Lab Practical FAU BSC2085L
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
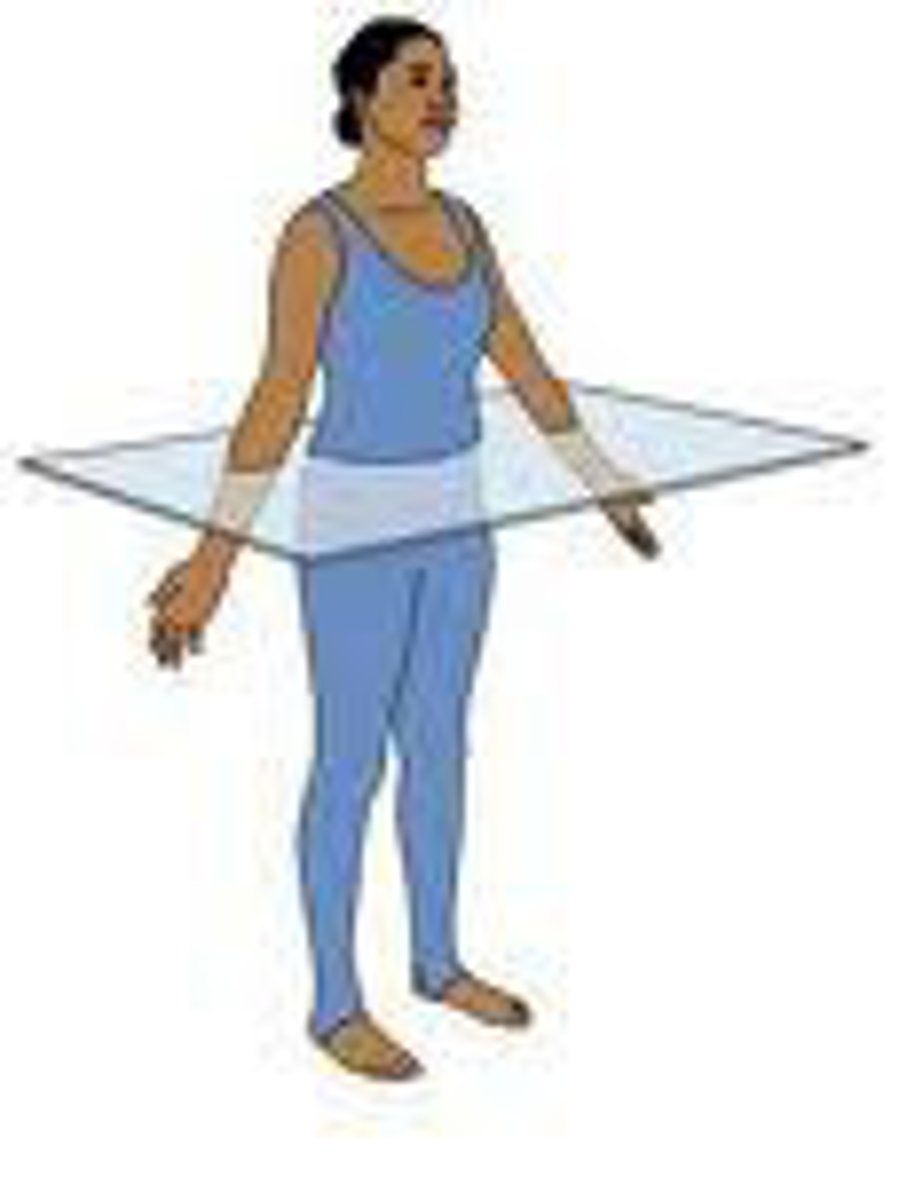
Anatomical Position
the body standing upright, with the feet at shoulder width and parallel, toes forward. The upper limbs are held out to each side, and the palms of the hands face forward
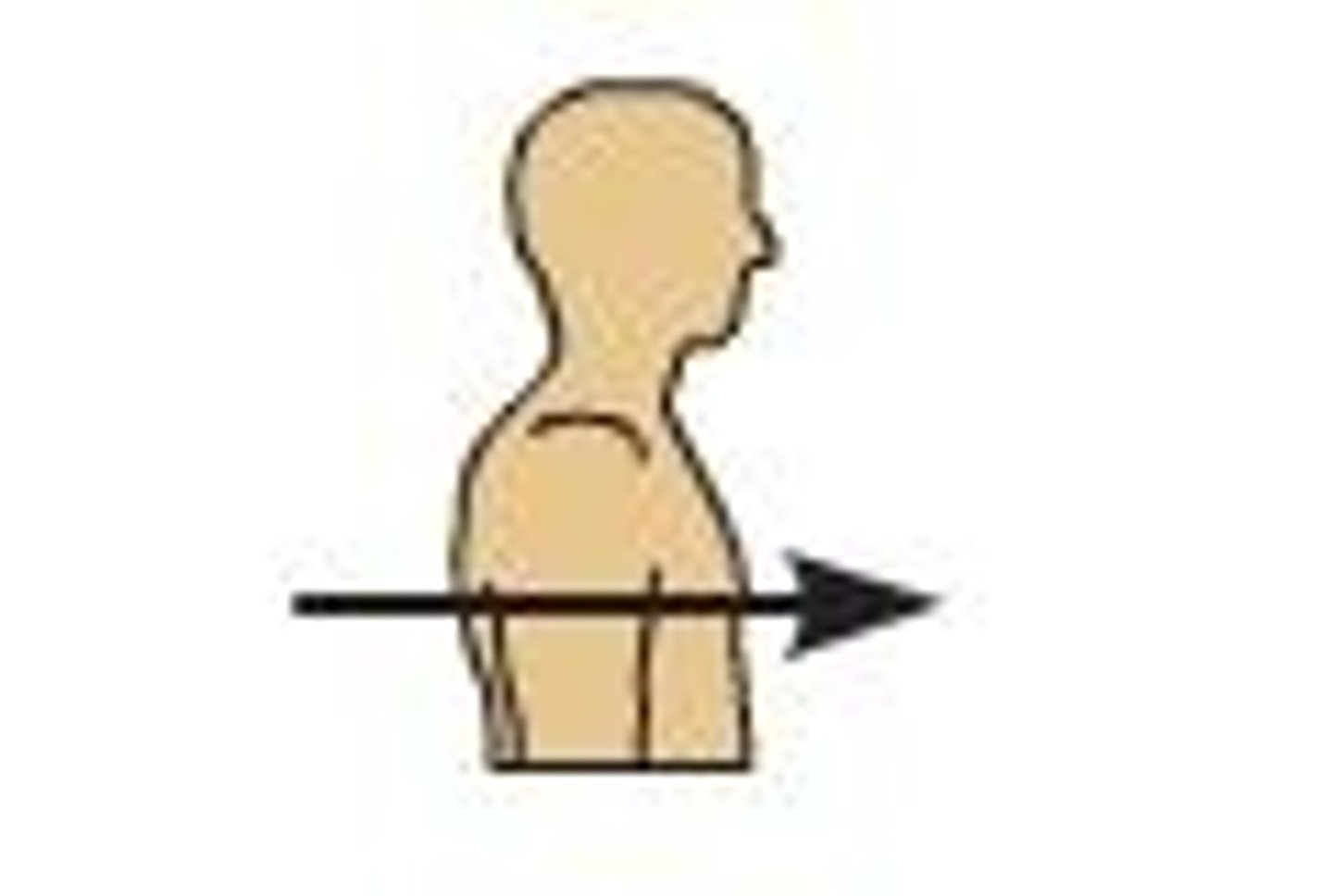
Anterior
front in humans
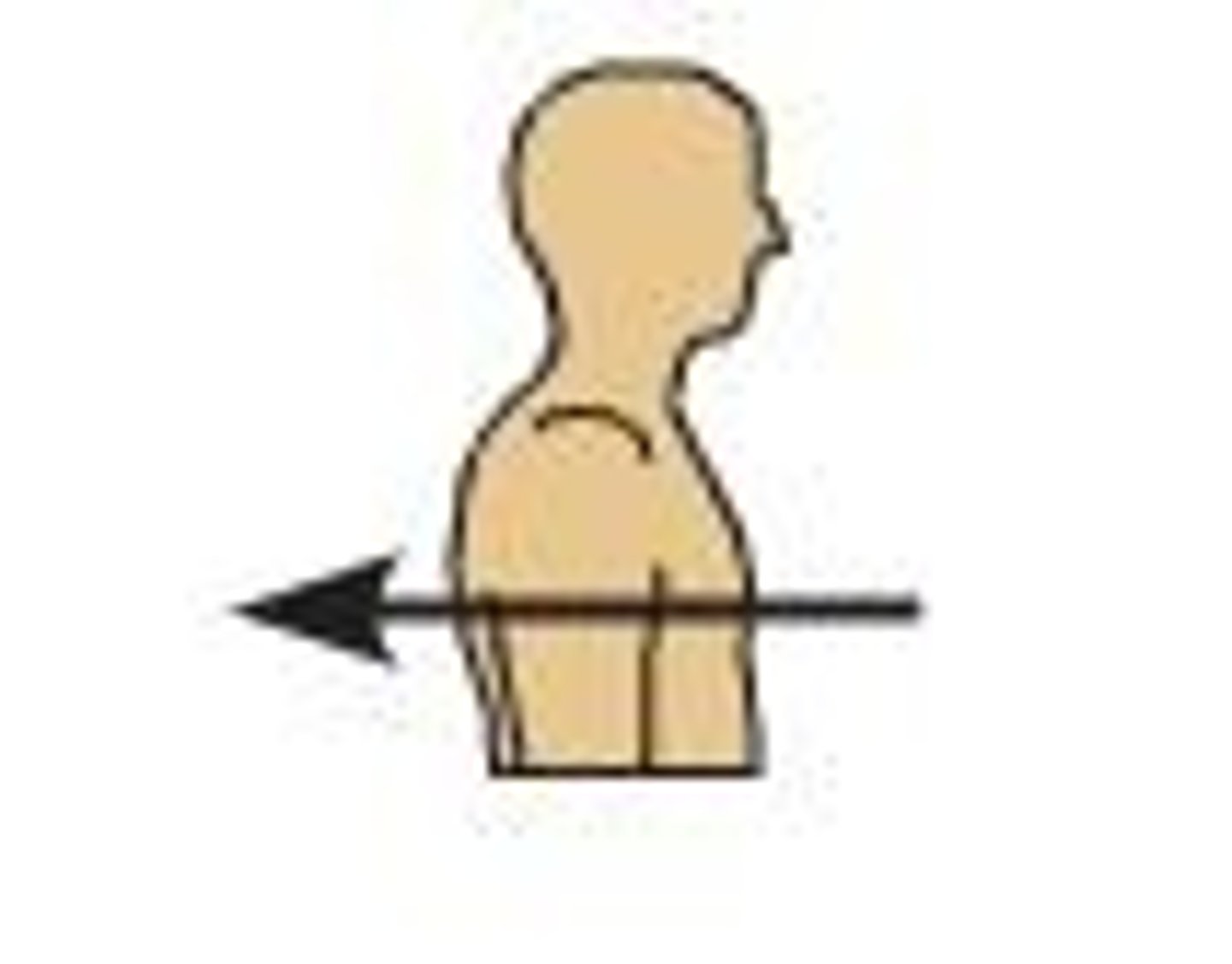
Posterior
back in humans
Superior
toward head
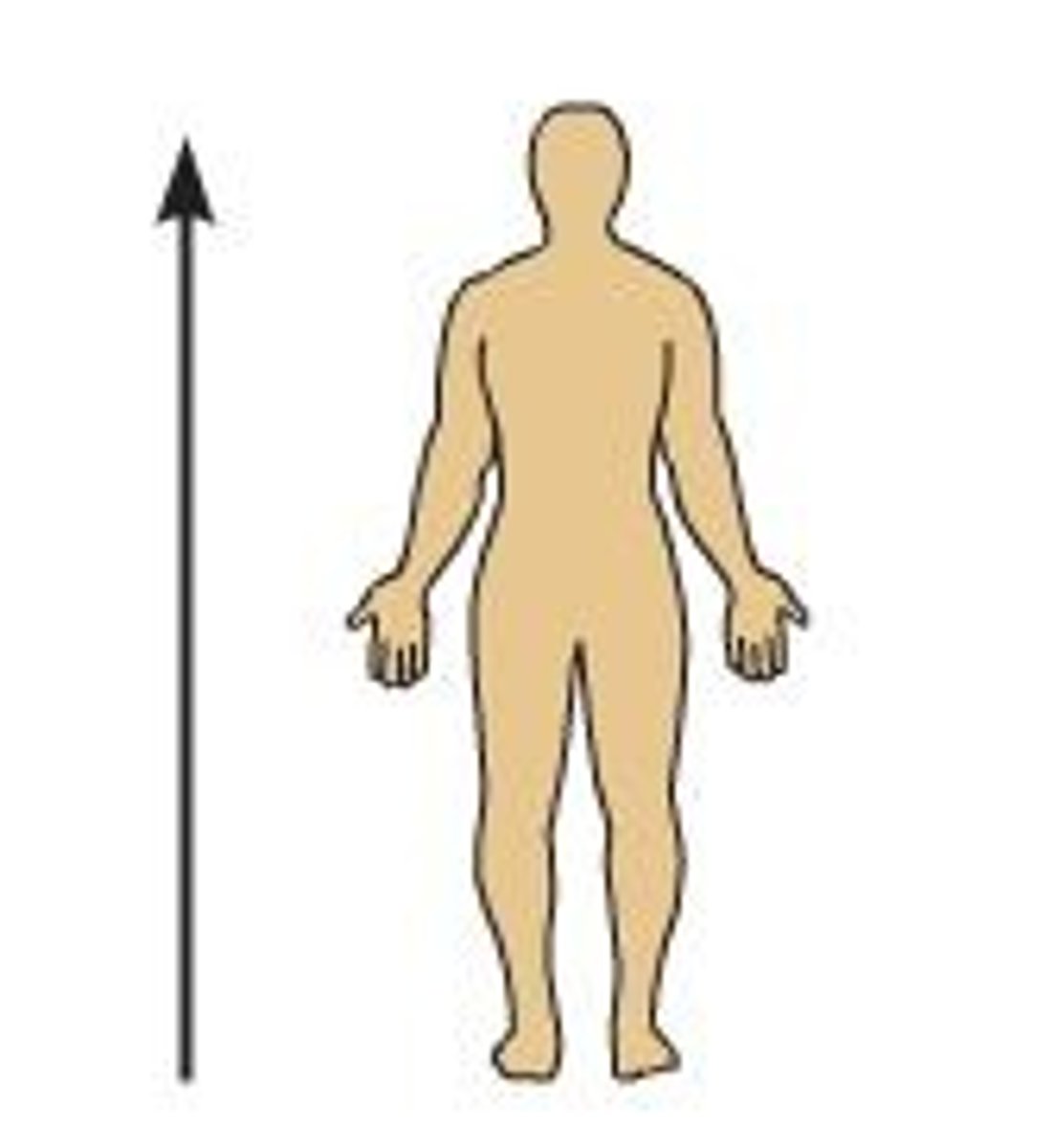
inferior
toward tail
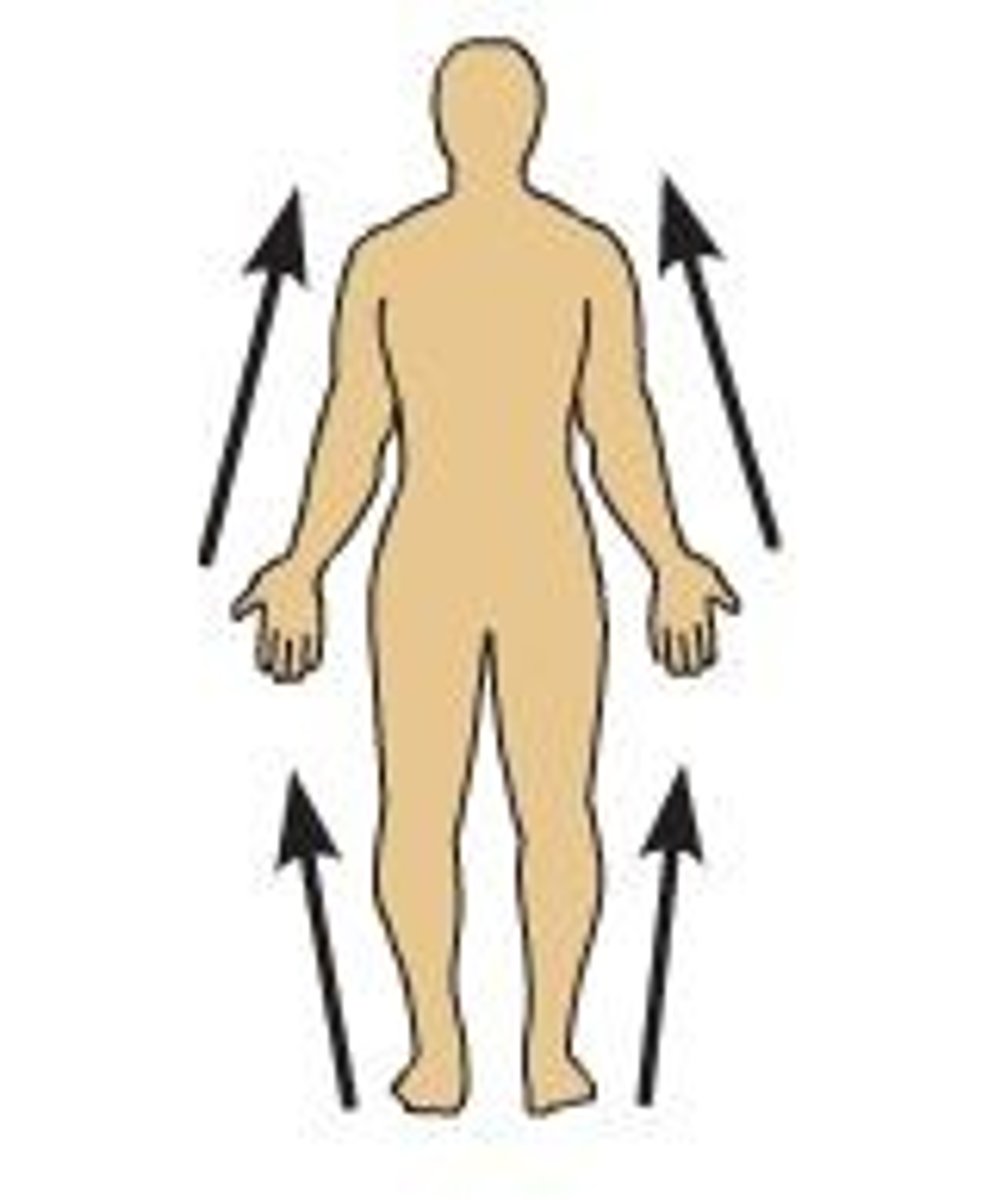
Proximal
closer to point of orgin
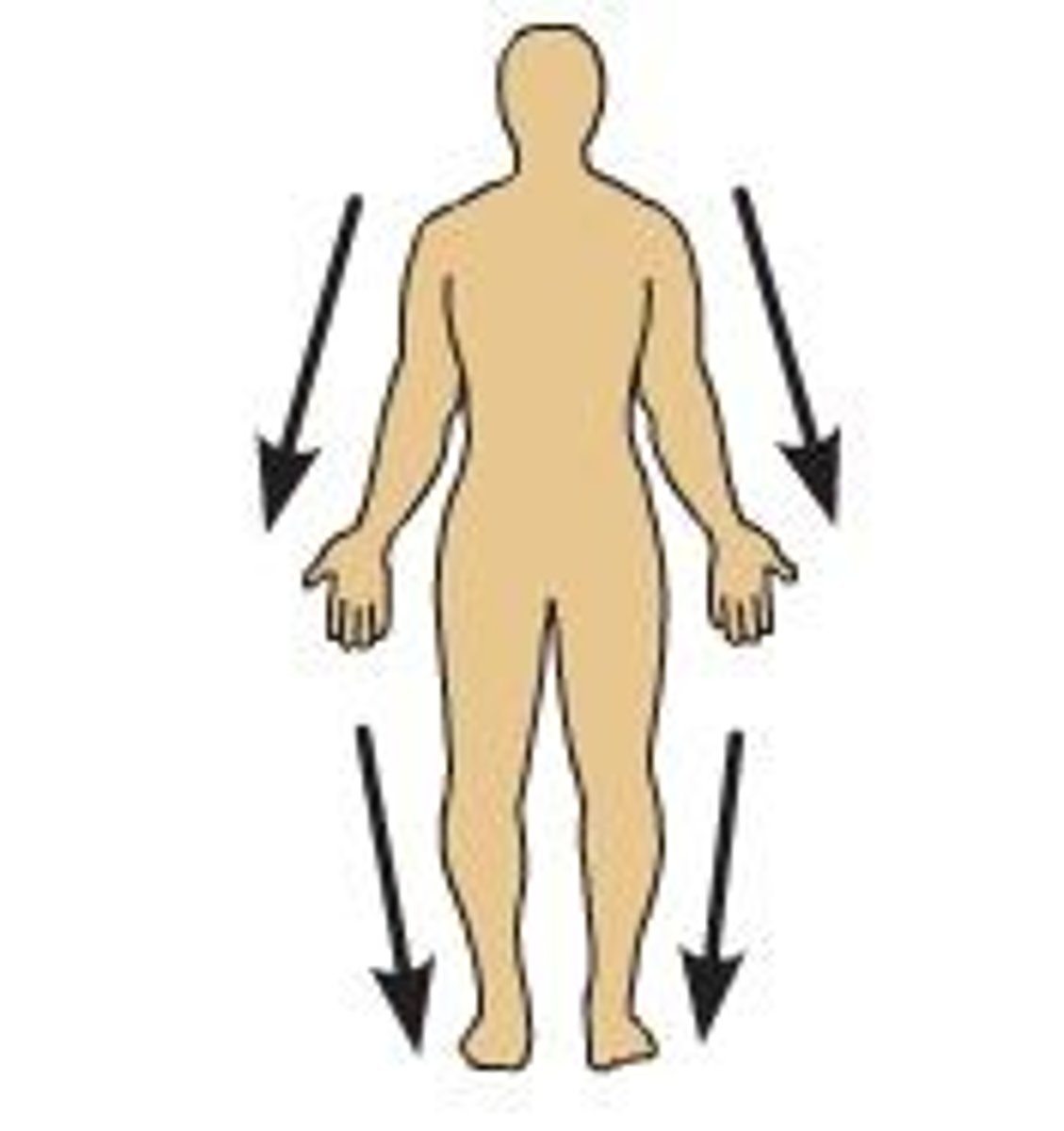
Distal
more distant (further away) from point of orgin
Medial
closer to midline
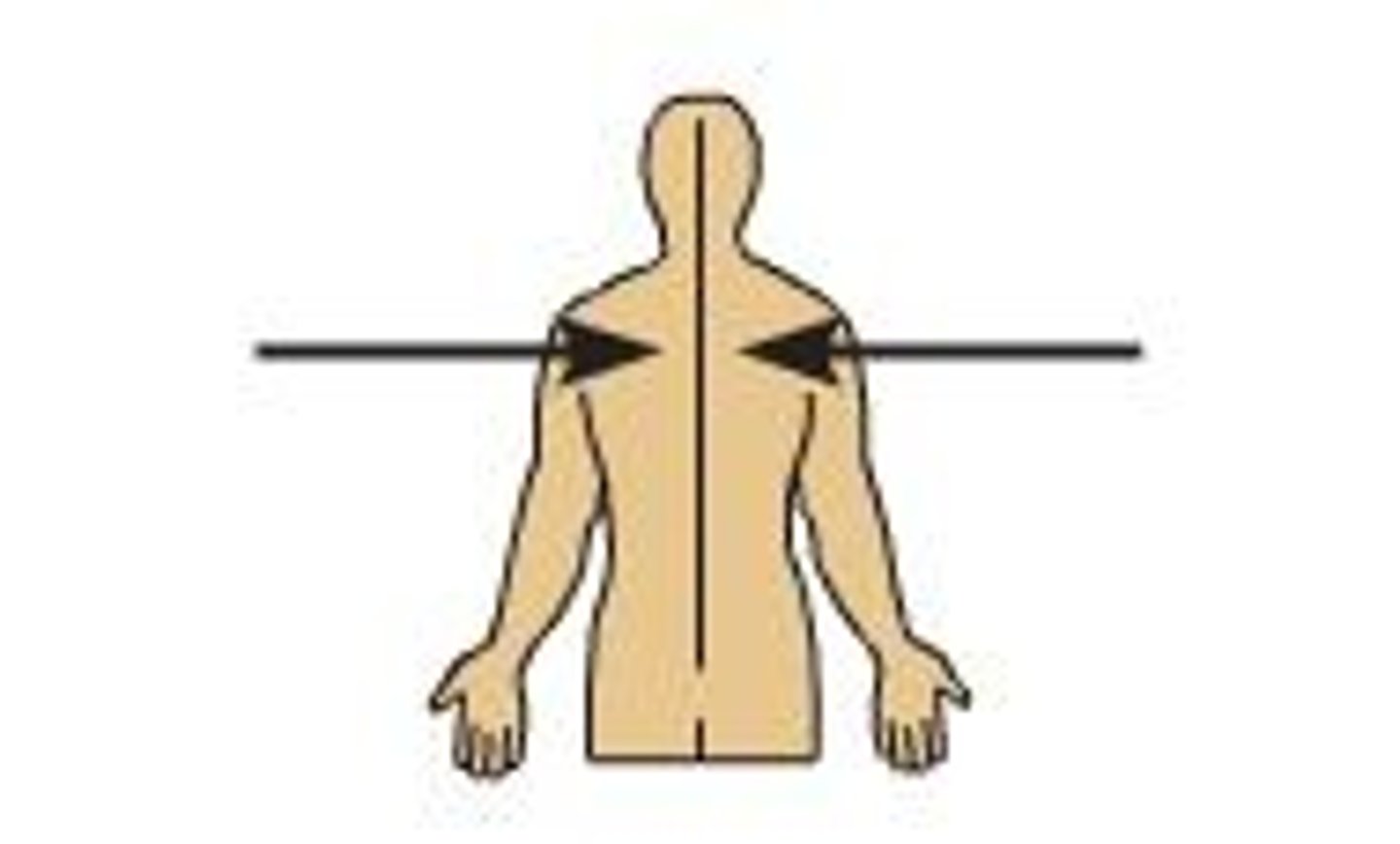
Lateral
further away from midline
superficial
structures closer to surface of body
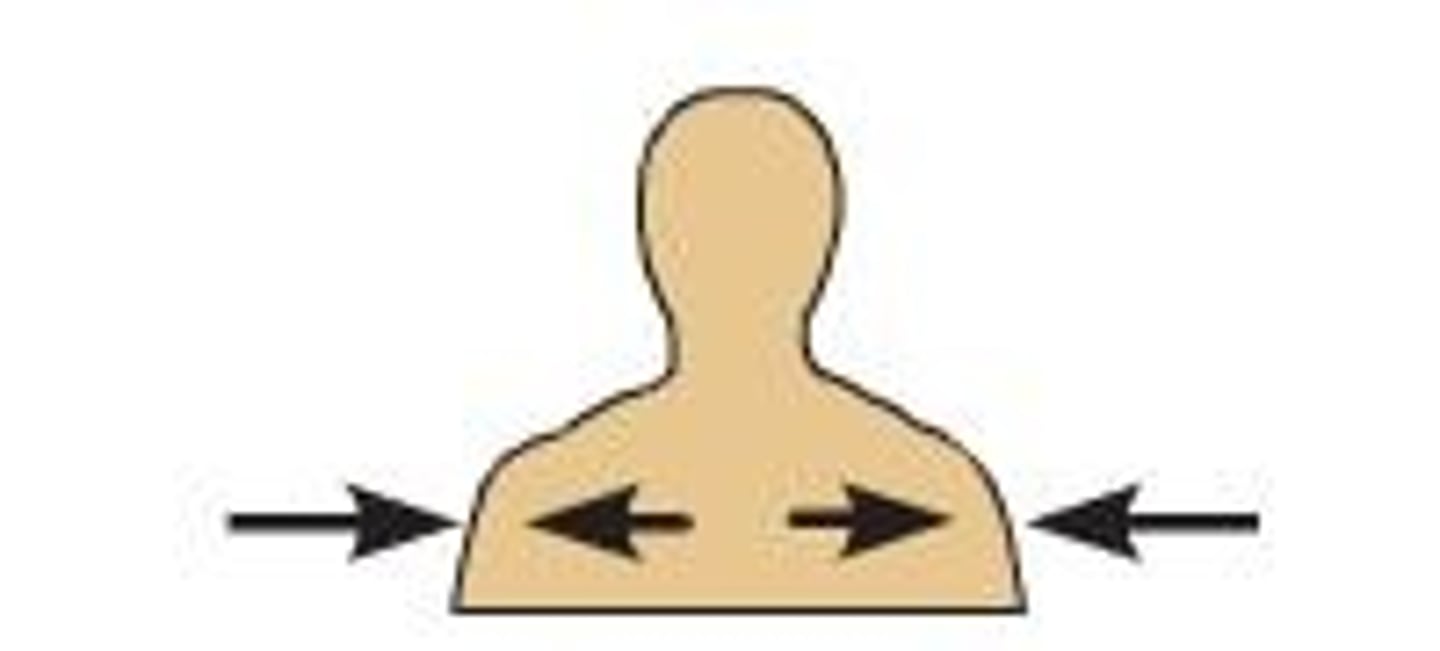
deep
further away from the surface
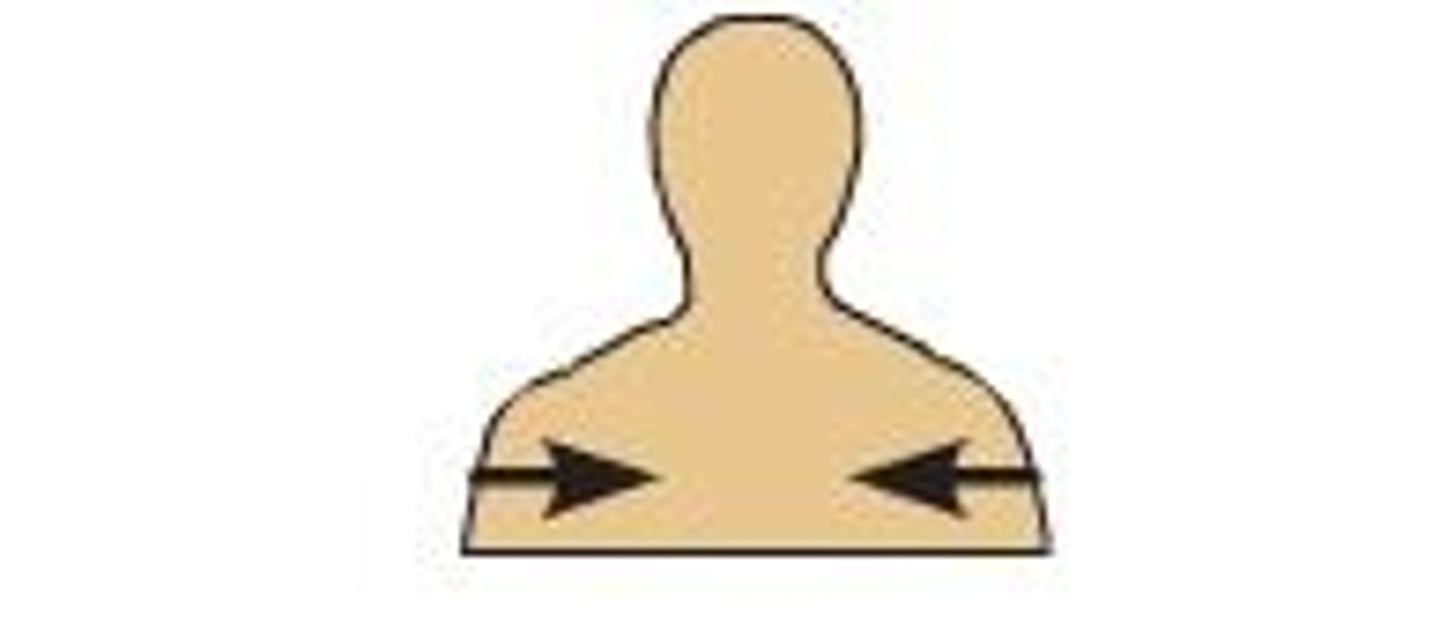
Axial skeleton
skull, rib cage, sternum and vertebral column
appendicular skeleton
limbs, clavicle, scapula, hip bone (coxal)
midsaggital plane
divides body or body part into equal left and right sections
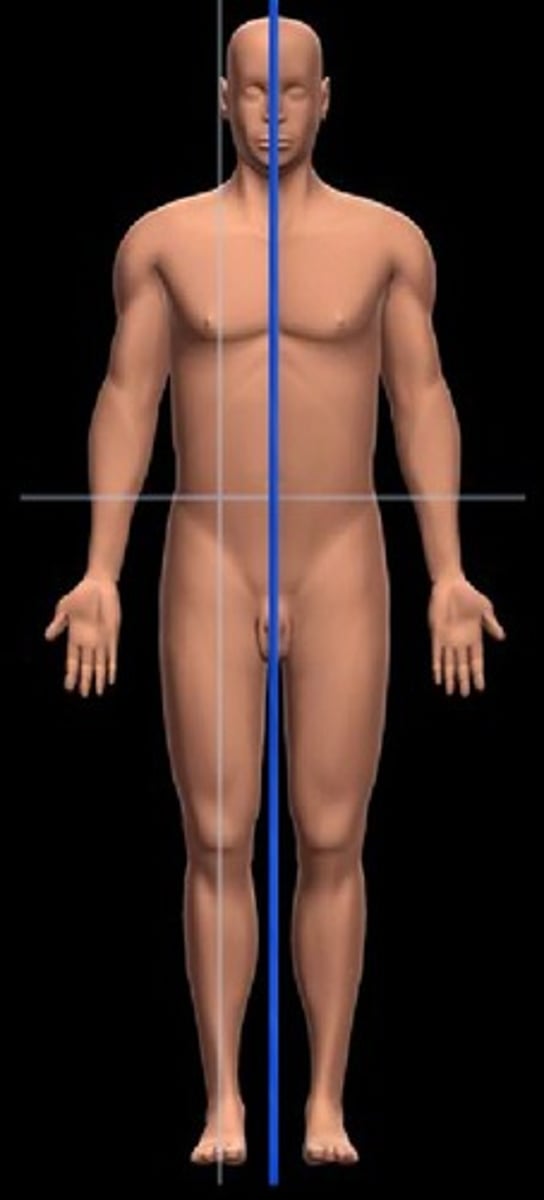
parasaggital plane
divides body or body part into unequal right and left sections
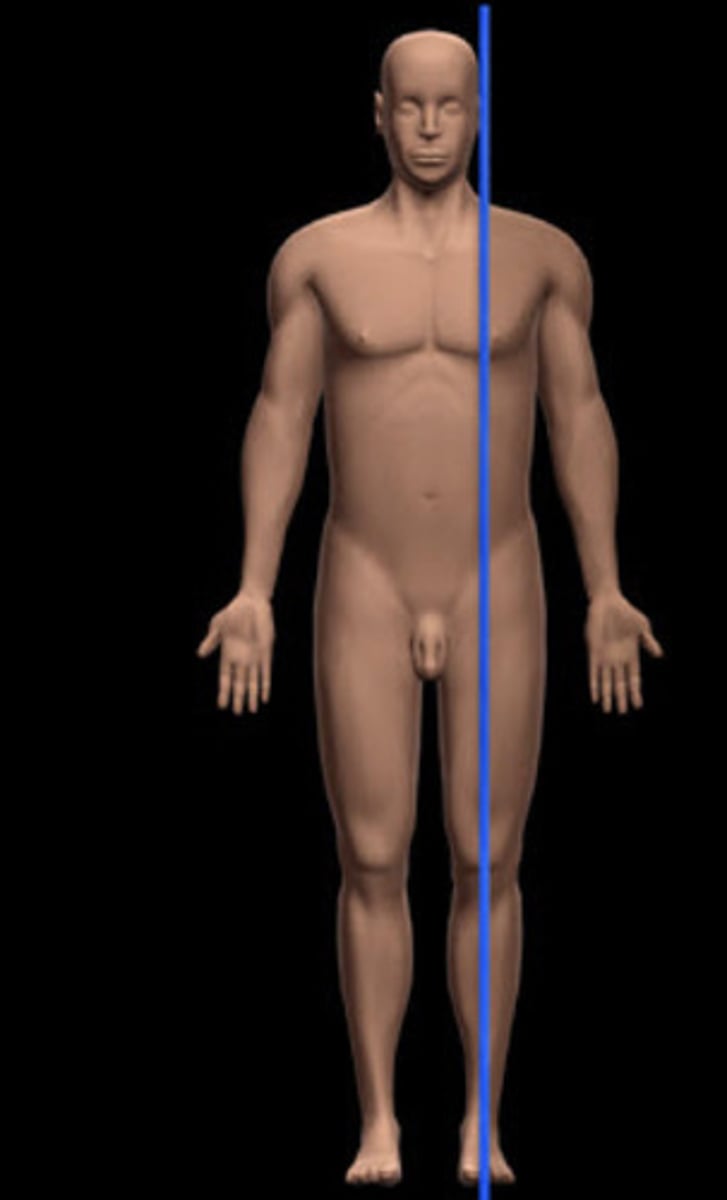
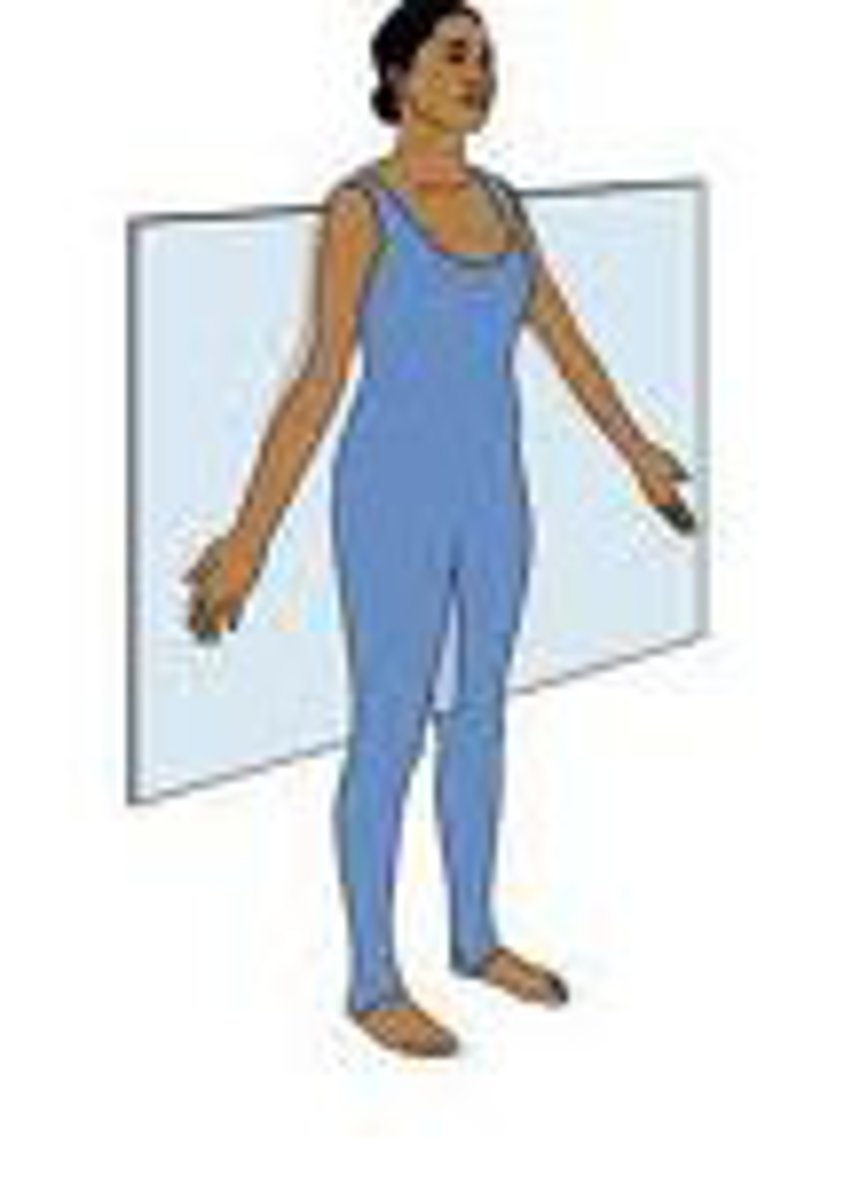
Frontal Plane
divides body or body part into anterior and posterior sections

transverse plane
divides body or body part into superior and inferior sections
cranial cavity
within skull; protects brain
vertebral cavity
within vertebral column; protects spinal cord
thoracic cavity
upper torso, contains heart and lungs
abdominopelvic cavity
contains both the abdominal and pelvic cavities
pleural cavity
surrounds lungs
Mediastinum
between pleural cavities; houses heart, great vessels, trachea (windpipe), and esophagus
pericardial cavity
within mediastinum; within serous membrane that surrounds heart
peritoneal cavity
surrounds the abdominal organs
visceral layer
tissue that covers organs in thoracic cavity
parietal layer
outermost layer, lines cavity walls
Plasma membrane
barrier that surrounds cells
nucleus
houses nucleous and DNA
phospholipid bilayer
thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules
simple diffusion
small, nopolar molecules that pass-through phospholipid bilayer without the help of membrane proteins
facilitated diffusion
molecules cross phospholipid bilayer with help of membrane protein
Osmosis
passive process; water moves across membrane from a area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
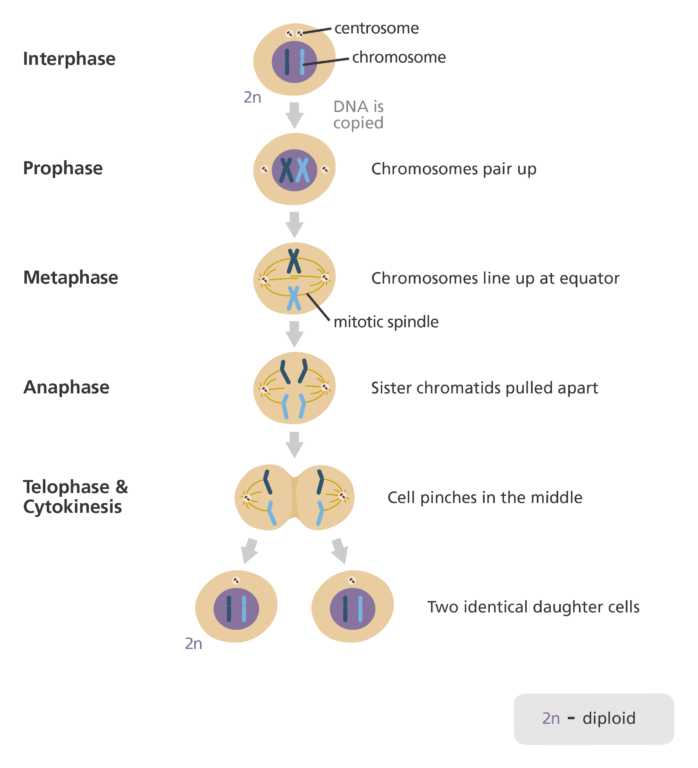
interphase
period of growth and preperation for cell division
G1 phase
initial growth phase
S phase
DNA synthesis (replication)
G2 phase
last cellular growth and centrioles are duplicated
Mitosis
newly replicated genetic material is divided between two daughter cells (prophase, metaphase,anaphase, telophase)
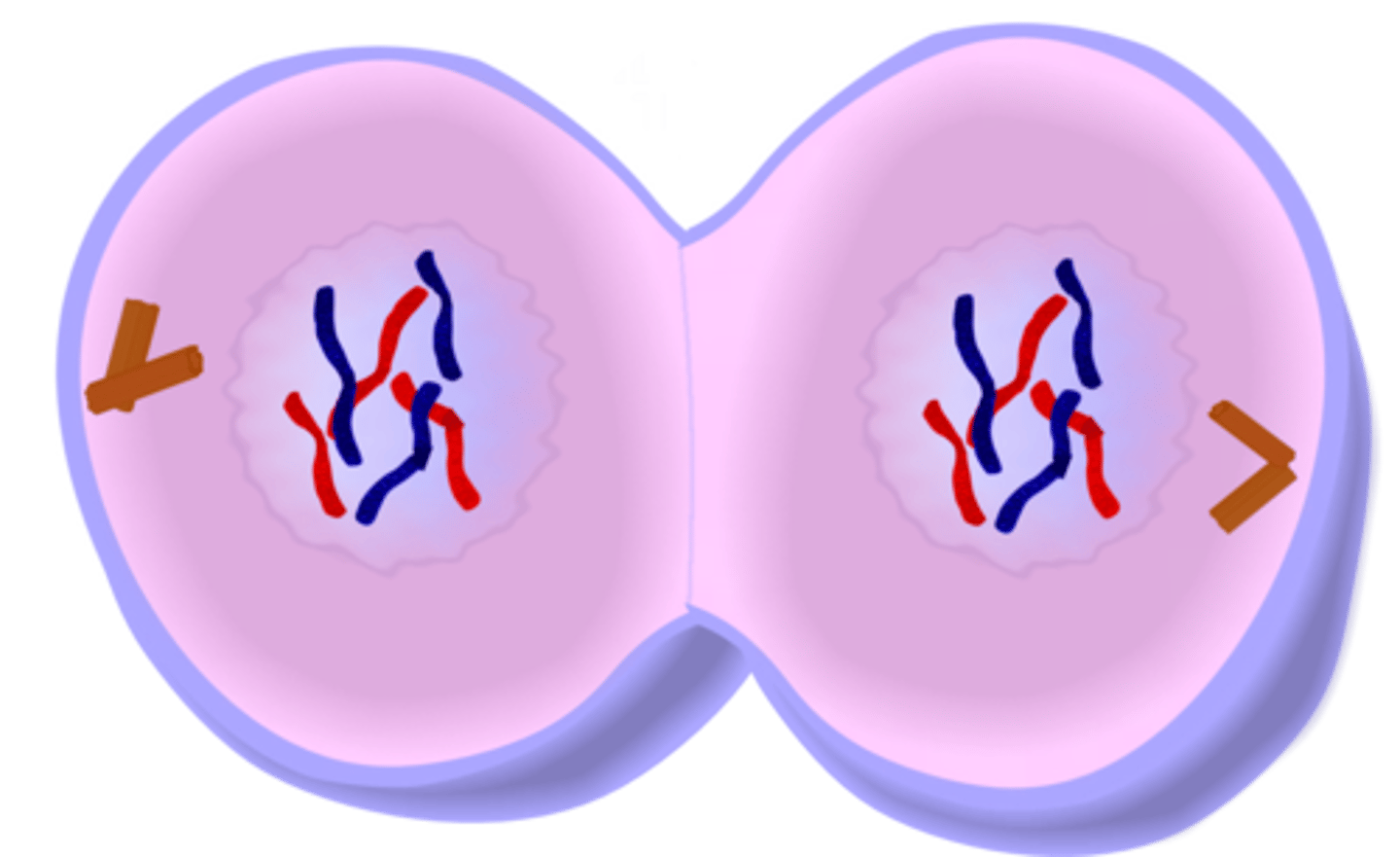
cytokenesis
cytosol (water based cytoplasm) is divided between two daughter cells
Prophase
DNA condenses into chromosomes and sister chromatids are joined at centomere

Metaphase
Spindle fibers from oppisite poles of cell arrange sister chromatids into line along middle (equator) of cell
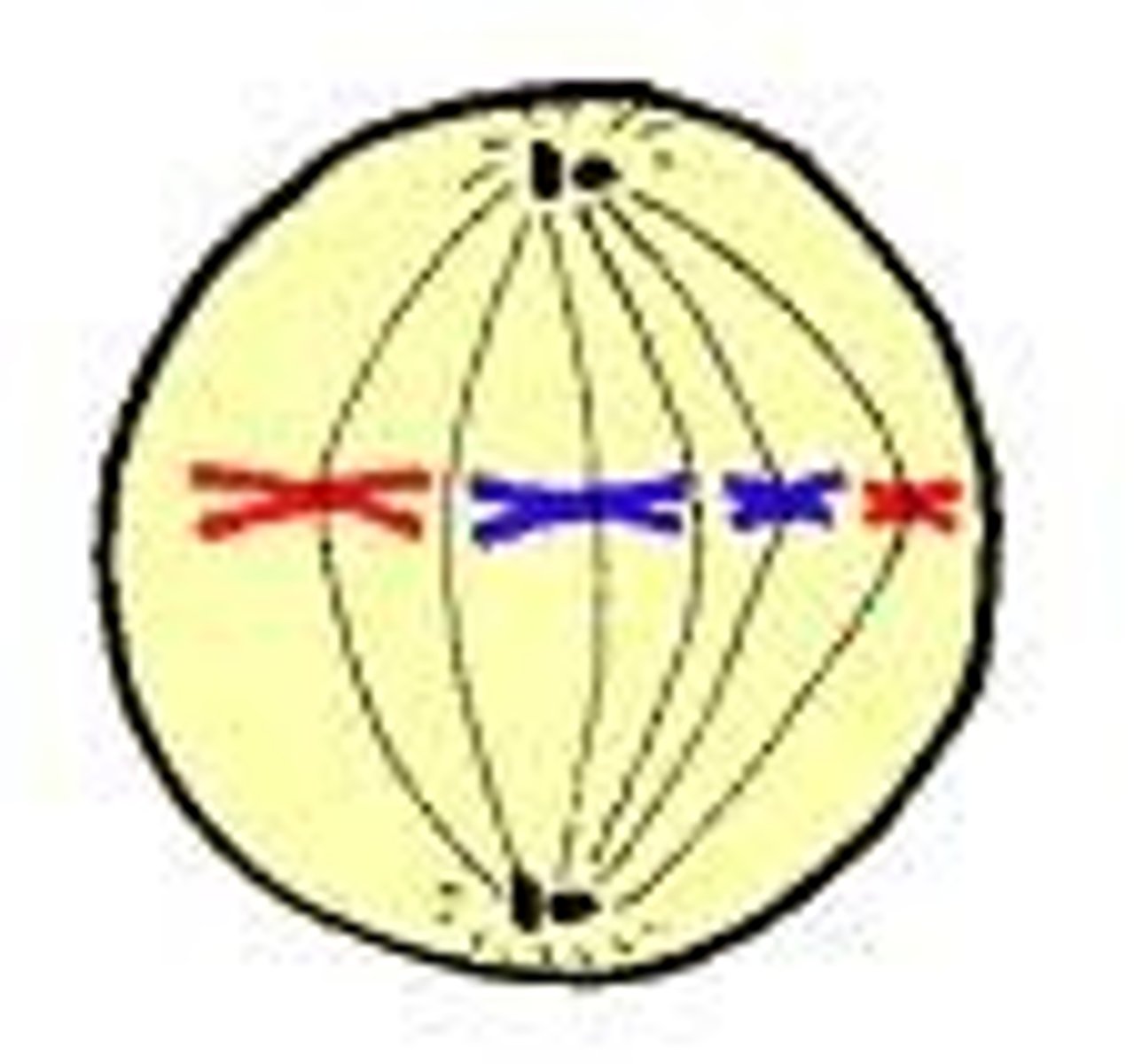
Anaphase
sister chromatids (copies of DNA molecule) pulled toward oppisite poles
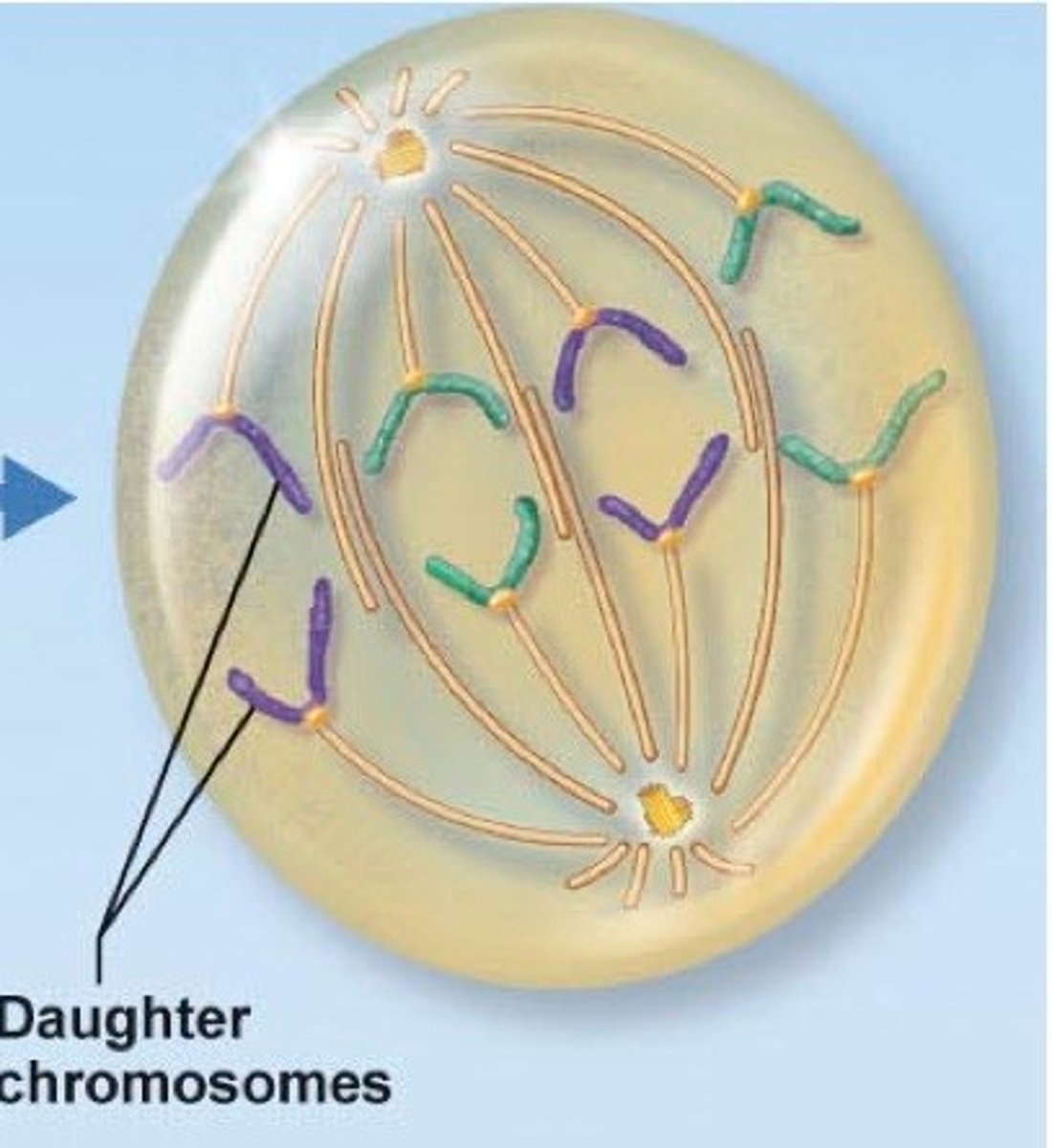
Telophase
As daughter cells seperate, nuculear envelope is reassembled and chromosomes uncoil, decondense
Loose connective tissue
mostly ground substance in space surrounding cells
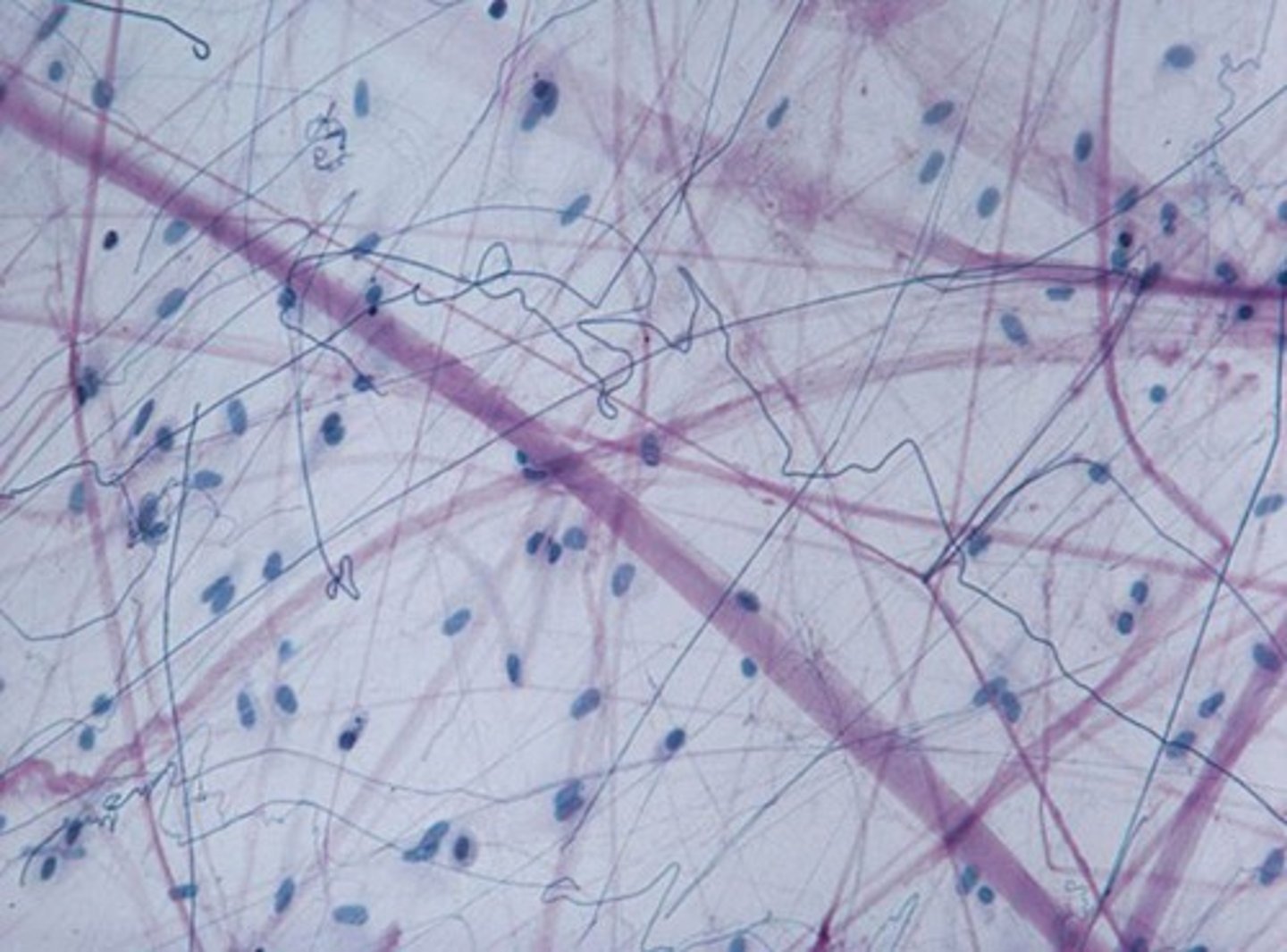
dense connective tissue
mostly protien fibers; three classes: irregular, regular, and regular elastic
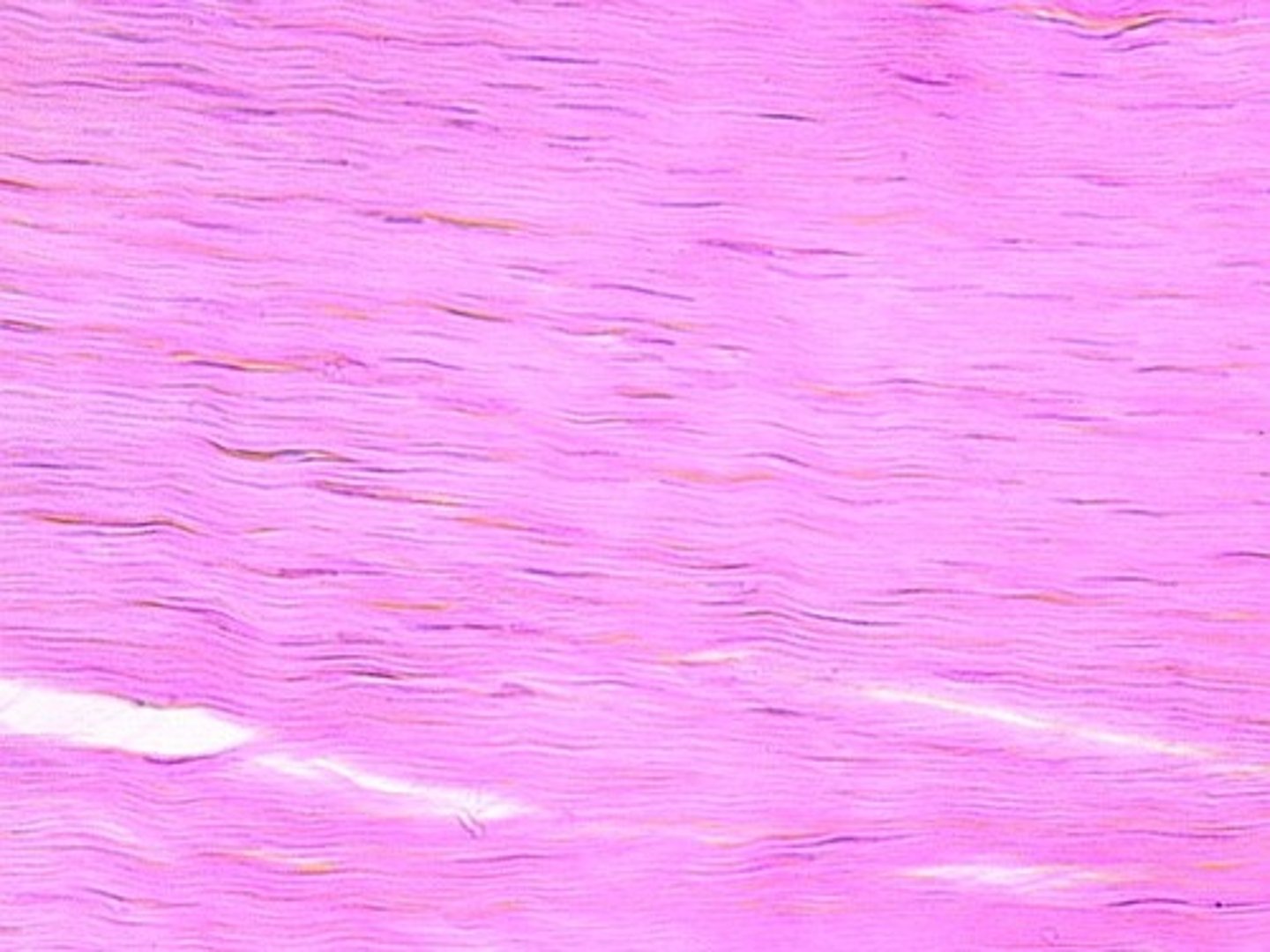

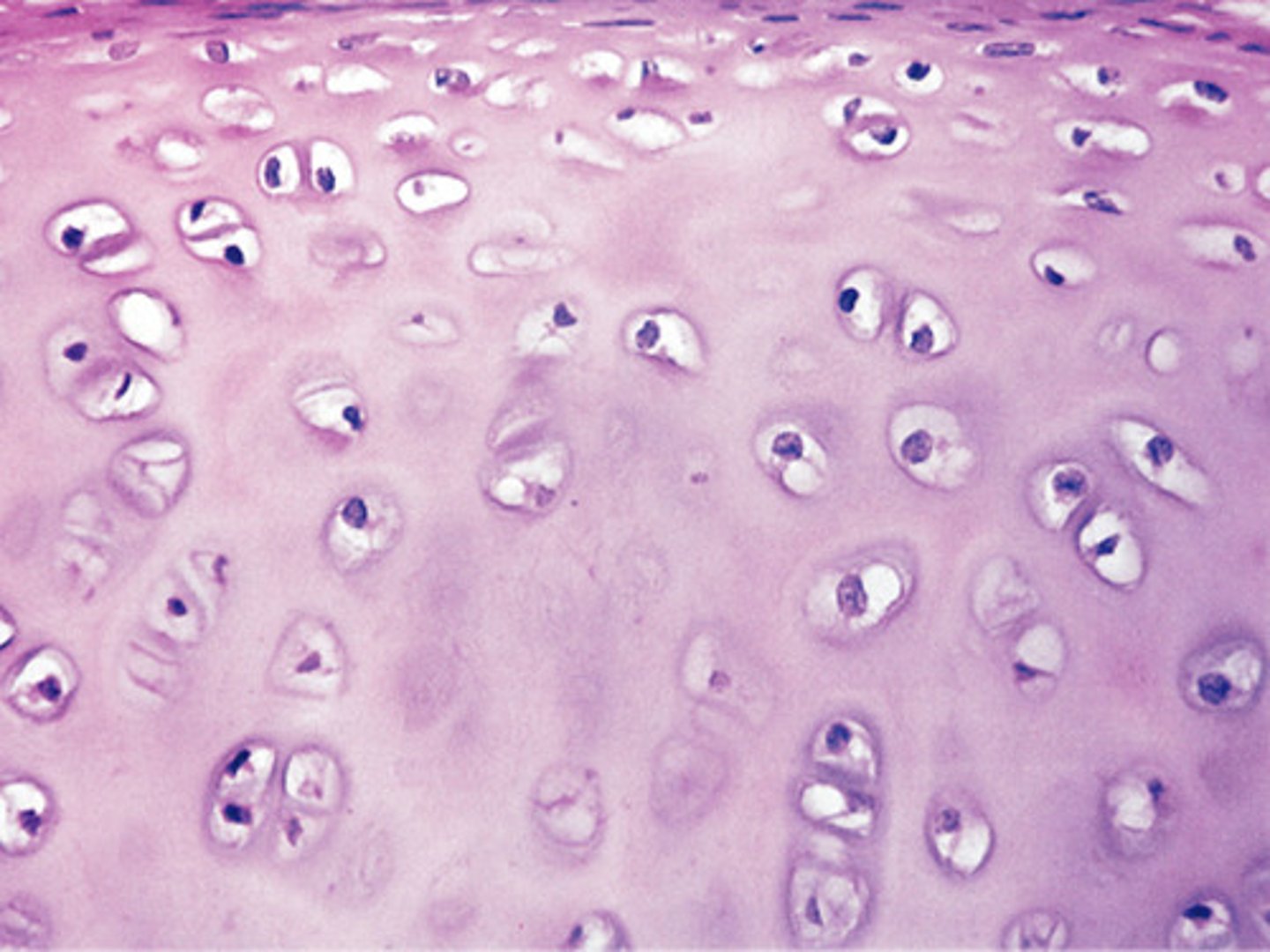
hyaline cartilage
most abundant cartilige, mostly ground substance
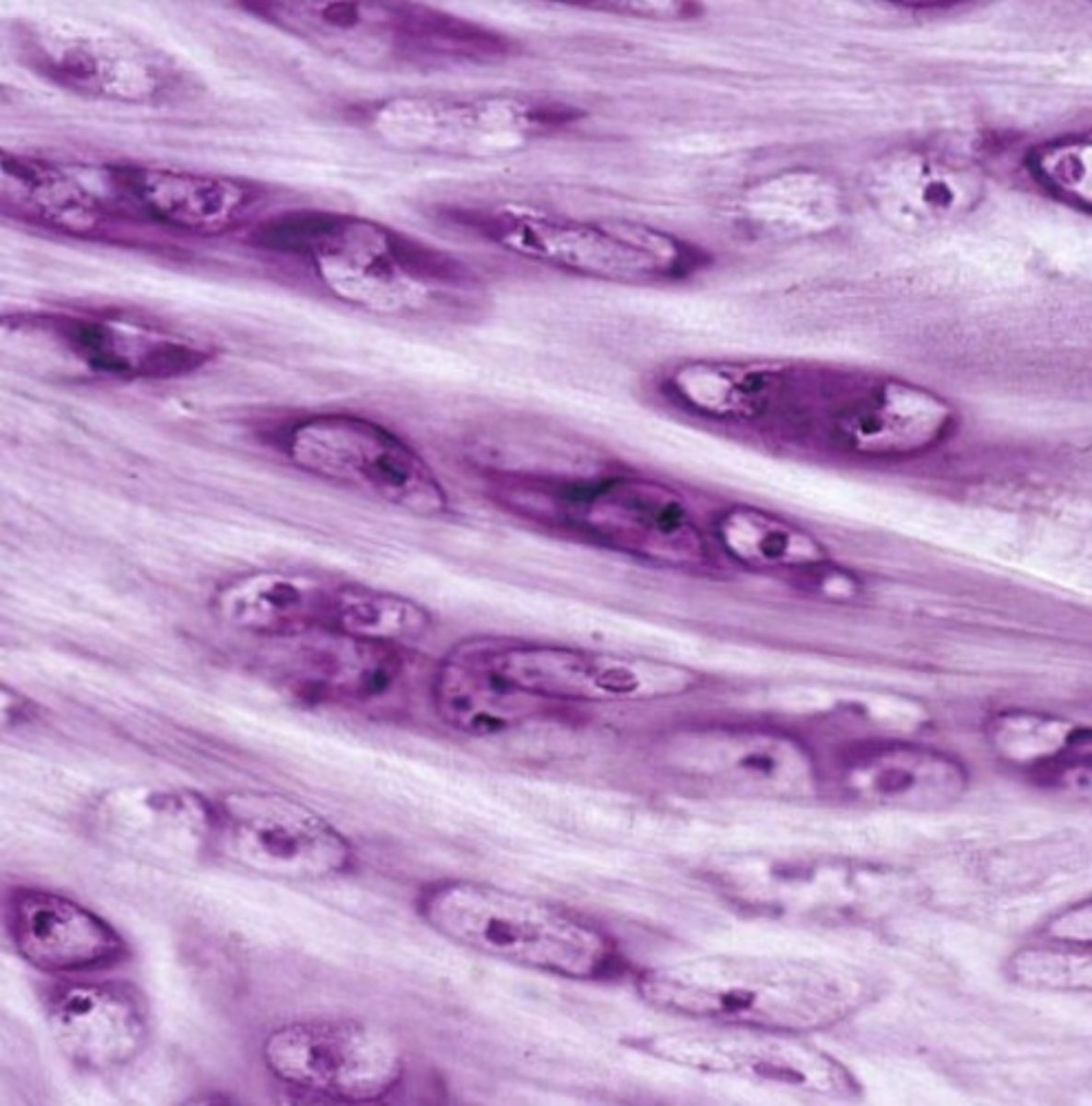
fibrocartilige
filled with bundles of collagen fibers; little room for ground substance in ECM, found in the invertebrail discs
elastic cartilage
mostly fibers in ECM, found in the ear
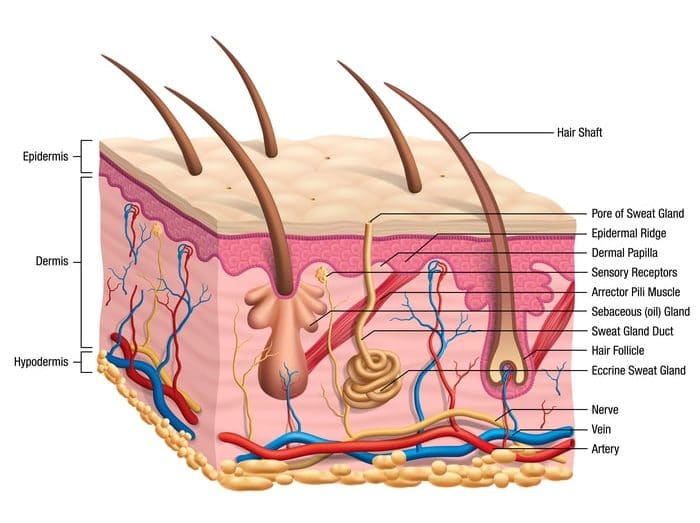
hypodermis
deepest layer of skin under the dermis (consists of adipose tissue/fat)
Epidermal layers in order
stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
stratum corneum
outermost layer, dead flattened keratinocytes
stratum lucidum
narrow layer of clear, dead keratinocytes; found only in thick skin (palms of hands and soles of feet)
stratum granulosum
three to five layers of cells; prominent cytoplasmic granules with keratin bundles or lipid-based substance
stratum spinosum
close to blood supply so cells in this layer are alive and mitotically active, Contains dendritic (Langerhans) cells
stratum basale
single layer of stem cells, most mitotically active layer, contains melanocyes and merkel cells (sensory receptors)
thin skin
only contains four epidermal layers (no stratum lucidum)
papillary layer
thin outermost layer of the dermis, below the epidermis
reticular layer
deep thicker layer; seperates dermis from hypodermis; mostly dense irregular connective tissue, contains lamellated corpuscles, blood vessels, sweat glands, hairs, sebaceous glands, adipose tissue
sebaceous glands
produce oily sebum that empties into hair follicule or small pore
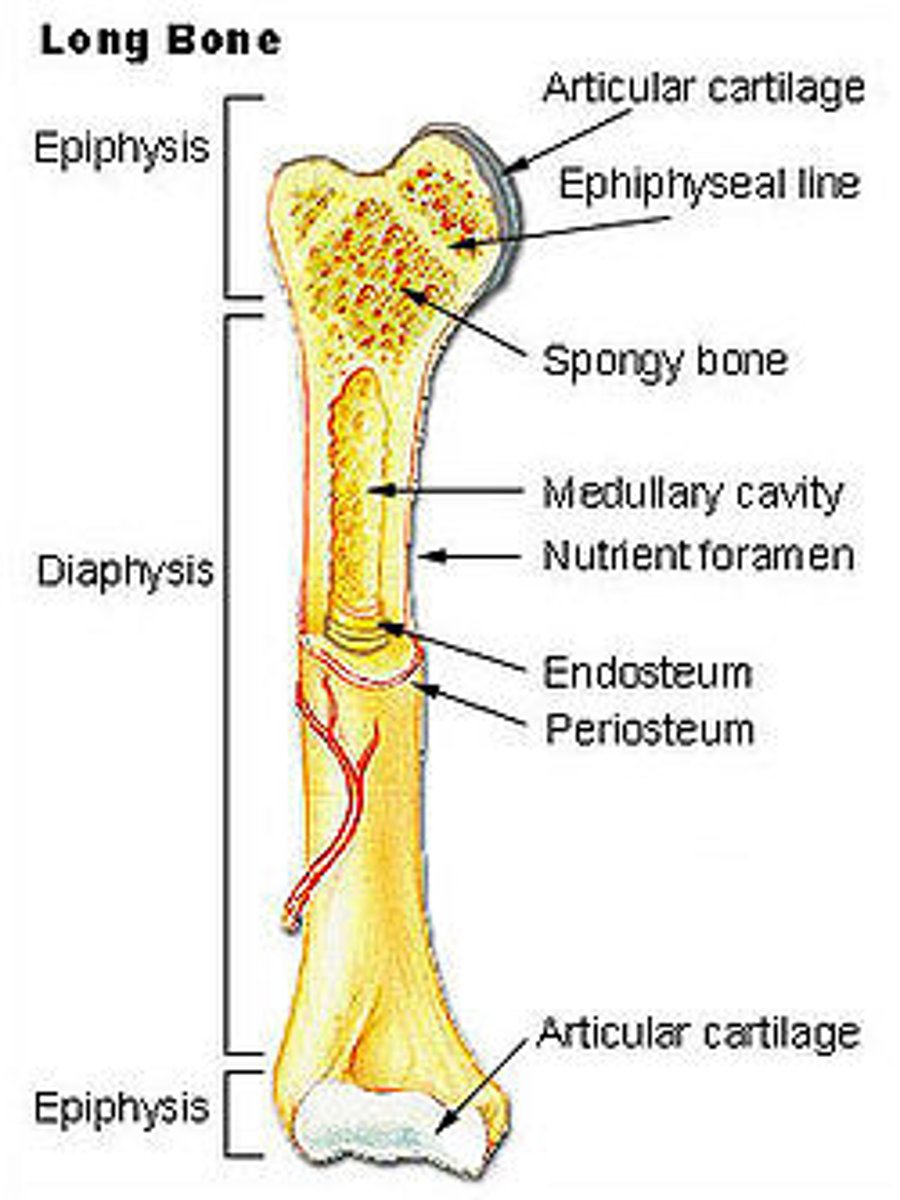
long bone
longer than they are wide (includes most bones in arms and legs)
short bones
roughly cube shaped or about aslong as they are wide (includes bones of wrist or carpals and ankle or tarsals)
flat bones
thin and broad bones (include ribs, pelvis, sternum (breastbone), and most skull bones
irregular bones
do not fit into other classes because of irregular shapes (vertebrae)
sesamoid bones
specialized bones located within tendons; usally small, flat, and oval-shaped (patella)
medullary cavity
hollow space in diaphysis that contains red or yellow bane marrow and lined by the endosteum
red bone marrow
produces blood cells
yellow bone marrow
stores fat
compact bone
hard outer layer of bones that provide strength and protection, made of osteons, contains blood vessels
spongy bone
trabeculae found at ends of long bone and inside epiphyses
Osteoblasts
Bone building cells
Osteoclasts
bone breakdown cells
axial skeleton
Portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
appendicular skeleton
movement, support, and muscle attachment (limbs)
vertebraral column
protects spinal cord
pectoral girdle
clavicle and scapula
pelvic girdle
ilium, ischium, pubis
Abdominal regions
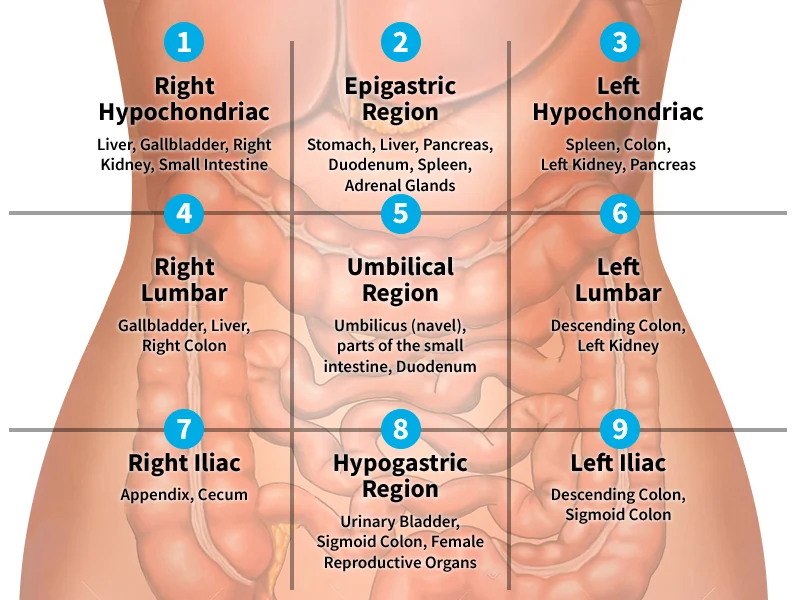
Axillary
armpit
Hallux
Big toe
Pedal region
top of foot (below big toe to ankle)
sural region
back of lower leg/calf
popiteal region
behind knee
Layers of epidermis
Stratum corneum, stratum lucidium, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
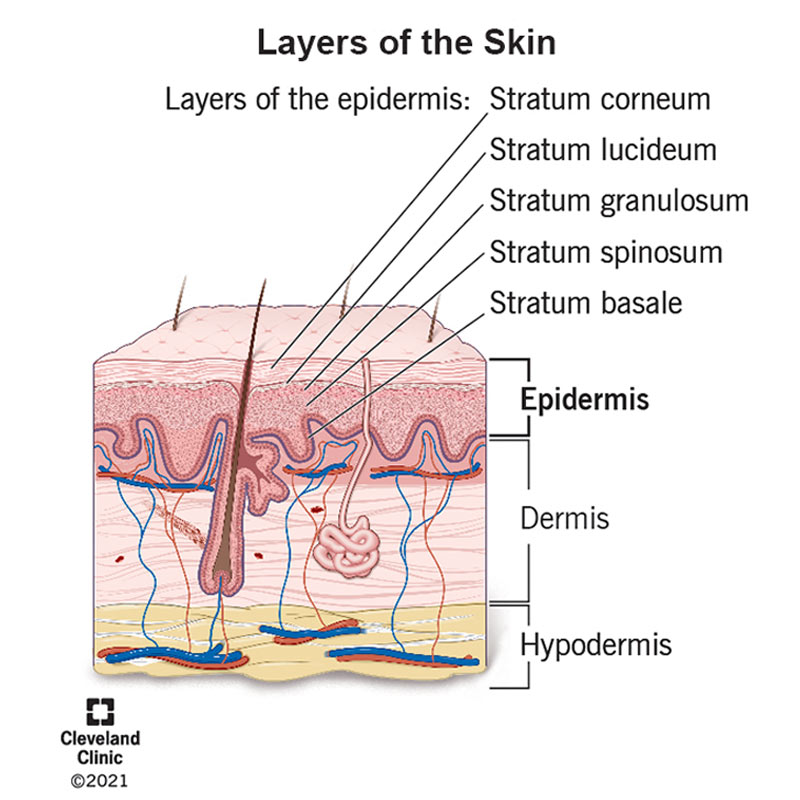
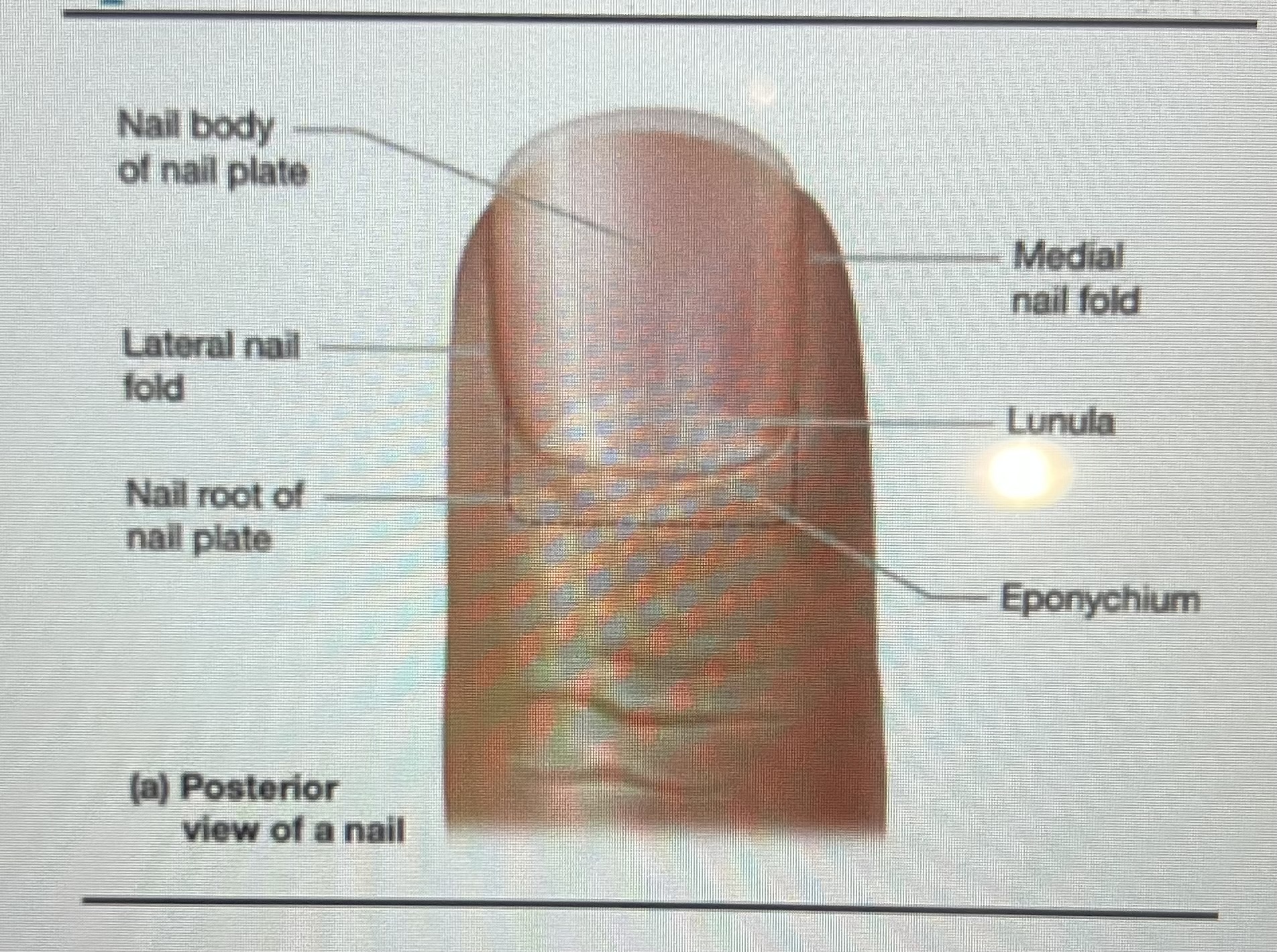
Parts of nail
Parts of Skin
cranial bones
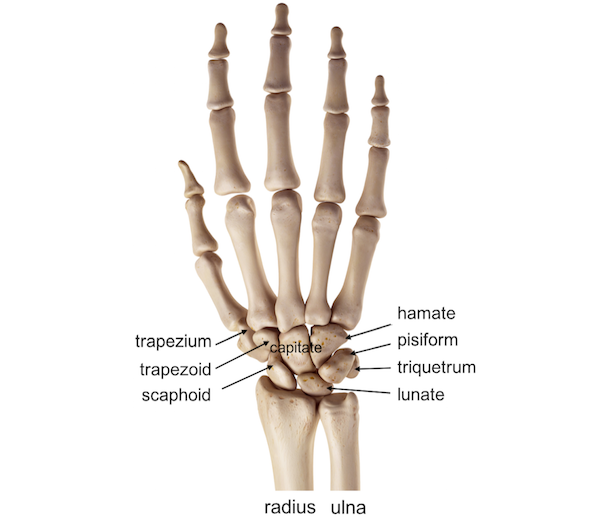
Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
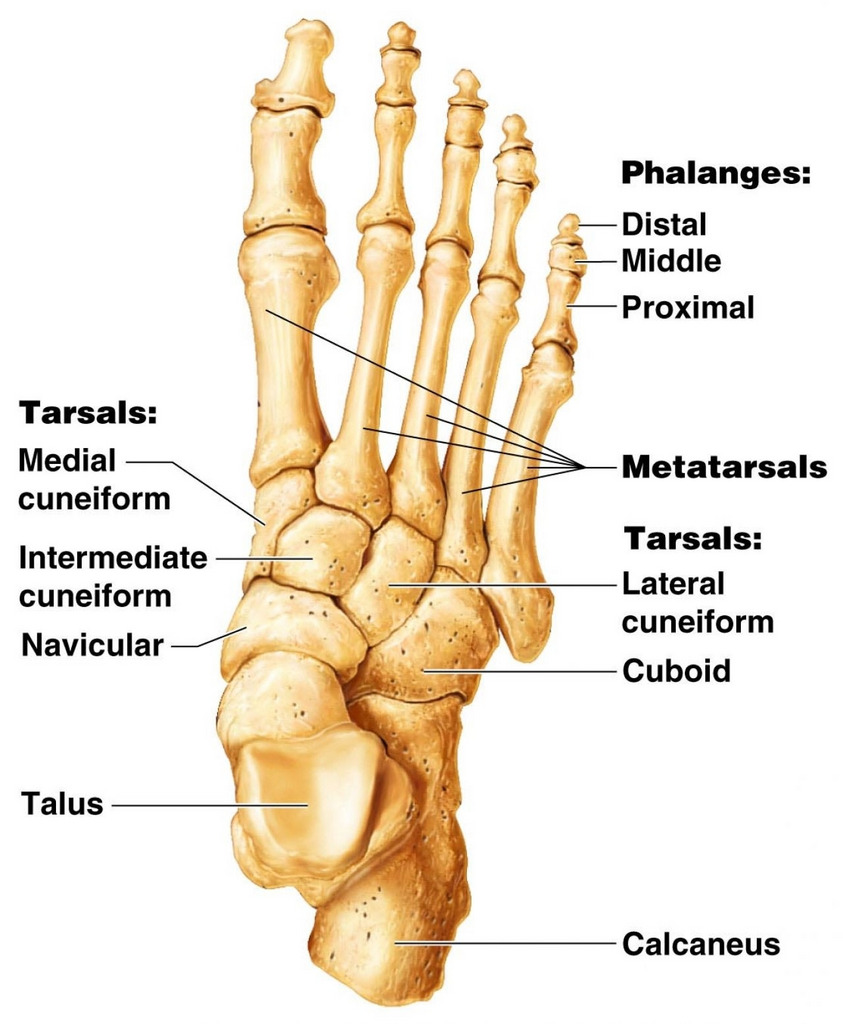
tarsal bones
Calcaneus, Talus, Navicular, Cuboid, lateral cuneiform, intermediate cuneiform, medial cuneiform
Mitosis stages
Interphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis