Air Pollutants
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Source: Incomplete combustion of waste, vehicle exhaust, boilers, furnaces, water heaters, wood stoves, fireplaces, and gas stoves
Sinks: Upward migration into the upper layers of the atmosphere, uptake by soils
Impact: Out competes O2 for hemoglobin, Low concentration fatigue, headaches, dizziness, confusion, nausea, death
Env. Effect: Contributes to ground level ozone, smog
Mitigation: Maintaining and adjusting combustion equipment, gas appliances, furnaces, flues, and chimneys
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Source: Combustion of any organic material. Gasoline, petroleum, coal, natural gas, biomass, aerobic respiration
Sinks: Photosynthetic organisms, Acid deposition (H2CO3) acidification of oceans
Impact: A greenhouse gas, absorbs thermal radiation and re-emits it at lower wavelengths
Env. Effect: Absorption of heat in the troposphere/increasing global temp. water/atmosphere acidification and ecological impacts
Mitigation: Using fuel sources that have low or no emissions, fertilizing ocean with iron
Tropospheric Ozone (O3)
Source: Tropospheric reaction of NOx, VOCs with O2 that requires sun and heat.
Sinks: Urban Photochemical Smog
Impact: Lung damage, breathing problems, reduced resistance to colds and infections, chest pain, coughing, eye irritation, asthma, emphysema, bronchitis, pneumonia
Env. Effect: SMOG, decreased crop yields, damage to plants, traps heat, contributes to thermal inversions
Mitigation: Mass transit, reduction of traffic congestion, drive less/walk more
Nitrogen Oxides(NOx)
Source: Combustion (gasoline, natural gas, coal, oil) Vehicles are a major source. Power plants and factories burning fossil fuels
Sinks: Acid deposition onto land/water, key reactant in creating photochemical smog
Impact: Respiratory illnesses, lung disease, component of photochemical smog and acid deposition
Env. Effect: Forms photochemical smog, acid precipitation. Damages plants, trees, aquatic life, and buildings.
Mitigation: Cap and trade allowances (ERCs), reduce combustion temperatures
Sulfur Oxides (SOx)
Source: Combustion of coal or petroleum high in sulfur.
Sinks: Cloud condensation/acid deposition (H2SO4); form particulate matter (PM)
Impact: Respiratory illnesses (bronchitis, emphysema, asthma)
Env. Effect: Reacts in atmosphere to form SO3 and H2SO4 (acid rain)
Mitigation: Cap & trade allowances (ERC’s); scrubbers
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Source: Evaporation of fuel, uncombusted exhaust, paints, carpets, furniture, insulation etc.
Sinks:Photolysis (UV), forms photo chemical smog
Impact: eye, nose and throat irritation, headaches, loss of coordination, nausea, damage to kidney, liver & central nervous system
Env. Effect: contributes to ground level ozone & smog, climate change
Mitigation: Reduce combustion of fossil fuels (hybrids, public transport. Reduce use of paint thinners & aerosols
Peroxacyl Nitrates (PANs)
Source: Transportation (created from ethanol in fuels); more stable than ozone & capable of long range transport
Sinks: Strong respiratory and Eye irritant. Potentially mutagenic. Can damage vegetation.
Particulate Matter (PM/SPM)
Source: Construction sites, unpaved roads, fields smoke stakes, fires. Fireworks, power plants, industries, automobiles, volcanoes
Sinks: Gravitational settling to land or water
Impact: damaged lungs/ respiratory diseases (asthma to COPD to Cancer), eye irritation, early death
Env. Effect: Decreased visibility, produces haze, dust on leaves damage crops (no photosynthesis), discolor/dirty buildings & other surfaces
Mitigation: Stricter emissions standards (pollution abatement), use of electrostatic precipitators
Radon (Rn)
Source: Forms naturally in soils containing uranium (byproduct of U decay)
Sinks: Decays to P0-218 then eventually to lead
Impact: Carcinogenic, can cause cancer
Env. Effect: N/A
Mitigation: Monitor/test basements
Asbestos
Source: Disturbed insulation due to renovation or damage
Sinks: Deposition
Impact: Lung cancer / Mesothelioma
Env. Effect: N/A
Mitigation: Use insulation that does not contain/don’t disturb materials that have asbestos in them
CFC’s
Source: Refrigerants, solvents, accelerants in aerosol cans, foam blowing
agents, pesticides, halons (group 17 chemicals)
Sinks: Photolysis with intense UV radiation (stratosphere)
releasing chlorine or bromine which depletes ozone.
Impact: Increased skin cancer rates; eye cataracts, weakened immunity.
Env. Effect: tratospheric ozone depletion allowing more UV-A & B to get to
Earth’s surface; decline in #’s (arctic krill) effecting food webs,
decreased crop yields
Mitigation: Decrease use, Montreal Protocol
Lead (Pb)
Source: Exhaust fumes from gasoline, metal smelting, paint, power
plants burning fossil fuels SINK: Deposition into soil and water; contaminates soil & crops
Sinks: Deposition into soil and water, contaminates soil and crops
Impact: Neurological effects in children, high blood pressure and heart disease in adults, kidney damage, cancer
Env. Effect: Decreased growth/reproductive rates in plants & animals,
Neurological effects in vertebrates.
Mitigation: Banning gasoline with this in it
Mercury (Hg)
Source: Coal burning power plans
Sinks: Condensation, precipitation, deposition
Impact: Damages the nervous system and the brain “mad hatters” toxic to nerve cells
Env. Effect: Capable of bioaccumulation and biomagnification
Mitigation: Cap and Trade (ERCs)
Sulfuric Acid
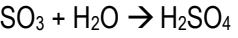
Nitric Acid
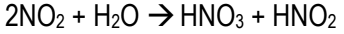
Carbonic Acid
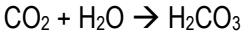
Photochemical Smog
