States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces in Pharmaceutical Formulations
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
What is a solution?
A chemically and physically homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
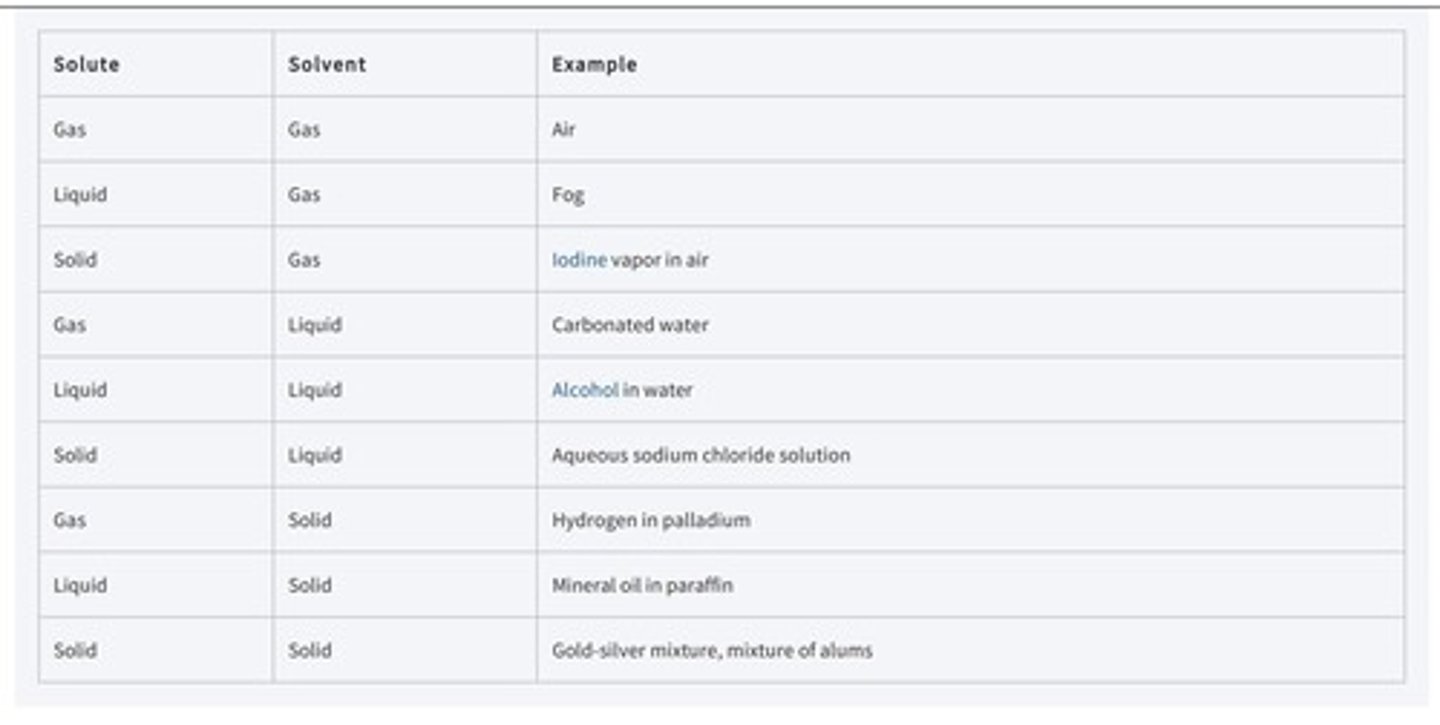
What are the two components of a binary solution?
Solute and solvent.
What is the solvent in a solution of a solid material in water?
Water is the solvent.
List one advantage of solutions.
Faster onset of activity.
List one disadvantage of solutions.
Less stable than solids.
What is molarity?
A concentration unit defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
How does normality differ from molarity?
Normality is based on chemical activity and is defined as gram equivalents of solute per liter of solution.
What is the formula for calculating molarity?
Molarity = # moles of solute / 1 Liter of solution.
What does percentage strength represent?
The quantity of substance per 100 parts.
What is ratio strength?
The ratio of 1 part of solute per total X parts.
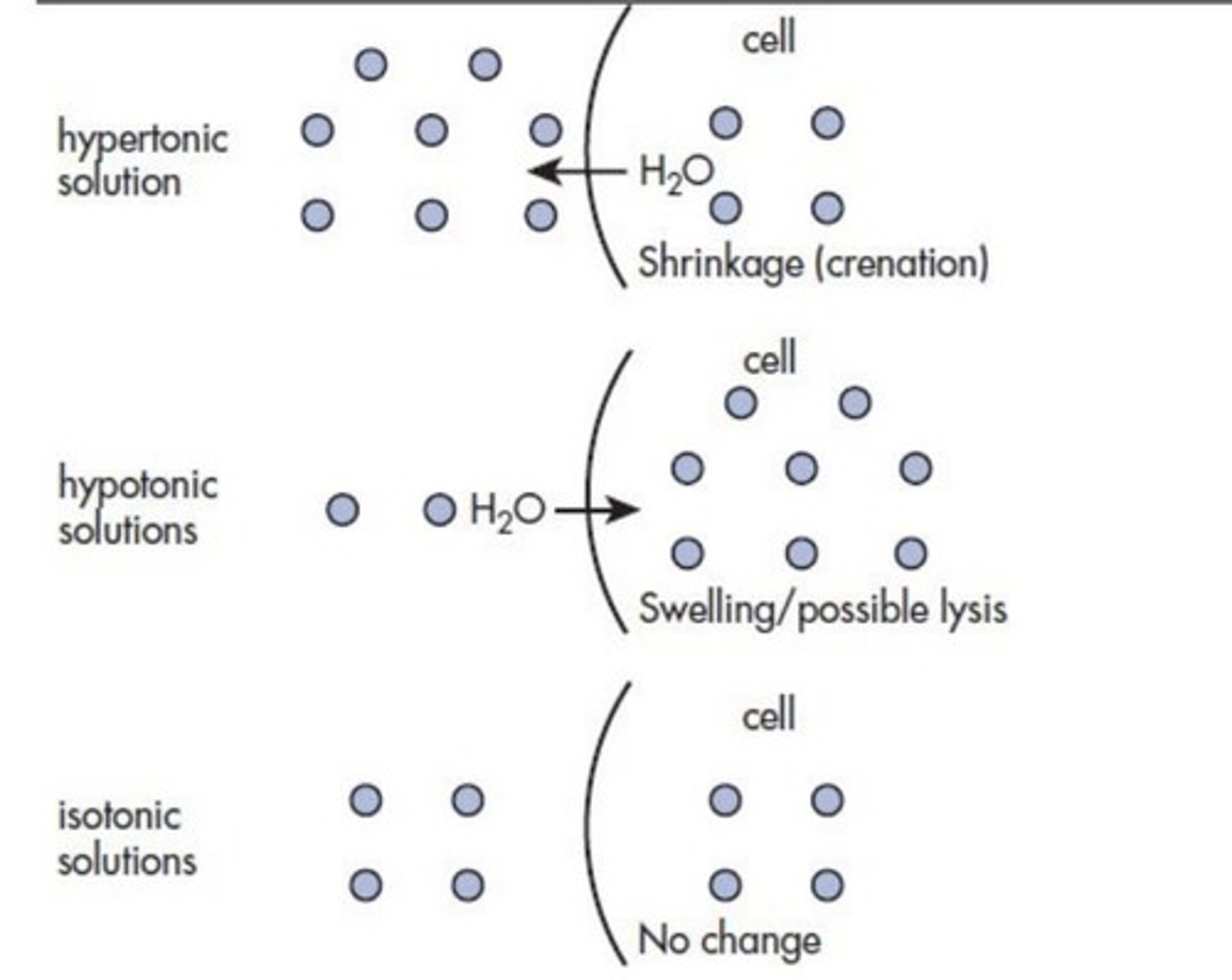
Define an isotonic solution.
A solution that has the same osmotic pressure as another solution, typically body fluids.
What are colligative properties?
Properties that depend on the number of solute particles in a solution, not their identity.
How can you calculate osmolarity from concentration?
Osmolarity can be calculated using the concentration of solute and its dissociation in solution.
What is an ideal solution?
A solution where there is no change in physical properties other than dilution when mixed.
What is the significance of Liso and ΔTf?
They are important in understanding colligative properties and their effects on solution behavior.
What are the classifications of aqueous solution systems based on solute type?
Non-electrolytes, strong electrolytes, and weak electrolytes.
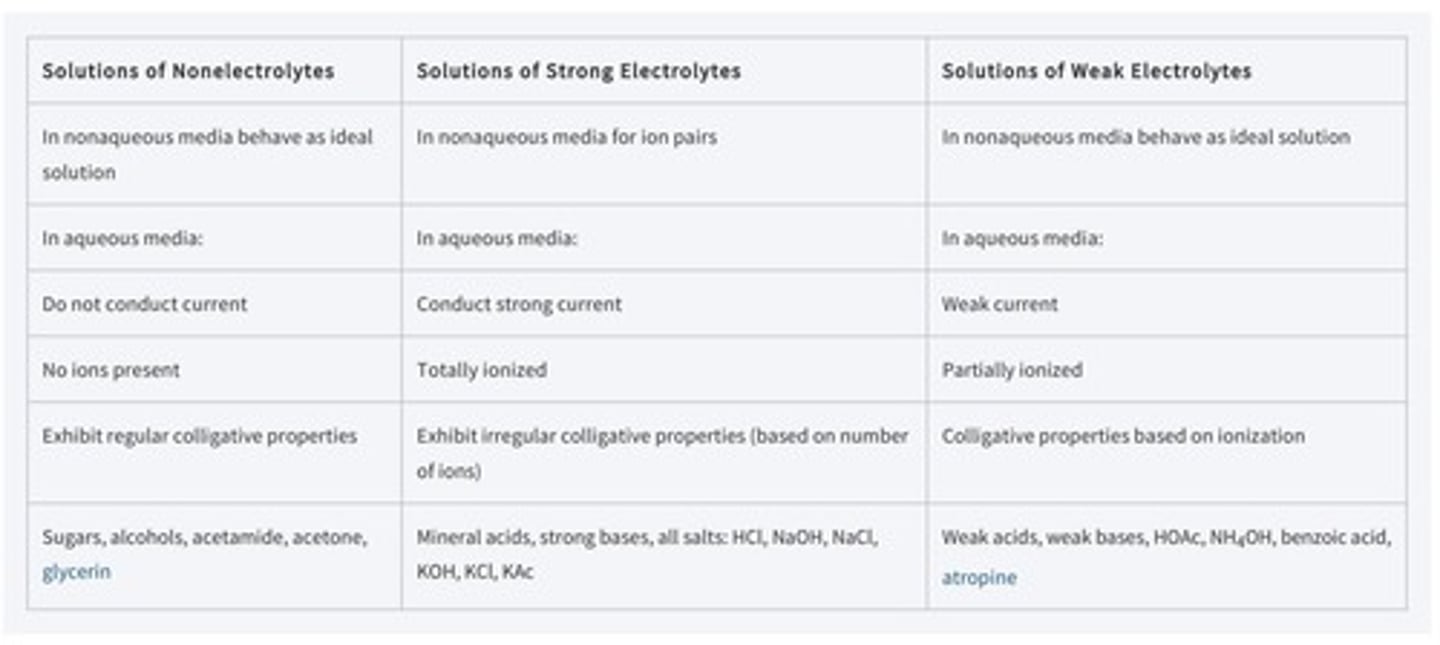
What is the relationship between molarity and normality for solutes with one replaceable hydrogen?
For such solutes, molarity and normality are the same.
What are the physiologic implications of colligative properties?
They affect the behavior of solutions in biological systems, such as osmotic pressure.
What is the main consideration when preparing an isotonic solution?
Performing calculations to ensure the solution matches the osmotic pressure of body fluids.
What is the impact of temperature on molarity?
Molarity can vary slightly with temperature changes.
What are the advantages of using solutions in medication?
They are homogeneous, flexible in dosing, and can be administered by any route.
What does Raoult's law state about vapor pressure in solutions?
The vapor pressure of each volatile constituent is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure constituent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.
What distinguishes real solutions from ideal solutions according to Raoult's law?
Real solutions do not show linear relationships for Raoult's law, while ideal solutions do.
What are the four colligative properties?
1. Vapor Pressure Lowering 2. Boiling Point Elevation 3. Freezing Point Depression 4. Osmotic Pressure.
What assumptions are made when applying colligative properties to pharmaceutical systems?
1. The solute is nonvolatile and the solvent is water. 2. Solutions are dilute. 3. For nonelectrolytes, values are the same for different solutes at the same molar concentrations. 4. For weak electrolytes, values depend on ionization. 5. For strong electrolytes, values depend on the number of ions.
What is the significance of isotonic solutions in pharmacy?
Isotonic solutions are important to avoid cell and tissue damage and patient discomfort when administered to sensitive areas.
What is the E-Method for calculating isotonic solutions?
The E-Method uses a 0.9% w/v NaCl solution or its equivalent.
What is the D-Method for isotonic solutions?
The D-Method states that a solution has a freezing point depression of 0.52 °C.
How do colligative properties vary with the concentration of solute?
Colligative properties depend only on the number of solute particles (ions or molecules) dissolved in the solution.
What types of solutes can be evaluated based on their behavior in water?
1. Non-electrolytes 2. Strong Electrolytes 3. Weak Electrolytes.
What is the definition of a solution in pharmacy?
A solution is a single phase, homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where a solute is molecularly dispersed or dissolved within a solvent.
Why is osmolarity important in pharmaceutical formulations?
Osmolarity is important to ensure compatibility with blood fluids and to avoid cell and tissue damage.
What is the relationship between colligative properties and the concentration of solutes?
Colligative properties are a function of the concentration of solutes.
What must pharmacists be able to do with solution concentrations?
Pharmacists must be able to convert between different expressions of solution concentrations, including percentages, molarity, normality, and osmolarity.
What happens to vapor pressure when a nonvolatile solute is added to a solvent?
The vapor pressure of the solution decreases compared to that of the pure solvent.
What is the effect of strong electrolytes on colligative properties?
The values of colligative properties depend on the number of ions produced when strong electrolytes dissociate.
What is the effect of weak electrolytes on colligative properties?
The values of colligative properties depend on the degree of ionization of weak electrolytes.
What is the impact of solute concentration on physical properties of solutions?
Physical properties of solutions vary according to the concentration of the dissolved solute.
What is the importance of considering osmolarity in drug products?
It is crucial to consider osmolarity to avoid adverse effects in sensitive areas, such as parenteral and ophthalmic formulations.
What does vapor pressure lowering indicate in a solution?
It indicates that the presence of a solute decreases the escaping tendency of solvent molecules, leading to a lower vapor pressure.
How do colligative properties relate to the number of solute particles?
Colligative properties are affected by the total number of solute particles in a solution, regardless of their nature.
What is the significance of freezing point depression in pharmaceutical solutions?
Freezing point depression is important for ensuring that solutions remain liquid at lower temperatures, which is critical for storage and administration.
What is the relationship between colligative properties and solution types?
Colligative properties can vary based on whether the solute is a non-electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or strong electrolyte.
What are the two main types of intermolecular forces?
Attractive and repulsive forces.
What are cohesive forces of attraction?
Attractive forces when like molecules are attracted to one another.
What are adhesive forces of attraction?
Attractive forces when different molecules are attracted to one another.
What is the significance of the potential energy diagram in relation to intermolecular forces?
It illustrates the energy changes associated with attractive and repulsive forces.
What are the types of intermolecular attractive forces?
Van der Waals, Dipole-Dipole, Dipole-Induced Dipole, Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole, Ion-Dipole, and Hydrogen Bond.
What characterizes hydrogen bonds?
They occur between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom, and are a uniquely strong type of dipole-dipole interaction.
What are Dipole-Dipole Forces (Keesom Forces)?
Forces that occur between polar molecules with permanent dipoles, involving interactions of charged ends.
What is the energy range for Dipole-Dipole Forces?
1 - 7 kcal/mole.
What are Dipole-Induced Dipole Forces (Debye Forces)?
Forces where a polar molecule induces a temporary dipole in a nonpolar molecule, resulting in weaker attraction.
What is the energy range for Dipole-Induced Dipole Forces?
1 - 3 kcal/mole.
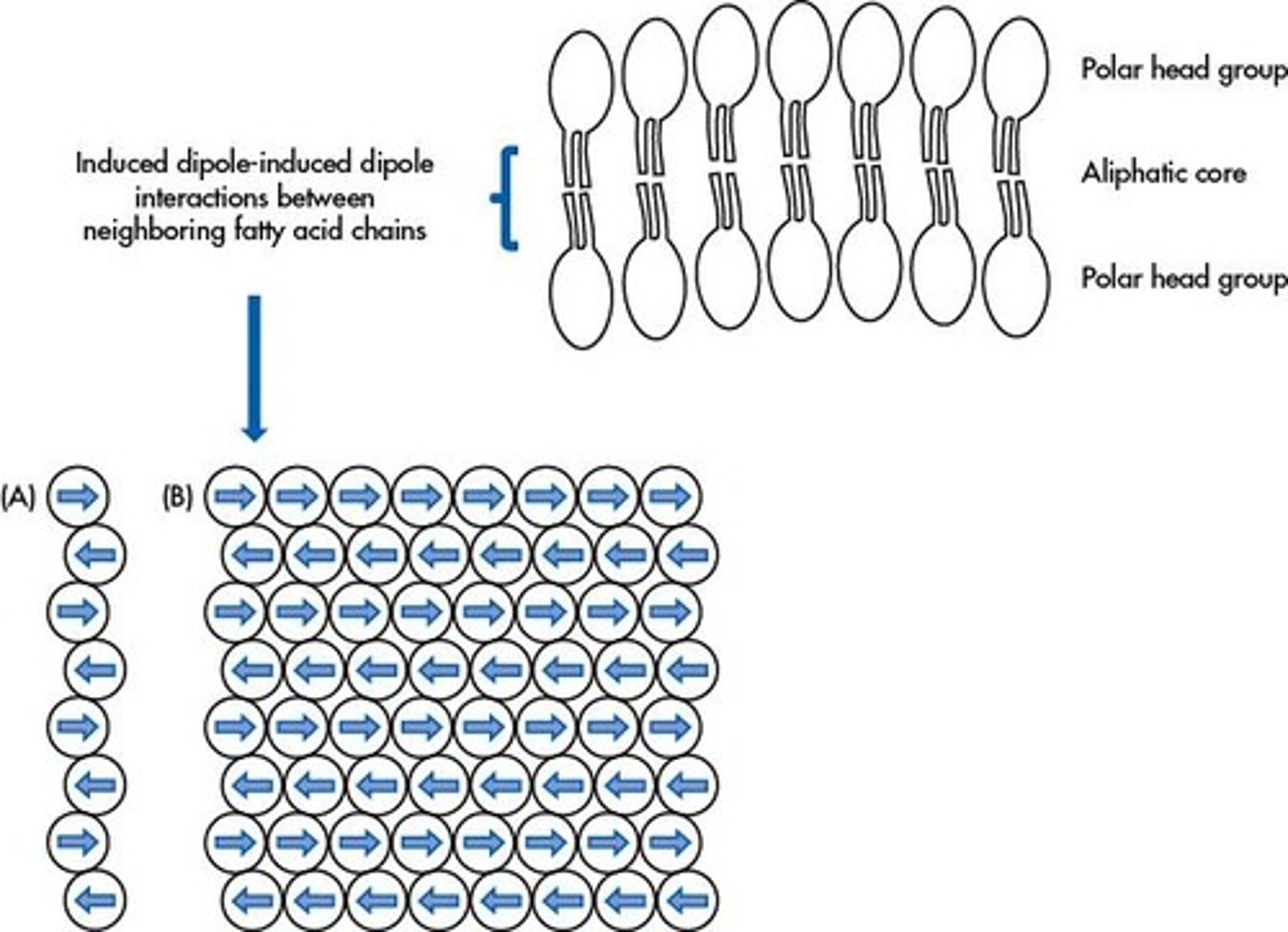
What are Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole Forces (London Forces)?
Forces originating from molecular vibrations in nonpolar molecules, resulting in temporary attractions.
What is the energy range for Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole Forces?
0.5 - 1 kcal/mole.
What role do Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole interactions play in phospholipid bilayers?
They provide a stabilizing force through cumulative weak attractions among alternating induced dipoles.
What are Ion-Dipole Forces?
Forces resulting from the interaction of polar molecules with ions, either positive or negative.
What is the energy range for Ion-Dipole Forces?
1 - 7 kcal/mole.
How do pharmaceutical salts utilize Ion-Dipole Forces?
They hold the drug molecule and the counterion together.
What is the relationship between the heat of vaporization and intermolecular forces?
The heat of vaporization is related to the magnitude of intermolecular forces in liquids.
What is the relationship between the heat of fusion and intermolecular forces?
The heat of fusion is related to the magnitude of intermolecular forces in solids.
What physical characteristics differentiate gases, liquids, and solids?
Gases have no fixed shape or volume, liquids have a fixed volume but take the shape of their container, and solids have a fixed shape and volume.
What is the significance of understanding chemical and physical stability in pharmaceuticals?
It is crucial for ensuring the efficacy and safety of pharmaceutical formulations.
What types of solid materials are used in pharmaceuticals?
Various types including crystalline, amorphous, and polymorphic forms.
What is the role of potential energy diagrams in understanding states of matter?
They help visualize the energy changes associated with transitions between states of matter.
What is the importance of distinguishing between gaseous, liquid, and solid states of matter?
It aids in understanding their physical properties and behaviors in pharmaceutical applications.
What happens to the hydrogen atom in a carboxylic acid during ion formation?
The hydrogen atom is removed, resulting in a negative charge.
What types of species can bond to form salts with carboxylic acids?
Inorganic species like sodium or potassium, or organic species like arginine or choline.
How is kinetic energy (KE) related to temperature for 1 mole of an ideal gas?
KE is given by the formula KE = 3/2 RT, where R is the ideal gas constant and T is the temperature in degrees Kelvin.
What are the characteristics of gases in the gaseous state?
Gases have high kinetic energy, no regular shape, can fill all available space, are compressible, and many are invisible.
What does Boyle's law state about the relationship between pressure and volume for a gas?
For 1 mole of gas at a fixed temperature, the product of pressure (P) and volume (V) is a constant.
What does Charles' law relate to in terms of gas behavior?
Charles' law relates the volume of a gas to its temperature (T).
What are the important blood gases in pharmaceutical sciences?
Oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
How are gases in the blood categorized?
Gases are categorized as hemoglobin-bound O2 in red blood cells and CO2, N2, and other atmospheric gases dissolved in plasma.
What defines the liquid state of matter?
Liquids occupy a definite volume, take the shape of their container, are denser than gases, and possess less kinetic energy.
What is vapor pressure and what does it depend on?
Vapor pressure is a physical property of liquids that depends on temperature, not on the volume, weight, atmospheric pressure, or other vapors.
What occurs at equilibrium vapor pressure?
The rate of vaporization equals the rate of condensation, resulting in a saturated vapor pressure above the liquid.
What is the boiling point of a liquid?
The boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure.
How are vapor pressure and boiling point related?
Vapor pressure and boiling point are inversely related.
What are the characteristics of solids in the solid state?
Solids have a fixed shape, are nearly incompressible, have strong intermolecular forces, and very little kinetic energy.
How do atoms behave in a solid?
Atoms in a solid vibrate in fixed positions about an equilibrium position with little translational motion.
What are some important characteristics of solids relevant to pharmaceutical formulations?
Surface energy, hardness, elastic properties, compaction, and porosity.
What is a phase diagram for a eutectic mixture?
A graphical representation showing the phase behavior of a mixture as temperature and composition change.
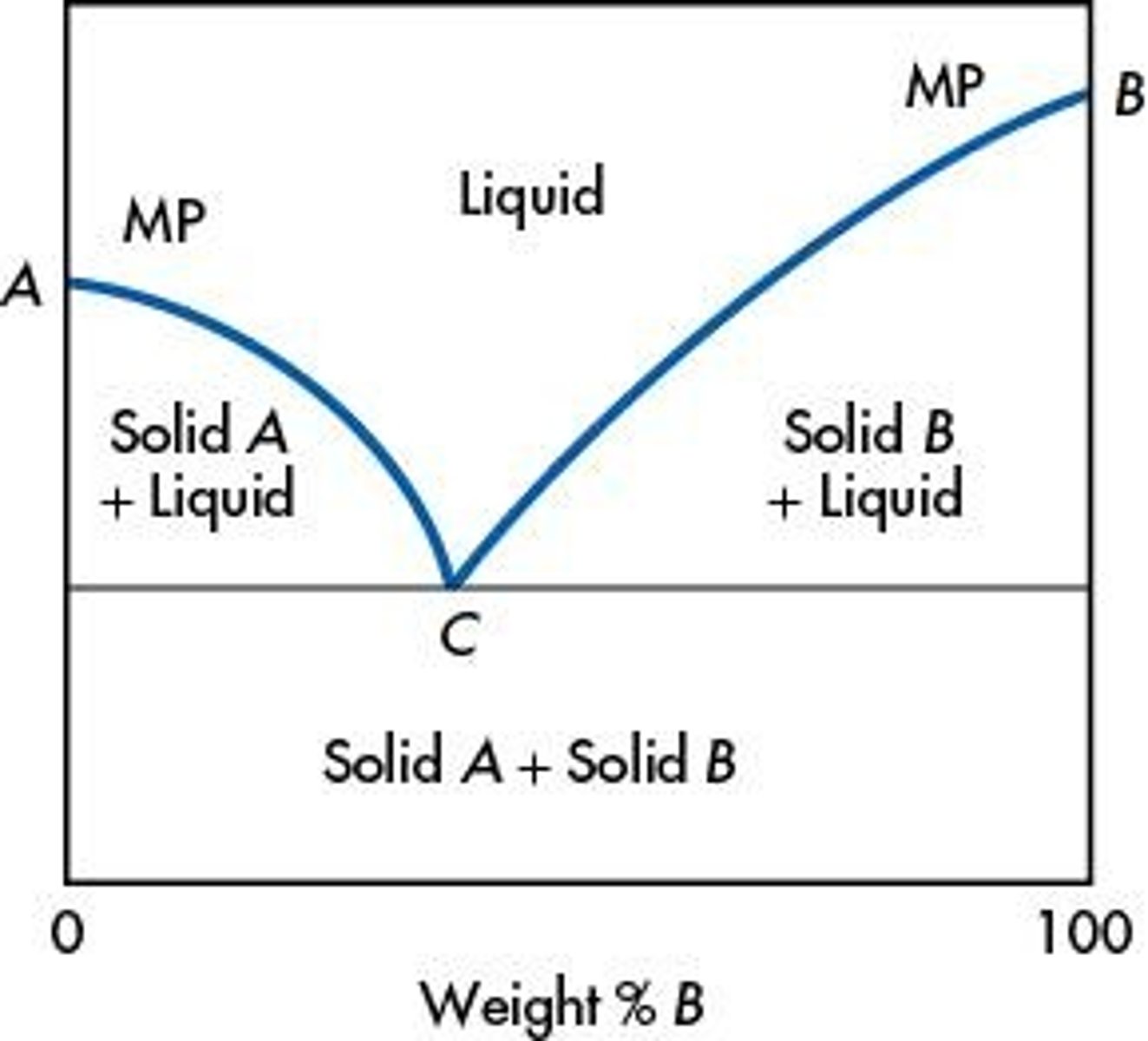
What is the significance of the citation provided in the notes?
It references the source of information regarding states of matter related to pharmaceutical formulations.
What is the relationship between kinetic energy and intermolecular forces in liquids?
Liquids possess less kinetic energy than gases and are influenced by intermolecular forces.
What happens to the kinetic energy of molecules at the surface of a liquid?
Molecules with the highest kinetic energy can break away from the surface and enter the gaseous state.
What is the difference in compressibility between solids, liquids, and gases?
Solids are nearly incompressible, liquids are less compressible than gases, and gases are highly compressible.
What is the role of friction in the flow of liquids?
Friction influences the flow of liquids, affecting their movement.
What is the significance of melting point in solids?
Melting point is a characteristic that defines the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid.