Exam 1: Documentation and Treatment Planing
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
why do we document?
Maintain a serial record of services rendered: what did I do?
Communication: see what other professions document
To get paid for our services: reimbursement
Quality assurance: are we doing best practice? are they achieving goals?
Research
Who pays for OT services?
1) Patient -> self pay
2) Insurance companies -> HMO (limited) or PPO (out of network)
2) Federal and state funded programs --> medicare and medicaid, VA
3) Employer ->workers comp
4) Auto-insurance -> motor vehicle accident
5) Other funding sources -> grants
medicare vs medicaid
care: Provided health care to elderly + FEDERAL
aid: Provided health care to poor people + FEDERAL + STATE
if there is no documentation...
it never happened
documentation records should be...
Organized
Legible
Concise
Clear
Accurate
Complete
Current
Objective
Correct grammar
Proper spelling
parts of the documentation process
1) initial evaluation report
2) progress note or progress summary
3) discharge summary
what does the initial evaluation report consist of? when is it done?
-first encounter
-occupational profile
-select instruments
-administer evaluation
-develop treatment plan
what is the first step of the documentation process?
initial evaluation report
what does the progress note/summary consist of? when is it done?
-during treatment
-SOAP note
-narrative note
-each setting has different doc requirements
ex: rehab -> talk about ADLs
ex: school -> talk about academic interventions
what is the second step of the documentation process?
progress note/summary
what does the progress note/summary consist of?
note performance:
-before
-during services
-now
-moving forward
what is the third step of the documentation process?
discharge summary
what is important to put on every page of the documentation
patient identifier (name, id ...)
what goes on the documentation records of OT patients?
1) Patient identifier on each page
2) Date, time and length of intervention -> (time in/out)
3) Type of documentation (Initial, Progress , Discharge)
4) Practitioner's signature (First name or initial, Last name, Professional designation)
where does the OT signature go on the documentation form?
end of note
in addition to a practitioner's signature, what might also be required?
a countersignature
when can we use abbreviations when documenting?
1) when they are acceptable
2) when they are approved by the facility
when documenting in paper, what is to be done when you make an error?
errors are corrected by drawing a single line through the word and initialing it
EMC?
electronic medical record
what is required for a practitioner to begin treatment?
a prescription
*especially for insurance
what is important to document for someone to receive treatment?
1) recent documented change in condition (decline in prior level of function --> OT is necessary!)
2) reasonable expectation for progress (rehab potential)
3) ongoing process
*must reflect need for skilled services
*care must reflect standard of practice
rehab potential
reasonable expectation for progress
- excellent, good, guarded, no (avoid using poor)
skilled services
services that must be performed or supervised by a licensed healthcare professional
OT vs wife
medicare only reimburses for what type of services?
skilled
*other payers tend to follow these guidelines
skilled services require the knowledge and training of a
professional
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: assess
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: analyze
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: maintain
unskilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: help
unskilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: watch
unskilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: observe
unskilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: interpret
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: modify
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: facilitate
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: inhibit
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: practice
unskilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: monitor
unskilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: establish
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: instruct/educate
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: fabricate/design
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: adapt
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: environmental modifications
skilled
is the following term skilled or unskilled terminology: determine
skilled
what conditions are likely to use the word "maintain" during the documentation process?
neurological conditions --> dementia
Any kind of documentation and treatment must show:
medical necessity for OT
-complications and safety issues related to limited occupations performance and occupational engagement
examples of conditions that demonstrate medical necessity for OT:
1) poor posture (functional mobility, safety)
2) weak grip (ADLs)
3) paresis (motor weakness, neuro. cond., safety)
4) perceptual deficits
5) cognitive disorders
first step of OT process
conduct and evaluation/assessment
what does the first evaluation/assessment consist of?
1) establish medical necessity -> after doc prescribes OT
2) highlight the need for skilled services (ex: patient lives alone and cannot prepare a meal)
3) states a change in condition (independent --> dependent)
4) states a profess expectation --> rehab potential
the evaluation/assessment must be completed when?
prior to providing any interventions
- evaluate before you assess
initial evaluation documentation includes:
1) reason for referral
2) client information (diagnosis)
3) occupational profile (past + current level of function)
4) assessment tools utilized and results (analysis of findings and justification for OT services + rehab potential)
5) expected outcomes and recommendations
what is the purpose of an intervention plan?
to design or propose a therapeutic program
an intervention plan is based on ...
one or more FOR
functional OT problem list consists of
affected area of occupation + contributing factors
* part of intervention plan
two types of goals
short term and long term
goals must be
measurable and attainable
in terms of time, intervention plans must provide
frequency and duration of treatment
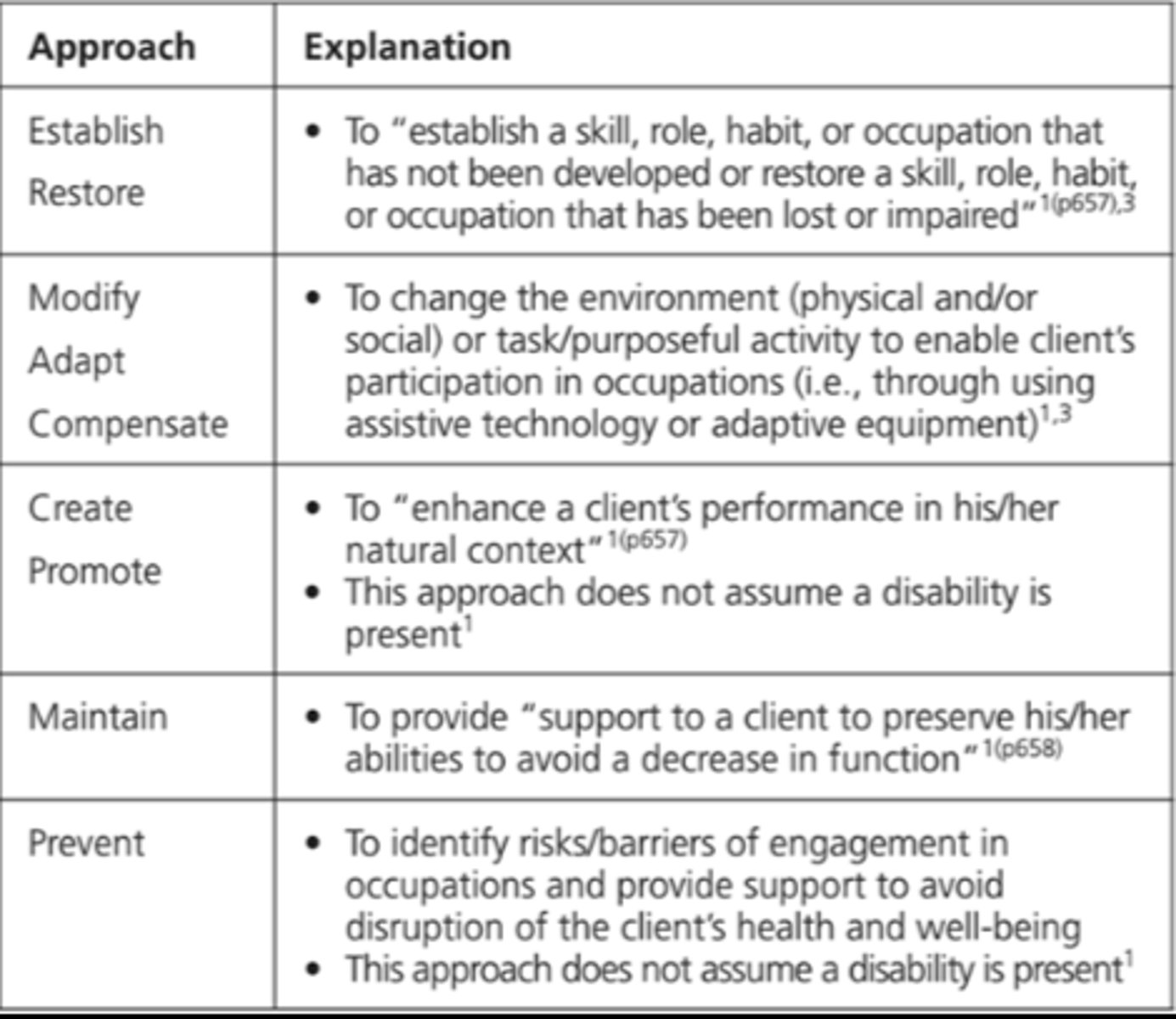
types of intervention approaches
create/promote
establish/restore
maintain
modify
prevent
steps of treatment planning
1) evaluate occupational performance
2) identify functional OT problems
3) establish the LTG for each OT problem
4) establish a STG for each LTG
5) select intervention methods
provides a standard for measuring the progress
intervention plan??
allows the therapist to plan and analyze the proposed course of action
the intervention plan?
functional OT problems are composed of
affected occupation + contributing factors
what does an OT do to evaluate occupational performance?
1) conduct an patient interview
2) observation
3) administer assessments
4) gather data
5) consider: pre-morbid status, current status, predicted status
when evaluating occupational performance, what client factors are important to consider?
age
education
culture
psychological status
functional status
where can we get info to get to know our client better?
-the patient themselves
-medical record
-assessments
-observing the patient
-other team members
-family/significant others
-resource materials
when gathering information about the client, what must we make sure to do?
access iff its valid!
how do we identify functional ot problems?
1) analyze evaluation results
2) use OTPF domains
- areas of occupation
- client factors
- performance skills
- performance patterns
- context
- activity demands
all of your treatment planing depends on
your clients functional problem
when determining your clients functional problem, what are two questions that we can ask ourselves?
1_ what aspect of occupational performance is affected?
2_ what factor is hindering performance?
an area of occupation might be impacted by
several influencing factors
ex: impaired ability to type; cognitive, ROM, fine motor coordination, others?
an influencing factor may impact
several areas of occupation
ex: poor endurance; community mobility, home management, mealpreparation, others?
reasonable expectation for performance of OT problem at discharge
LTG
LTG must be:
1) client -centered
2) occupation-based
3) measurable and observable
4) functional
5) attainable
stepping stones to reach LTG
STG
every LTG will have
at least one STG
what happens when a client reaches a STG?
a new one is written until the LTG is reached
T/F there is one correct way to write a well constructed goal
false
There is no ONE correct way to write a well constructed goal
T/F there are many ways to write a poorly constructed goal
true
format for writing goals
COAST
what does COAST stand for? what is it used for?
goal writing
C- client
O - occupation
A - assistance
S - specific conditions (not required*)
T - timeframe
OT services are an ongoing process, what does this mean? what do we have to be aware of?
- are goals being met?
- if not, do we need to modify the plan?
- determine if we need to: continue, discontinue, referral