PL SC 324 Lecture 4: Traits and Trade-offs
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Plant Traits
A very broad term, which comprises almost everything that can be quantified or qualified about an individual plant:
Size, size of parts, seeds, number and size, reproduction growth form.
r-Strategists evolve when
adults have higher mortality
K-strategies evolve when
adults survive
r-selection
reproductive strategies, Increase reproductive effort earlier
K-selection
Lower reproductive effort, later in life
Because the population is commonly near carrying capacity, they have evolved to be competitive.
Explain Grimes CSR Theory
3 broad ecological strategies of plants (Competitor, Stress-tolerator, Ruderal)
-Stress tolerators: tolerate environments that other plants cannot
-Ruderal: population disturbed areas like agricultural land, put lots of effort into quickly setting seed.
-Competitor: Dominate the area so no other plant can grow, ex: quack grass
When is competition lowest in plants and highest
Lowest: at low productivity (because plants are adapted to stress conditions). Highest: At high productivity (Plants are adapted to obtain resources quickly
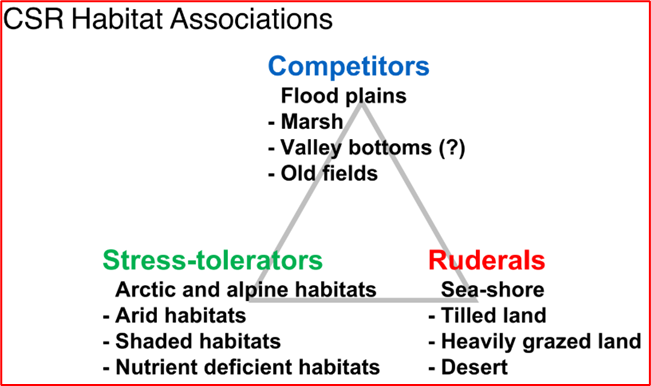
Name some of the CSR habitat associations
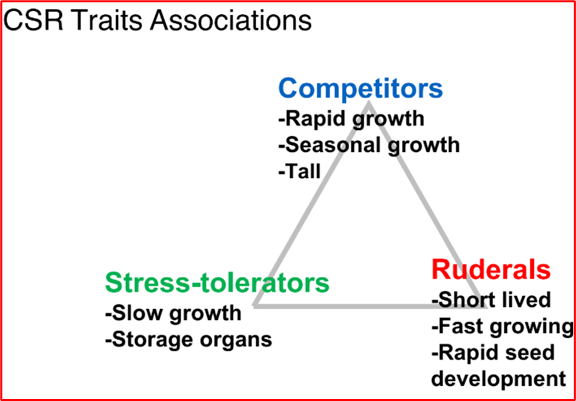
Name some of the CSR trait associations
Trade-offs
Evolutionary dilemma whereby genetic change conferring increased fitness in one circumstance inescapably involves sacrifice of fitness in another. A plant cannot optimize all aspects of its life history.
Explain some tradeoffs when it comes to seed traits
Seed size vs Seed number
-Larger seeds are more likely to be eaten, smaller seeds are less likely to survive environmental conditions.
Seed size vs seedling performance
-Larger seeds will be more competitive
Seed size vs Dormancy
-Large seeds tend to germinate sooner
Colonization vs Competitive ability
Palatability vs Competitive ability
Longevity vs Reproductive Output
Growth vs Reproduction
LMA vs Photosynthesis or nutrient efficiency
Do the RGR units activity
(It’s on eclass 😄 )