Neuron anatomy and function test - The Connected Mind
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review the diagram and information you have learned about the neuron. You will be tested on the anatomy of the neuron and its function in the brain, How it develops during adolescents, and the changes that take place.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is NOT a part of the nervous system?
Backbone
What are the two main cell types of the nervous system?
Neurons and neuroglia
How many neurons are found in the average human body?
Around 100 billion
What are the electrical messages called that neurons pass?
Impulses
Does a neuron send a message, receive a message, or both?
Both
Sensory messages
goes around from your sensory organs to your brain and tells your braun about the outside environment (ex: It’s cold, something smells bad)
Motor messages
goes from your brain about the outside environment and tells your muscles to contract, such as when you raise a hand to ask a questions or blink the eye
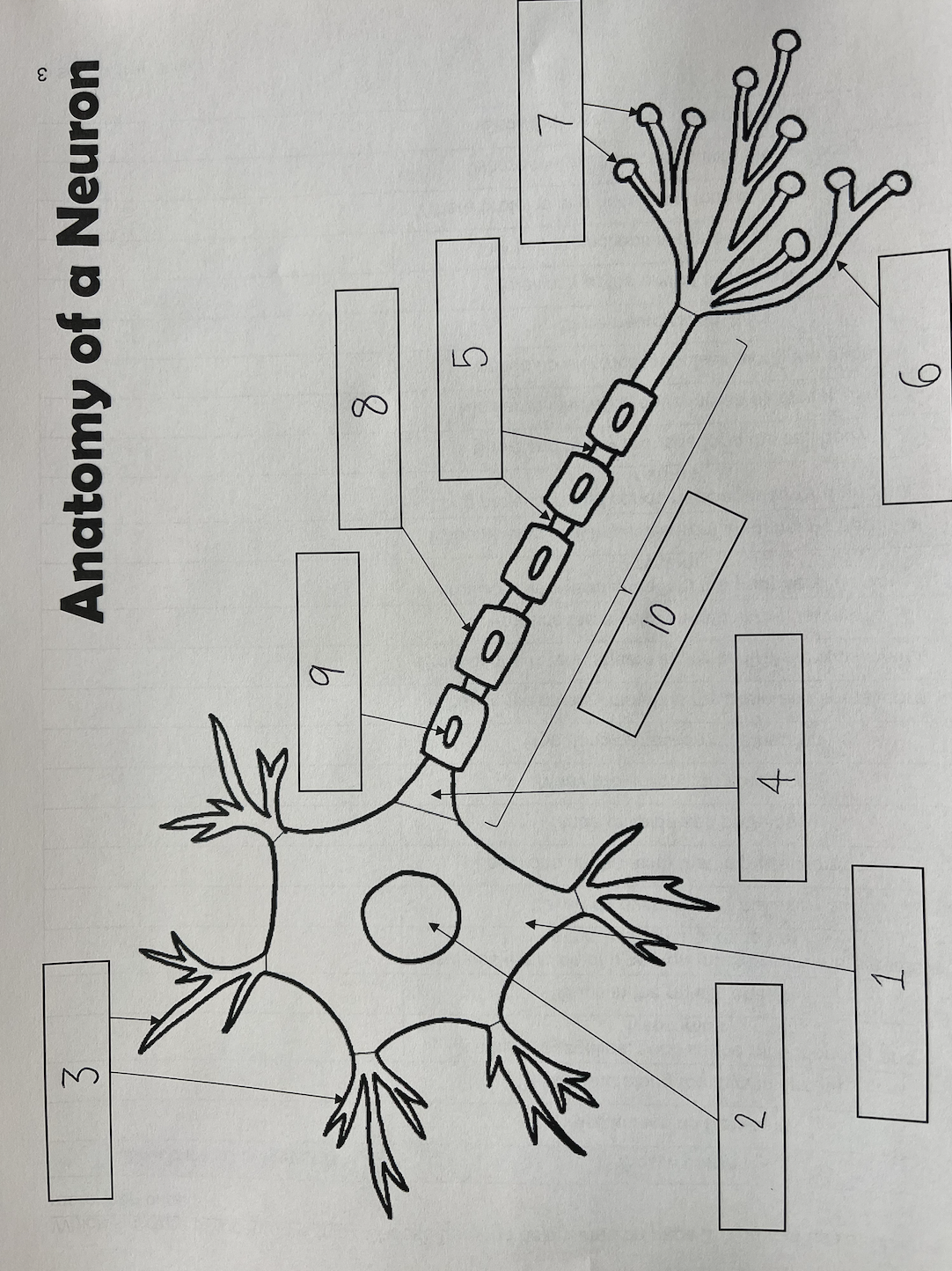
1
Cell body
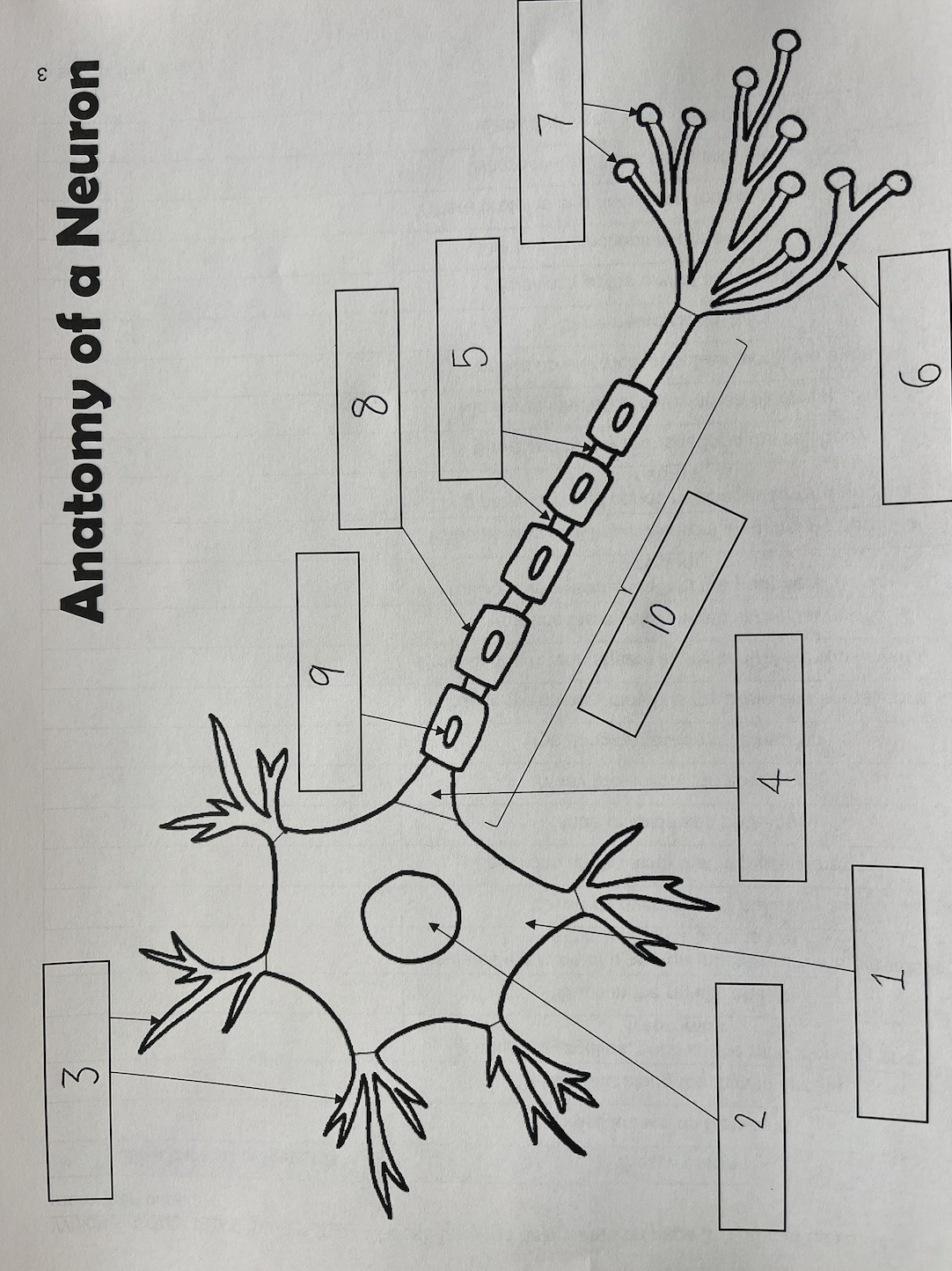
2
Nucleus
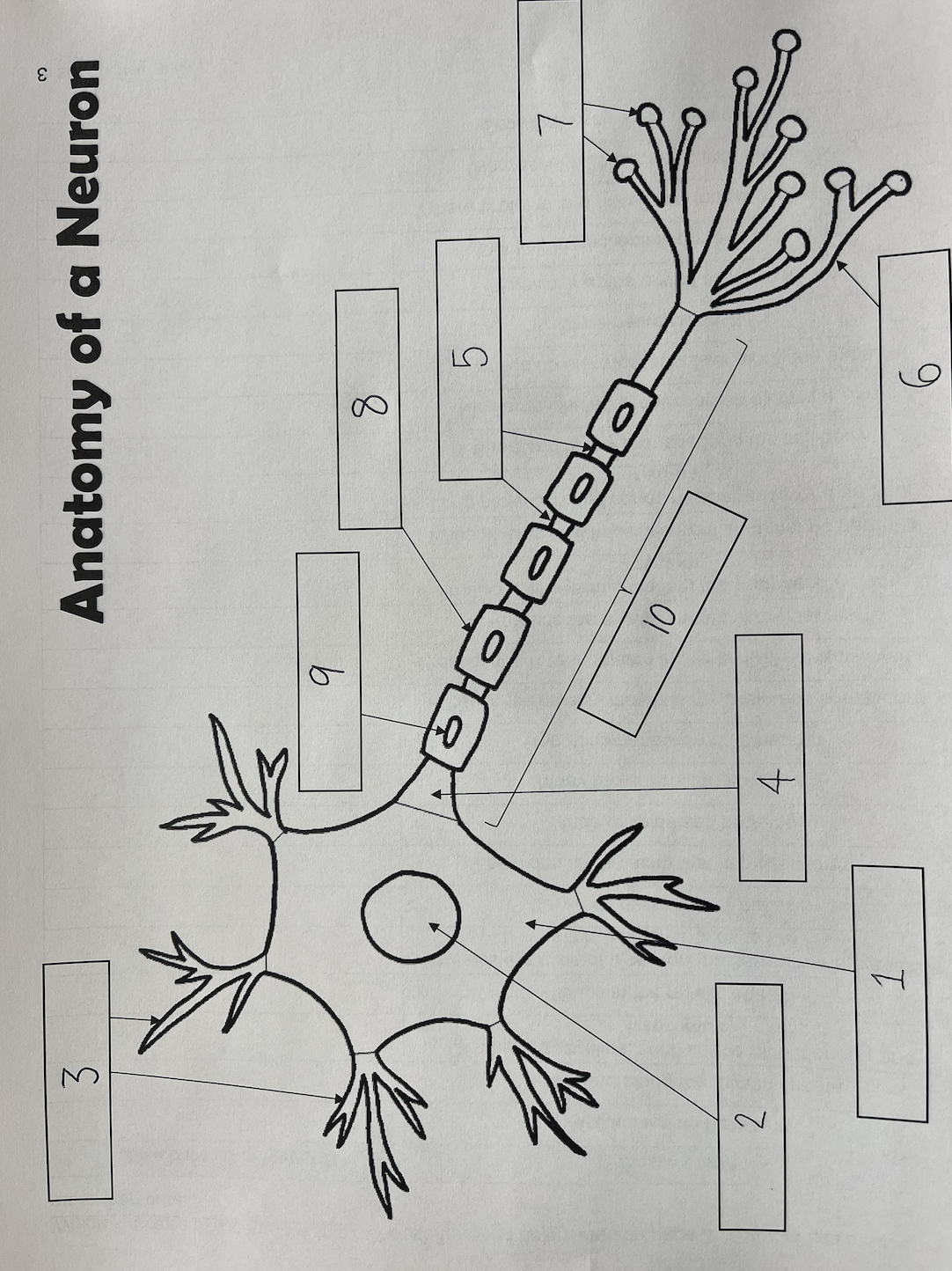
3
Dendrites
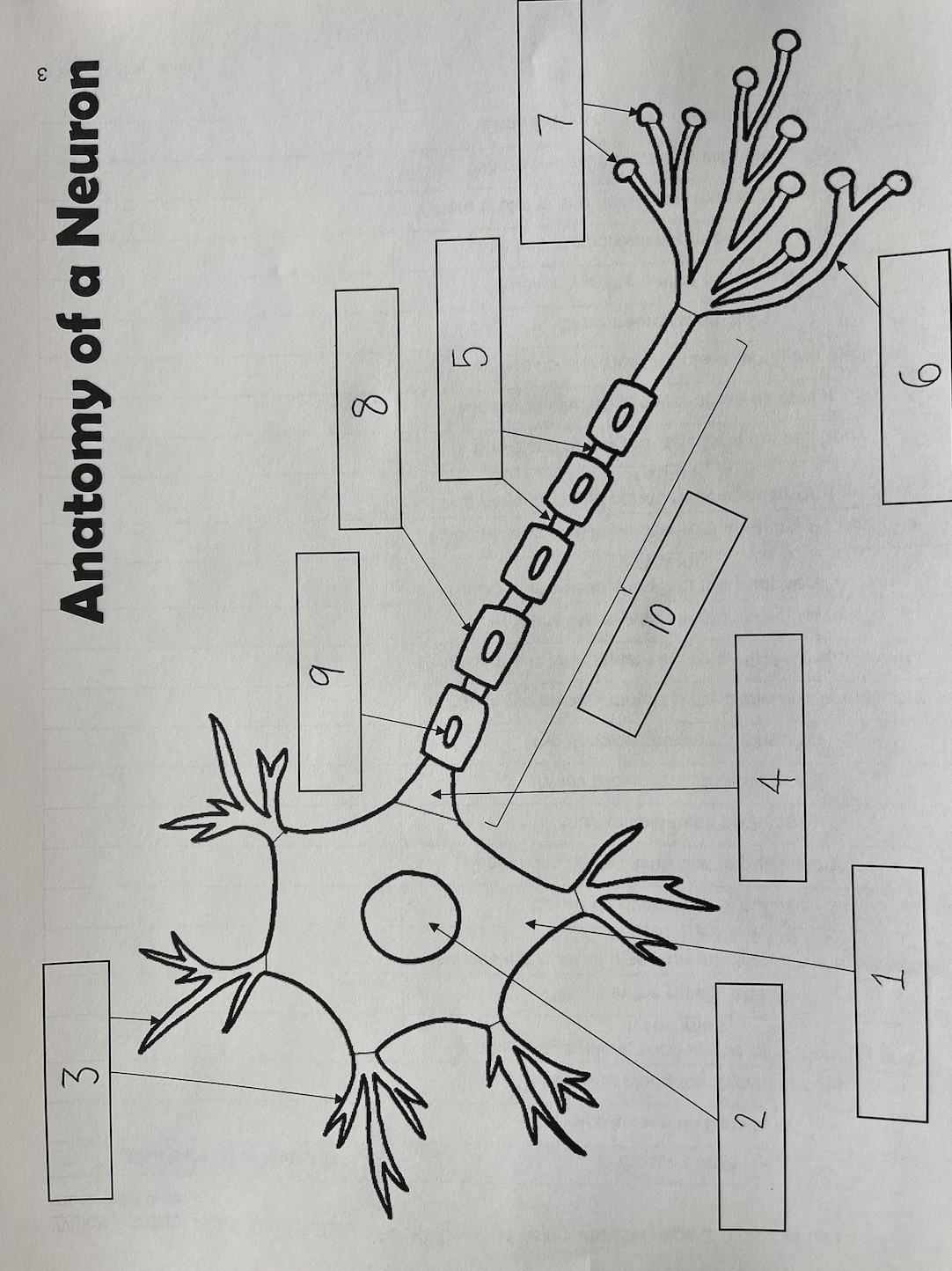
4
Axon Hillock
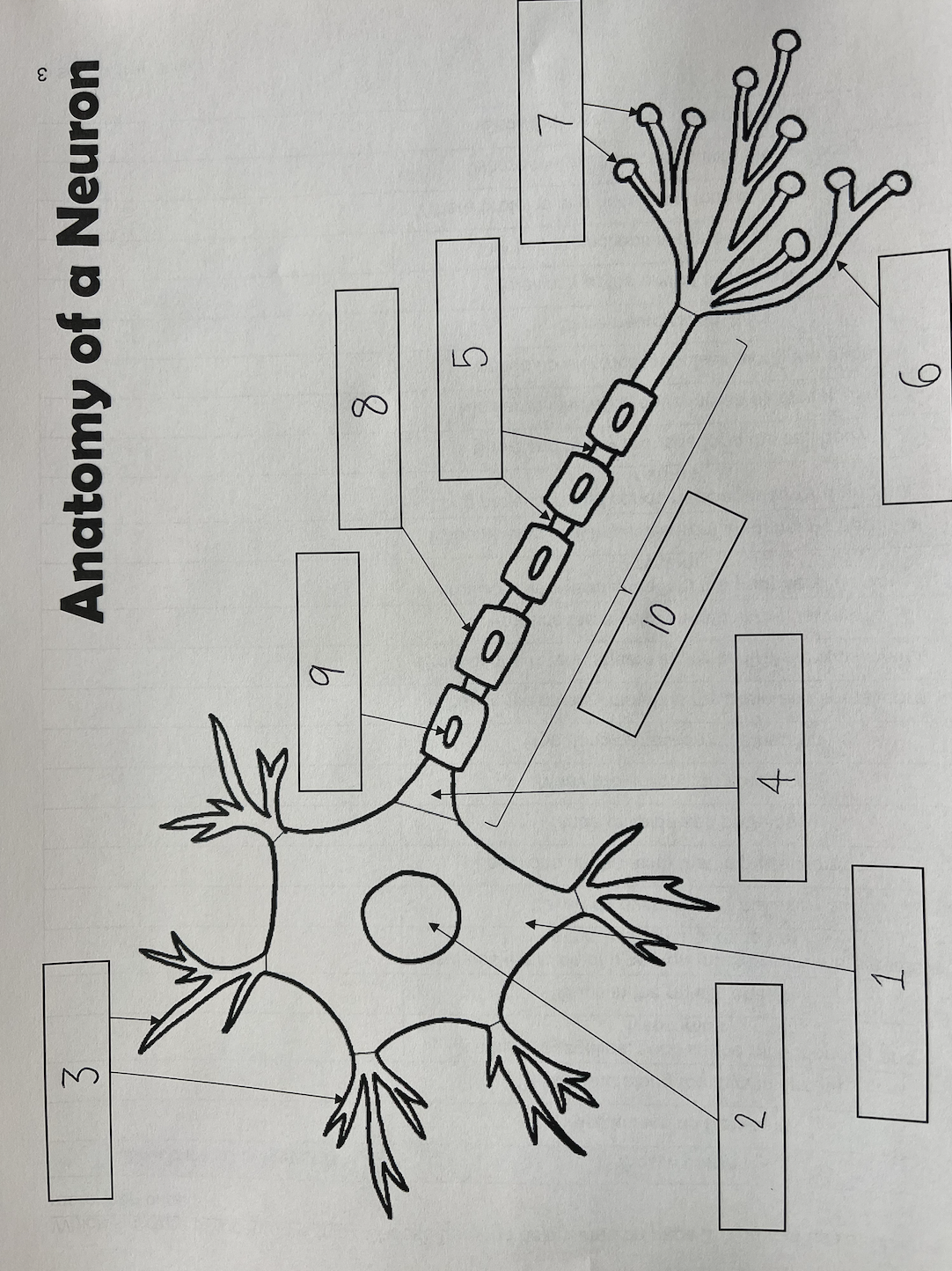
5
Nodes of Ranvier
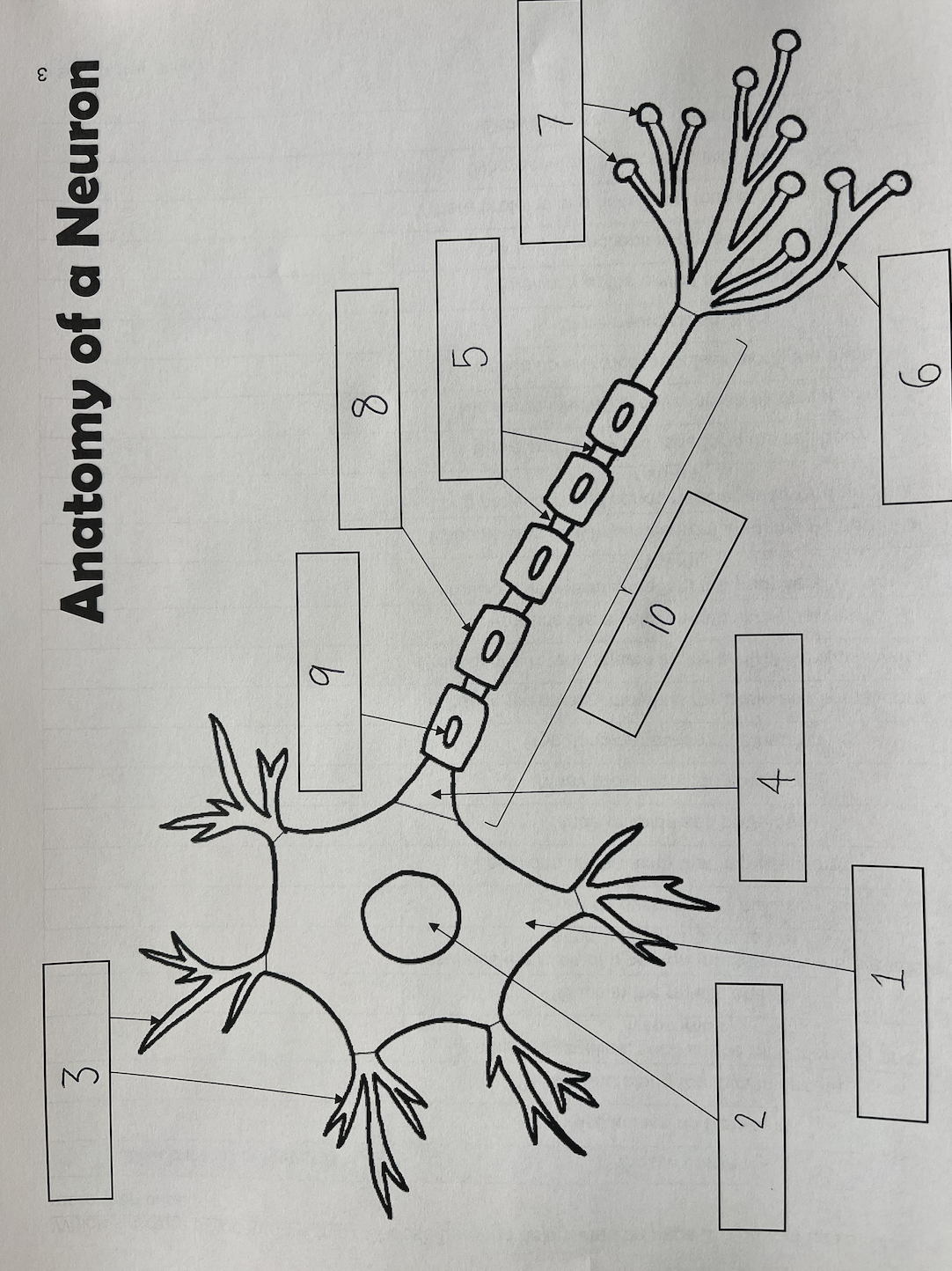
6
Axon terminal
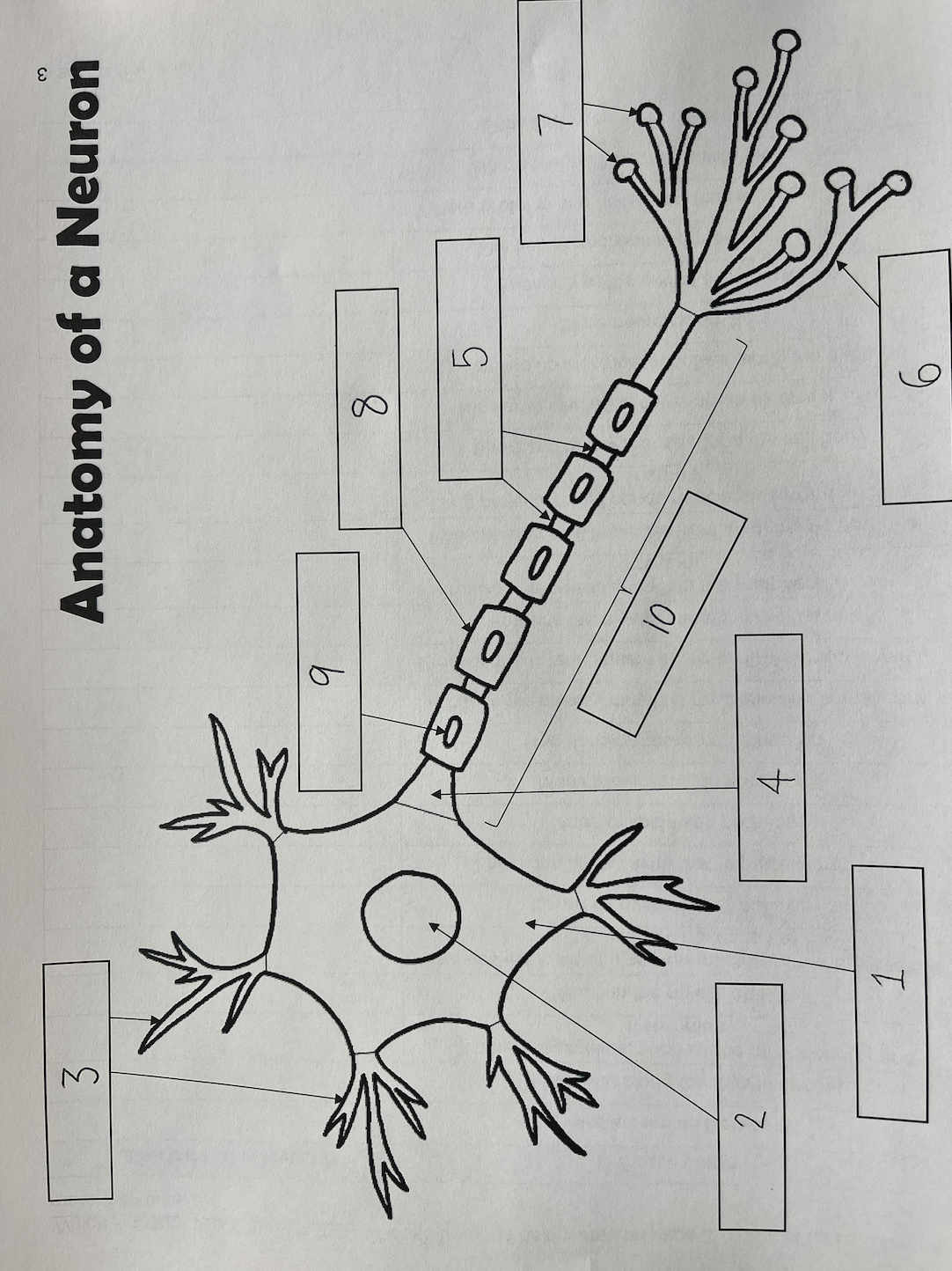
7
Synaptic End Bulbs
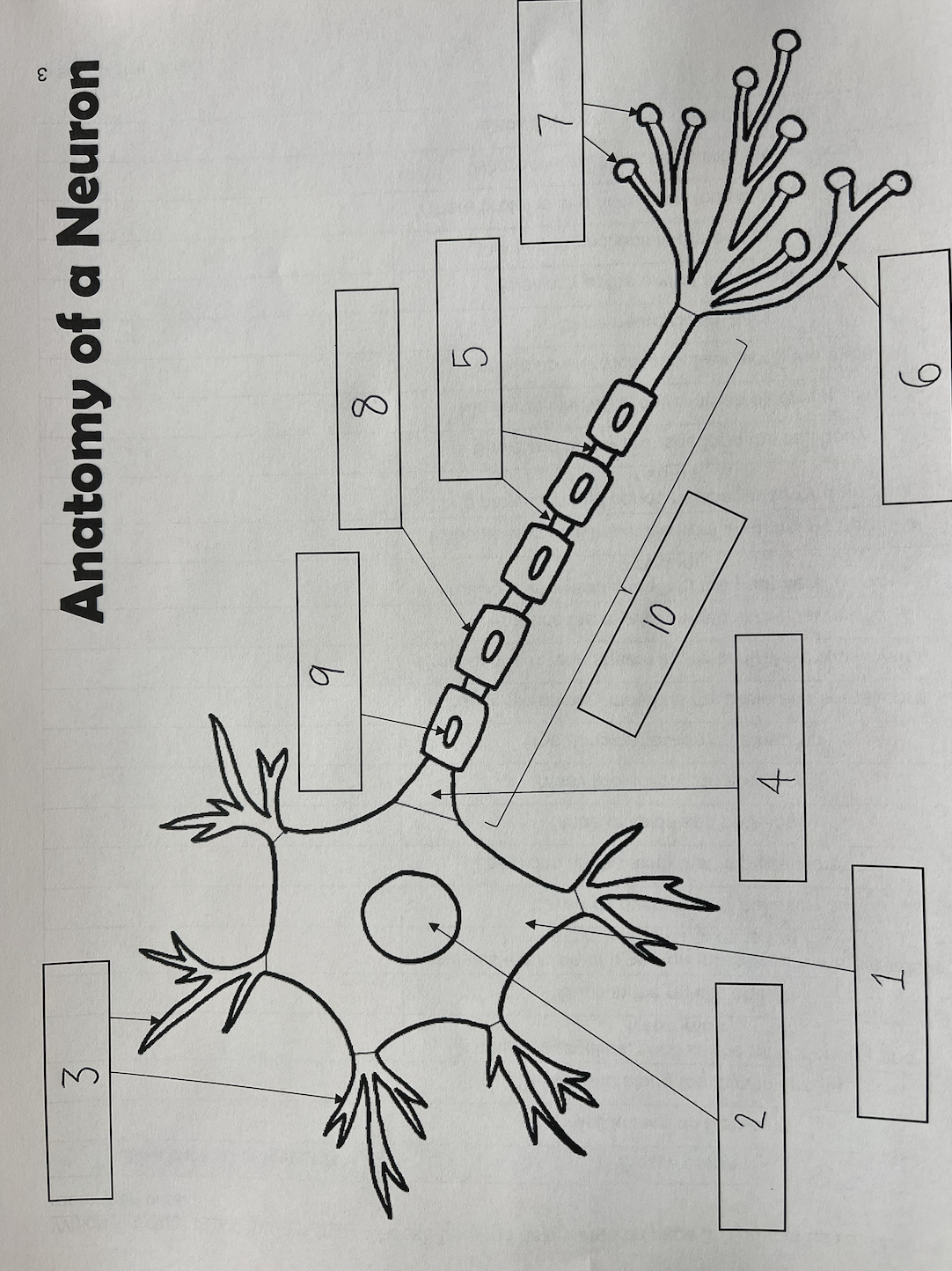
8
Myelin Sheath
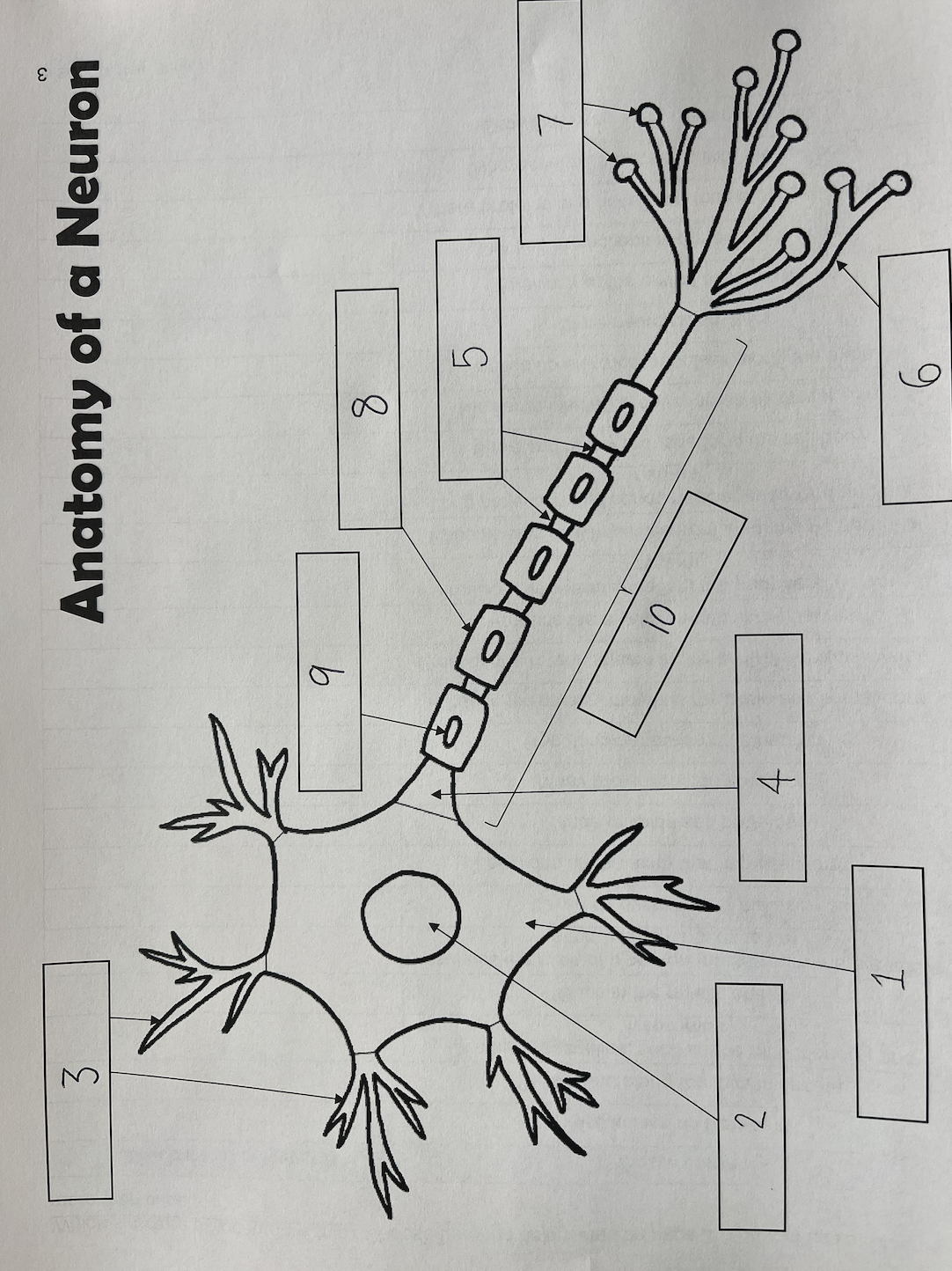
9
Schwann Cell
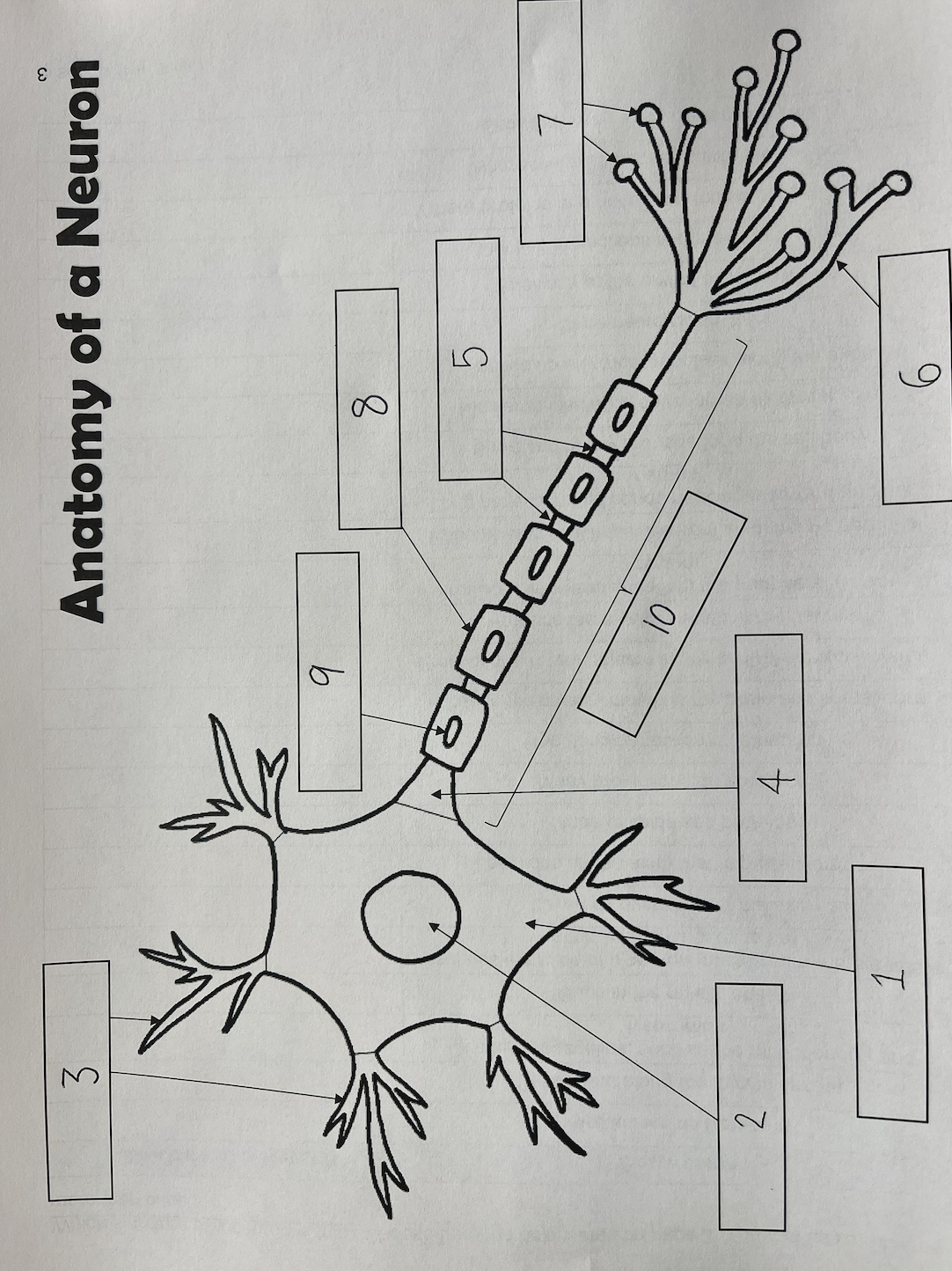
10
Axon
What system is the brain apart of?
the nervous system
Importance of myelin
• allows connected neurons to communicate with each other in a much more effective way
• our bodies rely on myelin to enable rapid transport of a message on the axon
• provides axon with insulation
How do neurons communicate?
through electrical and chemical signals
Why is the knowledge of neurons important when learning about the adolescent brain and technology?
Neurons are the basic building blocks of our brain; they help with transmitting information and forming connections; allows us to understand how the brain develops and how technology impacts it
Cell body
also known as the soma; contains organelles, such as the mitochondria and lysosomes; where proteins and necessary molecules are produced
Schwann cells
Cells found along the myelin sheath; produces the myelin sheath in the nerves as well as the peripheral nervous system; cells that wrap axons repeatedly
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath; locations on the axon that impulses jump to
Myelin Sheath
Insulates the axon of a neuron (makes sure the electricity stays where it needs to be); layered covering over the axon; made of lipids and proteins; similar to insulation covering an electrical wire; similar to electrical impulses along the axon
Dendrites
Many projections on a neuron; receives electrical impulses from neighboring neurons
Axon
One, long projection on a neuron; sends messages towards another neuron
oligodendrocytes
Produces the myelin sheath in the brain, the spinal cord, and the central nervous system
Synaptic End Bulbs
Swellings at the end of axon terminals; stores neurotransmitters
Axon Hillock
Where the axon connects with the cell body
Axon terminal
The fine projections at the end of the axon