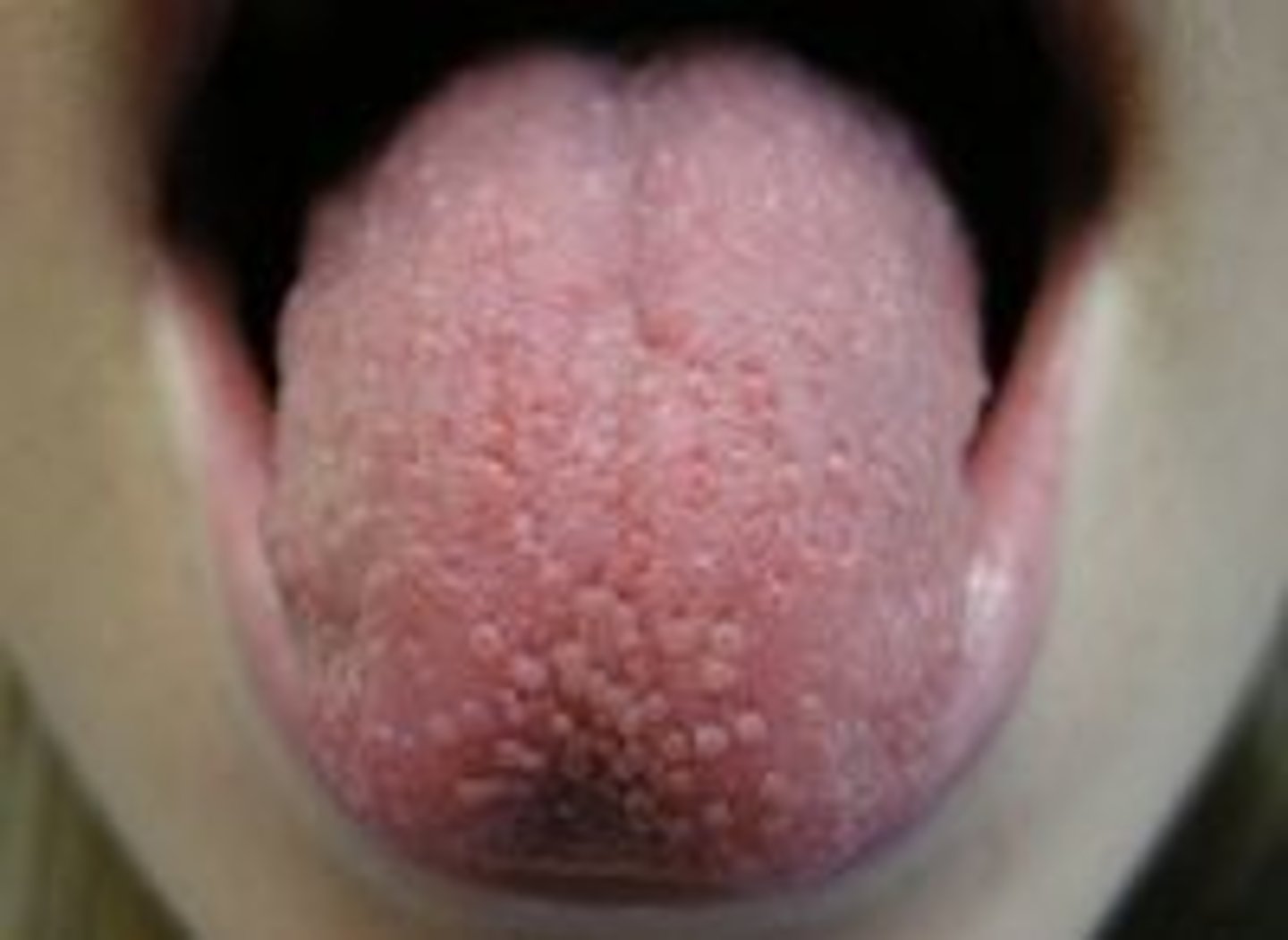
Taste buds
Nerve receptors found on sides of papillae; chemicals must dissolve in saliva to be detected
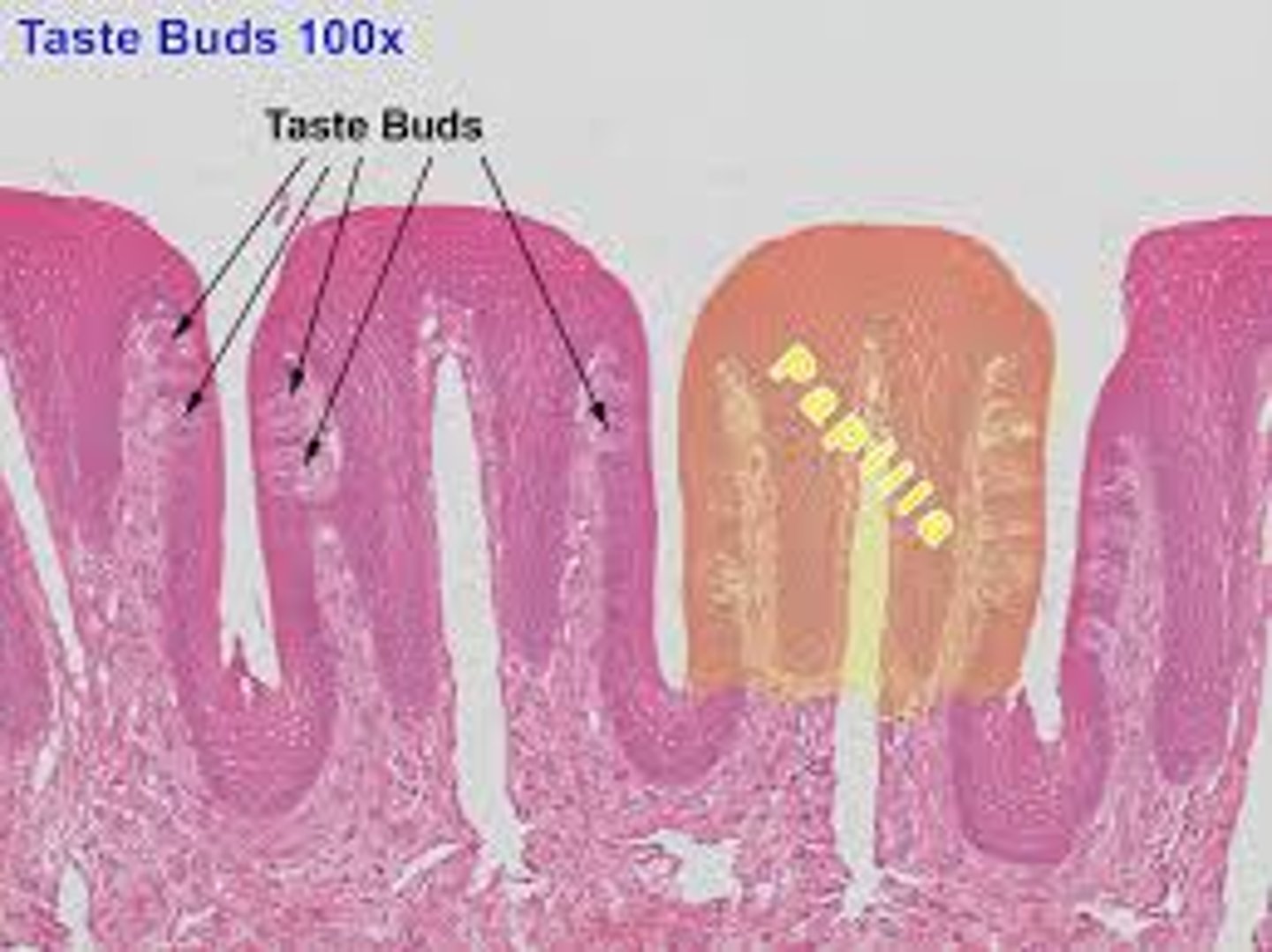
Long microvilli
Found at end of each neuron (taste buds); Smaller than cilia
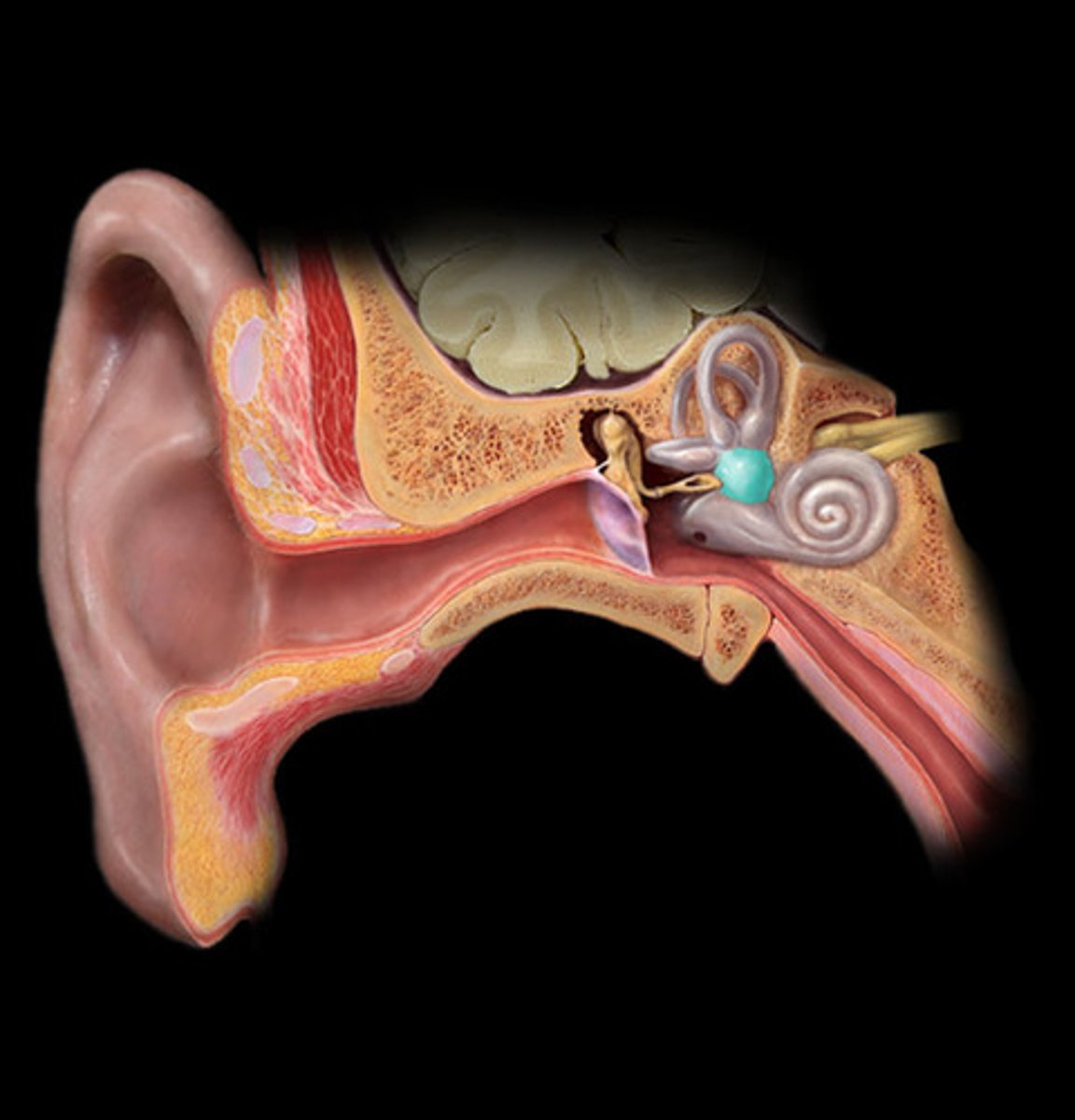
Ear
Houses two separate organs, each with separate sense; Hearing (detection of sound waves) & Equilibrium (balance)
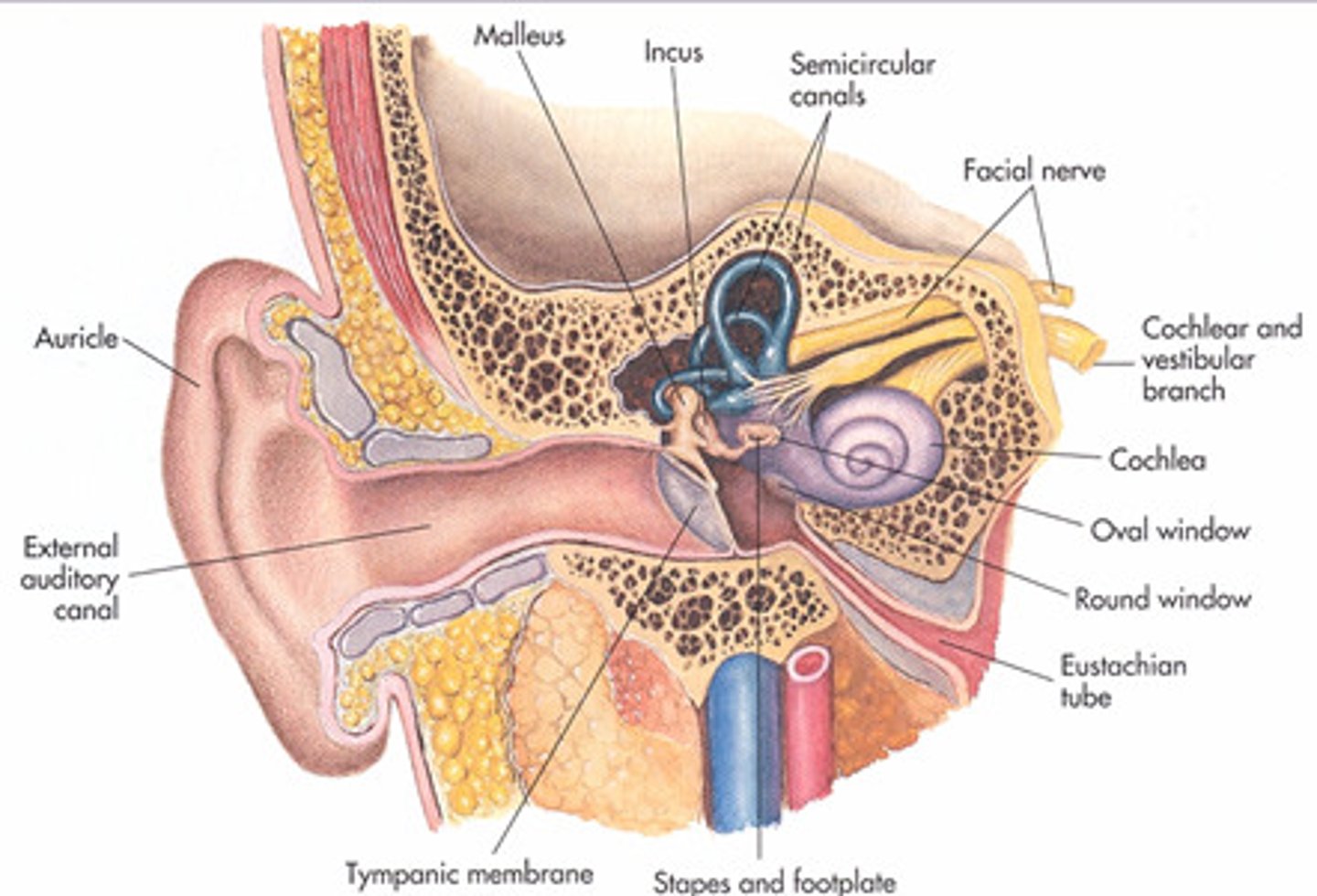
External ear
Involved in the sense of hearing only
Pinna
Collects sound waves like a funnel; animals with larger ones can detect subtle sounds (ex: burrowing of prey)
Auditory canal
Narrow passageway through the temporal bone of the skull
Ceruminous glands
Line auditory canal and produce ear wax (slightly acidic & antibacterial, traps dirt & is gradually moved out of ear)
Tympanic membrane (ear drum)
Converts sound waves into mechanical vibrations, which are transmitted deeper within the ear. Very thin membrane that can be ruptured by extremely loud sounds (Ex: gunshot near head)
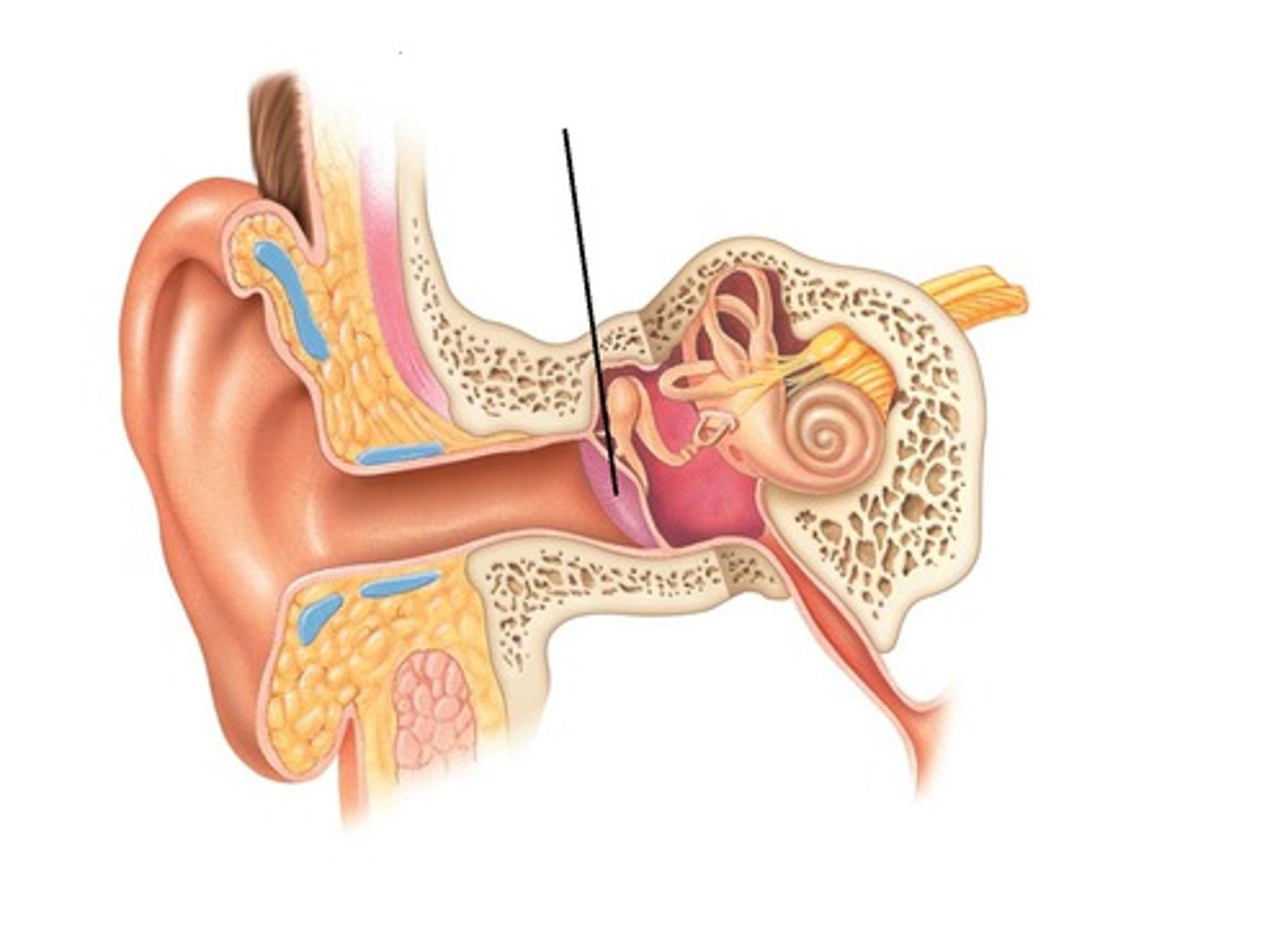
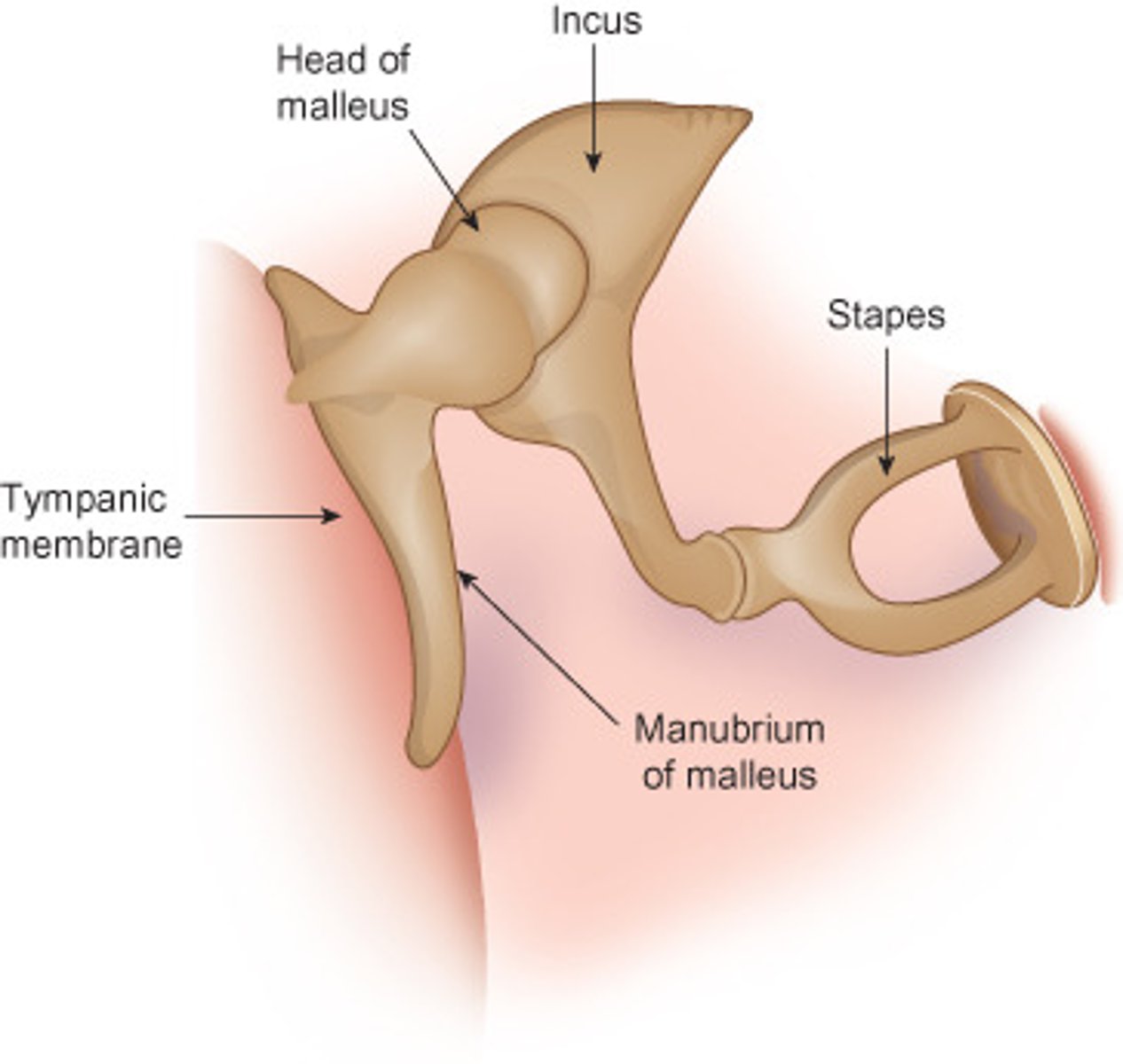
Ossicles
Cavity of middle ear filled with three bones: Malleus, Incus, Stapes. Convey vibrations from the tympanic membrane into the inner ear through a membrane called the oval window
Eustachian tube
Connects the middle ear chamber to the throat; can open to equalize pressure in middle ear when yawning or chewing
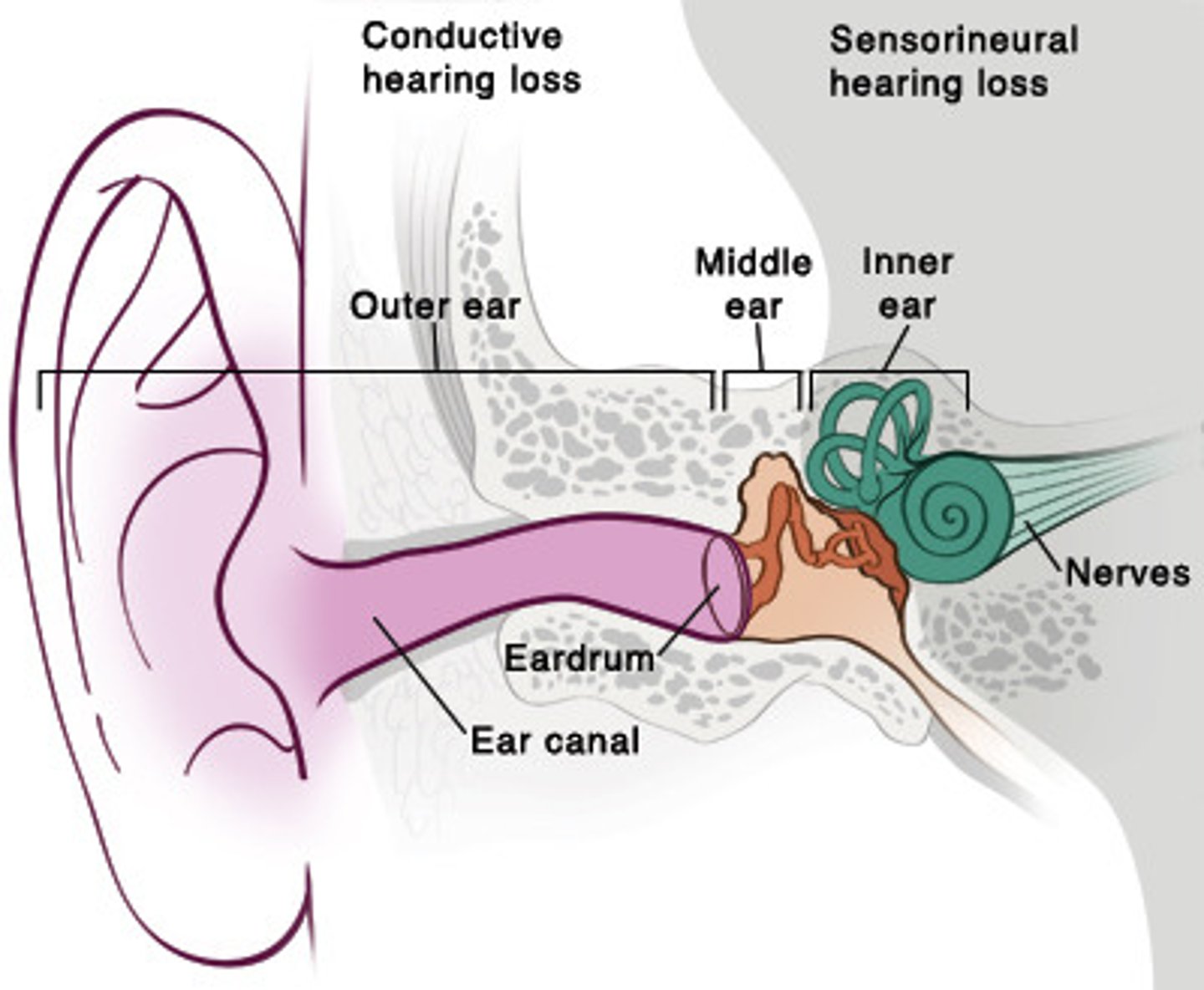
Inner ear
Contains organs for both hearing (cochlea) and balance (semicircular canals & vestibule)
Pathway of hearing
The sound waves vibrate through a fluid inside the cochlea, stimulating stereocilia
Stereocilia
Tiny hair cells that line the inside of the cochlea; each hair cell is stimulated by a different frequency
Round window
Bends outward, releasing pressure from the sound wave
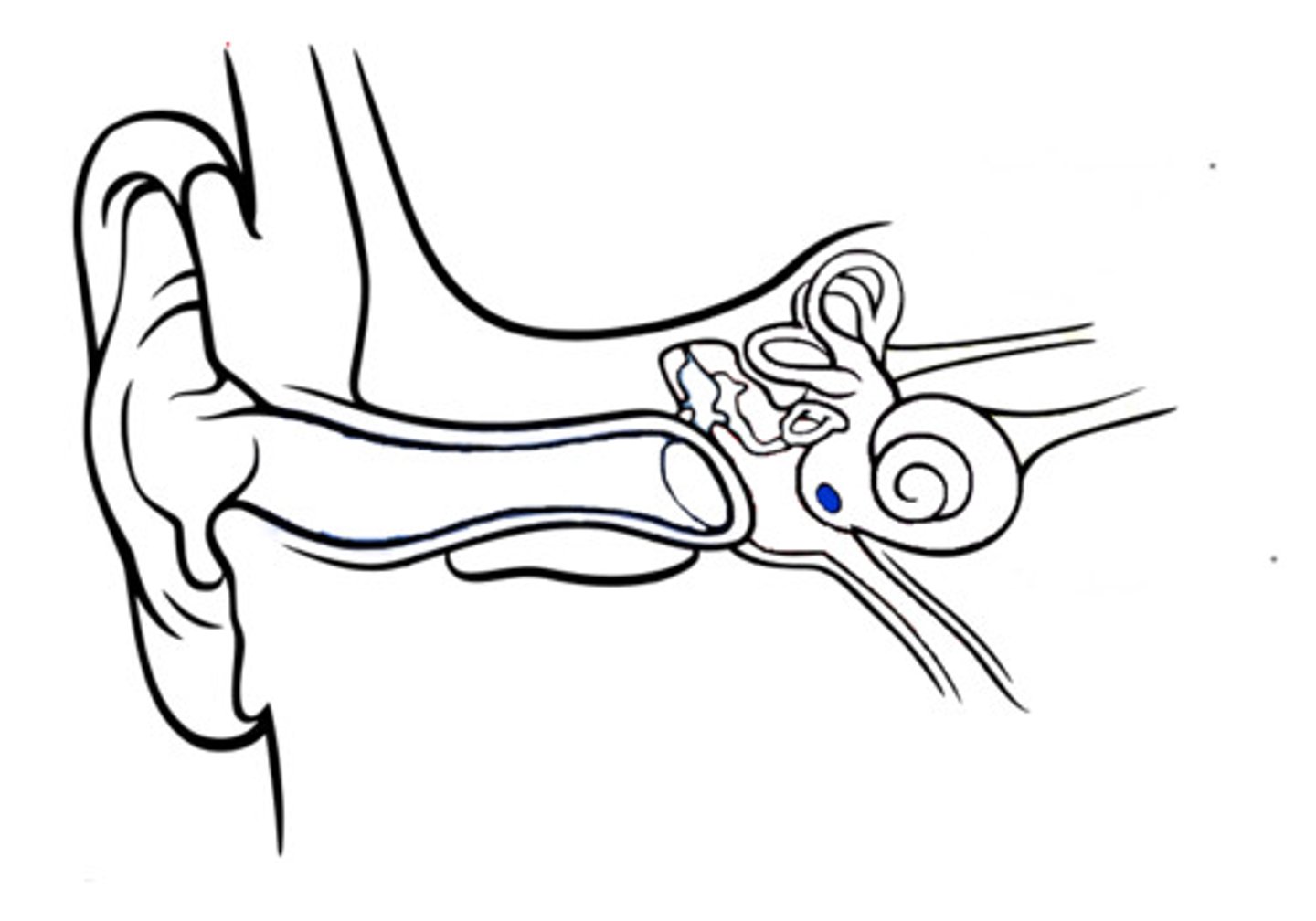
Vestibule
The portion of the inner ear that senses the position of the head & where stirrup attaches (at round window)
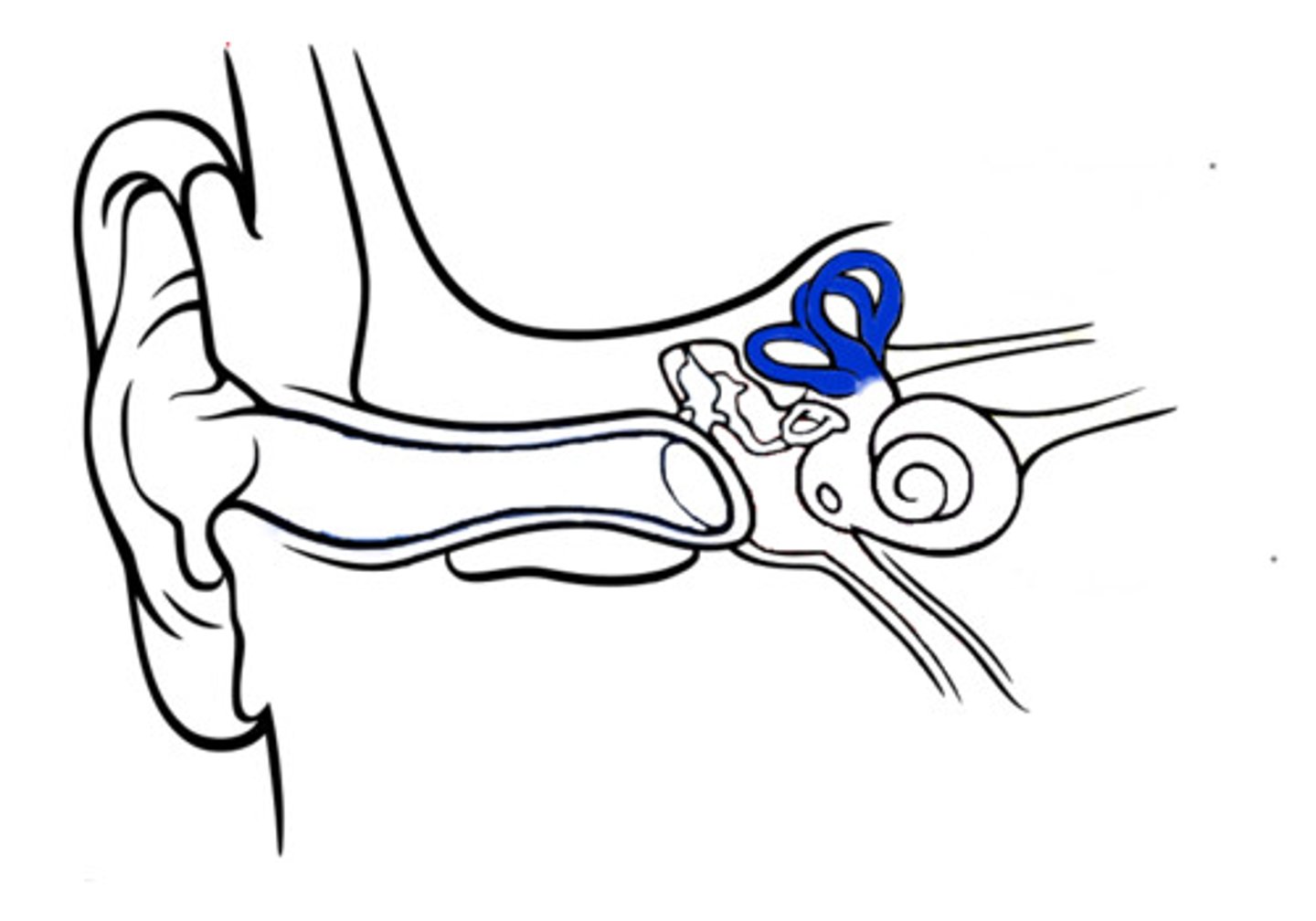
Semicircular canals
Three fluid-filled canals in the inner ear responsible for our sense of balance. Fluids help tell balance (fluids stay level); Dizziness can be caused by doing something like spinning & "mixing up" fluids
Range of human hearing
At best 20Hz-20,000Hz (this range shrinks later in life)
Tinnitus
Can be caused when the cilia are constantly stimulated over time; ringing of the ears
Hearing loss
Caused when stereocilia are damaged, as they cannot regenerate
Equilibrioception
Sensation of gravity, acceleration, and balance; detected within the vestibule (Relies on inner ear mainly, but uses vision to orient)