1.2.6 Price determination
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
How are prices determined in a free market economy?
By the interaction of demand and supply through buyer and seller participation, leading to equilibrium.
What is the equilibrium?
Where demand = supply
Price is the market clearing price - sellers are clearing their stock at an acceptable rate
What is disequilibrium?
A situation where supply does not equal demand, resulting in either excess demand or supply
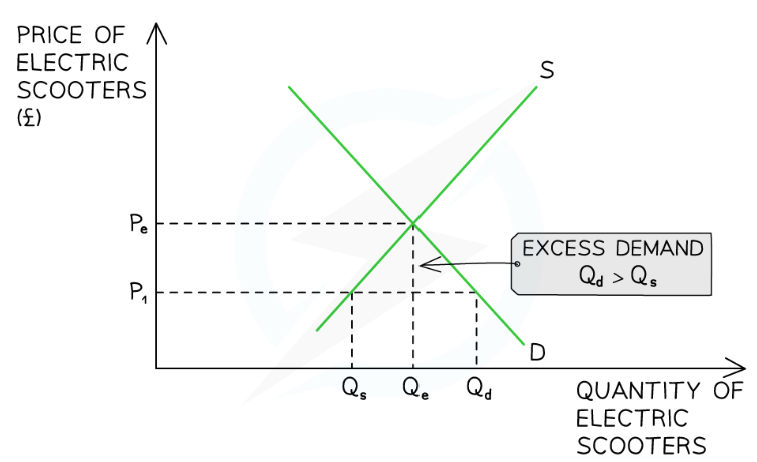
Market response to excess demand?
Sellers are frustrated that products are selling so quickly at a price that is obviously too low
Some buyers are frustrated as they will not be able to purchase the product
Sellers realise they can increase prices and generate more revenue and profits
Sellers gradually raise prices
This causes a contraction in QD as some buyers no longer desire the good/service at a higher price
This causes an extension in QS as sellers are more incentivised to supply at higher prices
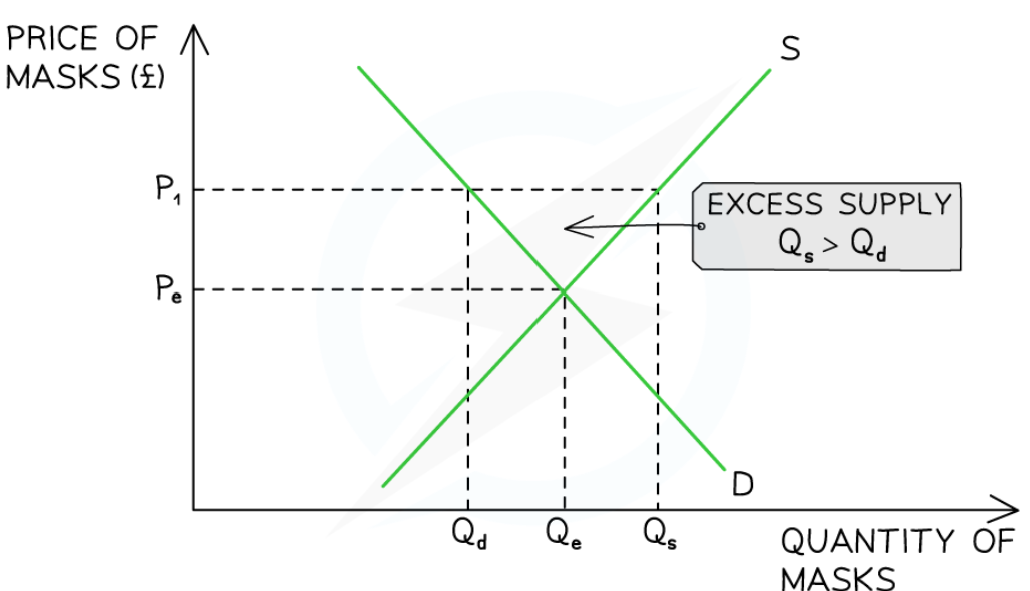
Market response to excess supply?
Sellers are frustrated that the masks are not selling and that the price is obviously too high
Some buyers are frustrated as they want to purchase the masks but are not willing to pay the high price
Sellers will gradually lower prices in order to generate more revenue
This causes a contraction in QS as some sellers no longer desire to supply masks
This causes an extension in QD as buyers are more willing to purchase masks at lower prices
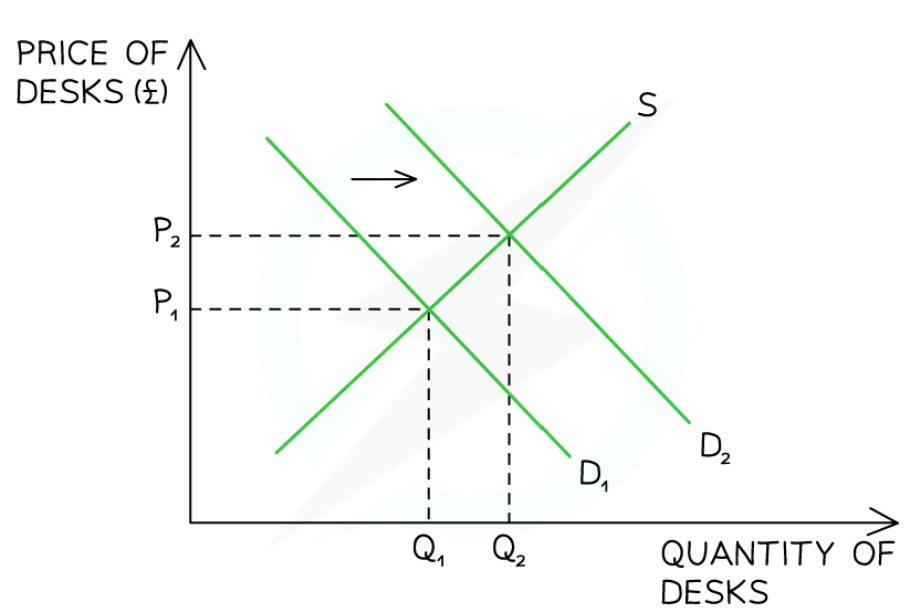
Real world example of excess demand (increase in price)
During COVID, demand for furniture e.g. desks exponentially increased
At the original market clearing price of P1, a condition of excess demand now exists
The demand for desks is greater than the supply
In response, suppliers raise prices
This causes a contraction of demand and an extension of supply, leading to a new market equilibrium at P2Q2
Both the equilibrium price (P2) and the equilibrium quantity (Q2) are higher than before
The excess demand in the market has been cleared
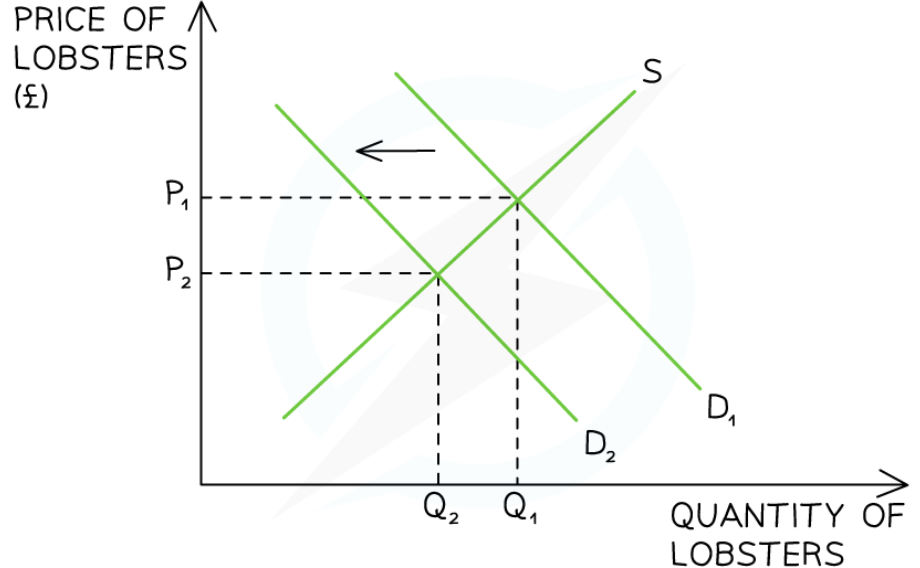
Real world example of excess supply (decrease of price)
Demand for lobsters in Maine, USA has been falling steadily in recent months
This has resulted in a price fall from $12.35 /pound on the 1st April to $9.35 /pound on the 1st May
At the original market clearing price of P1, a condition of excess supply now exists
The demand for lobsters is less than the supply
In response, suppliers gradually reduce prices
This causes a contraction of supply and an extension of demand leading to a new market equilibrium in P2Q2
Both the equilibrium price (P2) and the equilibrium quantity (Q2) are lower than before
The excess supply in the market has been cleared