Diagnostic Imaging- Final Exam: US Pt. 5 Vasculature, LNs, and Retroperitoneal Spaces
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
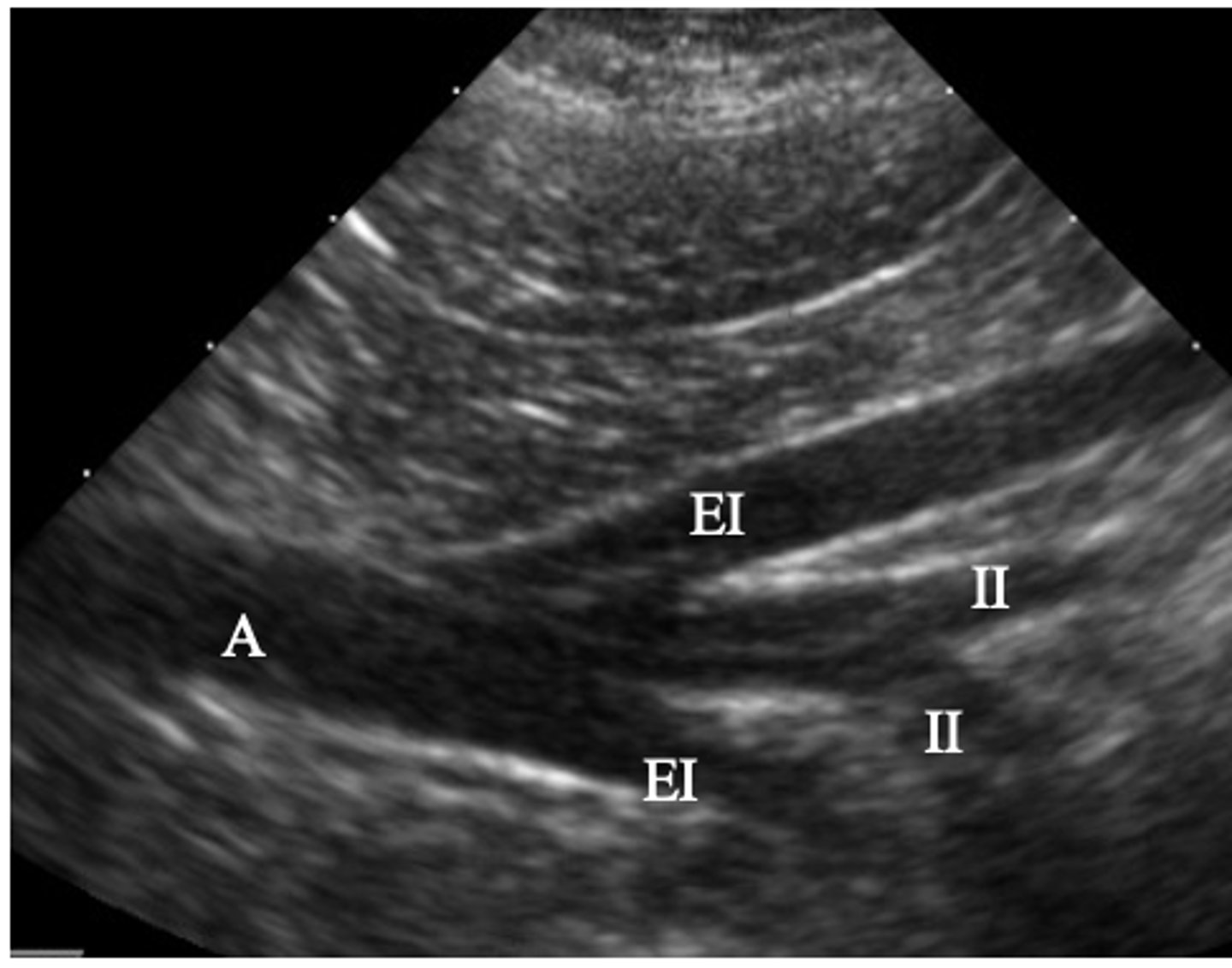
A- aorta
EI- external iliac artery
II- internal iliac artery
ID vasculature on US
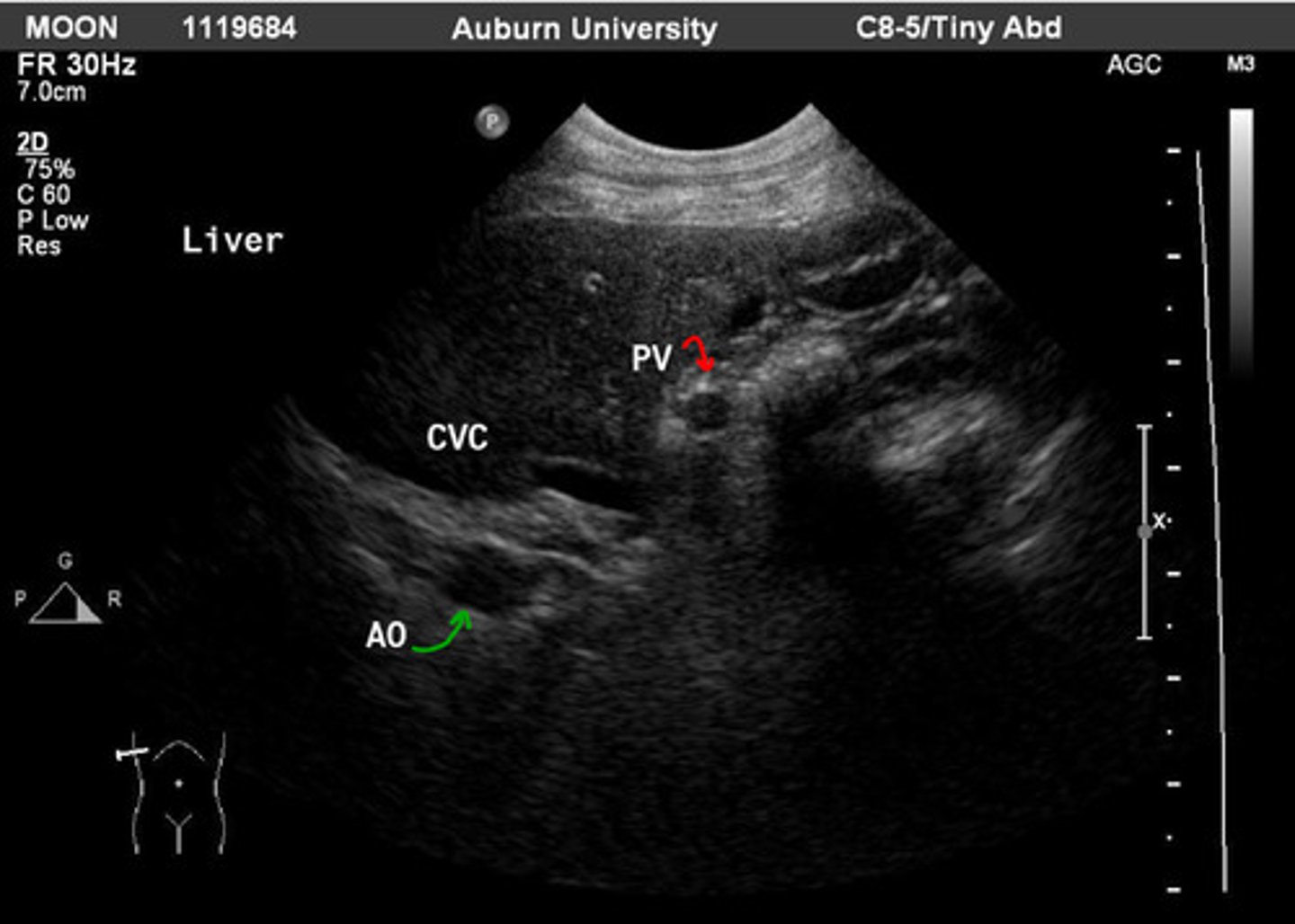
right intercostal window
which window can you see the hepatic hilus?
red- portal vein
green- aorta
ID green and red
red- portal vein
green- aorta
ID red and green
aorta
which is more dorsal: aorta or portal vein?
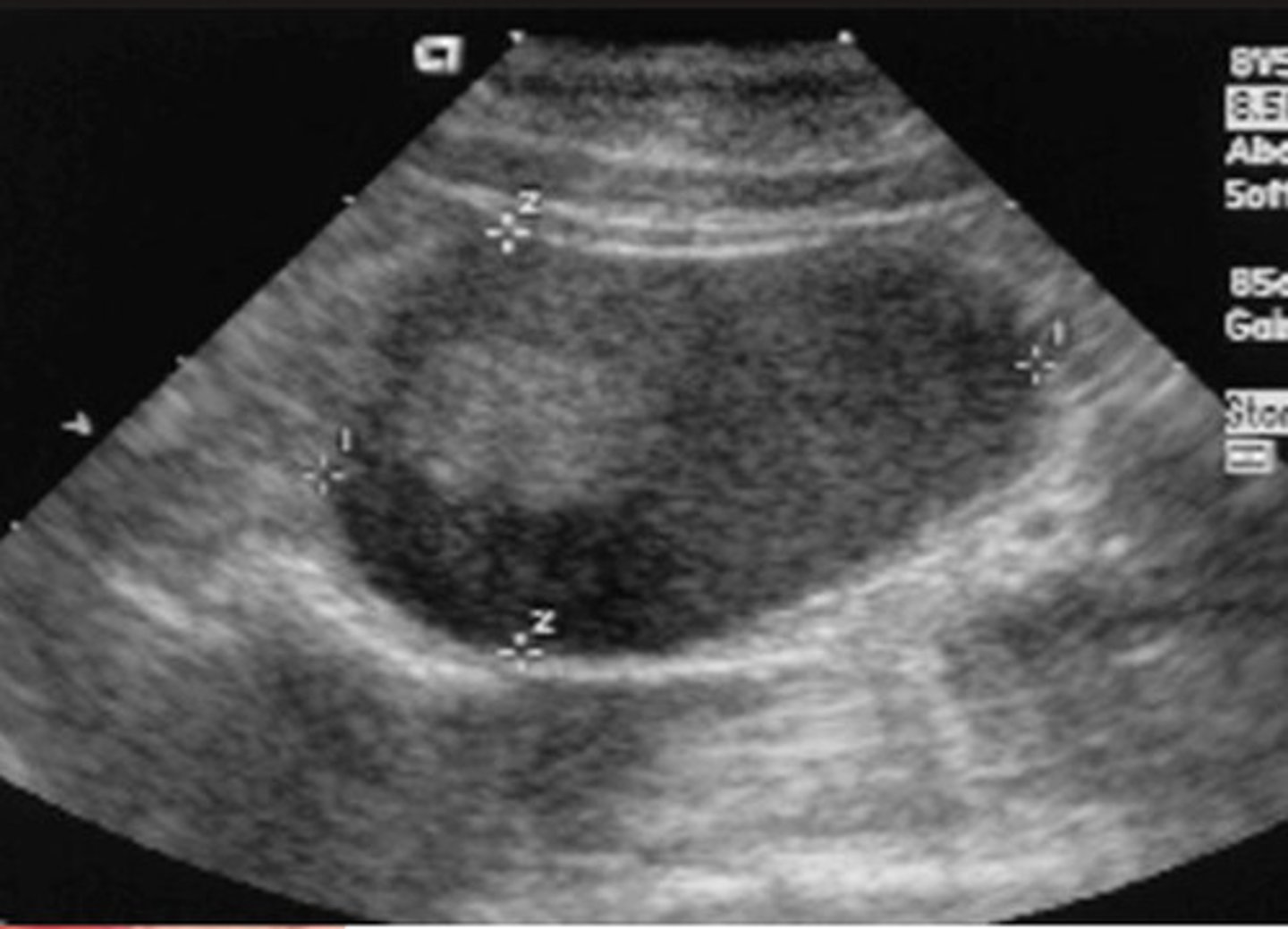
splenic vein
ID red structure in abdomen
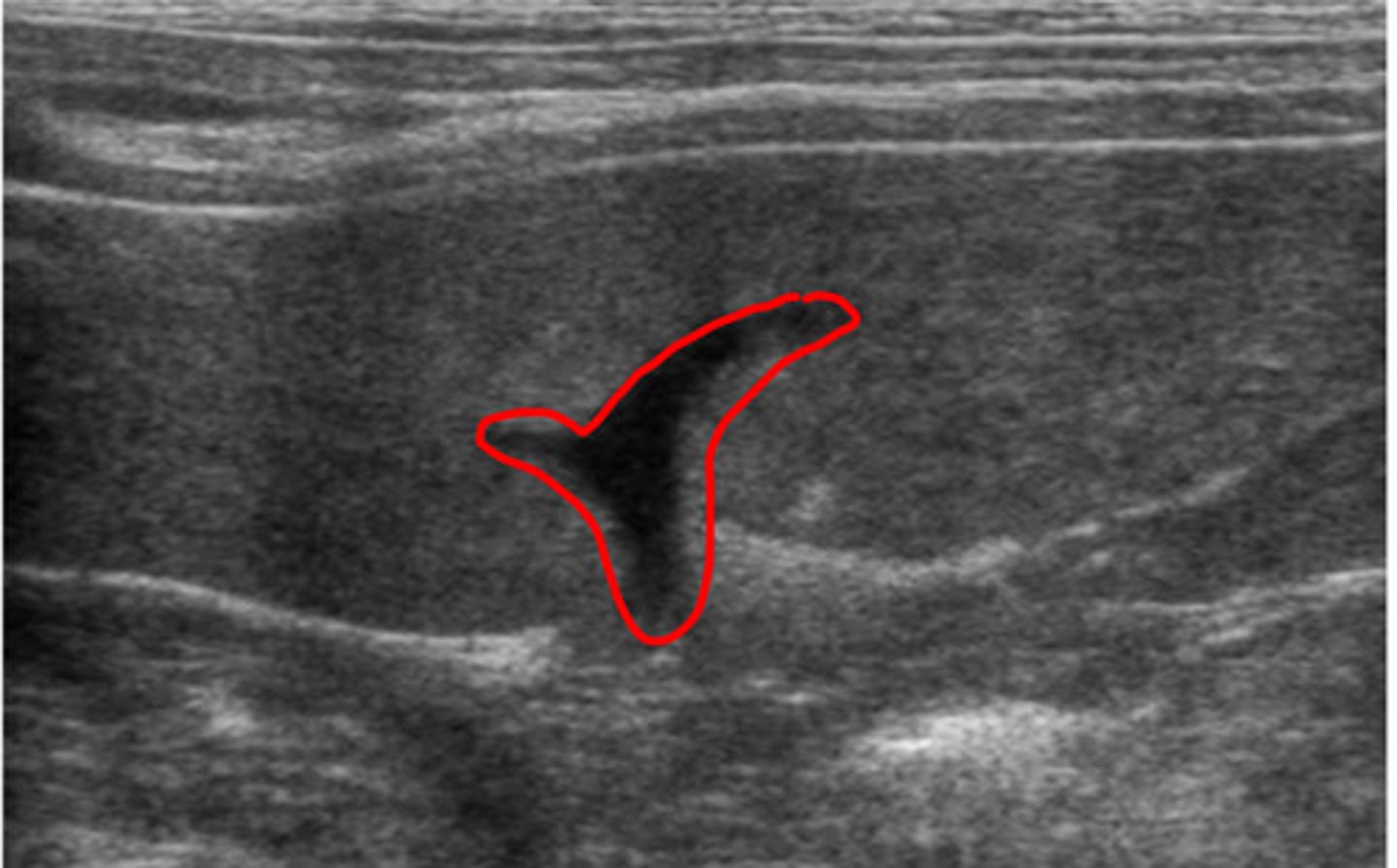
portal vein
the splenic vein drains into what?
-external iliacs
-internal iliacs
-median sacral
what are the arteries involved in the aorta trifurcation?
external iliac arteries
what arteries are the yellow arrows? (apart of the aortic trifurcation)
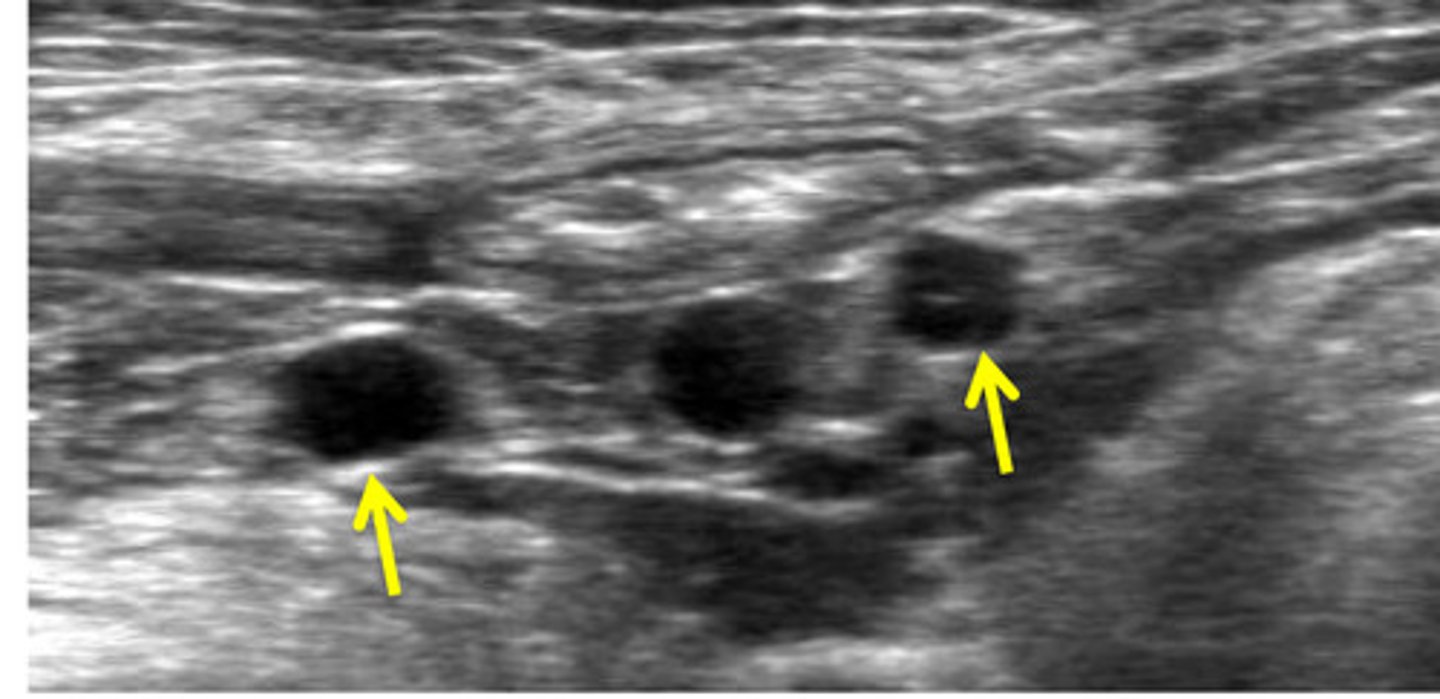
red- external iliac a.
blue- internal iliac a.
ID red and blue arrows (aortic trifurcation)
red- vena cava
blue- aorta
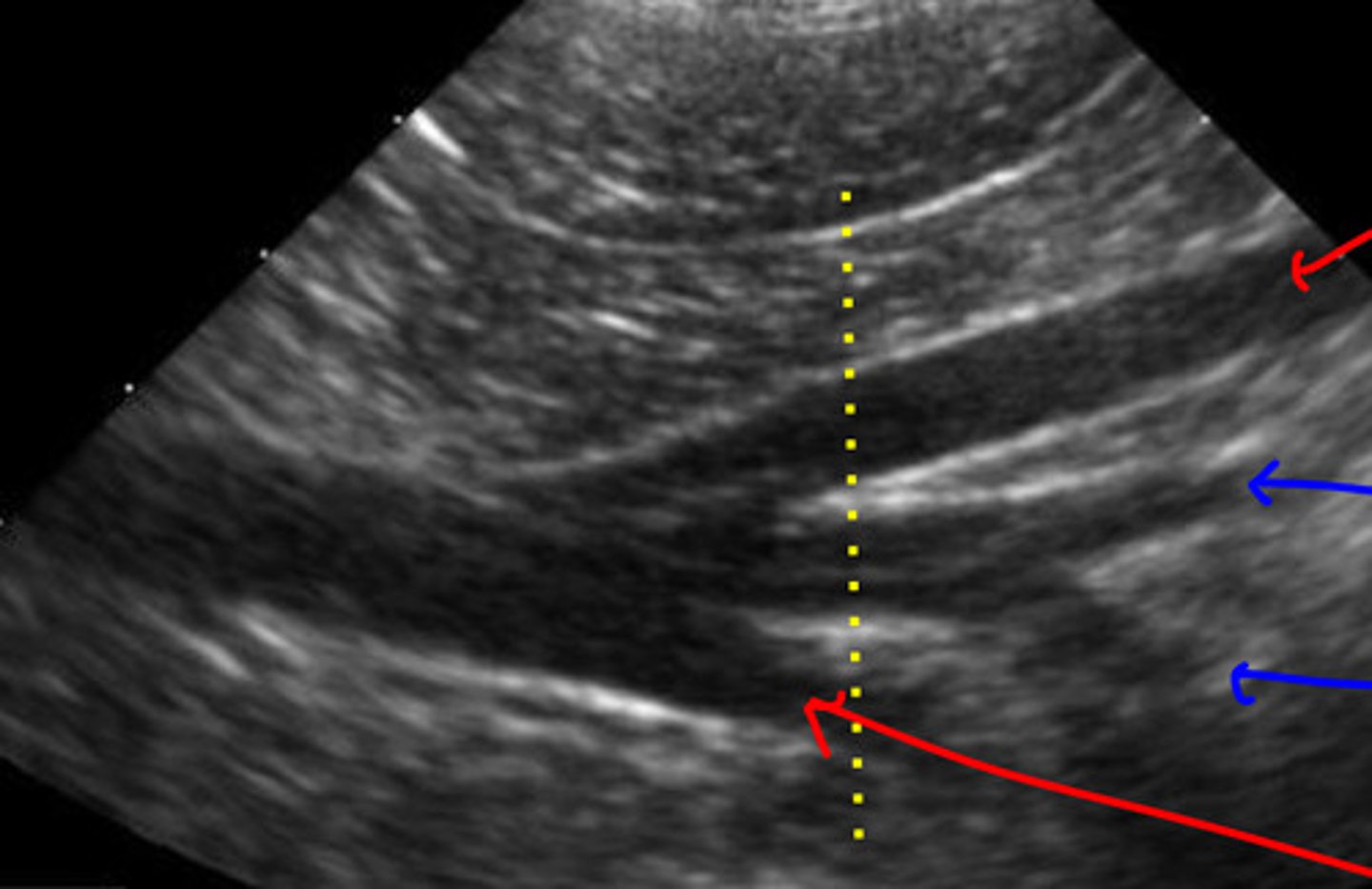
red- right side of body
blue- left side of body
orientation- transverse b/c round
ID red and blue, which one is on the right side of the body and which is on the left? what orientation is this?
vena cava
is the vena cava or aorta squishy?
anechoic
in a vascular US, normal blood is what echogenicity?
-dilation
-thrombi
-aneurysms
-"smoke"
-shunts
-abnormal flow
when evaluating vessels for abnormalities, what should you look for?
abnormal clot
what abnormality in this vessel?
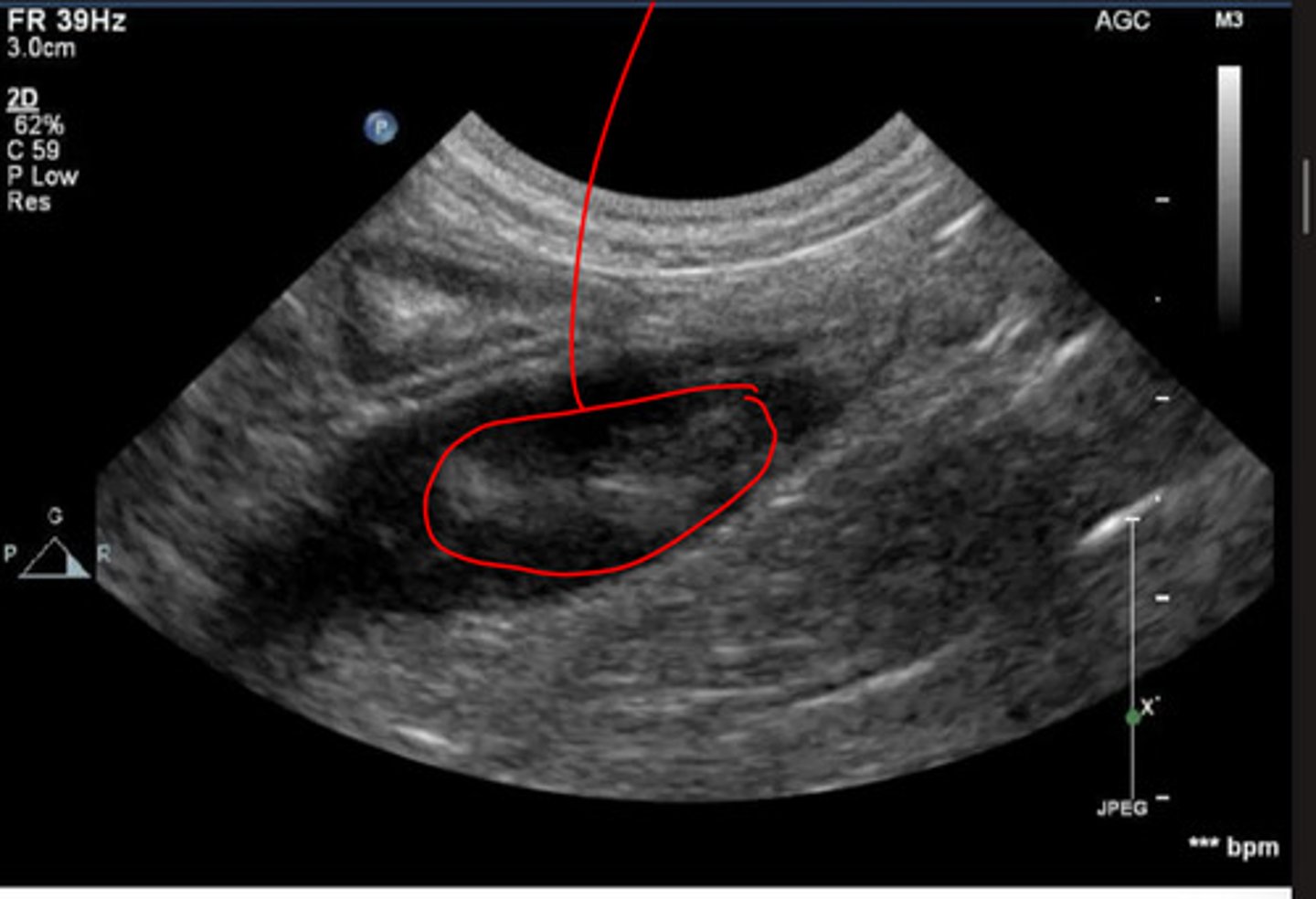
dilation of abdominal aorta
what is the abnormality in this aorta indicated by the red?
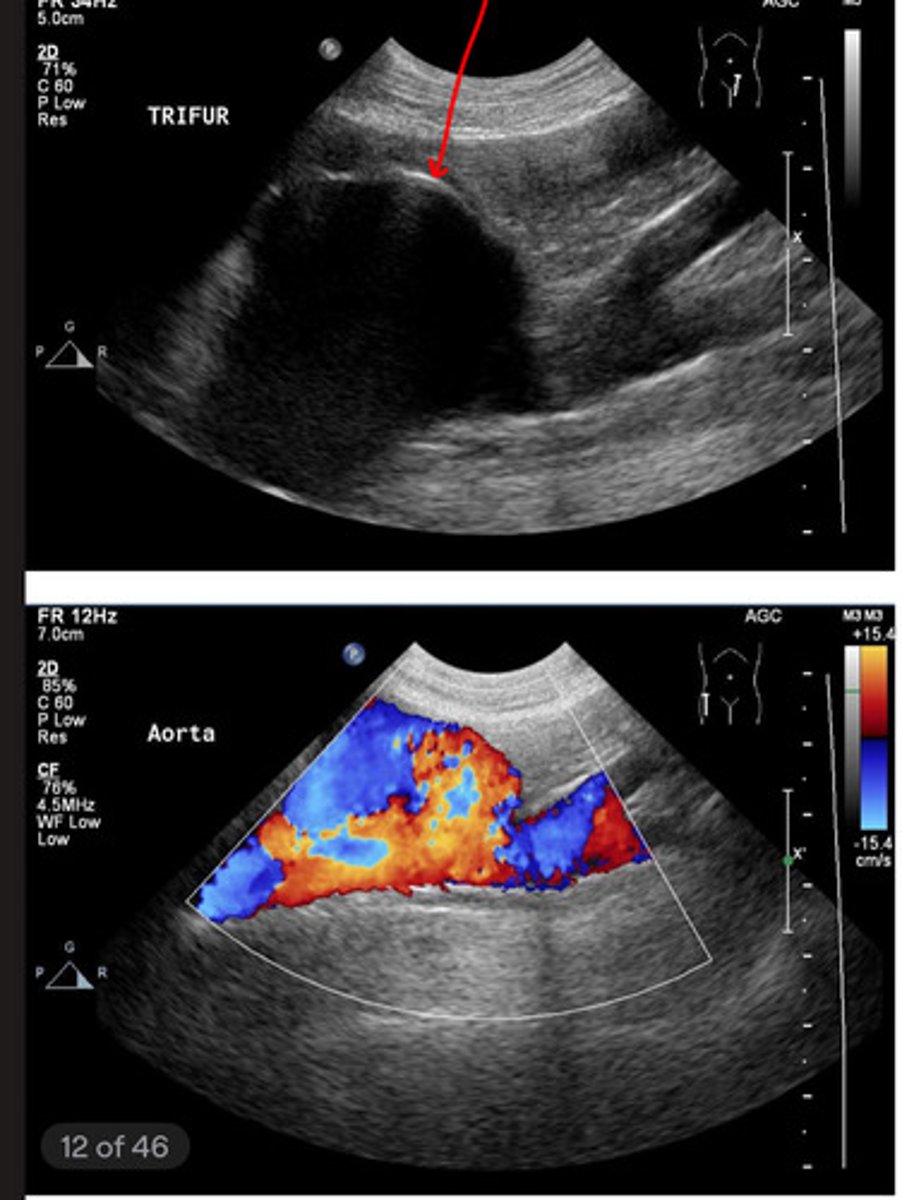
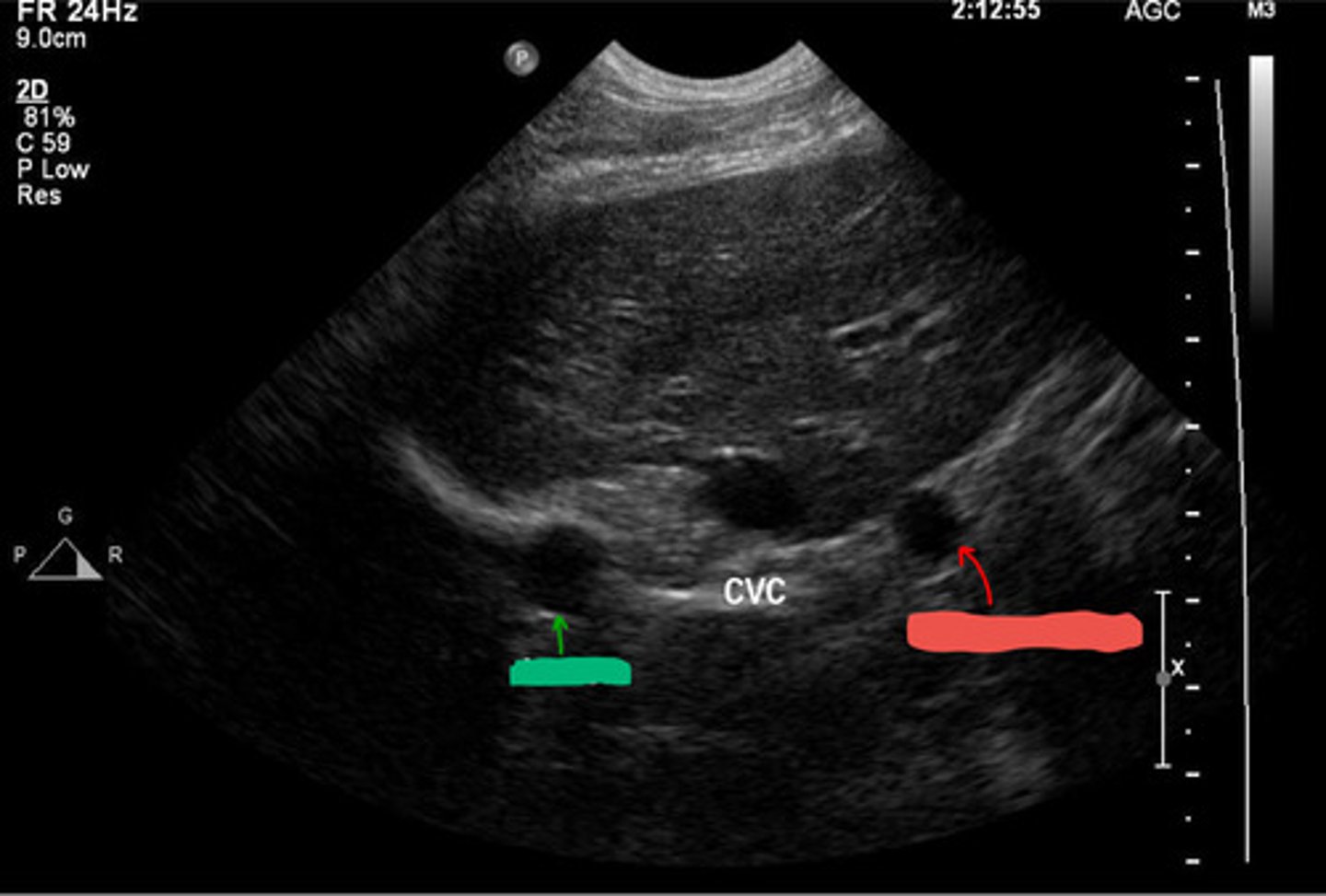
red- caudal vena cava
blue- aorta
what is the red and blue vasculature?
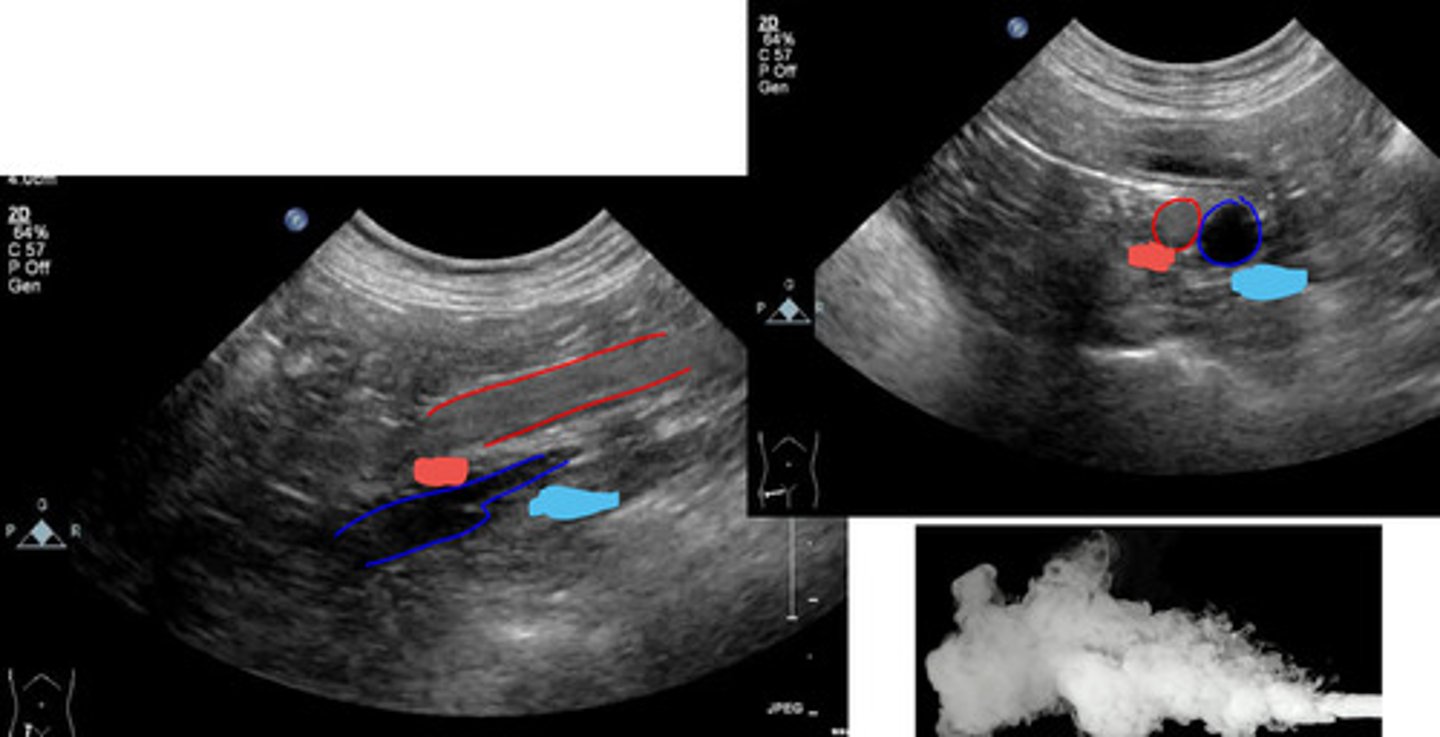
direction and relative velocity of flow
when evaluating vasculature, doppler color identifies what?
slow flow, nondirectional
power doppler is sensitive to what?
velocity of flow in specific vessel
when evaluating vasculature, doppler pulsed wave evaluates what?
used for high velocity flows in echocardiography
continuous waves in a doppler are used for what?
probe angle
doppler signal is dependent on ________?
Blue Away Red Towards
what does BART stand for?
identifies direction and relative velocity of flow
the doppler does what?
blue- away
red- towards
which vessel's blood flow is towards the probe and which is away?
the doppler would have flashes of color
if the animal were panting, what would the doppler do?
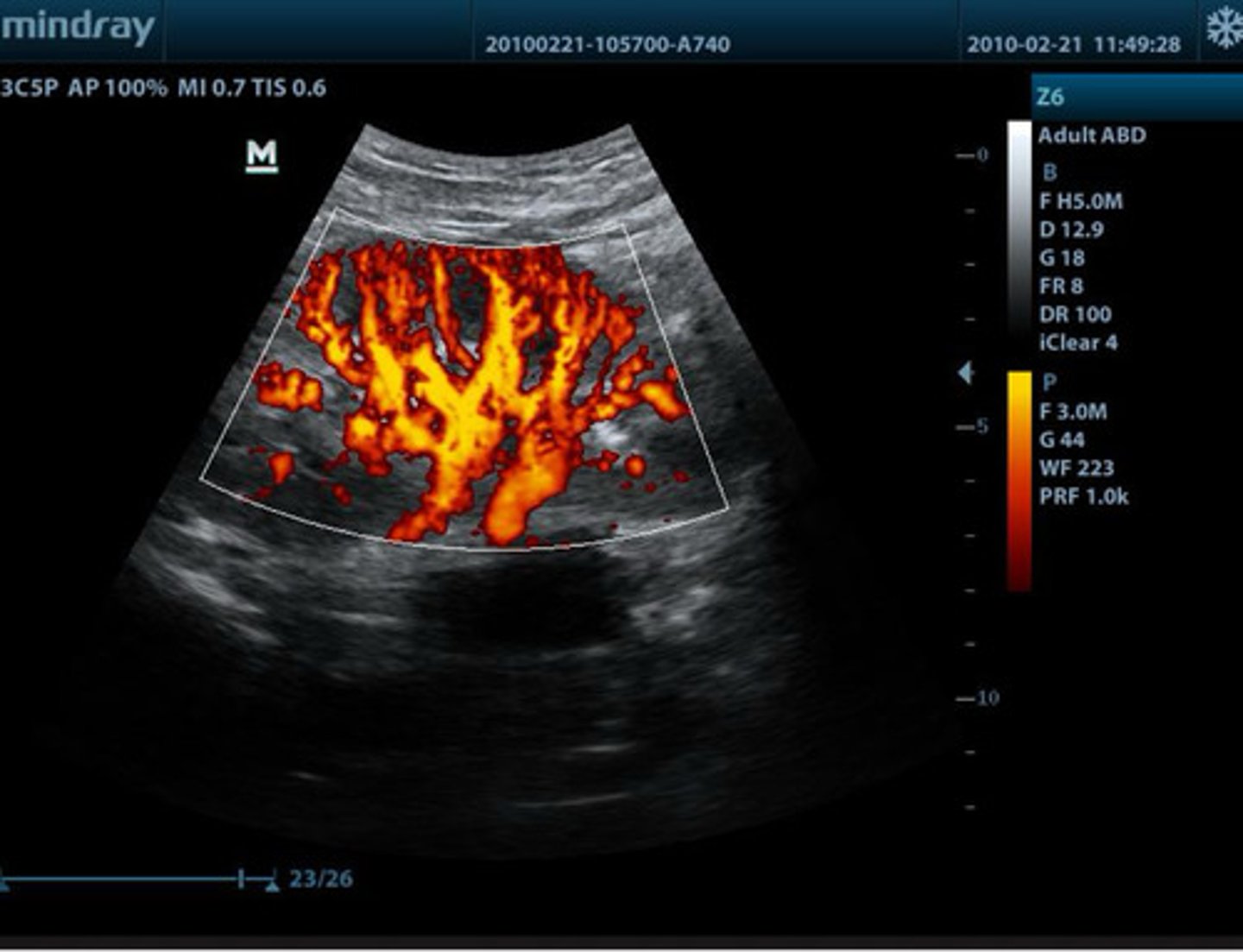
power doppler
what type of doppler is this?
color
blood flow causes changes in _______
velocity and direction of flow in a specific vessel
what does a pulsed wave doppler evaluate?
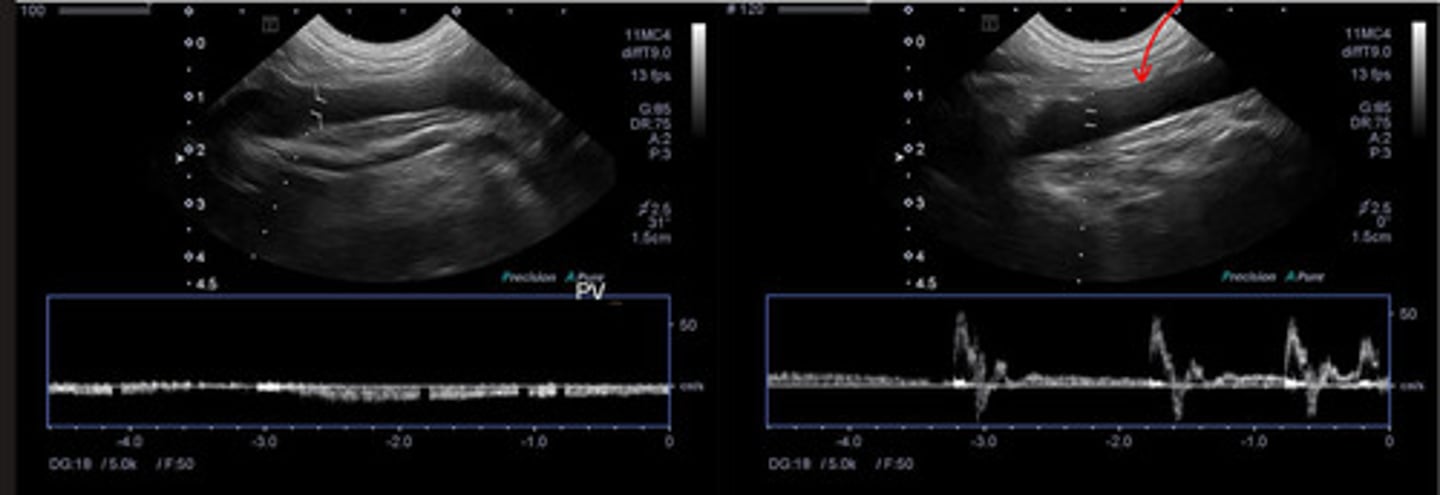
aorta
ID vessel indicated by red arrow on a pulsed wave doppler
difficult
are normal lymph nodes easy or difficult to find and evaluate on US?
younger
the lymph nodes may be more prominent in ________ patients
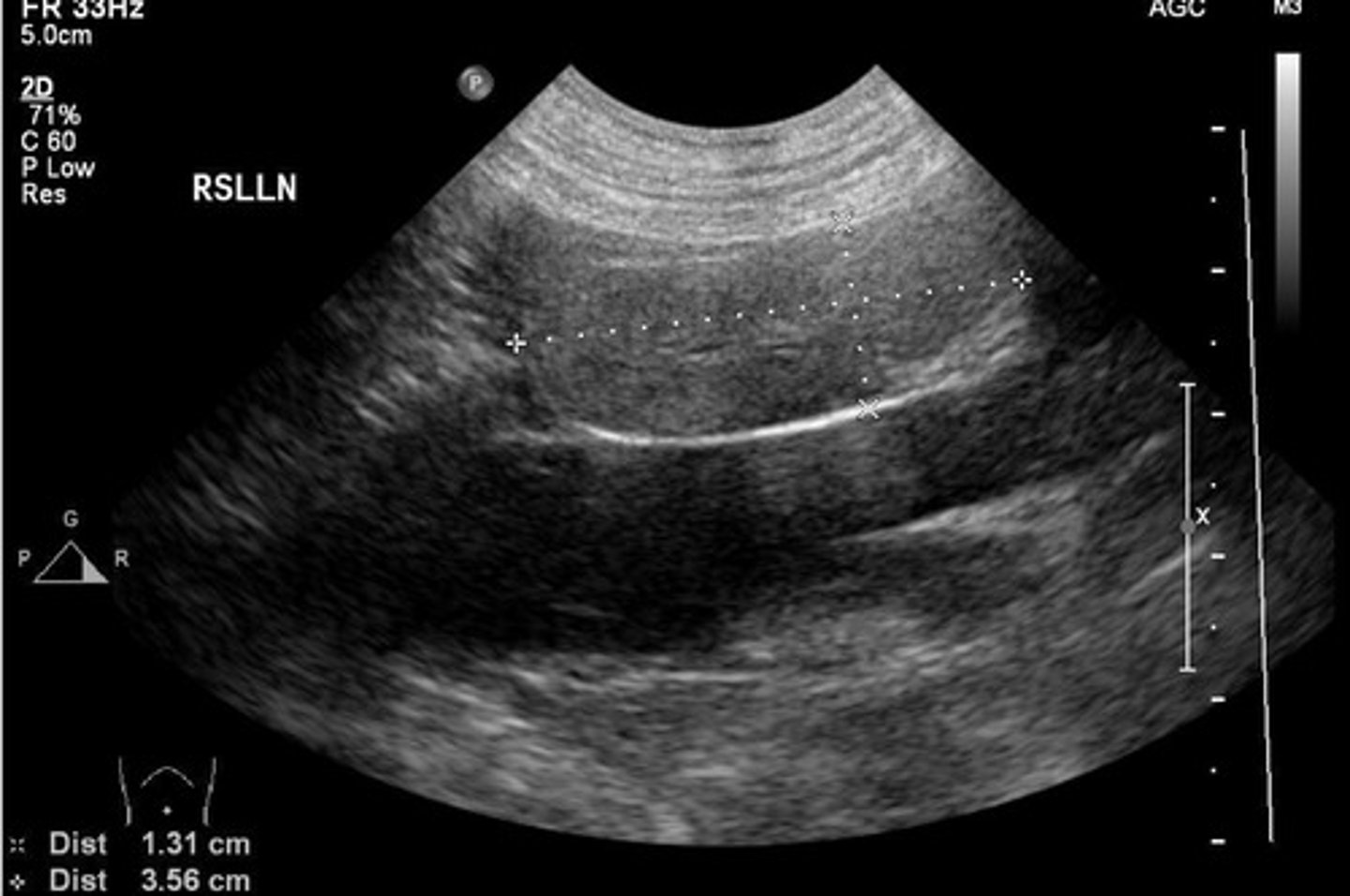
lymph node
ID structure
liver, stomach, duodenum, and pancreas
where does the hepatic lymph node drain?
liver, spleen, esophagus, stomach, pancreas
where does the splenic lymph node drain?
diaphragm, liver, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, pancreas
where does the gastric lymph node drain?
duodenum, pancreas, and omentum
where does the pancreaticoduodenal lymph node drain?
jejunum, ileum, and pancreas
where does the jejunal lymph node drain?
ileum, cecum, colon, kidneys, adrenals, bladder, uterus, prostate, and gonads
where does the colic lumbar aortic lymph node drain?
ureters, bladder, uterus, prostate, gonads, pelvic/pubic areas, abdominal skin, and muscles
where does the medial iliac, internal iliac and sacral lymph node drain?
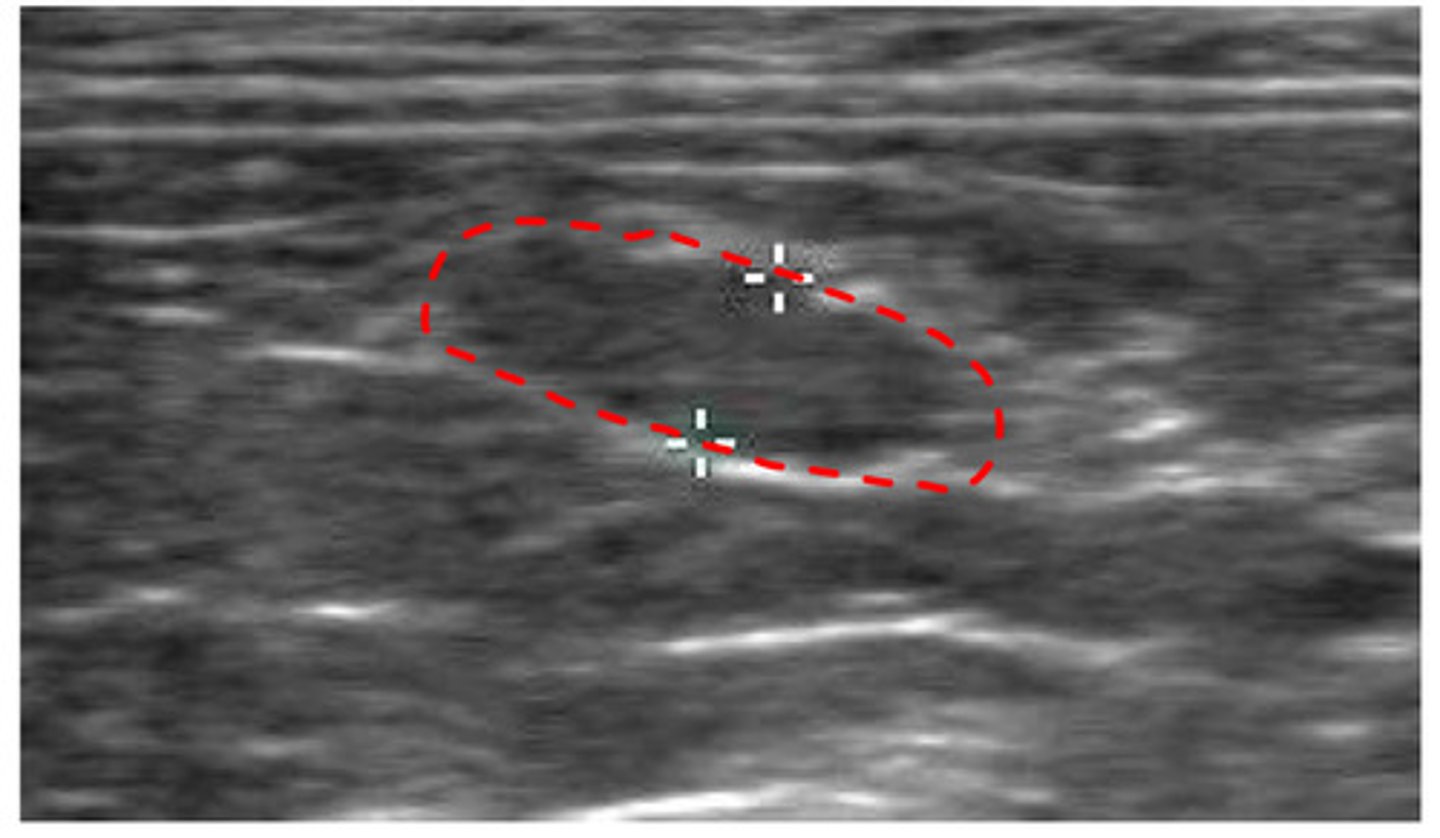
lymph node
what structure is this?
oval to fusiform
what is the shape of a normal lymph node?
True
T/F: lymph nodes have smooth margins
isoechoic to mildly hypoechoic to surrounding fat
what is the echogenicity of the lymph nodes?
hilar
______ blood flow may be visualized with doppler (lymph nodes)
longer than they are thick
the lymph nodes should be ________ than they are ______
<0.5
lymph node ratio of short axis: long axis <_____ is normal
~5-8 mm
the dog lymph node should be around how many mm thick?
lymph node
ID structure
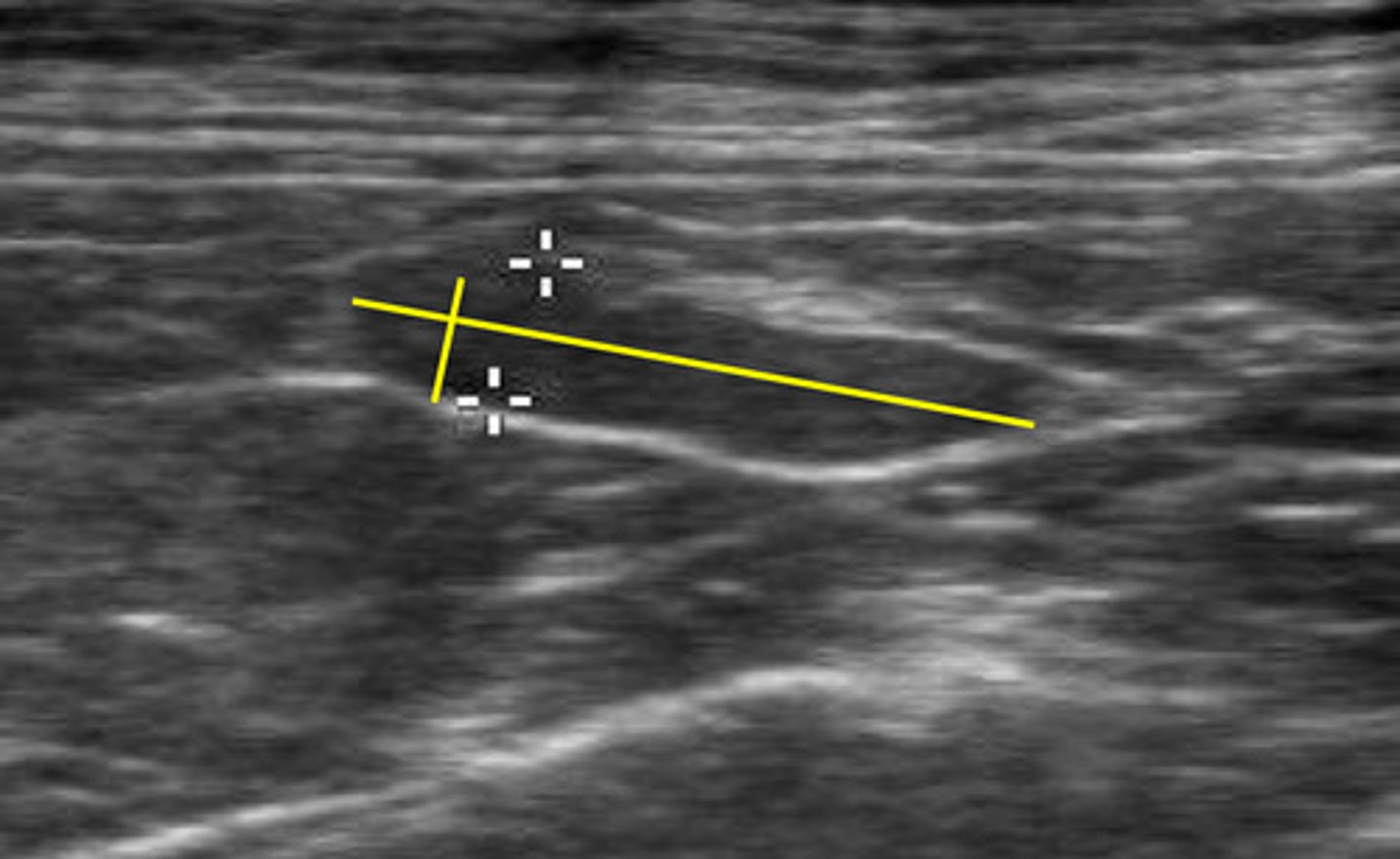
lymph node
ID
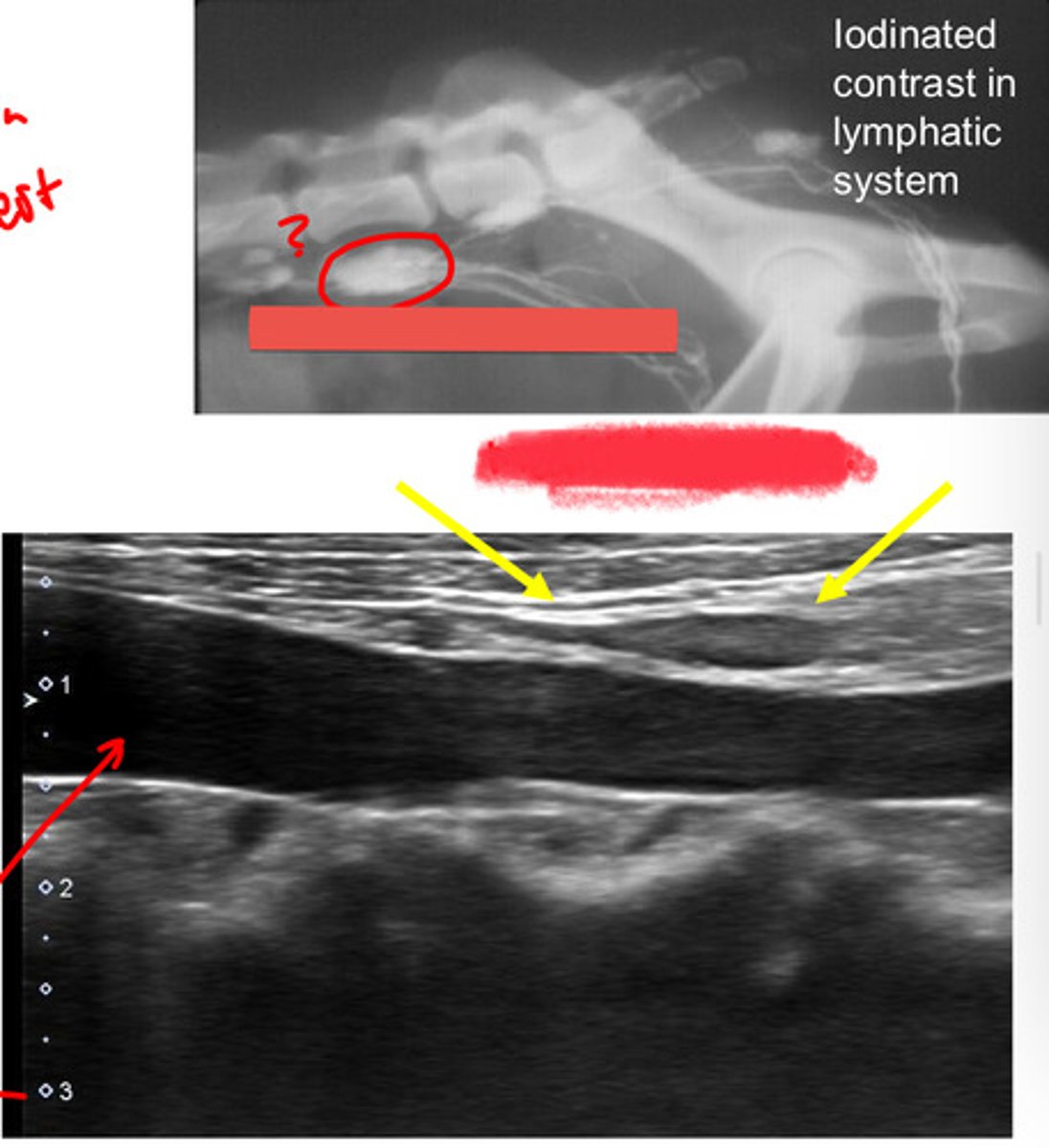
laterally adjacent to the external iliac arteries
location of the medial iliac lns?
most cranial in the pelvis (and LARGEST)
the medial iliac lns. are the most cranial or caudal in the pelvis?
lower urogenital tract, pelvis, and pelvic limbs
the medial iliac lns. drain what three areas?
-hypoechoic relative to surrounding fat
-hyperechoic relative to vessels
echogenicity of medial iliac lns.?
thin hyperechoic
what is the capsule of the medial iliac lns. echogenicity?
elongated oval shape
what is the shape of the medial iliac lns.?
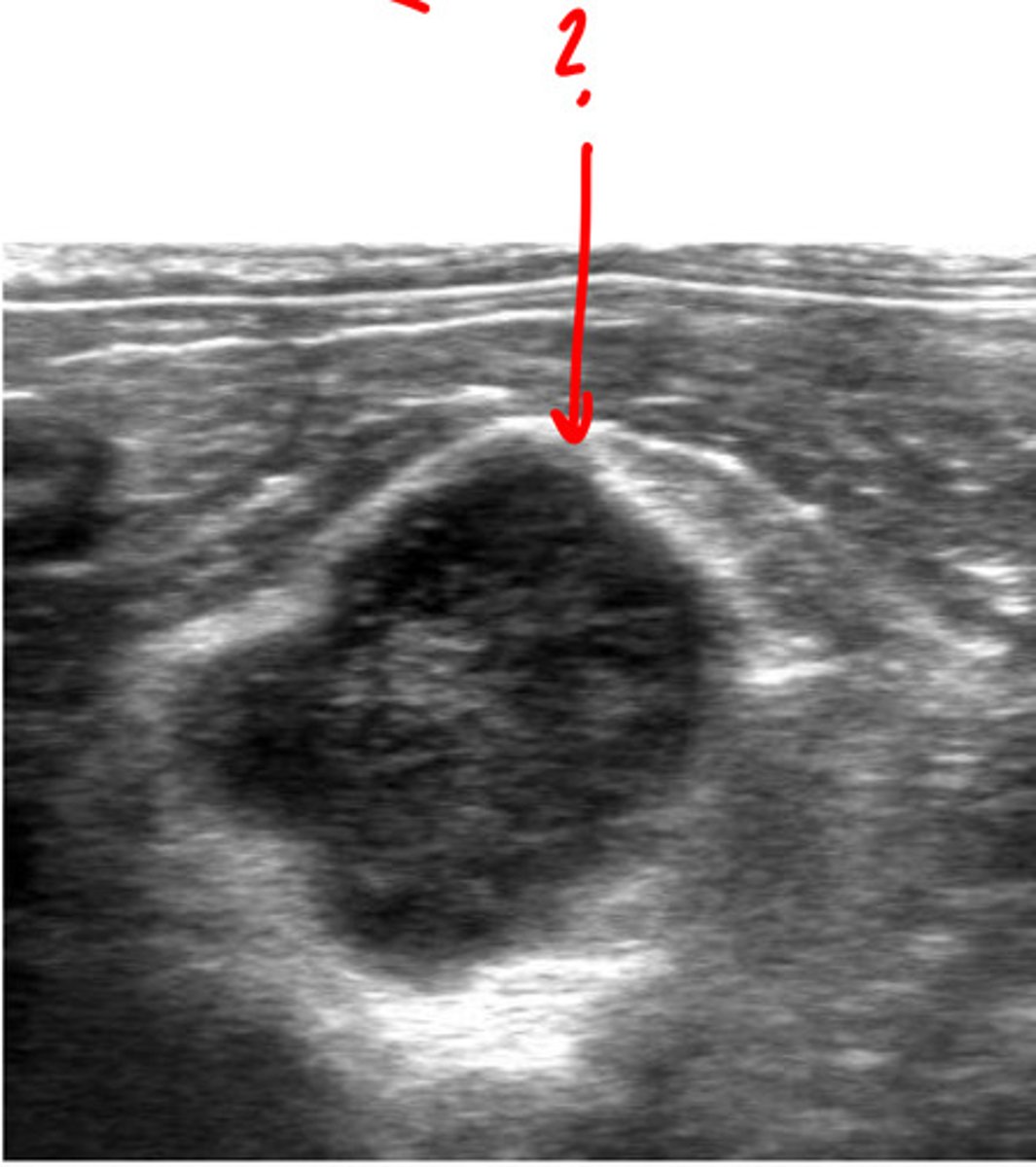
medial iliac lns.
ID lymph node
medial iliac lns.
ID lymph node (hint: trifurcation near)
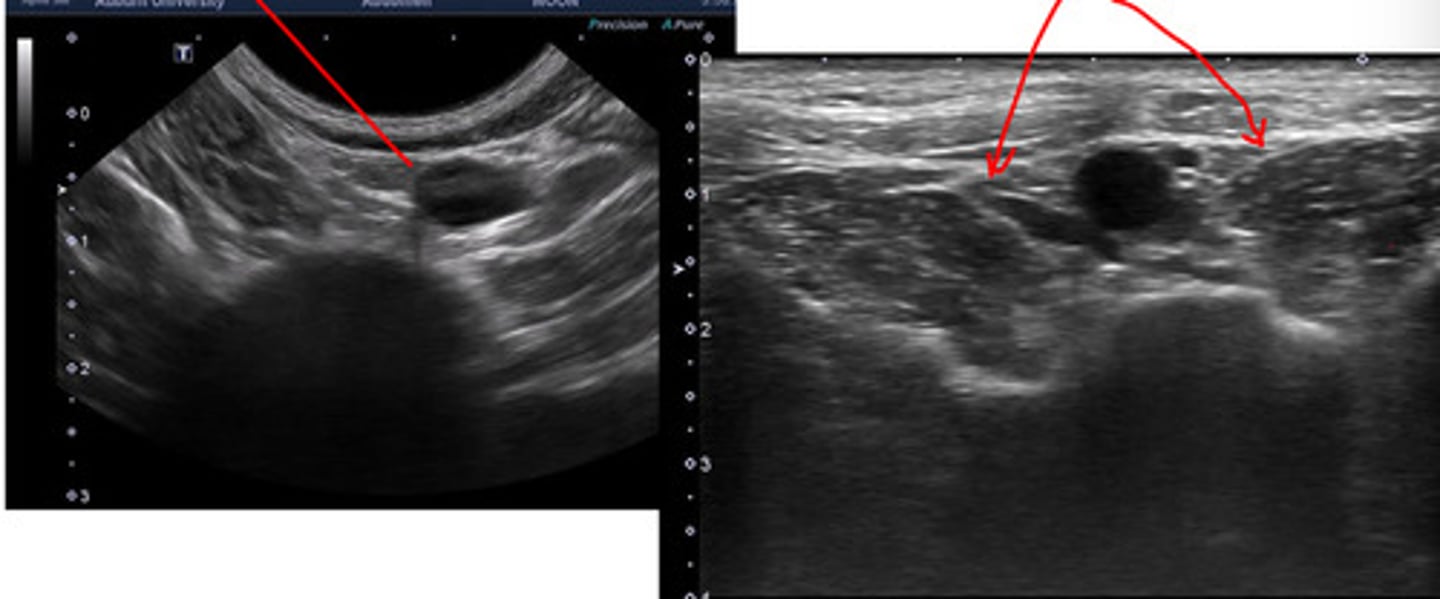
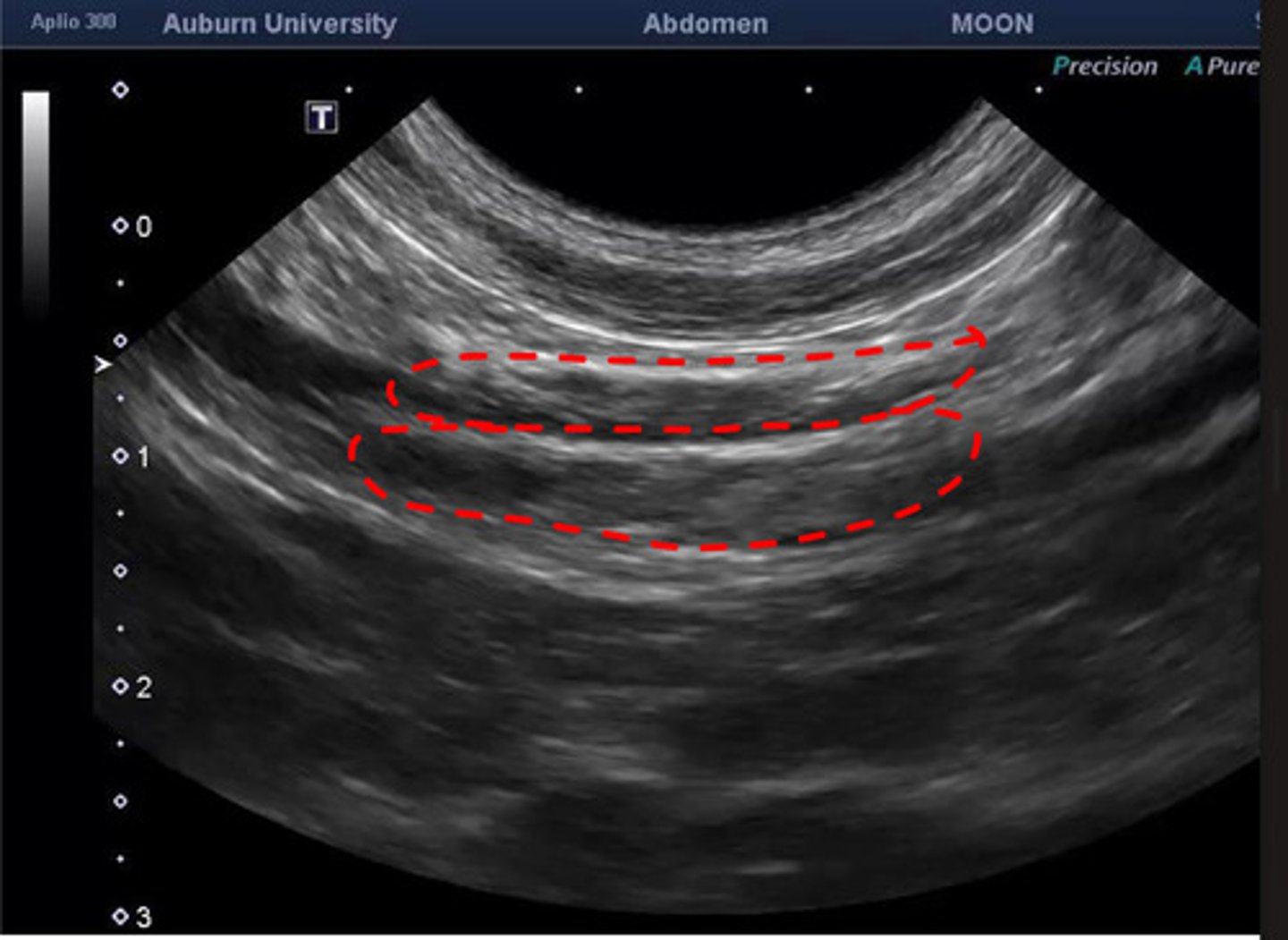
jejunal lns.
what are these lns.?
paired
the jejunal lns. are paired or unpaired?
cranial mesenteric
the jejunal lns. are 2 elongated structures on either side of the ____________ artery
jejunum, ileum and pancreas
what do the jejunal lymph nodes drain?
in the mesocolon
where is the colic ln. located?
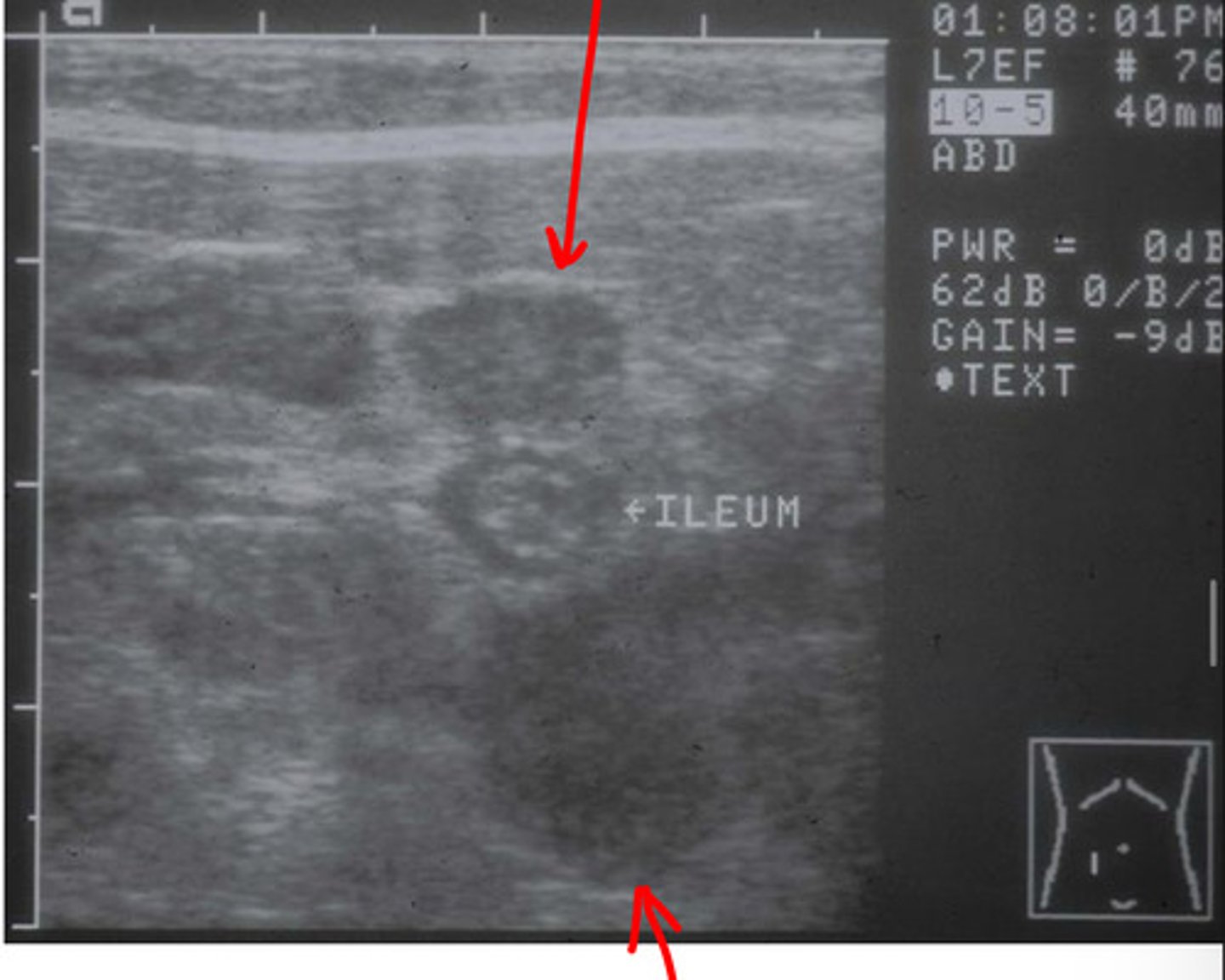
colic lymph nodes
which lymph node is a group of nodes located adjacent to ileocecocolic junction?
cats
the colic lns. are commonly identified in cats or dogs?
ileum, cecum, and colon
the colic lns. drain what?
colic lymph nodes
which lns. are these?
reactive or neoplastic
lymphadenopathy can be _____ or ______
metastatic
reactive lymphadenopathy is __________
hypoechoic
neoplastic lymohadenopathy is hyperechoic or hypoechoic?
increases size
lymphadenopathy causes what in regards to size?
irregular margination
lymphadenopathy causes what in regards to margination?
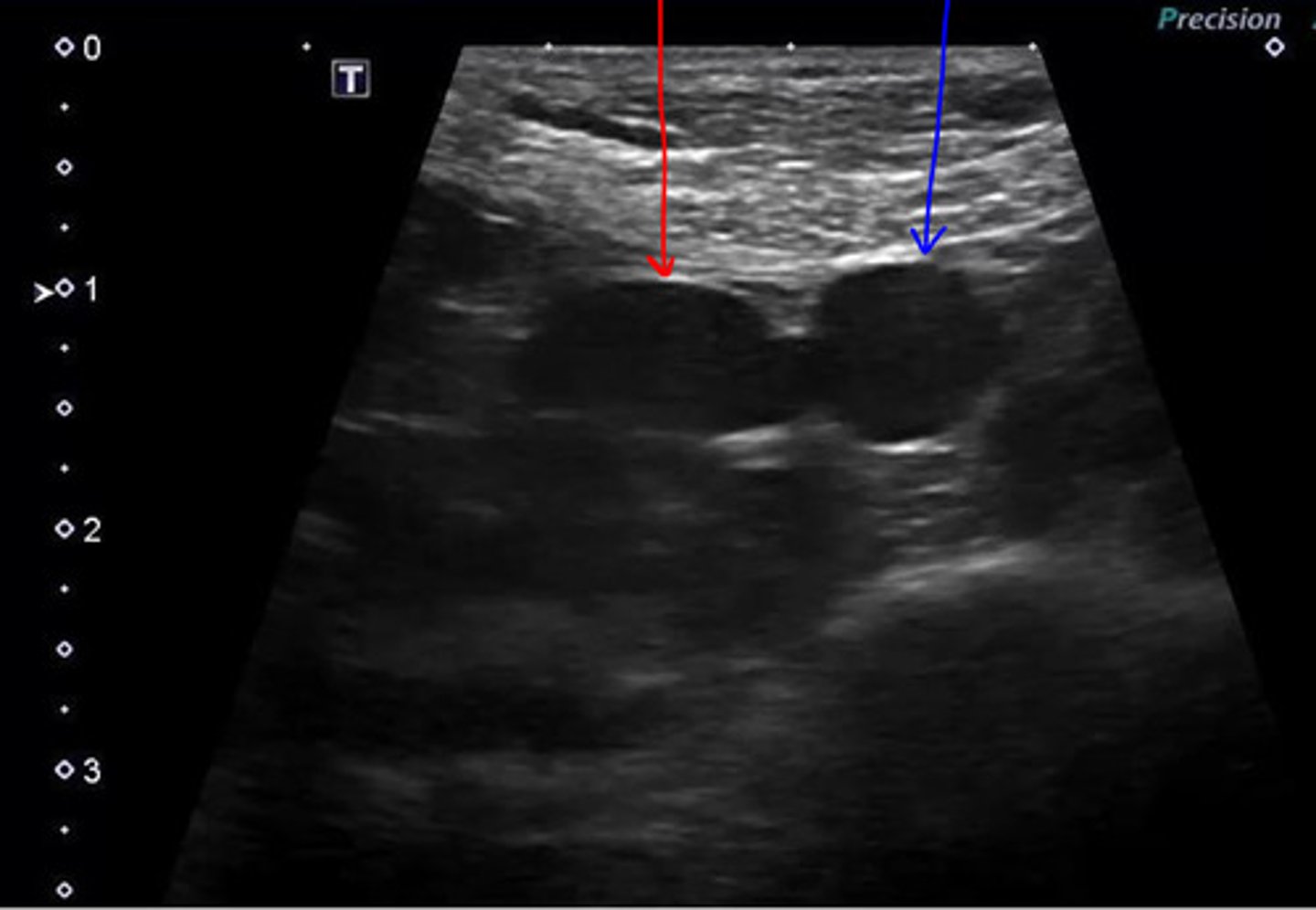
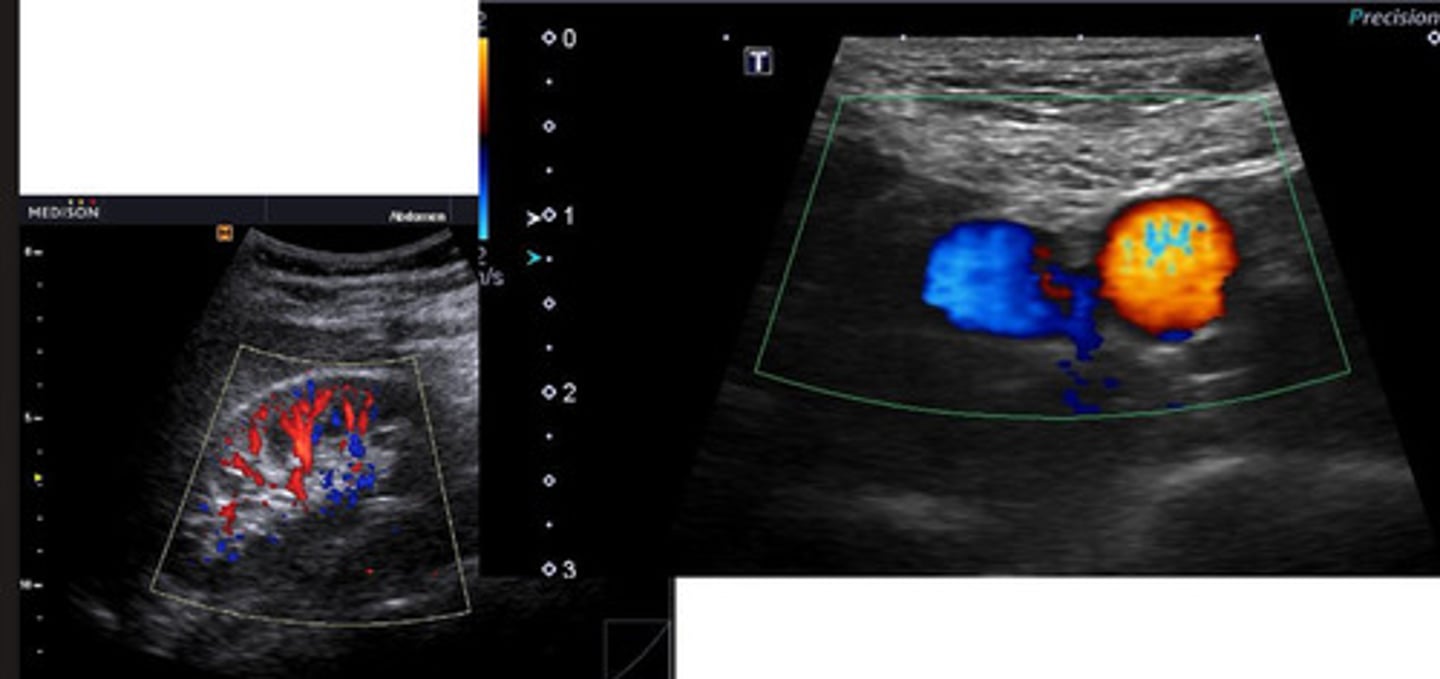
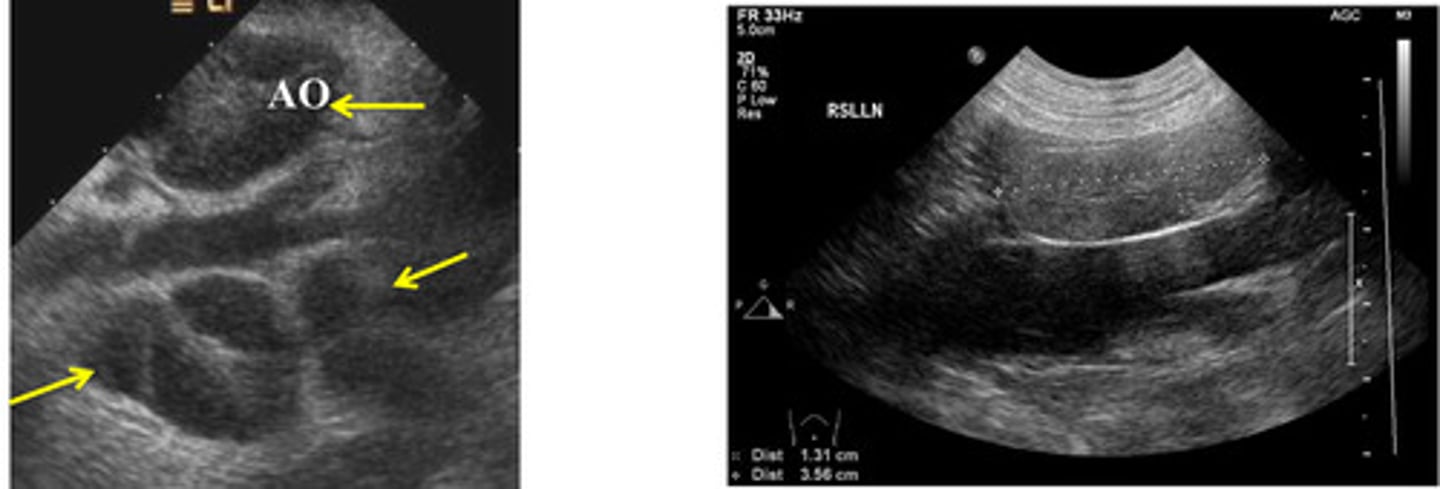
left- neoplasia
right- normal/reactive
which medial iliac ln. is neoplastic and which is normal/reactive?
normal
a reactive medial ln. is normal or abnormal?
lymphoma
which abnormality is this?