neurobiology of sex and sex differences chapter 12
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
gonadal hormones definition + examples
hormones that shape brain early so that they can eventually trigger normal reproductive behaviors. examples: testosterone and estradiol
why are sex differences established so early
evolutionary basis (need for reproductive strategies)
why is there gender variability
complexity of cordial/brain processing
evolutionary advantage (optimize adaptation)
reproductive behavior steps
attracting a mate → exchanging gametes → nurturing offspring
how many chromosomes
23 pairs (22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome)
androgen definition and what it releases
it’s a gonadal steroid (made in testes) that releases testosterone
estrogen definition and what it releases
it’s a gonadal steroid (made in ovaries) that releases estradiol
what is a gene
unit of heredity that determines characteristics
Sry gene definition
sex determining region of y chromosome that directs the formation of testes
Sry activated
male
Sry unactivated
female
sexual differentiation
if someone will have a male or female body
wolffian ducts
develop into male reproductive organs. in males, müllerian systems shrinks (a little)
müllerian ducts
develop into female reproductive organs. most of wolffian system degenerates (none)
when does sexual differentiation happen/ steroids have effect
during a sensitive period in early development
What does OAH stand for and what is it
Organization/ Activation hypothesis was based on the work of William Young. describes 2 sensitive periods for gonadal steroid influences
organization sensitive period
(gestation) testosterone secretion → start of masculinization. ends when females aren’t sensitive to androgens anymore
activational sensitive period
(puberty) gonadal hormones surge and activate brain networks
rat sex
lordosis by female + male mounting = intromission (7-9)
what does it take to masculizine the body, brain and behavior during gestation
one steroid signal (testosterone)
no androgen means
feminine behavior
what does full masculinity require
testosterone during development and adulthood
what happens if you castrate a male and inject it with estradiol (rat version of estrogen) in adulthood?
produces feminine reproductive behaviors
if you inject a female rat with testosterone during the sensitive period and also again during adulthood?
it will mount instead of showing lordosis (masculine behavior)
what do androgen and estrogen (steroids) also mediate in neurobiology
aspects of neural development such as cell survival/cell death in brain structures (that produce sex specific reproductive behaviors)
sexual dimorphism
marked sex differences in someone’s outward appearance. also occurs IN brain
what is POA
pre optic area
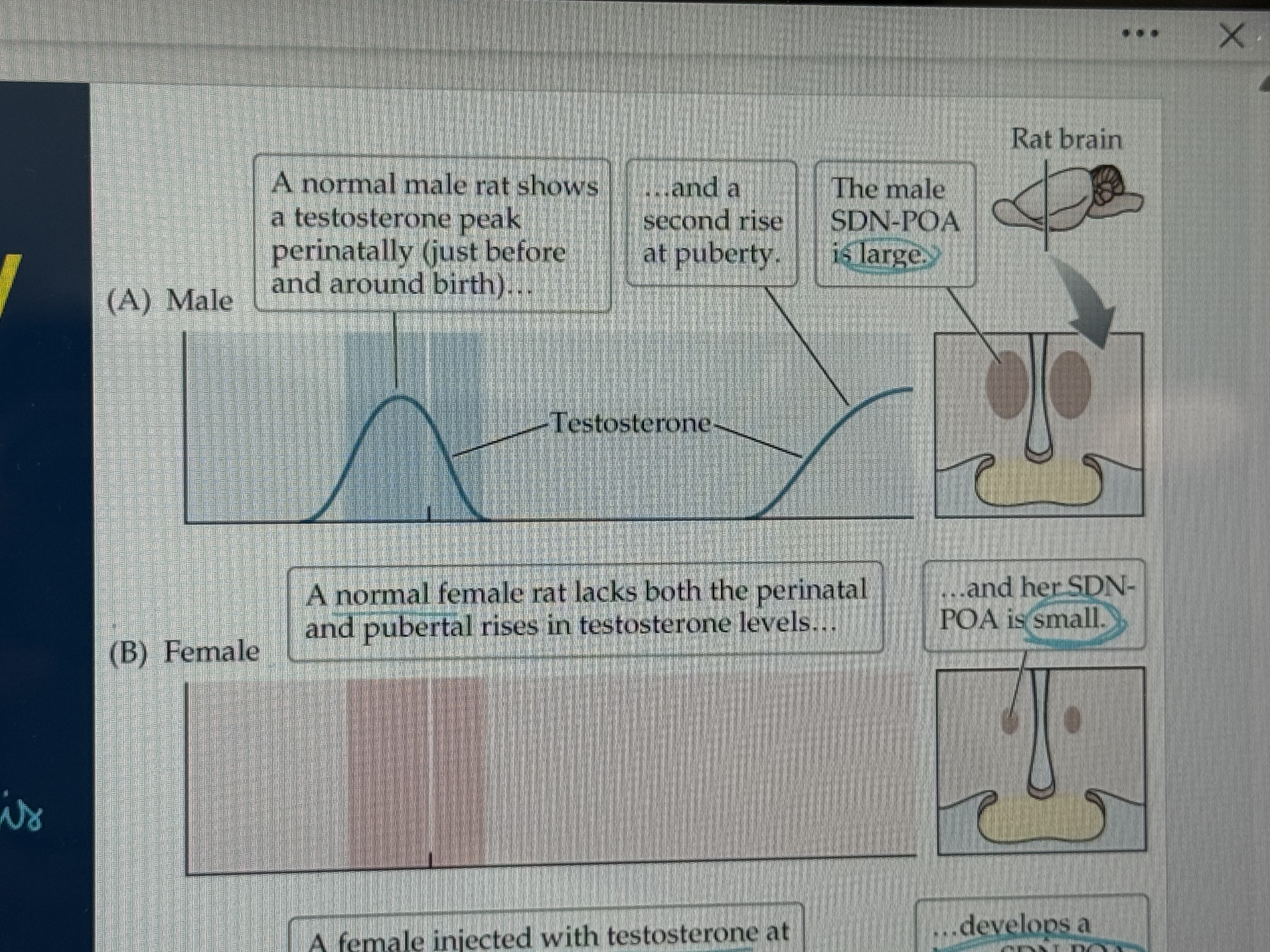
SDN-POA
sexually dimorphic nucleus of the POA (lesions disrupt ovulatory/copulatory behaviors)
SDN-POA and relation to OAH?
SDN-POA conforms to the organizational piece of the hypothesis
how does testosterone alter the SDN-POA
it makes it larger, which is why male’s are bigger
why is the sensitive period so important
changes made during this period can cause much bigger changes later on. you can’t get huge changes by injecting anything during adulthood
key CNS structures
SDN-POA
AVPV-POA
pBST
SNB
CNS structures important for gonadal steroid effects are usually _____ in males than females
larger
are there different neural circuits for male and female reproductive behavior?
prolly not
differences in male and female structure networks
differentially weighted (differences in synapse number/density, dendritic structures, functional differences in properties)
hippocampus and amygdala differences in males/females