Neural Network flashcards
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
cells that are connected to each other, forming networks and it is capable of both receiving and sending electrical signals
Neurons
A mathematical model for learning inspired by biological neural networks. Model mathematical function from inputs to outputs based on the structure and parameters of the network. Allow for learning the network's parameters based on data
Artificial Neural Network
Mathematical Representation of a Basic Neural Network Structure
h(x₁, x₂) = w₀ + w₁x₁ + w₂x₂
what is w₀ in the context of a neural network structure
the bias term
what is x in the context of a neural network structure
The input
what is w in the context of a neural network structure
The weights
Enumerate the types of Activation function
Step Function
Logistic Sigmoid
Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)
To use the hypothesis function to decide whether it rains or not, we need to create some sort of threshold based on the value it produces
Activation Functions
Give the formula of Step Function
g(x) = 1 if x ≥ 0, else 0
Give the formula of Logistic Sigmoid
g(x) = eˣ/(eˣ + 1)
Give the formula of Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)
g(x) = max(0, x)
An Activation Function that gives 0 before a certain threshold is reached and 1 after the threshold is reached.
Step Function
An Activation Function that uses a logistic function, which gives as output any real number from 0 to 1
logistic sigmoid
An Activation Function which allows the output to be any positive value. If the value is negative, it sets it to 0
Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)
What is the parallel of each neuron
unit
Types of Logic Gates with Neural Networks
OR Gate
AND Gate
General Form for Scaling to Multiple Inputs
g(Σᵢ₌₁ⁿ xᵢwᵢ + w₀)
Algorithm for minimizing loss when training neural networks:
Gradient Descent
Gradient Descent Algorithm
Start with a random choice of weights
Repeat:
Calculate the gradient based on all data points (direction that leads to decreasing loss)
Update weights according to the gradient
what is a problem with Gradient Descent
The problem with this kind of algorithm is that it requires to calculate the gradient based on all data points, which is computationally costly.
Variations of Gradient Descent
Stochastic Gradient Descent
Mini-Batch Gradient Descent
Stochastic Gradient Descent Algorithm
Start with a random choice of weights
Repeat:
Calculate the gradient based on one data point: (direction that leads to decreasing loss)
Update weights according to the gradient
What is an issue with Stochastic Gradient Descent
The gradient is calculated based on one point chosen at random. This kind of gradient can be quite inaccurate
Mini-Batch Gradient Descent algorithm
Start with a random choice of weights
Repeat:
Calculate the gradient based on one small batch: (direction that leads to decreasing loss)
Update weights according to the gradient
What is an advantage of Mini-Batch Gradient Descent
Computes the gradient based on on a few points selected at random, thus finding a compromise between computation cost and accuracy
limitations of perceptron output units
Only capable of learning linearly separable decision boundaries
Cannot solve problems like XOR gate
A neural network is an artificial neural network with an input layer, an output layer, and at least one hidden layer
Multilayer Neural Networks
Algorithm for training neural networks with hidden layers
Backpropagation
Backpropagation Algorithm
Start with random choice of weights
Repeat:
Calculate error for output layer
For each layer, starting with output layer, moving inwards towards earliest hidden layer:
Propagate error back one layer
Update weights
Neural networks with multiple hidden layers
Deep Neural Networks
Temporarily removing units - selected at random - from a neural network to prevent over-reliance on certain units
Dropout
a free, open-source platform developed by Google for building and deploying machine learning and deep learning models
TensorFlow
Computational methods for analyzing and understanding digital images
Computer Vision
How is Image Represented
Images represented as pixel values (0-255 for grayscale, RGB values for color)
Each pixel can be treated as input to neural network
Applying a filter that adds each pixel value of an image to its neighbors, weighted according to a kernel matrix
Image Convolution
Kernel for edge detection
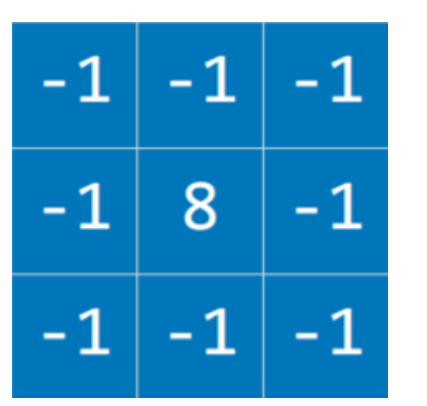
Reducing the size of an input by sampling from regions in the input
Pooling
Pooling by choosing the maximum value in each region
Max-Pooling
what is an advantage of Max-Pooling
Reduces computational complexity
Provides translation invariance
Neural networks that use convolution, usually for analyzing images
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Architecture flow of CNN
Convolution → Pooling → Flattening
Neural network that has connections only in one direction. Information flows from input to output without loops
Feed-Forward Neural Networks
Neural network that generates output that feeds back into its own inputs.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Advantages of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Can process sequences of data
Memory of previous inputs
Useful for tasks like language translation, text generation
Popular framework for building and training neural networks.
TensorFlow
What are the 3 main architectures of neural network
Feedforward networks for basic classification/regression
CNNs for image processing
RNNs for sequential data processing
Consider the neural network below, where we set:
w0 = -5
w1 = 2
w2 = -1 and
w3 = 3.
x1, x2, and x3 represent input neurons, and y represents the output neuron.
What value will this network compute for y given inputs x1 = 3, x2 = 2, and x3 = 4 if we use a step activation function? What if we u
1 for step activation function, 11 for ReLU activation function
How many total weights (including biases) will there be for a fully connected neural network with a single input layer with 3 units, a single hidden layer with 5 units, and a single output layer with 4 units?
44
Consider a recurrent neural network that listens to an audio speech sample, and classifies it according to whose voice it is. What network architecture is the best fit for this problem?
Many-to-one (multiple inputs, single output)

[[16, 12], [32, 28]]