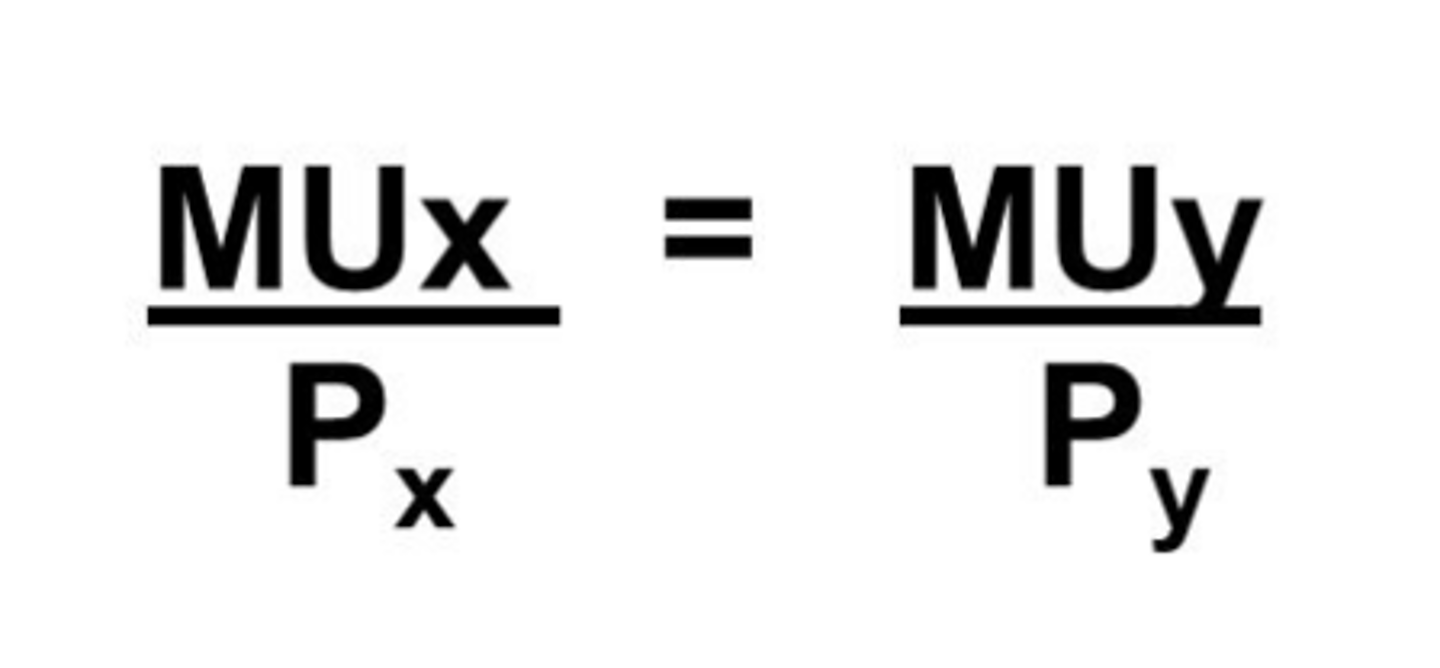AP Micro Unit 1: Economic Thinking
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
scarcity
the inability of our limited resources to satisfy human wants, pervasive
factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
command economy
An economic system in which the central planner (government) controls a country's economy.
market economy
Economic decisions are made by individuals or the open market, decentralized economy, has private property rights
mixed economy
An economy in which private enterprise exists in combination with a considerable amount of government regulation and promotion (what USA has)
opportunity cost
the value of the next best alternative not chosen, the cost of a CHOICE
explicit cost
a cost that requires an outlay of money
implicit cost
A firm's opportunity cost of using its own resources or those provided by its owners without a corresponding cash payment
opportunity cost
explicit cost + implicit cost
production possibilities curve
A graph that describes the maximum amount of one good that can be produced for every possible level of production of the other good.
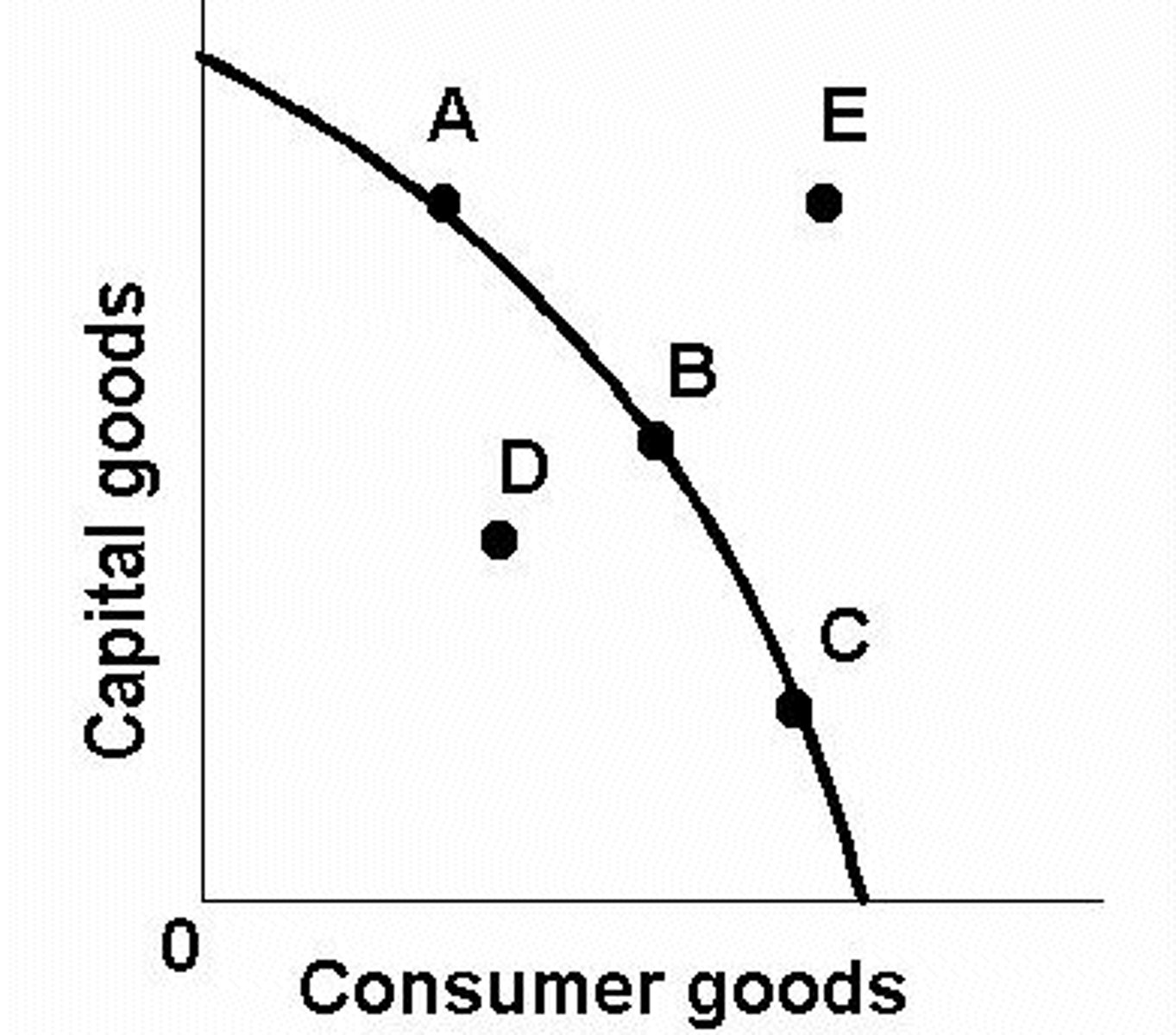
PPC increasing costs
2 resources are not perfectly adaptable to one anohter
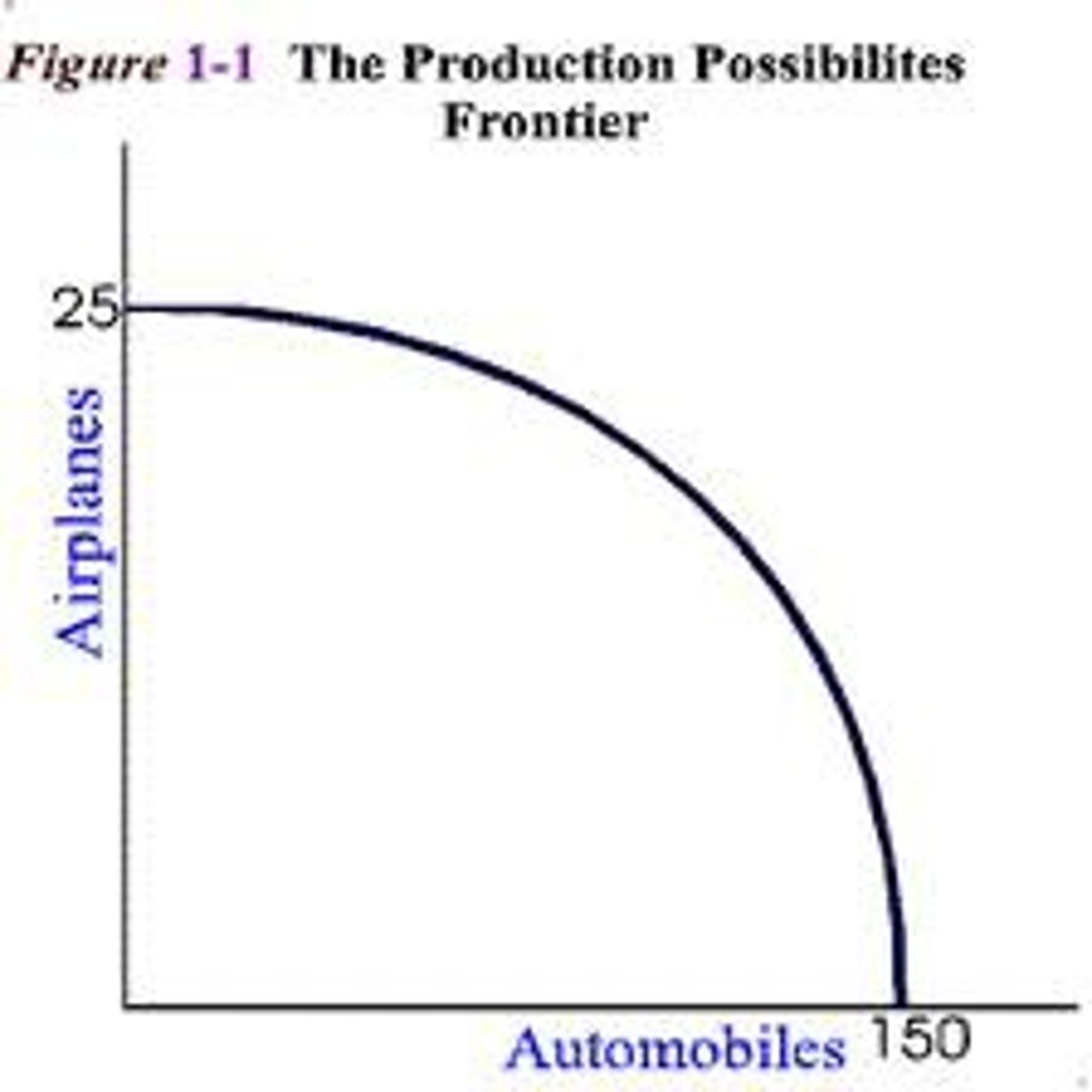
PPC constant costs
2 resources are "perfectly adaptable" for one another
productively efficient
Any point on the PPC is considered to be _________ _________
inefficient
Any point inside the PPC curve is considered to be _______
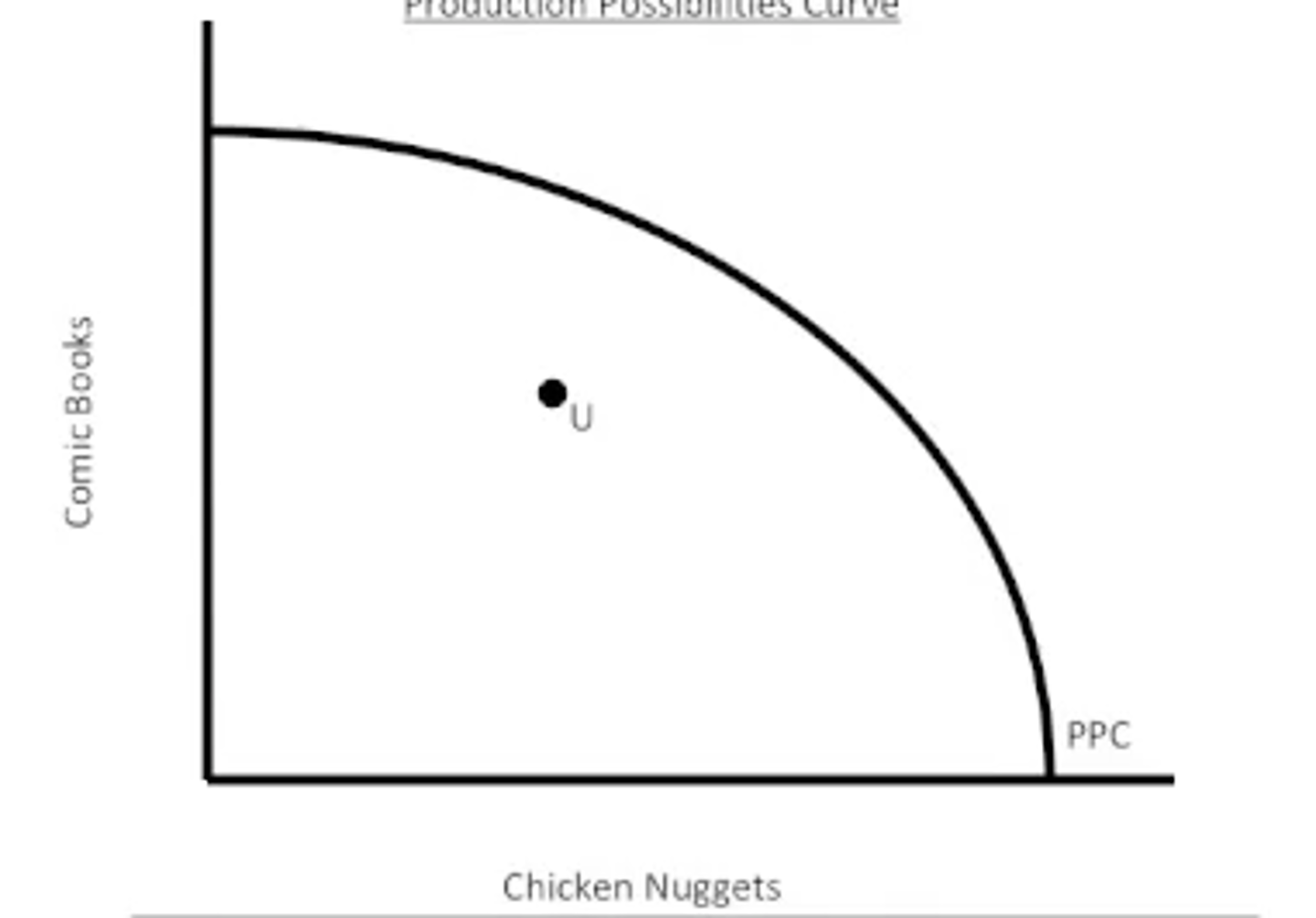
scarcity
Any point outside the PPC curve is ________, impossible because you cannot produce if you do not have the resources to. (point B on the graph)
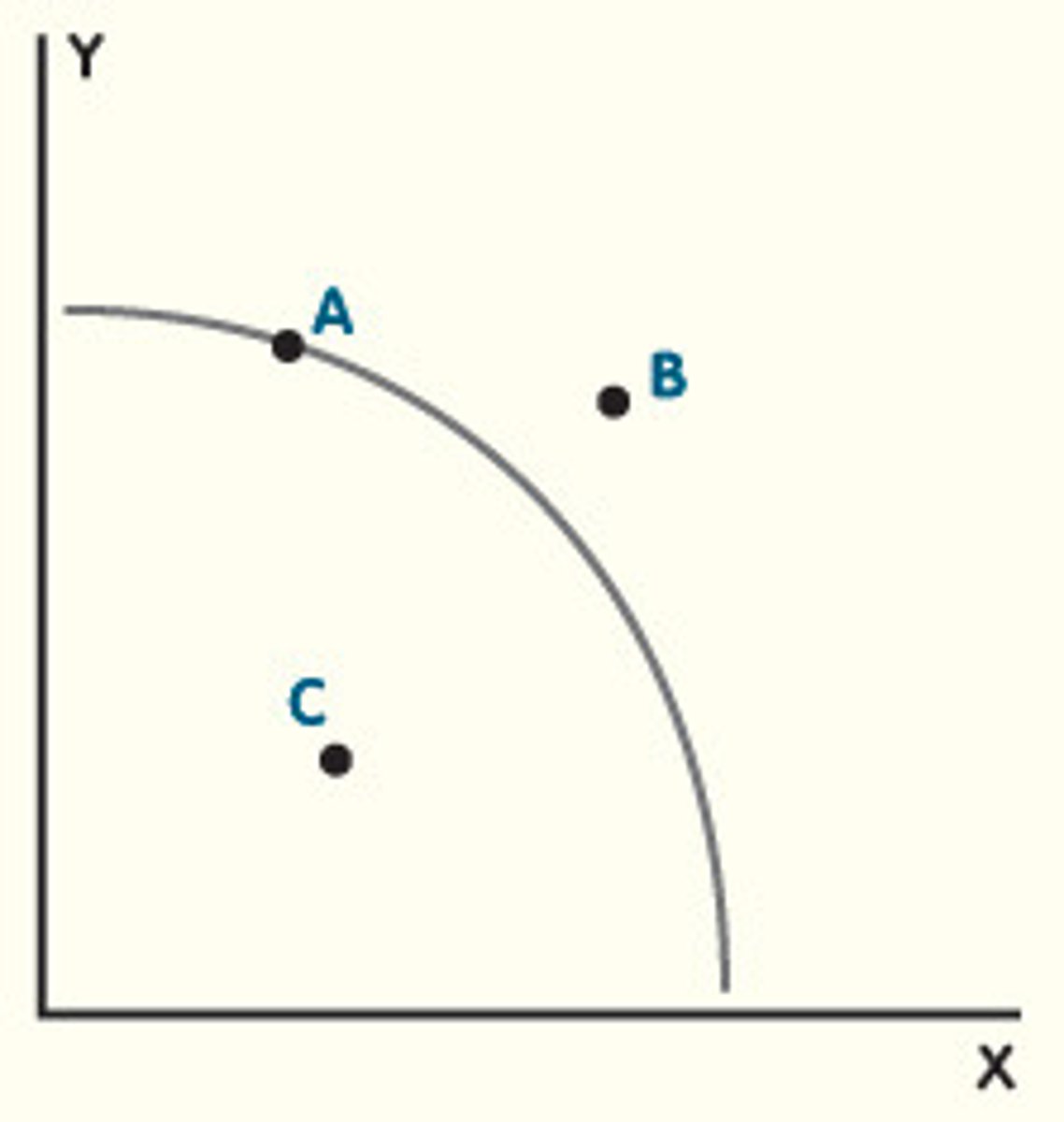
resources
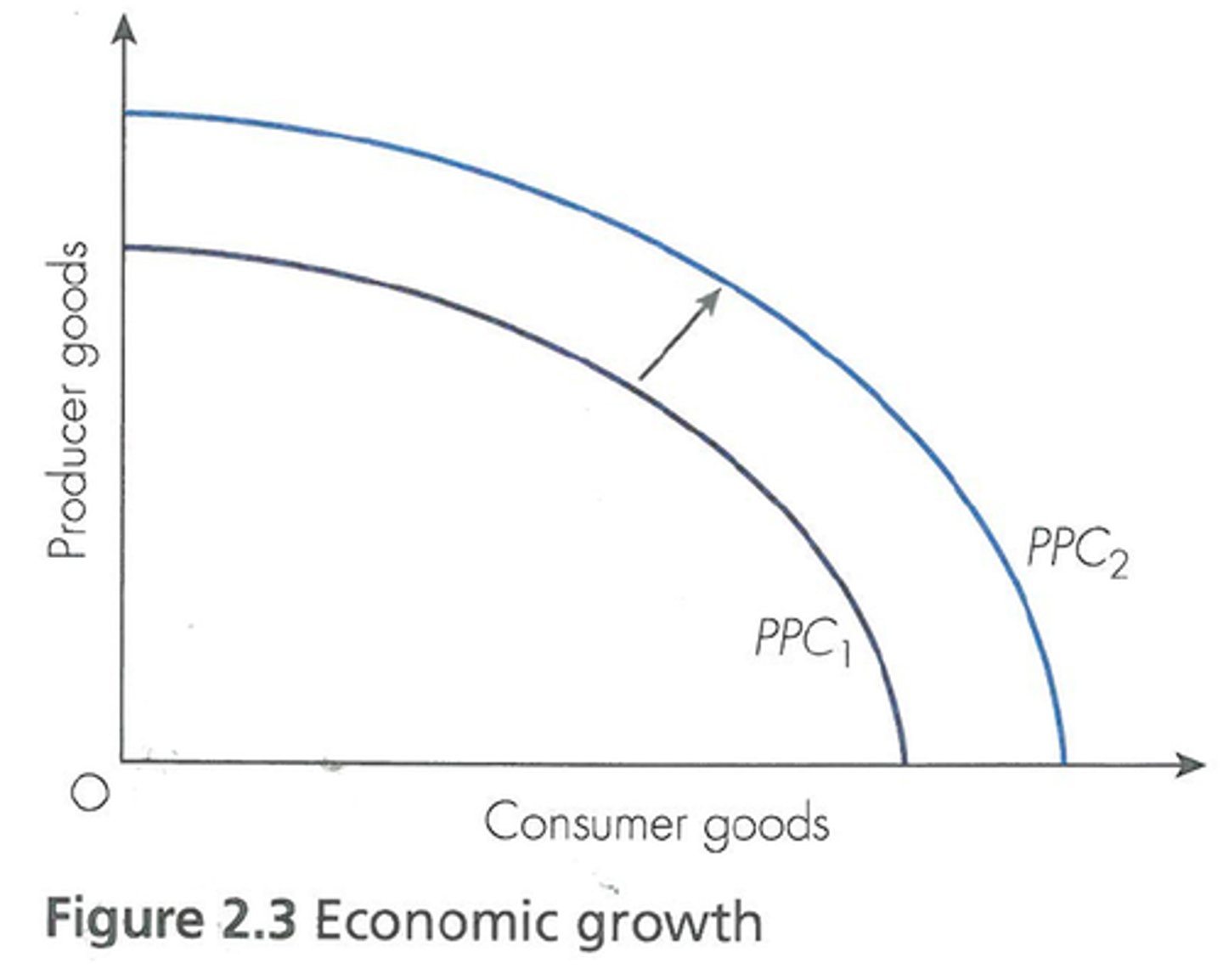
PPC shifts with changes in the quality or quantity of ______
PPC growth
shifts right
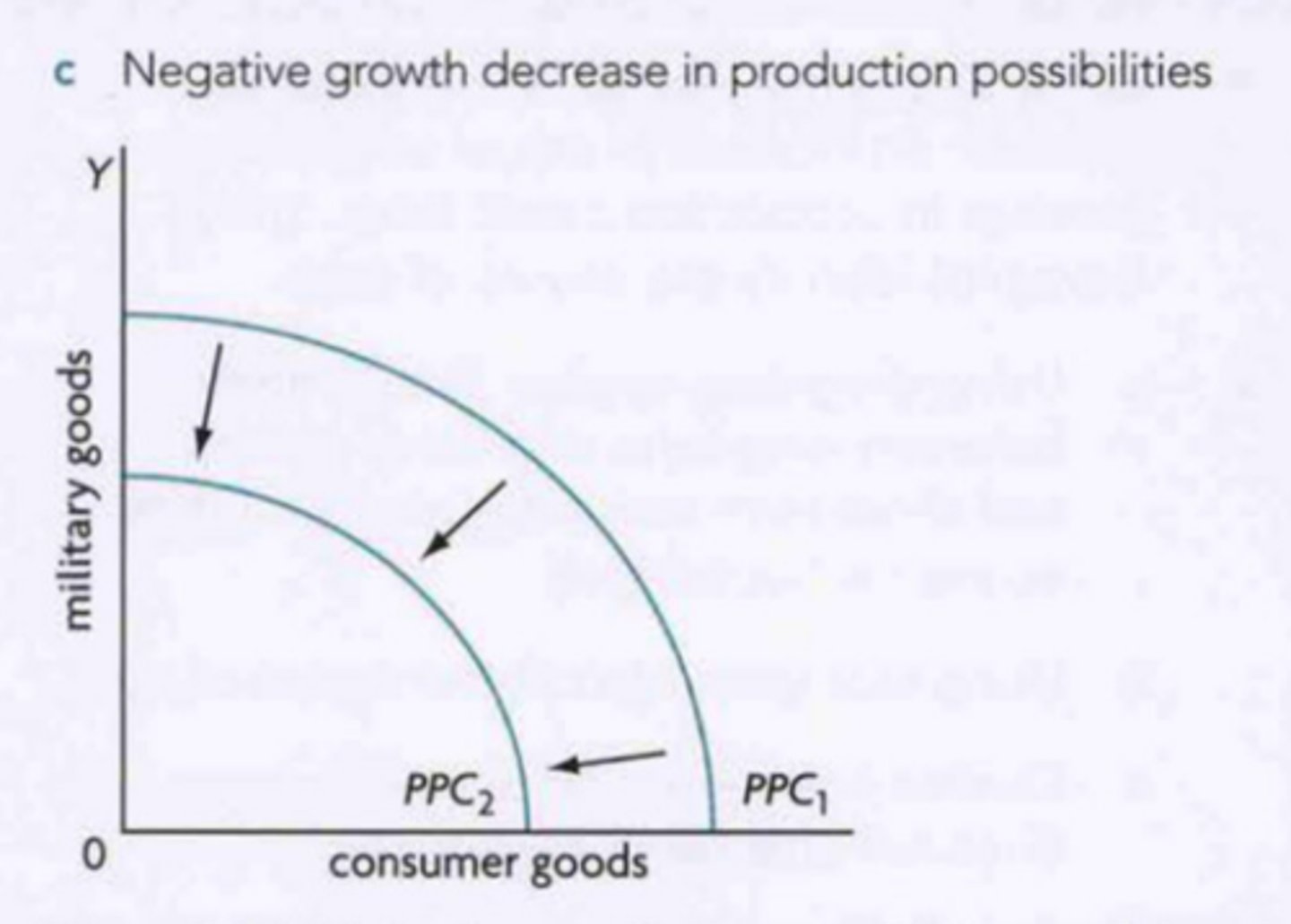
PPC negative growth
shifts left
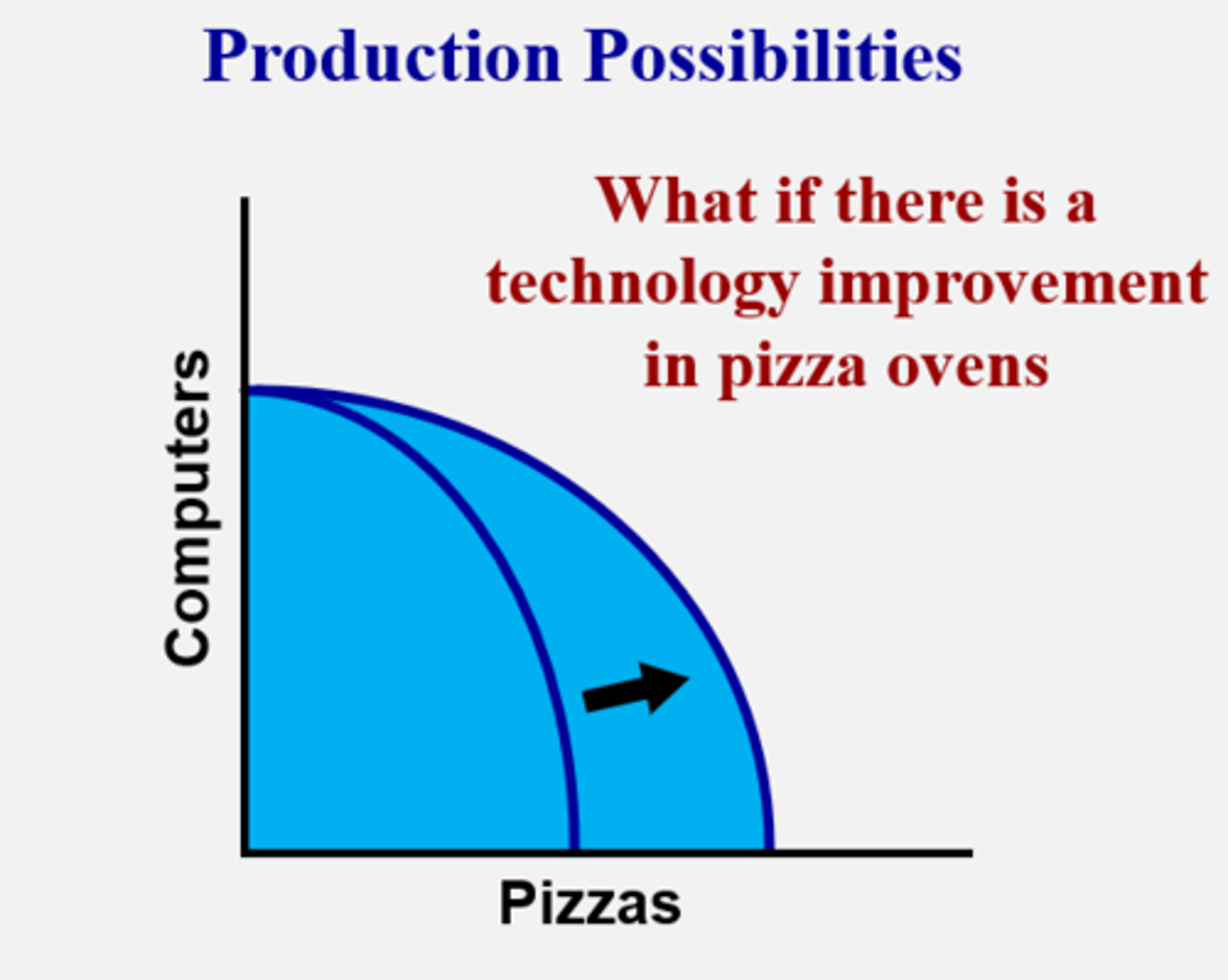
PPC technology
only impacts 1 good, the other good stays unaffected
absolute advantage
the ability to produce more goods or using fewer resources
higher
Absolute advantage with outputs: ______ number (ex: tons)
lower
Absolute advantage with inputs: ______ number (ex: hours)
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer. (always the LOWER number)
Input opportunity cost
"It Over": A = A/B
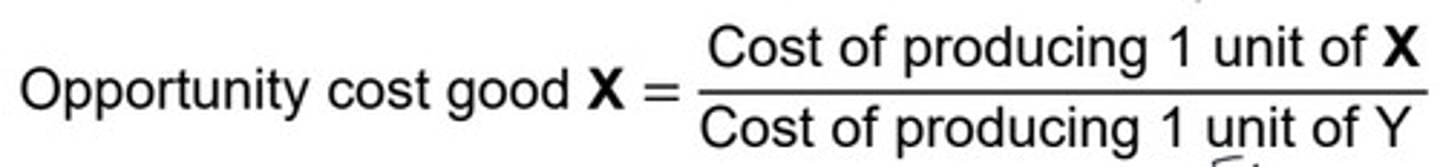
output opportunity cost
"Other over": A = B/A
mutually beneficial terms of trade
range of acceptable exchange rates
amount between the opportunity costs of the other product for one unit of the current product. (should be in between the range of the opportunity costs calculated)

marginal analysis
analysis that involves comparing marginal benefits and marginal costs
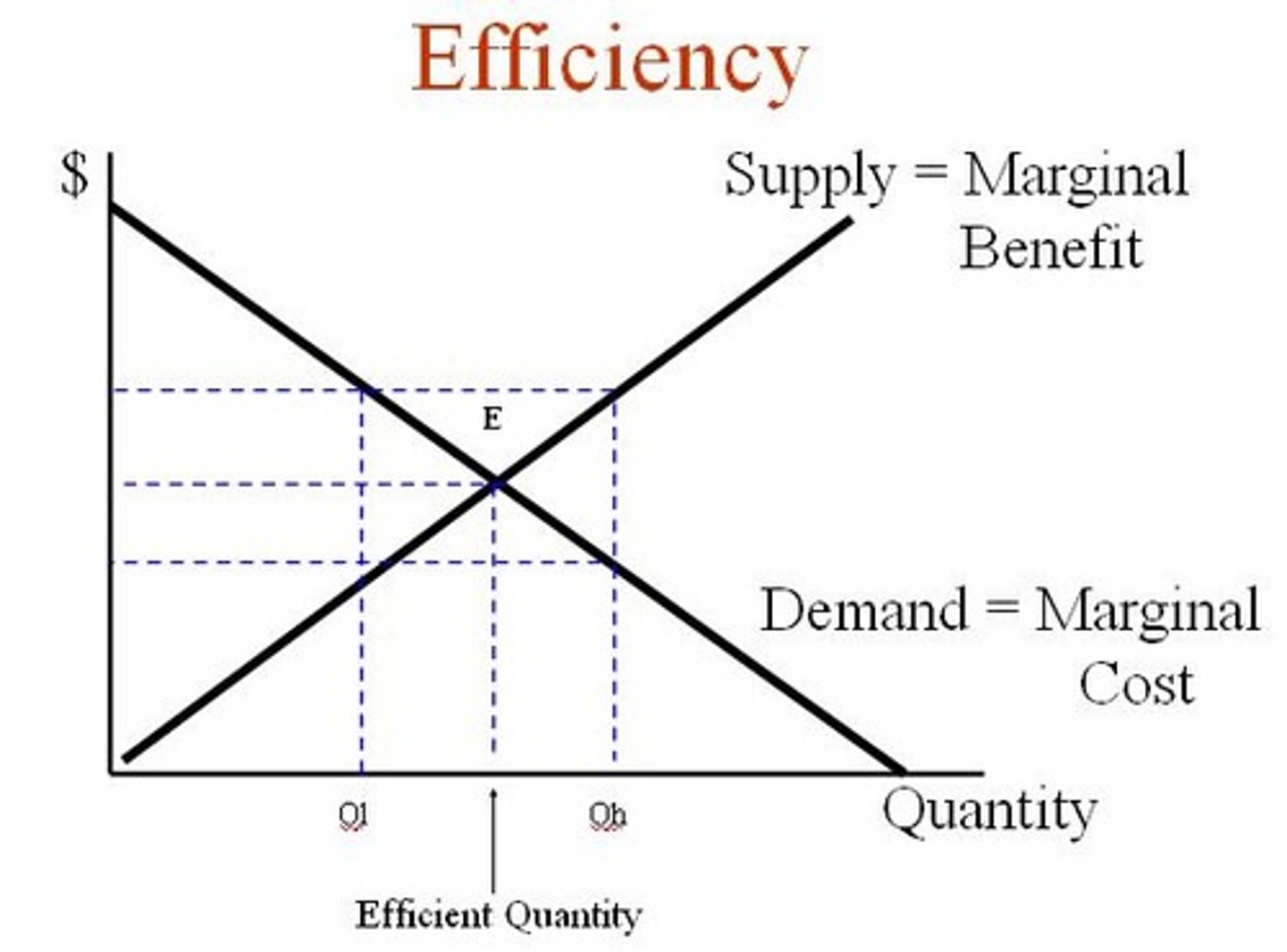
MB = MC
benefit maximizing point
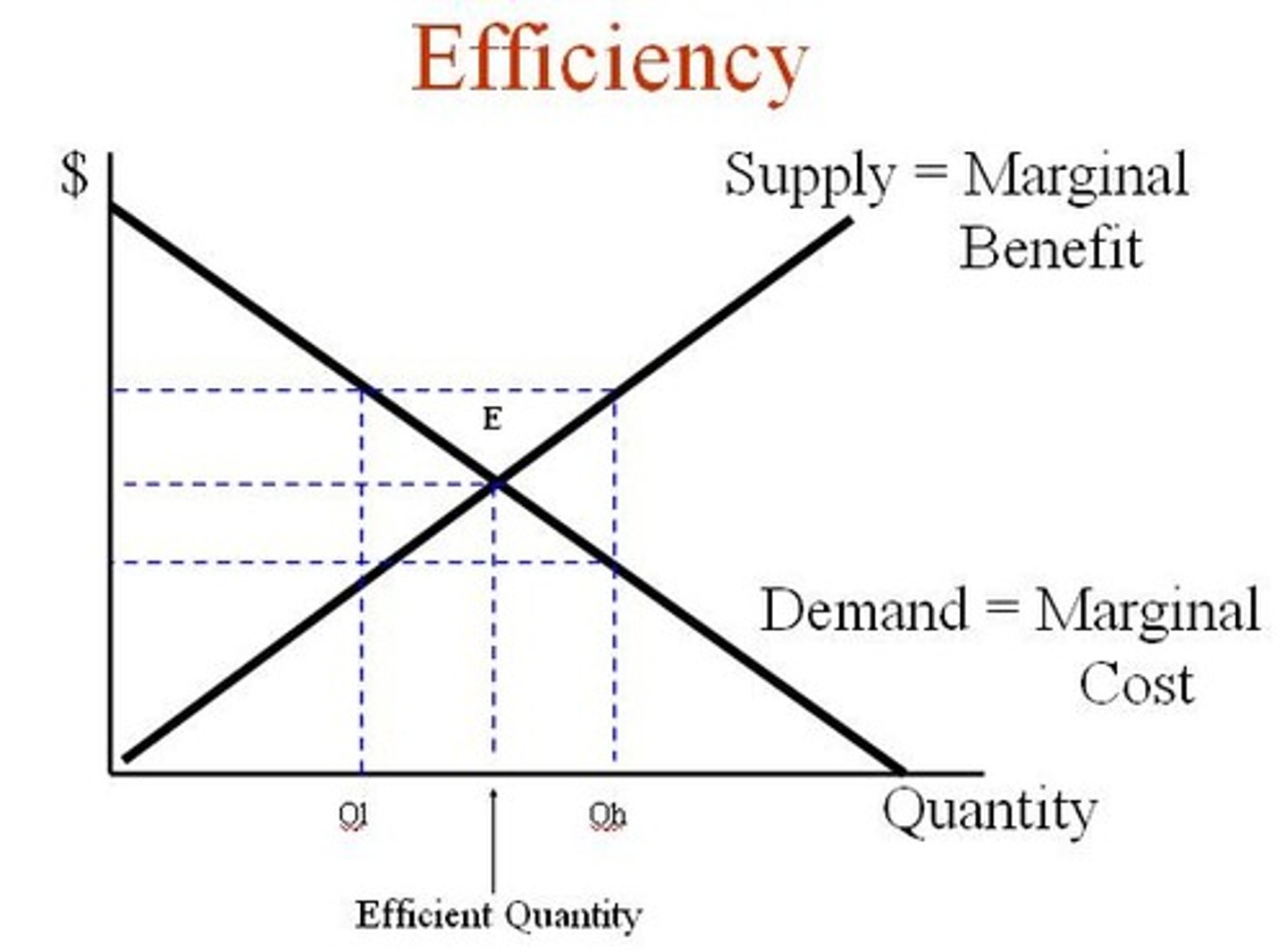
MB > MC
In marginal analysis, keep producing as long as ____
diminishing marginal utility
as a person increases consumption of a product, there is a decline in the marginal utility that person derives from consuming each additional unit of that product.
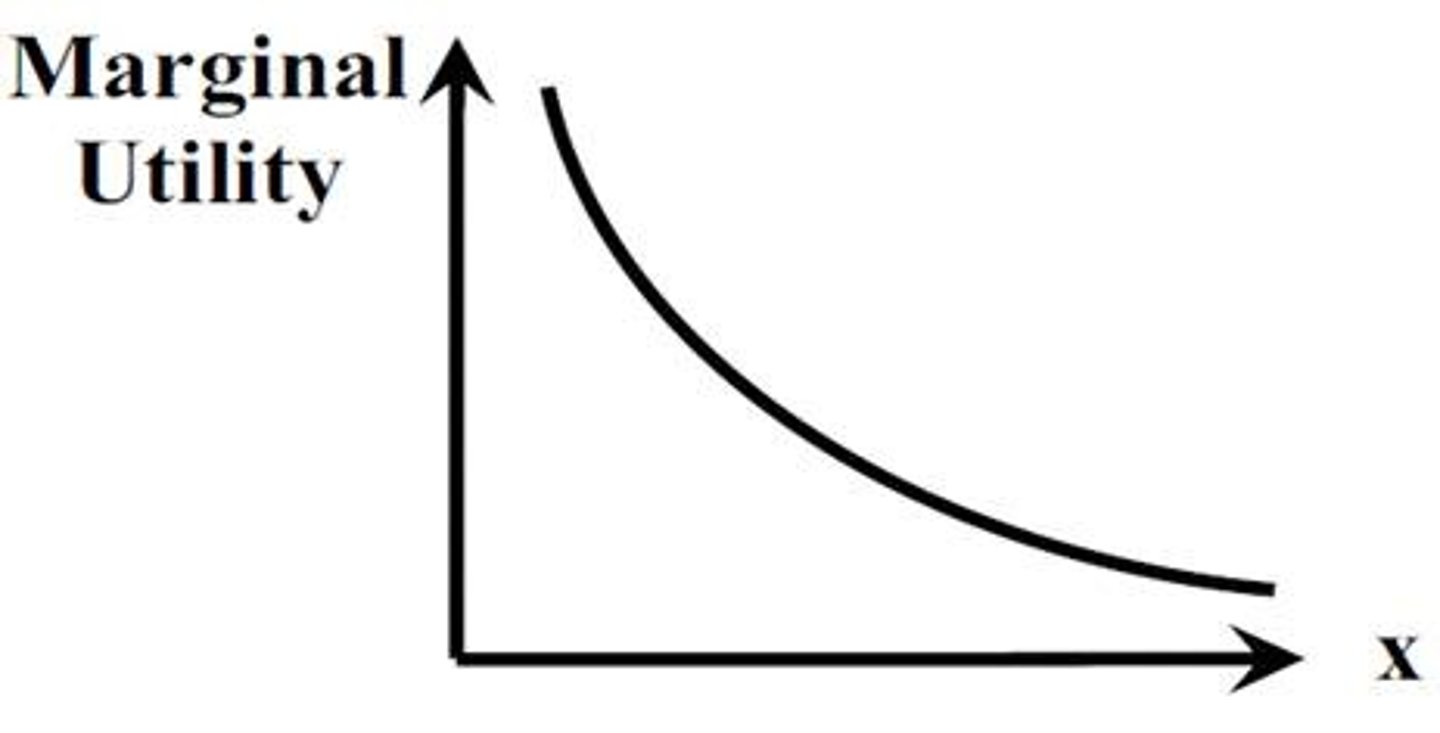
utility maximizing combinations
MUa/Pa = MUb/Pb (you should consume more of whichever one gives you more utils per dollar)