2.4: Ecological tolerance
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Law of the Minimum
living organisms will continue to live, consuming available materials until the supply has been exhausted.
Example: crop yield is proportional to the amount of the most limiting essential nutrient, whichever nutrient that may be. Growth may be restricted by the lack of a single element (maybe Nitrogen). If this is the case, adding more phosphorus will not improve the crops yield.
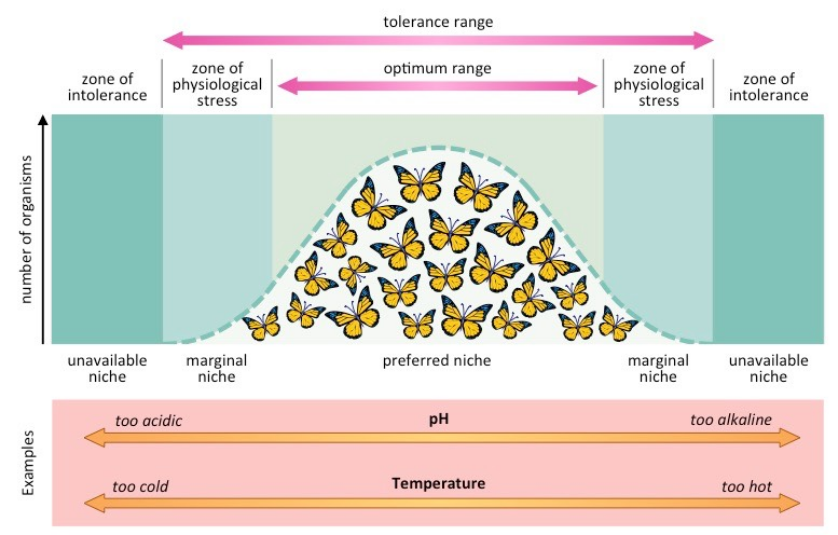
Law of Tolerance
the degree to which living organisms are capable of tolerating changes in their environment.
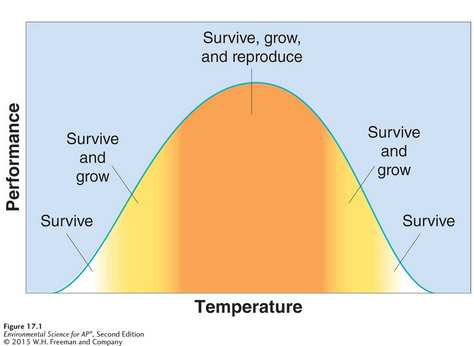
An organism's success is based on a complex set of conditions and each organism has a certain minimum, maximum, and optimum environmental factor or combination of factors that determine success.
These tolerances are in turn modified through direct and non-direct interactions with other species results in realized niches (unit 1).
Range of tolerance
The limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate.
Fundamental niche
The suite of abiotic conditions under which a species can survive, grow, and reproduce.
Realized niche
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives.
Takes into account competition with other species
Abiotic Factors
determine the fundamental niche
Temperature
Precipitation
Salinity
Biotic factors
determine the realized niche
Competitors
Predators
Disease
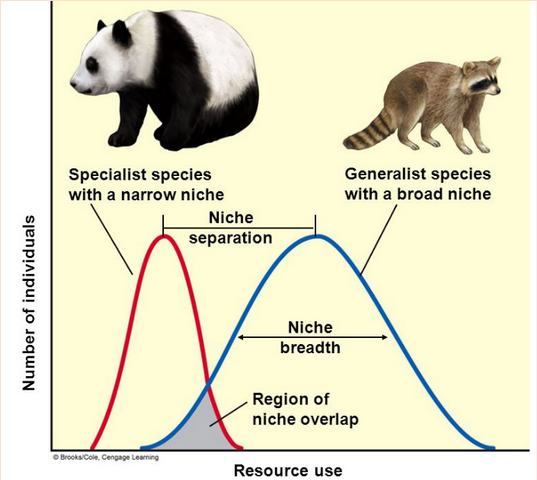
Niche generalist
A species that can live under a wide range of abiotic or biotic conditions.
Fare better than specialists under changing conditions (alternative habitats and food sources available)
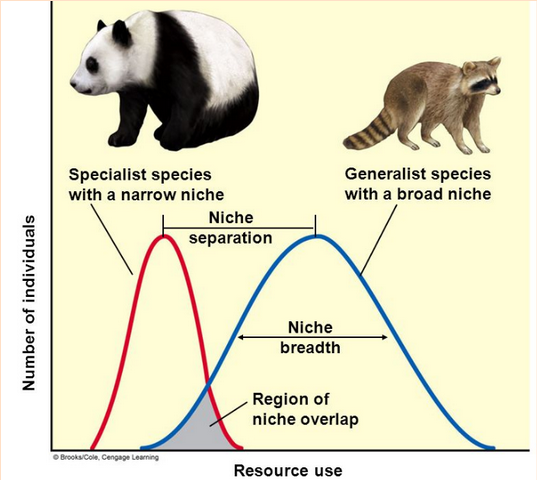
Niche specialist
A species that is specialized to live in a specific habitat or to feed on a small group of species.
Do well when environmental conditions remain relatively constant
Loss of a favored habitat or food source leaves them with few alternatives for survival.
Distribution
Areas of the world in which a species lives.
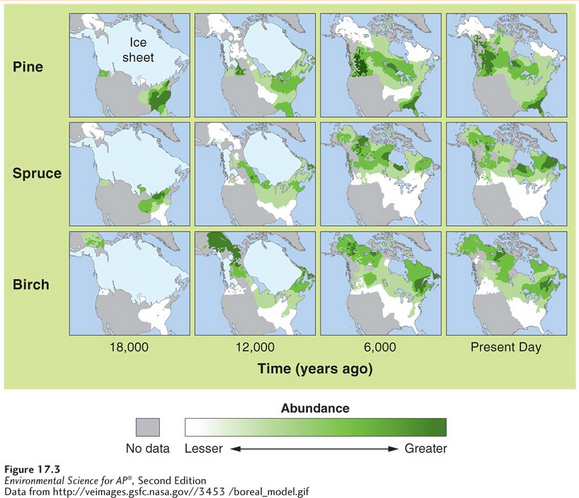
Pollen recovered from lake sediments indicates that plant species moved north as temperatures warmed following the retreat of the glaciers, beginning about 12,000 years ago.