Chapter 9.1 - Cytoskeleton, cell cycle, and microtubules
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
different cytoskeletal components
microtubules
microfilaments
intermediate filaments
general roles of cytoskeletal components
structure and support
intracellular transport
contracility and motility
spatial organization
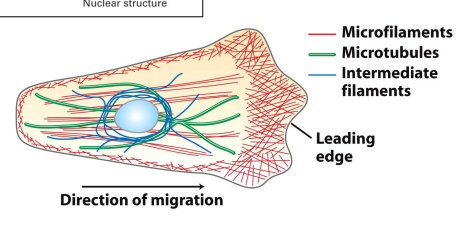
cell polarity
spatial differences in shape, structure, and function within a cell
what types of cells exhibit polarity and why
almost all cell types exhibit some form of polarity; enables them to carry out specialized functions
largest of the cytoskeletal components of a cell
microtubules
types of microtubules
cytoplasmic MT
axonemal MT
cytoplasmic MT def
found in the cytosol and have various fnctions
cytoplasmic MT functions
maintaing axons in nerve cells
formation of mitotic and meiotic spindles
placement and movement of vesicles
maintaing or altering cell shape
axonemal MT def
include the organized and stable MTs found in structures specialized for movement
what structures might axonemal MTs be found
cilia
flagella
basal bodies to which cilia and flagela attach
axoneme
central shaft of a cilium or flagellum, is highly ordered bundle of MTs
shape of MTs
straight hollow cylinders of varied length
what are MTs made of
longitudinal arrays of polymers called protofilaments
subunit of protofilament
heterodimer of tubulin, one alpha (a)-tubulin and one beta (b)-tubulin, these are globular proteins
how do the tubulin heterodimer subunits bind to each other
bind noncovalently
MAPs
microtubule associated proteins
what are MAPS composed of
a heterogenous collection of proteins with one domain that attaches to the side of a microtubule and another domain that projects outward as a tail
what do MAPs do
generally increase the stability of microtubules and promote their assembly
how is MAP activity controlled
by addition and removal of phosphate groups from amino acid residues
are the tubulin subunits ever found as individual monomers in the cell
no
what do both monomers of tubulin have
a GTP binding site
what can a-tubulin bind
GTP, it is physically trapped and NEVER hydrolyzed or exchanges
what can b-tubulin bind
either GDP or GTP (both hydrolyzable and exchangeable)
why do protofilaments have inherent polarity
all the dimers in the MT are oriented in the same way
orientaion of the dimers causes the protofilament to have polarity
t or f - the two ends of a protofilament are the same
false, the two ends differ both chemically and structurally
(-) end of the MT has
a-tubulin
(+) end of the MT has
b-tubulin
what does distribution of MTs help determine in the cell
shape of the cell
how are MTs arranged in cultured animal cells and how does that effect tje shape
extend in a radial array outwards from near the nucleus, gives cells a round, flattened shape
how are MTs arranged in columnal epithelial cells and how does that effect shape
oriented with their long axis parallel to the long axis to help support the cells elongated shape
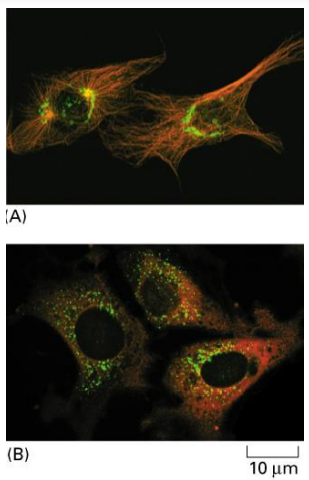
what does treatment of cells with nocodazole or colchicine do
promotes MT disassembly and can disperse the Glogi elements into separate golgi stacks scattered throughout the cytoplasm
what happens when you remove colchicine or nocodazole from a cell where you had previously added it
the MTs reassemble and the Golgi membranes return to their normal position in the cell interior
kinesin
antegrade MT motor
dynein
retrograde MT motor
myosin
third motor proteins that carries organells along actin fibers
what is the energy source of motor protein movement
molecular motors convert energy from ATP into mechanical energy
how do motor proteins move
move unidirectionally along their cytoskeletal track in a stepwise manner and undergo a series of conformational changes that constitute a mechanical cycle
three categories of molecular mototrs
move along microtubule tracks - kinesin and dynein
move along microfilament tracks - myosin
how is the mechanical cycle of motor proteins fueled
coupled to the steps of a chemical cycle, which provide the energy necessary to fuel the motor’s activity to move along the track
what does the coupled chemical cycle of motor proteins include
binding of ATP to the motor
hydrolysis of ATP
release of the products (ADP and Pi)
binidng of new molecule of ATP
t or f - motor proteins are able to keep movigng a bit after energy input
false, motor proteins have virtually no momentum and are subjected to tremendous frictional resistance; will stop moving almost immediately once energy input has ceased
what direction does kinesin move in
plus end directed microtubule motor
how long is each step
approximately the lenght of one tubulin dimer
how much ATP does a single kinesin step require
one ATP
kinesin movement relationshop to ATP concentration
proportional
mechanism of kinesin movement
hand-over-hand mechanism
processivity of kinesin
highly processive, can walk along a MT for considerable distances without falling off
how does cytoplasmiv dynein move
like kinesin but in the opposite direction (negative end directed)
t or f - microtubules may bind kinesin adn dynein silmultaneously
true
t or f - organelles may bind both kinesin and dynein silmultaneously with one of them inactive
true
can movement along MTs be regulated
yes
melanosome aggregation is via what protein
dynein
melanosome dispersion is via what protein
kinesin
dynamic instabuluty
process of alternating between growing and shrinking
what is faster, dissociation of GDP or GTP tubulin dimer
GDP tubulin dimer dissociation is much faster than GTP tubulin dimer dissociation
function of a MT in a living cell is dependent on
its location and orientation
assembly of MTs in vitro from ab-tubulin dimers occurs in what two distinct phases
a slow phase of nucleation in which a small portion of the MT is initially formed
much more rapid phase of elongation
in vivo, how is the rate of nucleation of MTs different
much more rapid as it occurs in association with a variety of specialized structures calls MTOCs
role of MTOCs in all cells
control number of MTs, their polarity, the numebr of protofilaments that make up their walls, and the time and location of their assembly
centrosome
best studied MTOC
phases of the cell cylce
M phase
interphase
M phase include
mitosis and cytokinesis
interphase consitst of
G1, S, G2h
how long does mitosis last
about an hour
what consititutes most of the cell cylse
interphase, 90%, last longer than M phase
what happens in each stage of the cell cycle
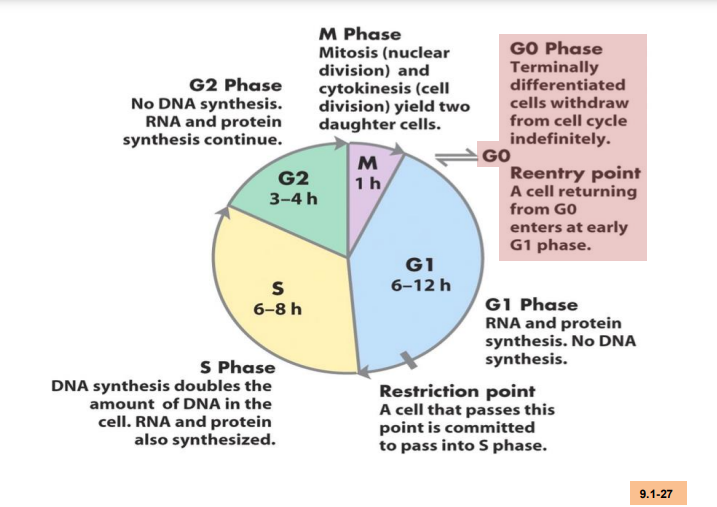
5 stages of mitosis
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
what are centrosomes made of
complex of proteins not all of which have been identified
centrioles
short cylinder of modified MTs
gorwth of MTs occurs by addition of subunits to which end
plus end of the polymer away from the cnetrosome
minus end of MT is associated with what
the centrosome
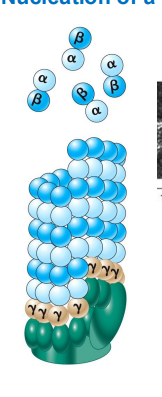
nucleation of microtubule begins with
gamma-tubulun at the minus end
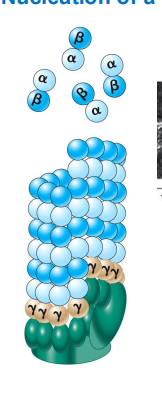
wat is nucelation initiated by
gammaTURCs - Tubuling Ring complex
the gamma-TURC is
a helical array of y-tubulin where ab=tubulin dimers assemble
thre classes of microtubules and where are they found
all in mitotic spindle
kinetochore
astral
polar
kinetochore MTs
connected to chromosomes (after first “finding” them via a kinetochore on the chromosome)
astral MT
project towards the cell cortex and interact with it thereby orienting the spindle of division
polar MTs
interact with microtubules from the opposite pole of the cell
what happens in prophase
protein synthesis stops
internal membrane systems that are normally associated with MTs disperse
endocytosis and exocytosis stop
Each centrosome (that divided in S phase) forms an MTOC and nucleation and elongation of microtubules begins
three major components of the nucelar envelope
nuclear pores
nucelar lamina (structural and composed of intermediate filaments)
nucelar membranes
t or f - the three components of the nuclear envelope are dissassembled in the same process
false, in spearate processes
how is the nuclear membranes integrity first disupetd
mechanically as holes are torn into the envelope by cytoplasmic dynein molecules associated with outer nucelar membrane
how is the nucelar lamina disrupted
phosphorylation of the human nuclear lamin causes de-polymerization of the intermediate filaments in the nuclear lamina
what happens to the organelles during prophase
mitochondria, lysosomes, and peroxisome remain relatively intact
Golgi is either absorbed by the ER or fragmented and partitioned
what happens to the mitotic spindle in prometaphase
definitive mitotic spindle is formed and chromosomes are moved by microtubules into the center of the cell
kinetochore
a complex of proteins associated with the centromere of a chromosome during cell division to which the + end of microtubles of the spindle poles attach
polymerization vs depolymerization of MT
Plus end can add (polymerize) or lose (depolymerize) subunits
what si polymerizing and depolymerizing during prometaphase
Polymerization AND depolymerization at the plus end
Depolymerization at the - end
when is the cell in metaphase
when the fully condensed chromosomes are all aligned at the metaphase plate
metaphase plate
a plane equidistant between the two poles of the spindel
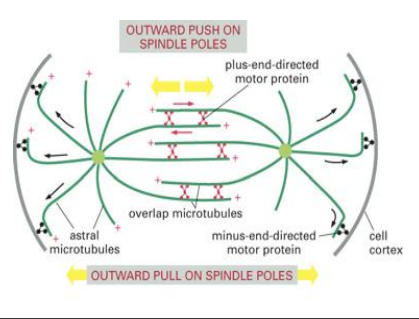
what happens in anaphase
Tubulin subunits are lost from both ends of kinetochore microtubules
Tubulin subunits are added to polar microtubules at the + end
Tubulin subunits are lost from the minus ends of polar microtubules
Note the role of motor proteins in pushing the polar microtubules apart
role of motor proteins in anaphase
pushing polar MTs apart
Pushing apart of the polar microtubules by a four headed kinesin family motor protein in image
final stage of mitosis
telophase
what happens in telophase
mitotic spindle disassembles
nuclear envelope of the two two nuclei are reassembled
chromosomes become dispersd
what happens in cytokinesis
cytoplasm is partitioned into two cells
how does cytokinesis happen
Cleavage depends on a belt-like bundle of actin microfilaments (the contractile ring) that form just below the plasma membrane in early anaphase
As cleavage progresses, the ring tightens around the cytoplasm
what is important for completing cytokinesis
Signals emanating from the central part of the spindle
spindle midzone
central part of the spindle
contraction of actin ring during cytokinesis is generated by
interactions between actin and the motor protein, myosin
regulation through cell cycle is controlled by
cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs)