Exam 3 patho: Acid-Base balance
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Disassociate
Separation of molecules into 2+ simpler fragments in order to participate in another rxn
Carbonic anhydrase (CA)
an enzyme that catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide (CO2) to make carbonic acid (H2CO3)
found in RBCs and renal tubular cells
Carbonic acid
H2O + CO2 —> H2CO3
basically CO2 dissolved in H2O
Acid
Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
A base that is used as a buffer system to change the pH of the blood
Bicarbonate buffer system
Uses H2CO3 (carbonic acid) & bicarbonate salt (NaHCO3)
Substitution occurs (weak acid or weak base substituted for strong ones)
Purpose of buffer systems and how do they work?
maintains the pH balance in the blood and other bodily fluids
It works by neutralizing excess acids or bases, ensuring that the blood pH remains within the narrow range necessary for proper physiological function.
Acids
molecules that can dissociate and release H+
example: HCl dissociates in water to form H+ and Cl-
(I dont get it) Volatile byproducts of a metabolic process
Carbonic acid is in equilibrium with CO2
Easily evaporates and can be eliminated by the lungs
Example: carbonic acid will release CO2 through exhalation
Method of CO2 being carried through BS
(I dont get it) Non-volatile byproducts of a metabolic process
Occurs from metabolism of dietary proteins, carbs, and fats
Oxidation produces HCL, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid
Incomplete oxidation
Glucose results in lactic acid
Fats produce ketoacids
Eliminated by kidneys after being buffered
Base
ion/molecule that can accept an H+
Example: HCO3- can accept H+ to form H2CO3
Sources of bases (2) from metabolism and types of each
Metabolism of amino acids
aspartate, glutamate
Metabolism of organic anions
citrate, lactate, acetate
What are the 3 buffer systems the body can use to respond to changes in pH?
Chemical
Respiratory
Renal
Normal body pH
7.35-7.45
Chemical buffer systems function
prevent big swings in pH by using moment-to-moment pH adjustments
Most common
What are the 3 types of chemical buffer systems?
Bicarbonate buffer system
Transcellular H+/K+ exchange
Bone
How does the bicarbonate chemical buffer systems work?
Uses substitutions of a weak acid for a strong acid, or a weak base for a strong base
allows for easier addition or removal from body
The chemical buffer system is a method of ______ for ions
substitution
Example of substitution when expelling CO2
HCl + NaHCO3 —> H2CO3 + NaCl
H2CO3: can be taken to lungs and expel CO2
NaCl: body can easily take this up
Transcellular H+/K+ exchange chemical buffer systems
Regulating the movement of hydrogen (H+) and potassium (K+) ions across cell membranes to maintain pH
If H+ is high in blood, H+ taken out of BS and put inside cell
This will then decrease the amount of acid in the BS
K+ is now in the BS — if this happens too much, this can result in too much K+ in the BS
Bone chemical buffer system
H+ extracellular ions can be exchanged for ions in the bone to decrease pH
bone will help buffer the acidic ECF
H+ will dissolve in bone tissue
What is the mechanism of action for bone chemical buffer systems?
H+ will dissolve in bone tissue, which will release sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) into the ECF
this helps buffer the excess acids in the BS
CO2 transport Methods (3)
As CO2
As a bicarbonate ion
Carbahemoglobin
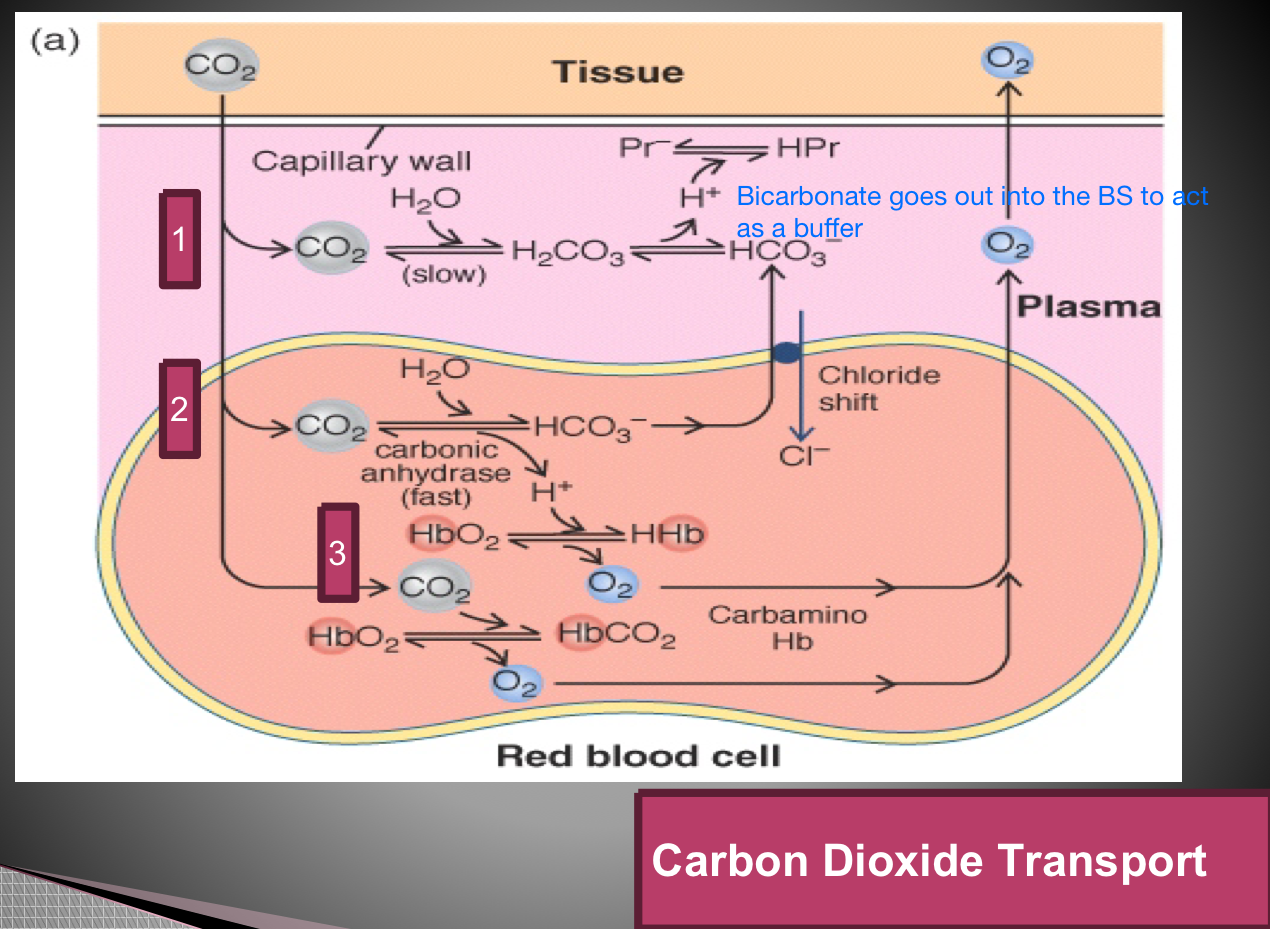
Protein buffers?? Slide 14 — look in patho book for explanation
Respiratory control for pH balance
Regulates CO2 levels by changes in respiratory rate by sensing CO2 levels through chemoreceptors in the brainstem and periphery
Can be stimulated within minutes
Does not completely correct acid-base in lungs (lasts 24-48 hrs)
How does changing respiratory rate impact pH?
Chemoreceptors in brainstem and periphery
Hyperventilate = get rid of CO2 = increase pH (more alkaline)
Hypoventilate = hold onto CO2 = decrease pH (more acidic)
How does respiration regulate CO2 and therefore pH?
H2CO3 —> CO2 + H2O
More CO2 present = more acidic
H2O and CO2 can combine to increase pH/decrease acidity
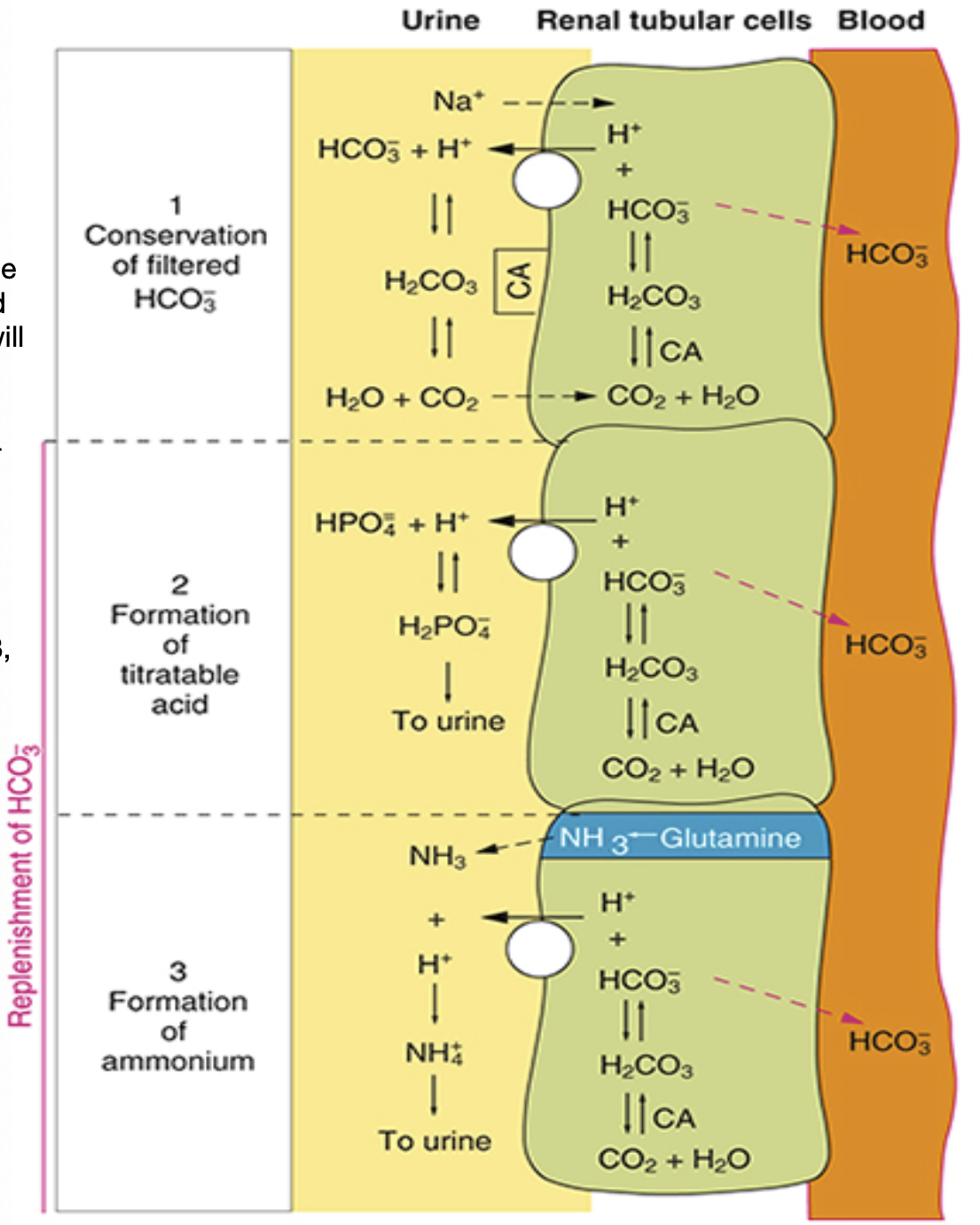
Renal control mechanisms
Regulating the levels of H+ and bicarbonate in the blood
most effective
Takes the longest
What are the 3 renal control mechanisms?
H+/HCO3 exchange — CA catalyst
Distal renal tubule regulates acid-base balance
Transcellular H+/K+ exchange
GO BACK TO THE RENAL CONTROLS — DO NOT UNDERSTAND!!!
**Kidney has the ability to pull ions back into the ______ cells to eliminate excess _____
Tubular cells
Acid
What does the distal renal tubule regulate?
Acid-base balance
How does the distal renal tubule regulate acid-base balance?
Reabsorb HCO3 from urine
H+/HCO3 exchange
CA catalyst used to combine
H+ + HCO3- —> H2CO3 —> CO2 + H2O
When CA is inside the tubular cell, what will form?
H2CO3 —> HCO3- + H+
What is released from the nephrons to act as a buffer to increase the blood pH?
HCO3- is used to increase pH
H+ is released into the urine filtrate
Role of distal renal tubule
Reabsorb HCO3- from urine
What forms H2CO3? What does H2CO3 dissociate into to decrease blood pH?
Intracellular carbonic anhydrase makes H2CO3
H2CO3 —> HCO3- + H+
HCO3- and H+ are the end product of the distil renal tubule mechanism. What is the end result of this?
HCO3- goes into the ECF and acts as a buffer (base)
H+ is eliminated in the urine
This results in decreased pH
What is the purpose of carbonic anhydrase?
speeds up the exchange of ions and the speed of HCO3- and H+ production
What will the kidney excrete that addresses alkalosis? What is the result of this?
the kidney will make the bicarbonate exit via excretion to prevent blood from getting more basic
this results in increased K+ in the kidney
Phosphate (PO4-) and Ammonia (NH3) Buffers
Phosphate and ammonia will buffer the H+ ions
Helps bring down acid levels in our body
Allows acid to be excreted in the body, which CANNOT be pulled back into the tubules cell and will
remain in the urine filtrate
Phosphate (HPO4-) mechanism
HPO4- binds with H+ ion
forms a lipid molecule (H2PO4), making it lipid soluble
this means it cannot be pulled back into the into the tubule and must be excreted through the urine
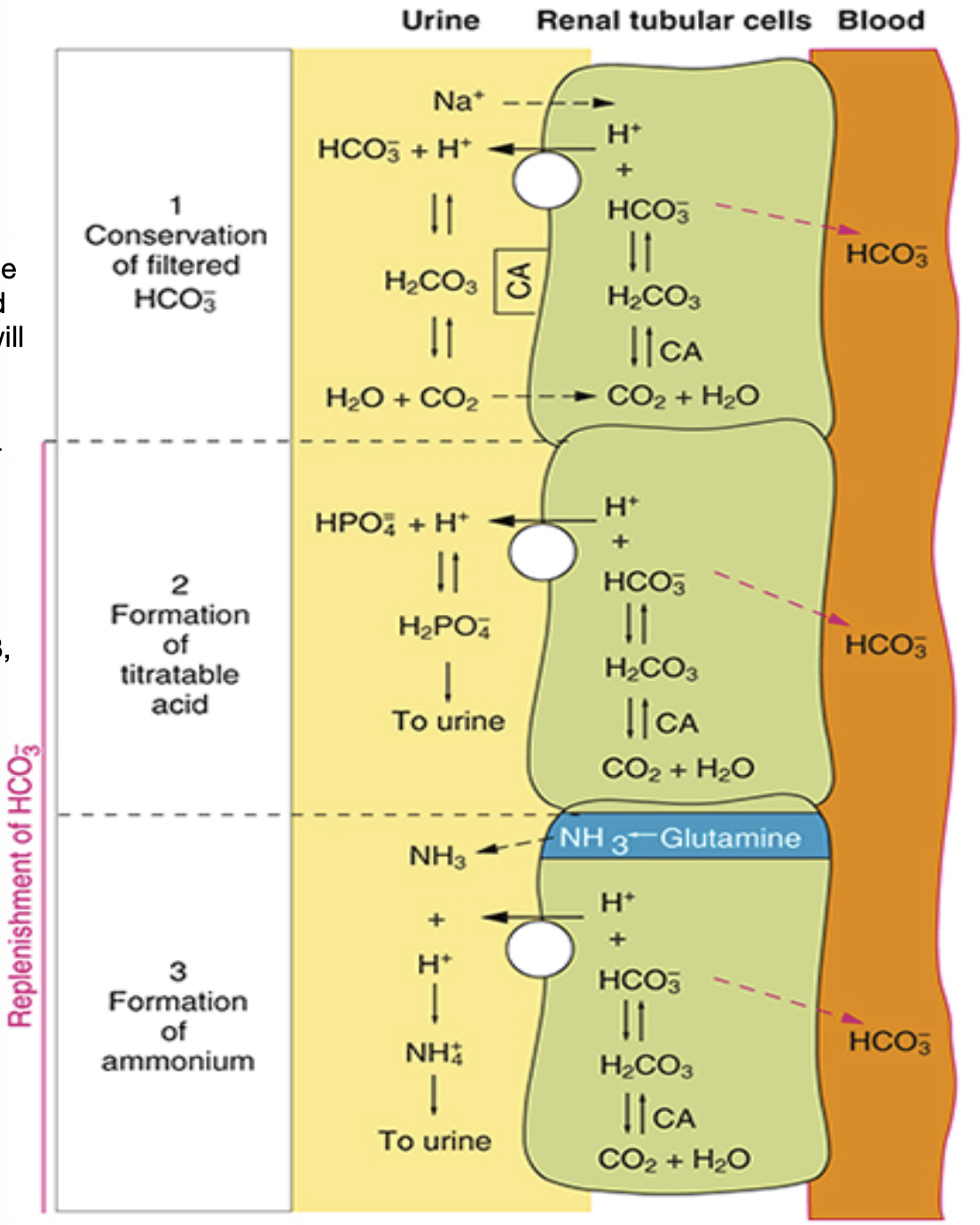
Ammonia (NH3) mechanism
Diminishing AAs produces NH3, which is excreted out into the urine filtrate
NH3 meets H+ and becomes NH4+
NH4+ does not come back into the tubular cells
ROME
R: Respiratory
O: Opposite (pH is opposite of CO2 levels)
M: Metabolic
E: Equal (pH is equal with HCO3-)
Normal pH in body
Metabolic acidosis pH and HCO3 levels increase or decrease?
Decreased pH
Decreased HCO3-
Causes of metabolic acidosis (4)
Production of metabolic acids
Decreased renal function
Increased bicarbonate losses
Hypercholermic acidosis
What can result from the production of metabolic acids?
Acute lactic acidosis
Ketoacidosis
Acute lactic acidosis
when there is a buildup of lactic acid in the bloodstream, leading to a dangerous drop in the body's pH
Ketoacidosis
high levels of blood acids called ketones build up
How does decreased renal function cause acidosis?
When kidney can’t get rid of H+ and can’t reproduce bicarbonate
How does decreased bicarbonate result in acidosis?
Bicarbonate works to decrease pH, so an absence will prevent pH from being increased
What symptoms may occur due to bicarbonate losses? (2)
Diarrhea
Fistulas
Ileostomies may be needed
Hypercholermic acidosis
Abnormal absorption of chloride ions
pH is lowered due to an increase in chloride levels, leading to an excess of acid
Will urine be acidic or alkaline with metabolic acidosis?
Acidic because kidneys are getting rid of H+ and NH4+
Metabolic alkadosis
Excess base in the blood
Does pH and HCO- increase or decrease during metabolic alkalosis?
pH increases
HCO- increases
Causes of Metabolic Acidosis
Excess Base Loading
Loss of fixed acid
Fluid depletion (bc of the above stuff)
Excess base loading examples (too much base in your body)
Over ingestion of antacids (too many tums)
IV infusion excess (giving someone to much base)
Milk-alkai syndrome
How can we lose fixed acid that results in alkalosis? (4)
Vomiting
GI suction
Bulimia
Diuretics
How is metabolic alkalosis compensated for?
Hypoventilation
Respiratory acidosis
the lungs can't remove enough carbon dioxide (CO2), causing the blood and body fluids to become too acidic
Does pH and PCO2 increase or decrease during respiratory acidosis?
pH decreases
PCO2 increases
Causes of respiratory acidosis
Acute — rapid increase in CO2 (ex: can’t take a deep breath)
Chronic — COPD
Increased CO2 production — can occur with fever + sepsis
Compensation for respiratory acidosis
Acid in urine
Issues with respiratory system, we cannot compensate with breathing unless provided an O2 mask
Respiratory alkalosis
the blood pH is elevated due to low levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood
This typically occurs because of hyperventilation
Does pH and PCO2 increase or decrease during respiratory alkalosis?
pH increases
CO2 decreases
Cause of respiratory alkalosis
Hyperventilation
central stimulation of medullary center of brain
Mechanical ventilation
Hyperventilation syndrome
Types of central stimulation of medullary center of brain
Pain
Pregnancy
Sepsis/febrile states
Encephalitis/TBI
How is respiratory alkalosis compensated for?
Alkalne urine