Chapter 5 (the integumentary system)
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
The Integumentary System
the skin
What are the two membranes of the integumentary system?
Cutaneous membrane and accessory membrane
what is within the cutaneous membrane
epidermis and dermis
what layers are within the Dermis
papillary layer and reticular layer
what are the structures in accessory structures
Hairs, Nails, Exocrine glands, sensory receptors, and cutaneous plexus
Cutaneous plexus
a network of blood vessels
subcutaneous layer
separates the integument from the deep fascia.
epidermis
the outer layer of the skin is made of multiple layers of cells. Primarily being keratinocyte
stratum basale
attached to the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes. most cells here are basal cells.
stratum spinosum
composed of 8-10 layers of keratinocytes bound together by desmosomes. this is the start of keratin production.
stratum granulosum
composed of 3-5 layers of keratinocytes. this is where cells grow thinner and flatter.
stratum lucidum
found only in thick skin, separates corneum from the underlying layer, and is densely packed with dead cells filled with keratin.
stratum corneum
the outermost protective region with 15-30 layers of keratinized cells, dead cells still tightly connected by desmosomes.
list the order of the epidermis, starting from bottom to top.
Stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratu, lucidum, and stratum corneum.
strata
Multiple layers of cells
thin skin
covers most of the body surface, four layers of strata
Thick skin
found in palms of hands and soles of feet, five layers of strata.
does thick skin contain stratum lucidum
yes
papillary layer
above the reticular layer and is composed of areolar tissue.
what does the papillary layer contain
Capillaries, lymphatic vessels, and sensory neurons.
reticular layer
interwoven meshwork of dense, irregular connective tissue.
what does the reticular layer contain
blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerve fibers, and accessory organs
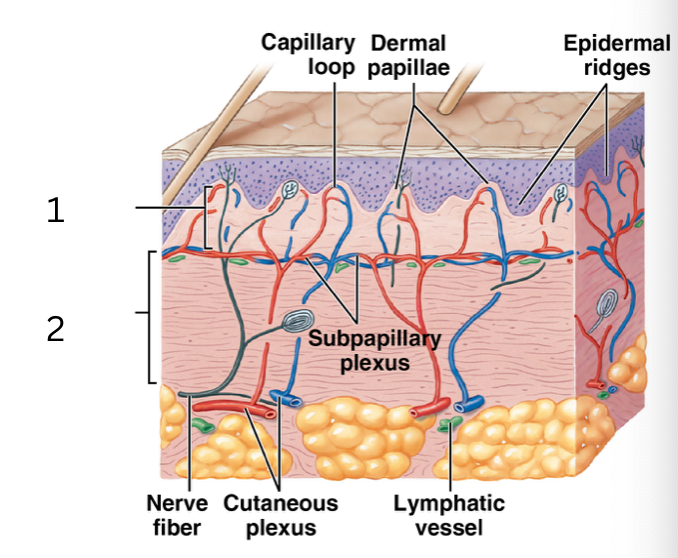
what layer of the dermis is 1
papillary layer
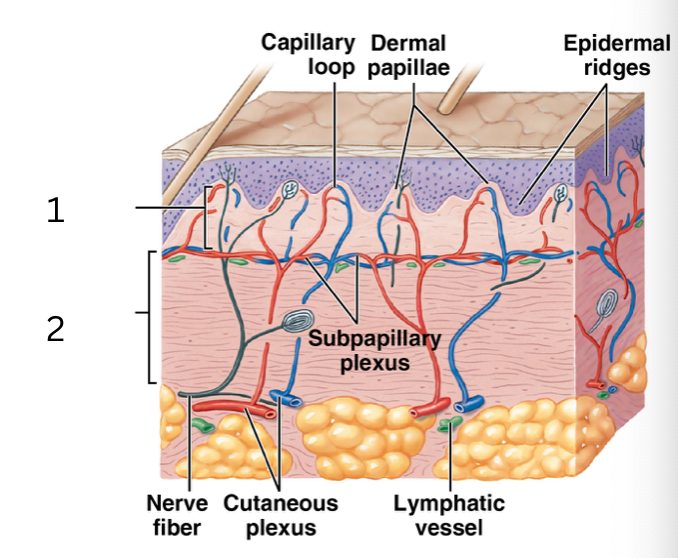
what layer of the dermis is 2
reticular layer
epidermal ridges
formed from the deeper layer of the epidermis
dermal papillae
the superficial layer of the dermis
how do finger tips get ridges
an interaction between the epidermal ridges and dermal papillae
melanin
brown or black pigment that is produced by melanocytes
carotene
orange-yellow pigment from vegtables
hemoglobin
red pigment found in red blood cells
the more blood there is in your skin your skin will be
red
if there is less blood within your skin, your skin will be
pale
jaundice
yellowing of the skin due to a high level of bilirubin
bruising
discoloration of the skin due to broken blood vessels underneath the skin
when the bruising is red
o2 bound hemoglobin
when the bruising is blue
hemoglobin without O2
when the bruising is purple
mix of red and blue
when the bruising is green/ yellow
hemoglobin breaking down and processing
first degree burn
extends into the epidermis, causes redness in the skin
second-degree burn
extends into the dermis
third- degree burns
extends into the hypodermis, burns off nerves and is less painful
split-thickness graft
transfer of the epidermis and superficial portions of the dermis
full-thickness graft
transfer of the epidermis and both layers of the dermis
autograft
patients own undamaged skin
allograft
donor tissue
xenograft
animal graft
rule of nines
method of estimating the percentage of surface area affected by burns
terminal hairs
large, coarse, darkly pigmented
vellus hairs
smaller, shorter, delicate
where can you find terminal hairs
scalp, armpit, pubic region
where can you find vellus hairs
found on general body surface
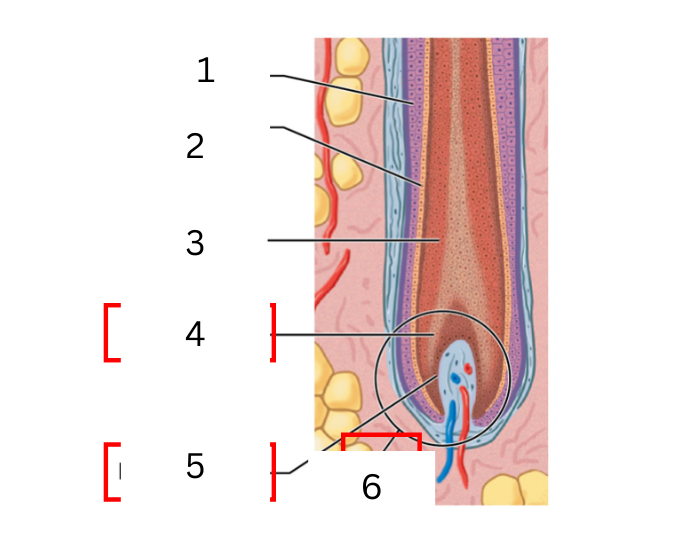
on the hair was is 1
cuticle
on the hair was is 2
cortex
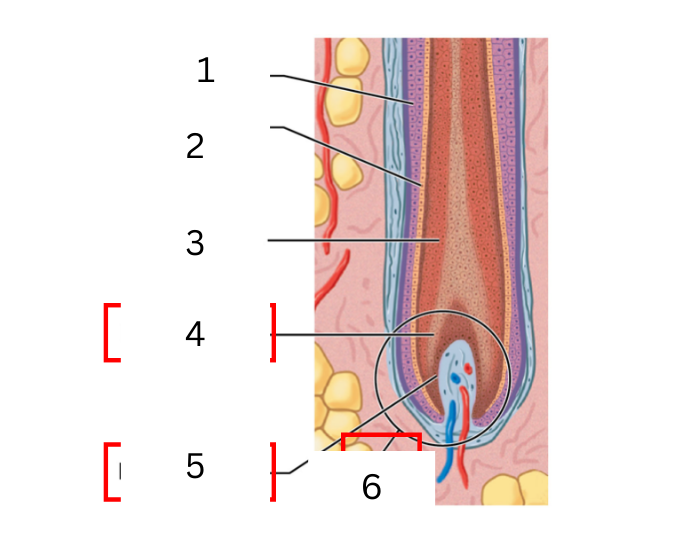
on the hair what is 3
medulla
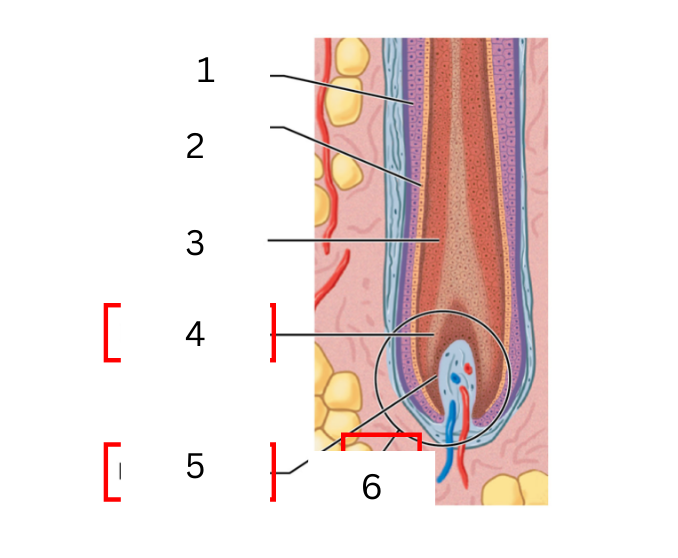
on the hair what is 4
hair matrix
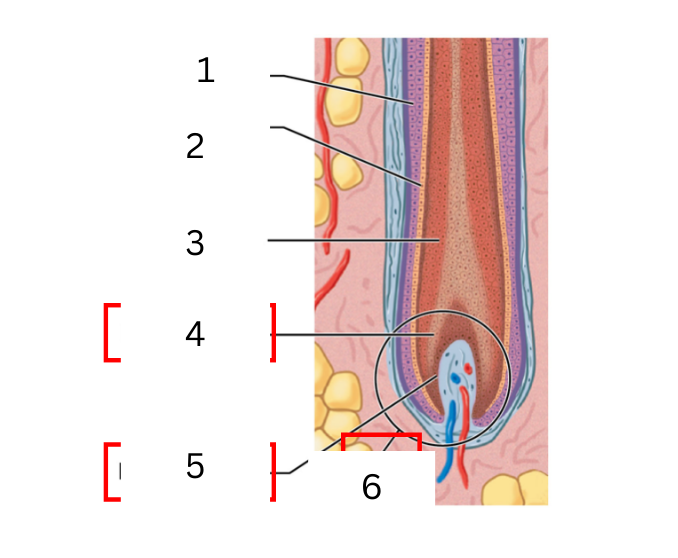
on the hair what is 5
hair papilla
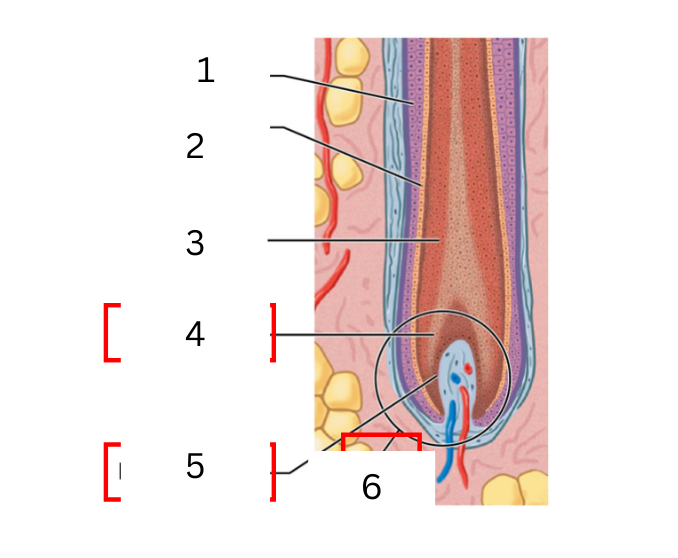
on the hair what is 6
hair bulb
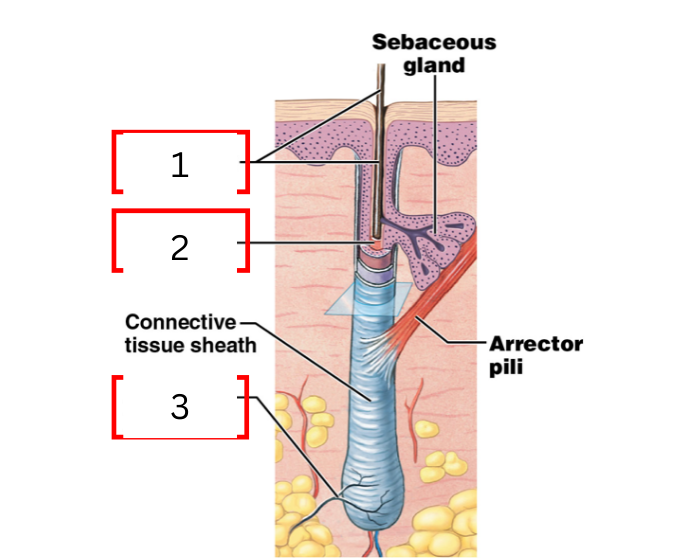
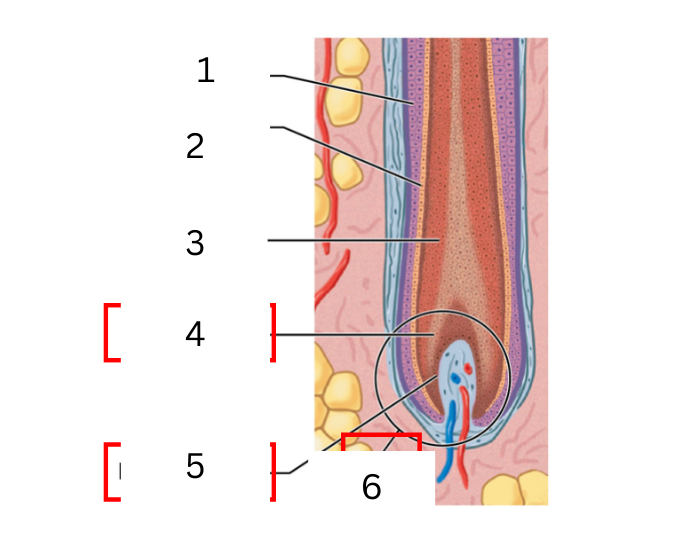
what is 1 on the hair follicle
hair shaft
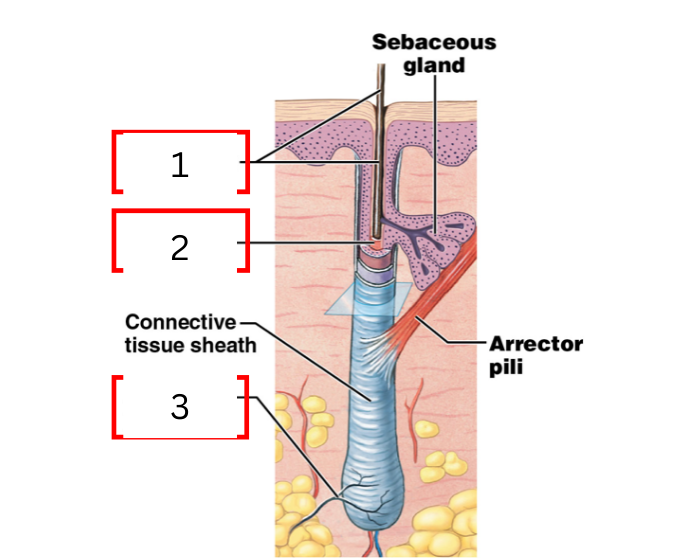
what is 2 on the hair follicle
hair root
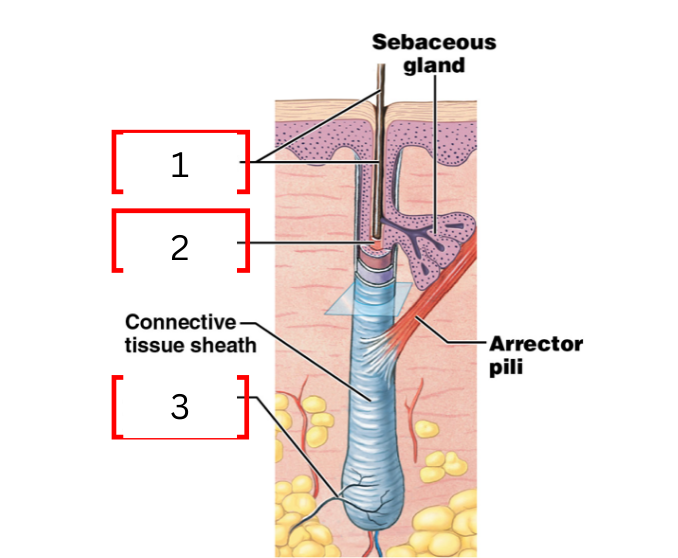
what is 3 on the hair follicle
root hair plexus
hair shaft
region of the hair beneath the skin surface
hair root
region of hair attached to the follicle wall (anchors the hair)
root hair plexus
sensory nerves surrounding the base follicle
medulla
a layer of daughter cells formed at the center of the matrix
cortex
intermediate layer that is deep into the cuticle
cuticle
daughter cells produced at the edges of the matrix form the surface of the hair
hair bulb
expanded base of hair follicle where hair growth occurs
hair papilla
connective tissue filled with blood vessels and nerves
hair matrix
actively diving basal cells in contact with hair papilla
keratinocyte
primary cell type in the epidermis
melanocytes
produces melanin
what are the two phases of hair growth
active phase and resting phase
active phase of hair growth
lasts 2-5 years, with hair growing 0.33 mm per day.
resting phase
the hair loss the attachment to the follicle and becomes a club hair. then, new hair formation begins
sudoriferous glands
sweat secretion
where can you find sudoriferous glands
around the surface of the skin
what are the two types of sudoriferous glands
Eccrine sweat glands and apocrine sweat glands
apocrine sweat glands
glands that metabolize excretions that produce the body odor smell.
where are apocrine sweat glands found
in the axillae, nipple, and pubic regions.
eccrine sweat glands
produces watery secretions with electrolytes
where is eccrine sweat glands found
most skin surfaces, the highest number are on palms and soles
sebaceous glands
secretion of sebum (oil)
sebum
a mixture of cholesterol, proteins, and electrolytes. lubricates the skin and hair shaft.
where is sebaceous glands located
most glands are connected to the hair follicles; few are connected to the skin's surface
what are the phases of integument repair
inflammation, migration, proliferation phase, scarring phase
inflammation phase
initial injury that causes bleeding and mast cell activation
migration phase
scabbing forms that the surface
proliferation phase
deeper portions of the clot dissolve. fibroblasts produce new collagen fibers
scaring phase
the scab is shed, and the epidermis is completely healed.