Genetics Exam 5: The Genetic Code and Protein Synthesis
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
The genetic code
The set of rules that translate the sequence of nucleotide bases (A, U, G, C in RNA) into a sequence of amino acids to build proteins.
Codons
Three nucleotide sequences that map to specific amino acids.
Why are codons 3 nucleotides long?
Three nucleotides provide 64 combinations, enough to encode all 20 amino acids with redundancy.
Frameshift mutations
Mutations caused by the addition or deletion of nucleotide bases that disrupt the normal reading frame.
Triplet code
A code where each amino acid is encoded by three nucleotides.
Ribosomal filter assay
An experimental approach used to determine which codons produce which amino acids by feeding synthetic RNA codons into a translation system.
Properties of the genetic code
It is (almost) universal, continuous, overlapping, a triplet code, degenerative, and has start and stop codons.
Continuous code
Codons are read one after another without skipping bases.
Nonoverlapping code
Each base is part of only one codon.
Universal code
The same codons mean the same amino acids in almost all organisms.
Degenerate code
Multiple codons can code for the same amino acid.
Start codon
AUG, which codes for methionine.
Stop codons
UAA, UAG, UGA, which signal the termination of protein synthesis.
Codon wobble
The ability of the third base of a codon to pair with more than one nucleotide, allowing one tRNA to recognize multiple codons.
Amino acid coding
The process of translating nucleotide sequences into amino acids using codons.
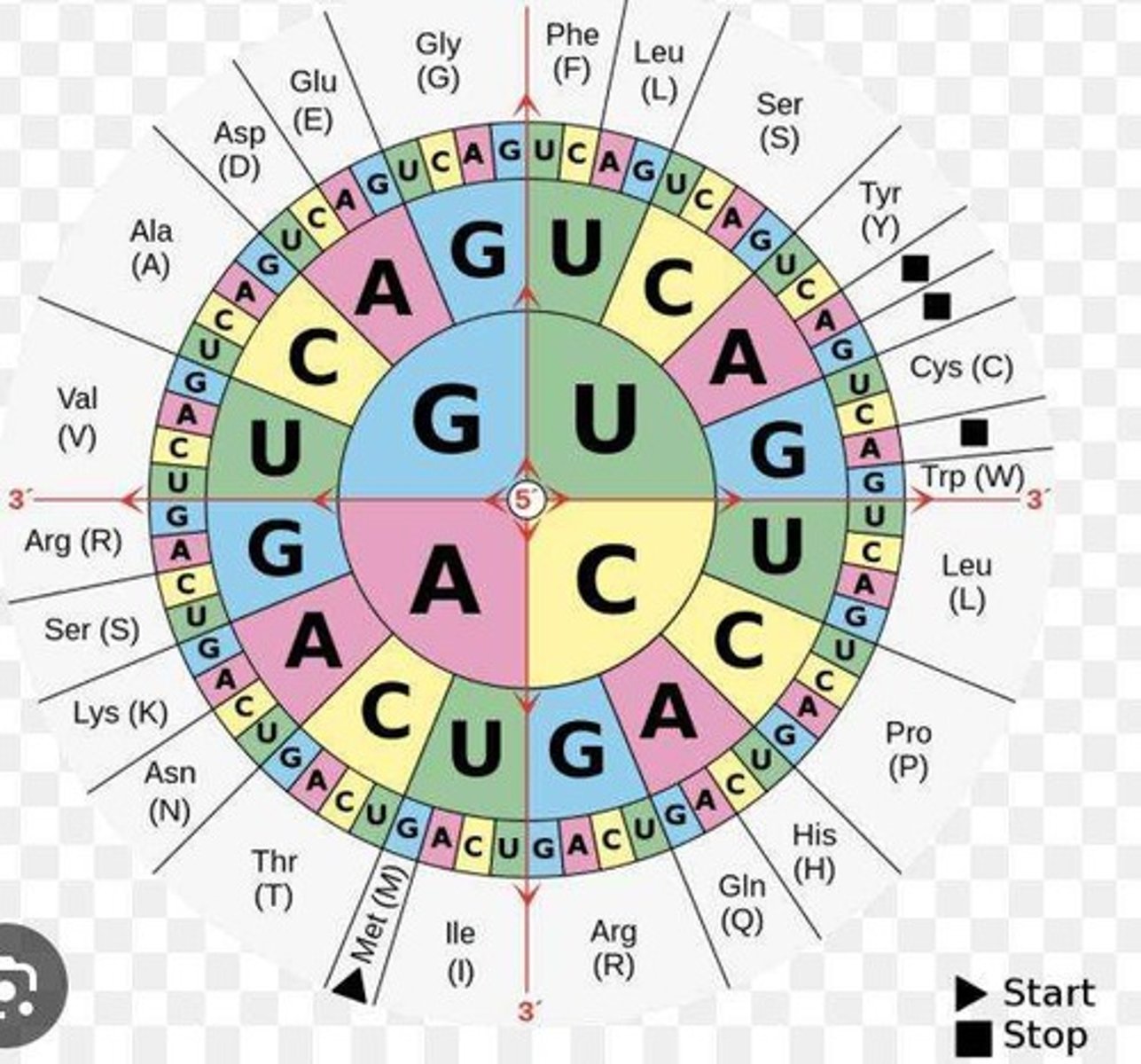
Codon wheel
A tool used to convert between amino acid and nucleotide codons.
Nucleotide bases
The building blocks of RNA, which include adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
Synthetic RNA
Artificially created RNA sequences used in experiments to identify codon-amino acid relationships.
Amino acids
Organic compounds that combine to form proteins, encoded by codons.
Anticodon
A sequence of three nucleotides in tRNA that pairs with a corresponding codon in mRNA.
Ribosomes
Molecular machines that facilitate the translation of mRNA into proteins.
tRNA
Transfer RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
N-terminus
The start of a polypeptide chain; contains a free amino group (-NH2)
C-terminus
The end of a polypeptide chain; contains a free carboxyl group (-COOH)
Peptide
A short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
Peptide bond
A covalent bond formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, releasing water
Protein domain
A region of a protein (typically 50-300 amino acids) that folds into a stable 3D structure and has a specific function, like DNA-binding or catalytic activity
Enzyme
A protein that catalyzes a chemical reaction
Pleiotropy
One gene, many phenotypic effects (Greek for 'many ways')
Inborn error of metabolism
A genetic disorder caused by the absence or malfunction of a metabolic enzyme, leading to substrate accumulation or product deficiency
Auxotroph
A mutant organism that cannot synthesize a particular compound required for its growth, often identified by its failure to grow on minimal media
Complete media
Contains all 20 amino acids, 4 nucleotides, and vitamins + sugars, salts, and biotin
Minimal media
Contains ONLY sugars, salts, and biotin - wildtype can grow on this but metabolic mutants cannot
Proteins
Proteins are made of amino acids, which are linked by peptide bonds into polypeptides. The amino acid sequence determines the protein's structure and function.
α-carbon
The central carbon atom in an amino acid to which the amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom, and R group are attached.
Tripeptide
A peptide consisting of three amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Primary structure
Order of amino acids in the polypeptide chain specified by coding sequence in DNA/RNA.
Secondary structure
Regular folding of a single chain maintained by weak bonds (hydrogen pairing) between adjacent or nearly adjacent residues.
Tertiary structure
Three-dimensional structure of an entire polypeptide chain, dependent on the distribution of secondary structures and R-groups.
Quaternary structure
Arrangement of multiple polypeptides into a single multi-subunit complex.
Alpha helix
A common secondary structure in proteins characterized by a right-handed coil.
Beta sheet
A common secondary structure in proteins characterized by parallel or antiparallel strands.
Codon for methionine
AUG, also the start codon.
tRNA structure
tRNA has an anticodon loop that pairs with mRNA codon and a 3' end that has the amino acid attachment site.
Peptidyl transferase activity
The ribozyme component of the ribosome responsible for forming peptide bonds between amino acids.
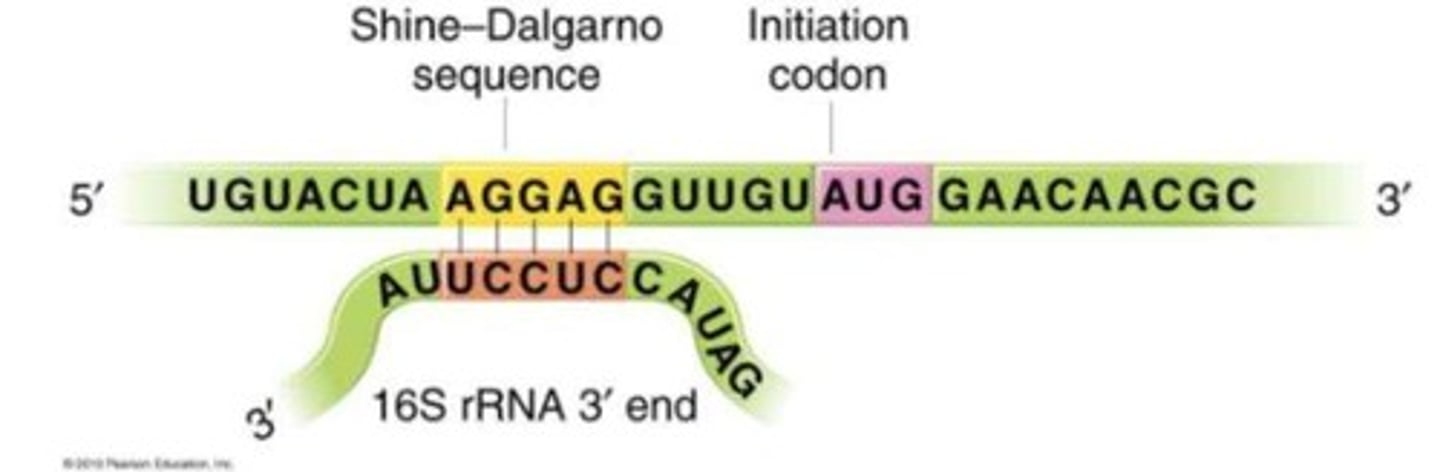
Shine-Dalgarno sequence
A ribosomal binding site in bacterial mRNA recognized by the 16S rRNA during initiation of translation.
Shine Dalgarno
Binds to a complementary sequence in the 16S rRNA (in small ribosomal subunit).
Shine-Dalgarno sequence
Located in the 5'UTR of mRNA about 8-12 nts before the AUG start codon.
IF-1
Initiation Factor that blocks the A site.
IF-3
Blocks 50S attachment and helps mRNA binding to 30S.
fMet
A Met amino acid modified by an enzyme called transformylase.
30S ribosomal subunit
Binds to mRNA and initiator tRNA.
70S initiation complex
Formed when the large ribosomal subunit is added, kicking out initiation factors and hydrolyzing GTP.
Alkaptonuria
Patients secrete homogentisic acid (HA) in their urine due to a lack of an enzyme needed to process HA.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
A genetic disorder characterized by a musty odor, neurological problems, and fair skin due to high phenylalanine levels.
Albinism
Inability to produce melanin, resulting in a lack of pigment in hair, skin, and eyes.
Pleiotropic
A term describing a phenotype that affects many systems.
Gene at 12q24.1
The location of the gene associated with PKU.
Global incidence of PKU
Ranges from 1/5000 to 1/10,000.
Tay-Sachs Disease
A genetic disorder with a low incidence worldwide, but 1/3600 in the Ashkenazi Jewish population, caused by a deficiency in the Hexosaminidase enzyme.
Beadle and Tatum
Developed the One-Gene One-Enzyme hypothesis using Neurospora crassa and X-rays.
Homogentisic acid (HA)
A compound secreted by patients with Alkaptonuria.
Phenylalanine
An amino acid that accumulates in PKU.
Tyrosine
An amino acid that is not produced in sufficient amounts in PKU.
DOPA
A precursor in the melanin synthesis pathway that is affected in albinism.
Intellectual disability
A potential symptom of PKU, along with delayed development and behavioral problems.
Ochronotic pigmentation
Pigmentation due to deposits of homogentisic acid in patients with Alkaptonuria.
Incidence of Albinism
Approximately 1/30,000 for Caucasians and African Americans in the US.
Microcephaly
A condition characterized by an abnormally small head, associated with PKU.
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
Typically fatal between 3-4 yrs of age; caused by mutations in enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT); severe mental and physical impairment due to uric acid buildup; characterized by horrifying uncontrollable compulsive behaviors.
Kartagener Syndrome
Rare disorder occurring in 1/32,000 live births; presents with sinus and lung abnormalities, sterility, and sometimes dextrocardia; caused by defects in proteins that comprise cilia and flagella.
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome
A genetic disorder with many known mutations and complex inheritance; characterized by cognitive developmental issues, polydactyly, kidney disease, and retinal degeneration due to disruption of the motor protein complex that makes cilia move.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Characterized by sickle morphology of red blood cells which are more fragile and prone to breaking; causes pain, anemia, and organ damage due to poor oxygenation; heterozygotes show milder symptoms and have protection against malaria.
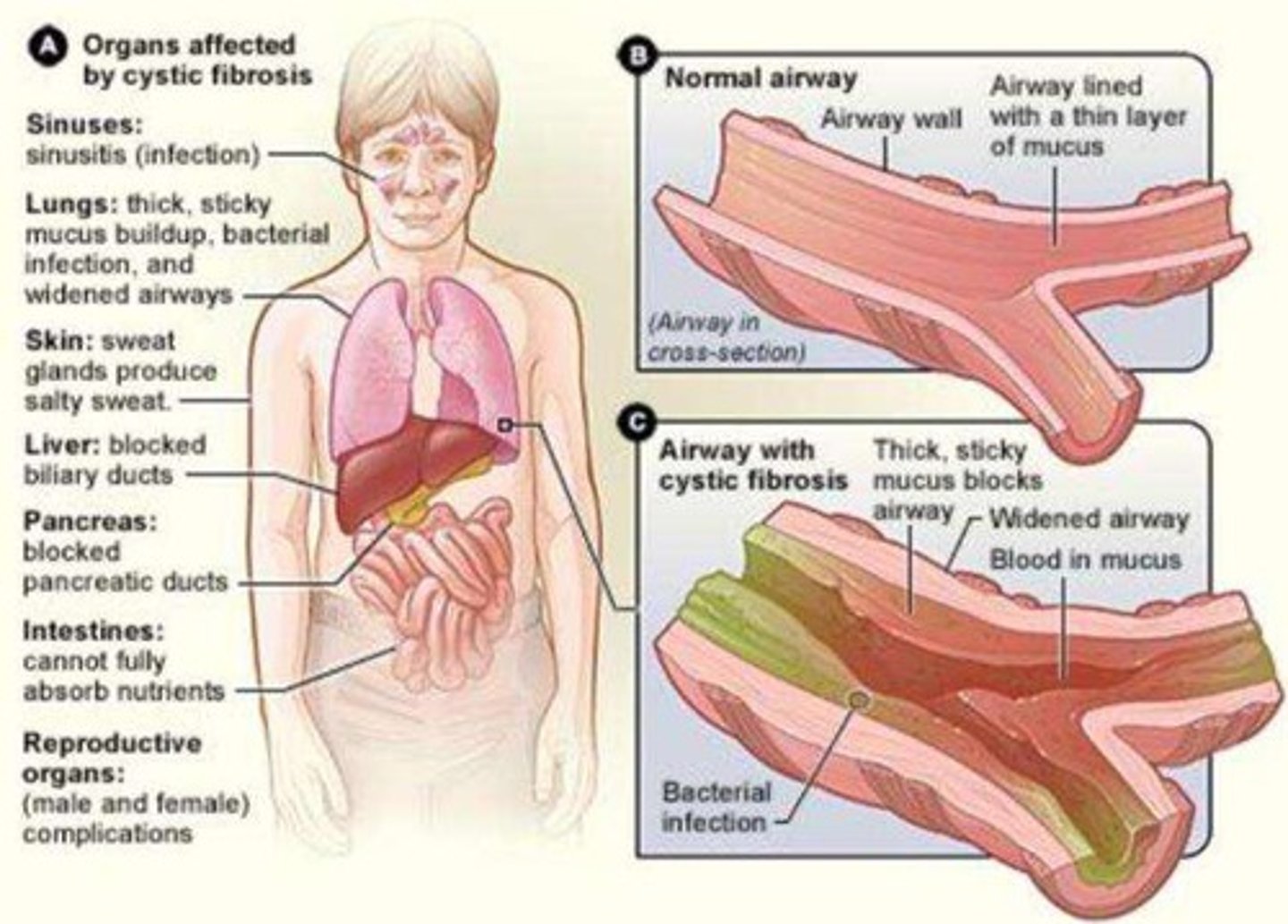
Cystic Fibrosis
Pleiotropic autosomal recessive disorder occurring in 1/2000 Caucasians; most common mutation deletes 3 bp in frame resulting in loss of 1 amino acid; affects CFTR protein leading to thickened mucus causing pulmonary and digestive problems; life expectancy 20-40 years.
Organs affected by cystic fibrosis
Sinuses: sinusitis; Lungs: thick mucus buildup, bacterial infection; Skin: salty sweat; Liver: blocked biliary ducts; Pancreas: blocked pancreatic ducts; Intestines: nutrient absorption issues; Reproductive organs: complications.
Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease
A transmissible brain disorder in mammals caused by the presence of prions (misfolded proteins) in the brain.
Lac Operon
A classic example of an inducible operon in E. coli that is usually off but can be turned on in the presence of lactose, allowing the bacterium to metabolize lactose only when available.
LacZ
Encodes ß-galactosidase, which breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
LacY
Encodes lactose permease, a membrane protein that imports lactose into the cell.
LacA
Encodes transacetylase, whose function is believed to detoxify byproducts of lactose metabolism.
Promoter (P)
The region where RNA polymerase binds to begin transcription in the lac operon.
Operator (O)
A DNA segment where the lac repressor binds, blocking RNA polymerase in the absence of lactose.
LacI gene
Encodes the lac repressor protein, which binds to the operator to prevent transcription when lactose is absent.
Allolactose
A lactose derivative that binds to the lac repressor, changing its shape so it cannot bind to the operator, allowing transcription to occur.
Heterozygosity in Sickle Cell Anemia
Heterozygotes are affected but exhibit much milder symptoms and have a protective effect against malaria infection.
Cystic Fibrosis Life Expectancy
Patients typically have a life expectancy of 20-40 years.
Sinusitis
An infection of the sinuses often associated with cystic fibrosis.
Thick Mucus in Cystic Fibrosis
Causes bacterial infections and widened airways in the lungs.
Salty Sweat
A characteristic symptom of cystic fibrosis due to sweat glands producing excess salt.
Blocked Biliary Ducts
A complication of cystic fibrosis affecting the liver.
Blocked Pancreatic Ducts
A complication of cystic fibrosis affecting the pancreas.
Nutrient Absorption Issues
A complication of cystic fibrosis affecting the intestines.
Reproductive Organ Complications
Complications in male and female reproductive organs due to cystic fibrosis.
Cilia and Flagella Defects
The cellular basis of Kartagener Syndrome, linked to multiple genes.
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that transcribes genes, leading to lactose metabolism.
Catabolite repression
A mechanism that prevents the full activation of the lac operon when glucose is present.
cAMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, a molecule that binds to CAP and enhances transcription when glucose is low.
CAP
Catabolite activator protein that binds to cAMP and enhances transcription of the lac operon.
Inducible system
A system that allows bacteria to conserve energy by only expressing genes when needed.
François Jacob and Jacques Monod
French scientists who discovered gene regulation using the lac operon in the 1960s.