ch 1 openstax
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
T/F: microbes are living organisms that can’t be seen by the naked eye
F, not all microbes are living (viruses) some can be seen with naked eye
T/F: all microbes are prokaryotic
F, many are eukaryotic too, also archea
T/F all microbes are single celled organisms
F
T/F: all microbes are single celled prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
F, not all microbes are singled celled
Compare the terms prokaryotes vs bacteria
bacteria is the name of a domain (taxonomy), prokaryote is a classification of cells that lack a nucleus
what makes archaea a seperate domain from bacteria
their rRNA sequences are significantly different from bacterias, they have a closer evolutionary relationship to eukarya than bacteria
In modern taxonomy, how do scientists determine how closely two organisms are related?
by comparing their genetic material and proteins
Explain why the branches on the “tree of life” all originate from a single “trunk.”
the analysis of rRNA sequences points towards bacteria, eukarya, and archae all evolving from a common ancestor cell
binomial nomenclature
system of naming organisms where you use the genus followed by specific epithet
In the name Homo sapien, what part is the genus and what part is the epithet?
genus: homo epithet: sapien
rules for binomial nomenclature
the genus part of the name is always capitalized, epithet is never capitalized. the whole name is in italics
taxonomic names are usually derived from these languages:
Latin, Greek, or English
rules for abbreviating taxonomic names
use capitalized first initial of genus name followed by a period, then the full species (epithet) name
whats wrong w this abbreviation? Escherichia coli → E. Coli
species name should be lowercase
whats wrong w this abbreviation?Escherichia coli → E Coli
missing period after E
whats wrong w this abbreviation?Escherichia coli → E. coli
not in italics
whats wrong w this abbreviation?Escherichia coli → E. coli
nothing
T/F, we primarily classify microbes by directly observable traits like appearance
F
T/F: we primarily classify microbes by comparing their biochemical and genetic properties.
T
what are Bergey’s Manuals
A collection of manuals that are the standard references used for identifying and classifying different prokaryotes.
Within one species of microorganism, there can be several subtypes called _____
strains
different strains of microbes have nearly identical ______ but different _______
genomes, attributes (behavior)
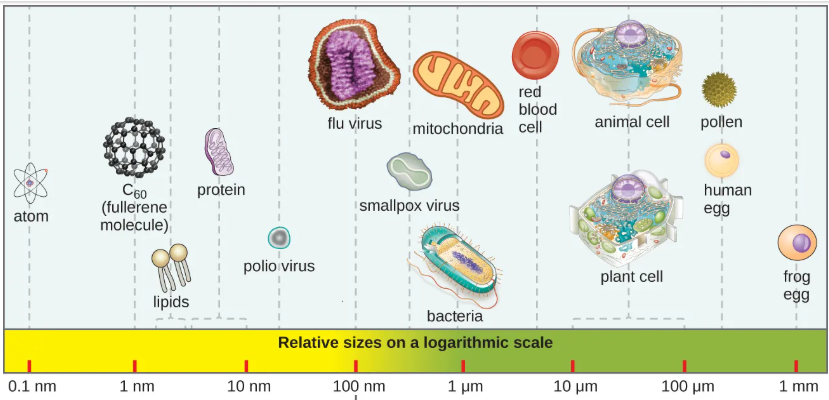
whats the minimum measurement for something to be visible to the naked eye
100 micrometers
list these from largest to smallest: protein, fliu virus, E.coli, mitochondria, human ovum, red blood cell, plant cell
protein
virus
mitochondria, E. coli
red blood cell
plant cell
ovum
T/F: Microorganisms differ from each other in size, structure, habitat, metabolism, and other characteristics.
T
T/F: Microorganisms all have the same type of metabolism.
F
Microbes are found in which domains?
Eukarya, Bacteria, Archaea
What do microbes in the domains Bacteria and Archea have in common?
all prokaryotes (no nucleus)
Difference between microbes in the domain Eukarya and the domains Bacteria/Archaea
all microbes in eukarya are eukaryotic (nucleated) but microbes in Archea/Bacteria are not
T/F: most bacteria are harmful and pathogenic
F
T/F: most bacteria are harmless or beneficial
T
define pathogen
a microbe that causes disease
T/F bacteria have a cell membrane
F, they have cell walls
Most bacterial cell walls contain a polymer called_______
peptidoglycan
types of bacterial shapes
coccus, bacillus, vibrio, coccobaccilus, sprillium, spirochete
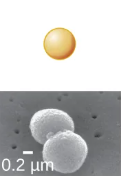
this shape is called what
coccus

this shape is called what
spirochete
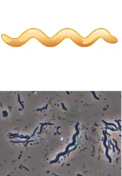
this shape is called what
spirrillum

this shape is called what
bacillus
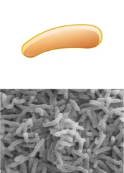
and perhaps what is this
vibrio
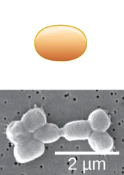
this is called what
coccobacillus
Archea and Bacteria are both unicellular prokaryotes but have differences in:
metabolic pathways, genetics, cell wall/membrane composition
T/F: Archaea have peptidoglycan in their cell walls like Bacteria
F
Archea cell walls are often composed of ________, a similar substance to Bacterias _____
pseudopeptidoglycan, peptidoglycan
T/F: Like bacteria, archea can be found in all habitats including extreme environments
T
T/F: Some Archea live in the human body and are pathogenic
F, they do live in the body but none have been found to be pathogens
name the 2 types of prokaryotic microbes
Bacteria, Archea
name the 3 types of Eukaryotic microbes
Protists, Fungi, Helminthes
protist definition
an informal grouping of eukaryotes that are not plants, animals, or fungi
protozoa definition
a category of protists that are animal like in the sense that theyre motile and heterotrophic
autotrophic definition
organism that makes its own food, eg, plants
heterotrophic definiton
organism that cannot make its own food and has to eat things, eg, dog
name 2 types of Protists
algea, protozoa,
T/F, Cyanobacteria are considered a type of algae, but not protists
T
Algae
a category of microbes mostly made up of protists that are photosynthetic and can be multicellular or unicellular
the cell walls of protist algea are made of _____
cellulose
Photosynthesis reactants and products
Sun + CO2 + H2O → Glucose, O2