Biology - Blood and the Circulatory system
1/58
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What substances go into cells?
Glucose and Oxygen
What substances go out of cells?
Carbon dioxide, water, lactic acid
What is a double circulatory system?
Where there are two circuits where blood passes through the heart twice. It allows oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to be seperated
How does a single circulation differ from a double circulation?
Blood flows to and from the heart through a single pathway. The deoxygenated and oxygenated blood do not mix, instead flowing in one continuous loop and not returning to the heart once oxygenated.
Why are some animals able to survive on only a single circulatory system?
Some animals like fish do not need double circulation systems as they require a lower metabolic rate needed to be maintained, and they require less flow rate to tissues around the body as they are smaller.
Why can unicellular organisms rely on diffusion for movement in and out of cells whilst larger organisms cannot?
Unicellular organisms have a large surface to area ratio, which increases the rate of diffusion, and there is a small diffusion distance. Larger organisms have a small surface area to volume ratio, meaning that there is a larger diffusion distance which makes it ineffective.
How does a multicellular function without diffusion?
Multicellular have transport systems such as organs like the circulatory system which moves gases around the body to ensure cells have adequate levels of oxygen for respiration.
What is the blood made up of?
Blood plasma, red blood cells, platelets, white blood cells
What is the function of blood plasma
The transport medium which carries blood cells and substances around the body
What waste product is produced in the liver?
Urea forms in the liver from the breakdown of proteins, and is carried by blood plasma to the kidneys where it is removed as urine.
What is the function of red blood cells?
Transport oxygen from the lungs to other cells in the bodyand help remove carbon dioxide from the body.
Adaptations of the red blood cell
Bi-concave shape which increases surface area:volume = increases diffusion. Packed of haemoglobin which binds to oxygen. No nucleus so there is more space for haemoglobin.
What is the function of white blood cells?
Part of the immune system which fights foreign invaders.
What are some different white blood cells?
Some produce antibodies to fight microorganisms, others produce antitoxins to neutralize poisons released by pathogens. Phagocytes engulf and digest microorganisms.
What is the function of platelets
They clot blood by producing a network of protein fibres that capture red blood cells and platelets to form a clot to prevent you from bleeding out and bacteria entering. They have no nucleus and are small fragments of cells.
How does carbon dioxide exit the body?
Carbon dioxide produced by cells is carried in the blood plasma to exit the body.
How does blood plasma play a role in kicking the carbon dioxide out of the body?
Insoluble products of digestion pass into the plasma and are carried to individual cells to be taken care of :)
Other functions of the blood plasma
Hormones are transported in the blood plasma and target body tissues. Blood plasma also carries heat energy throughout the body, which helps regulate body temperature. Waste products like carbon dioxide and urea. Proteins, antibodies, and antitoxins
What are the ‘lines of defence’ of the body?
Skin / external barriers
Phagocytes (non-specific)
Lymphocytes (specific)
How do phagocytes work?
Phagocytes engulf microbes, digesting the pathogens using enzymes. They are much bigger than red blood cells with a large spherical/lobed nucleus.
How do lymphocytes work?
Some white blood cells produce antibodies that destroy a particular microbe. Antibodies produced are specific to only one type of infection.
Describe the process of lymphocytes
Lymphocytes have antigen receptors which detect a certain type of antigen molecule. Once recognized, the lymphocyte goes through mitosis and creates a clone of memory cells and plasma cells. They then release the antibody molecules to fight off the pathogens.
What are memory cells
A clone of lymphocytes remain after they fight off a certain pathogen to ensure that future invaders of the same kind can be dealt with faster and more efficiently. This also means that you are immune.
How do vaccinations work
Vaccines contain dead/weakened/part of a pathogen, and white blood cells respond to the vaccine as if it were a normal disease. This is called active immunity. This then allows the person to be immune to the disease for a certain period of time as the memory cells are able to fight off future diseases of the same kind (SECONDARY RESPONSE)
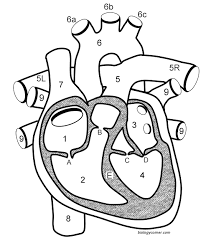
Label the structure of the heart
Right Atrium
Right ventricle
Left Atrium
Left ventricle
Pulmonary artery
aorta/aortic arche
Vena cava
Inferior vena cava
Pulmonary vein
Where does the blood in an artery flow to
Away from the heart
Blood pressure of the artery
High (40-100 mmHG)
Structure + appearance of artery blood
Thick wall, thin lumen, elastic muscle walls so they recoil easily. Bright red oxygenated blood
Where does the blood in a vein flow to
Towards the heart
Blood pressure of the vein
Low (5-20 mmHG)
Structure + appearance of blood in the vein
Large lumen, thin wall, valves to ensure blood travels with less resistance as there is lower pressure. Dull red deoxygenated blood
Flow of capillary
Carries blood through organs to cells
Blood pressure of capillaries
Medium (20-30 mmHg)
Structure and blood colour of capillaries
One cell thick for faster diffusion, has blood of both colors
How many chambers does the fish heart have (name them)
4 - bulbus arteriosus, atrium, sinus venosus, ventricle
Right atrium function
Collects deoxygenated blood and pumps to the right ventricle
Aorta function
Carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to rest of body
Function of the left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta
Function of the right ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood out of the heart
Function of the pulmonary veins
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
Function of the pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
Function of the vena cava
Carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium
Function of the left atrium
Collects oxygenated blood and pumps it to the left ventricle
Why do fish not require double circulatory systems?
Fish are not as active as other animals, so a single circulatory system is sufficient for their low metabolism and respiration levels.
Consequences of smoking to the lungs and circulatory system
Gives you lung cancer, Coronary heart disease (build up of fatty deposits in arteries), angina (chest pain due to decreased blood flow)
Causes of Coronary Heart disease
Smoking, atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, genetics, lack of exercise
How can CHD be treated/prevented?
Eating healthily, exercising, quitting smoking, managing stress. Cholesterol lowering drugs and angioplasty
How does heart rate change during exercise?
Increases during exerciseW
Why does heart rate change during exercise?
Muscles need to contract more = more respiration is needed for more oxygen to reach the lungs = heart pumps blood faster to distribute more oxygen
How does the heart rate change under adrenaline and why?
Increases as the body prepares itself for action, supplying muscles with more oxygen and diverting oxygen to muscles instead of internal organs
Function of hepatic blood vessels
Supply or remove blood from or to liver
Function of hepatic arteries
Takes blood away from heart to liver
Function of hepatic vein
Takes blood away from liver into the heart
Function of the hepatic portal vein
Takes blood from digestive organs to liver
Function of the renal artery
Takes blood to the kidneyF
Function of the renal vein
Takes blood away from the kidney
Function of the pulmonary artery
Takes blood from the heart to the lungs
Function of the pulmonary veins
Takes blood from the lungs to the heart
What does plasma carry?