Chemistry 1252 - Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers: Chapter 9 - Gasses & Chapter 10 - Liquids and Solids
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
Gas Pressure
The force exerted on a given area (P=F/A)
2
New cards
The relationship between pressure and temperature
Proportional ( P1/T1 = P2/T2)
3
New cards
The relationship between temperature \n and volume
Proportional (T1/V1 = T2/V2)
4
New cards
The relationship between pressure and volume
Inversely Proportional (P1 x V1 = P2 x V2)
5
New cards
The relationship between volume and amount (moles) of gas
Proportional ( V1/N1 = V2/N2)
6
New cards
What makes a gas behave ideally?
Low pressure and high temperature
7
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
8
New cards
How the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture is related to the total pressure of the \n mixture.
Add all of the partial pressures together to get the total pressure of the mixture.
9
New cards
Mole Fraction
Number of moles of a component / Total moles
10
New cards
Diffusion
Prosses by which molecules disperse in space in response to differences in concentration
11
New cards
Effusion
The escape of a gas molecule through a tiny hole such as a pinhole in a balloon into a vacuum
12
New cards
How molar mass impact molecular speeds of gases.
The average speed of a molecule is inversely proportional to the square root of their masses
13
New cards
How temperature impact molecular speeds of gases.
The average kinetic energy of the gas molecule is proportional to temperature
14
New cards
The factors that make a gas behave non-ideally.
Low pressure and high temperature
15
New cards
Van der Waals Equation
Used on gasses that do not behave ideally
16
New cards
The two correction factors on the Van der Waals Equation
Molecule attraction and volume of molecules
17
New cards
Intermolecular Forces
Forces BETWEEN atoms/ molecules
18
New cards
Intramolecular Forces
Forces that hold an atom together in a molecule
19
New cards
Dispersion Forces
force that is present in all substances (caused by induced/ instantaneous dipoles)
20
New cards
Dipole-Dipole Forces
The force that is found in permanently polar molecules
21
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds (NOT REAL BONDS)
Forces that are found in liquids when Hydrogen is bonded to either Nitrogen, Oxygen, or Fluorine
22
New cards
Strength of intermolecular forces from least to greatest
Dispersion < Dipole-Dipole < Hydrogen Bonds
23
New cards
How polarizability impacts the strength of intermolecular forces
As polarizability increases, the IMFs also become stronger.
24
New cards
How polarizability impacts boiling point
As polarizability increases, so do boiling points.
25
New cards
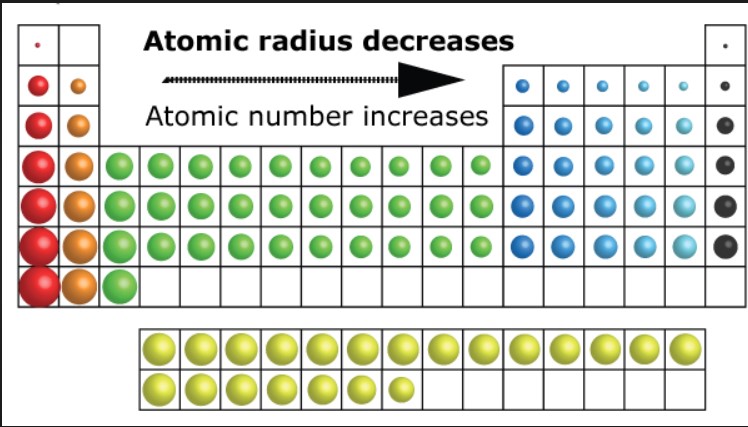
How to rank polarizability of atoms/compounds
Smaller atoms are less polarizable than larger ones
26
New cards
Viscosity
A measure of a liquids resistance to flow
27
New cards
Relationship of viscosity and IMFs
Proportional, the stronger the IMFs the more viscus the liquid
28
New cards
Relationship of viscosity and Temperature
Inversely proportional, the higher the temperature the lower the viscosity.
29
New cards
How the strength of intermolecular forces impacts surface tension.
Proportional, as the stronger the IMFs the more surface temperature it has.
30
New cards
Vaporization
Liquid to Gas (endothermic)
31
New cards
Fusion
Solid to liquid (endothermic)
32
New cards
Sublimation
Solid to gas (endothermic)
33
New cards
Condensation
Gas to liquid (Exothermic)
34
New cards
Freezing
Liquid to solid (Exothermic)
35
New cards
Deposition
Gas to solid (Exothermic)
36
New cards
Boiling point
the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the external pressure surrounding the liquid.
37
New cards
Normal Boiling point
Boiling point when surrounding pressure is equal to 1 atm
38
New cards
Change in temperature equation
q= amount x Specific heat x Change in temperature
39
New cards
Change in temperature (phase change)
q= Amount x theta H of phase change
40
New cards
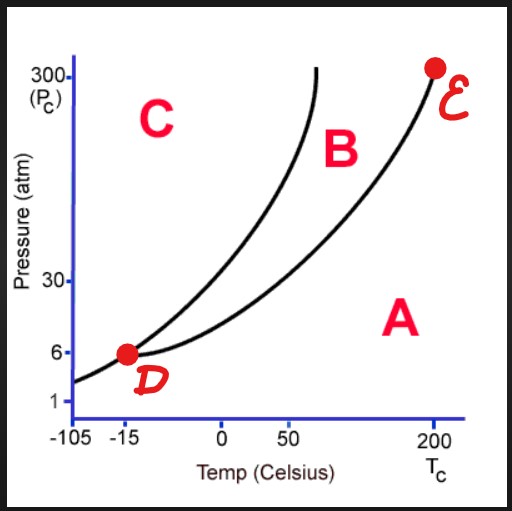
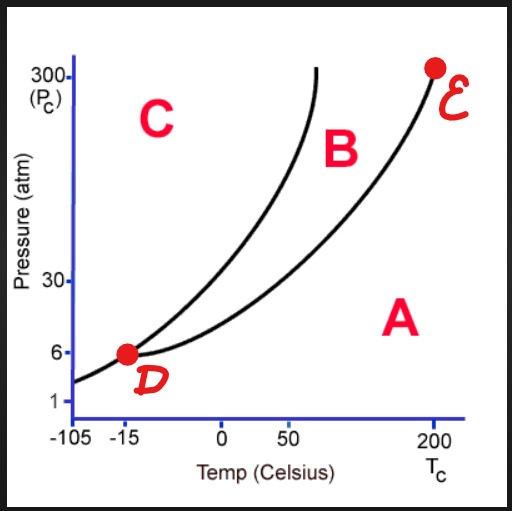
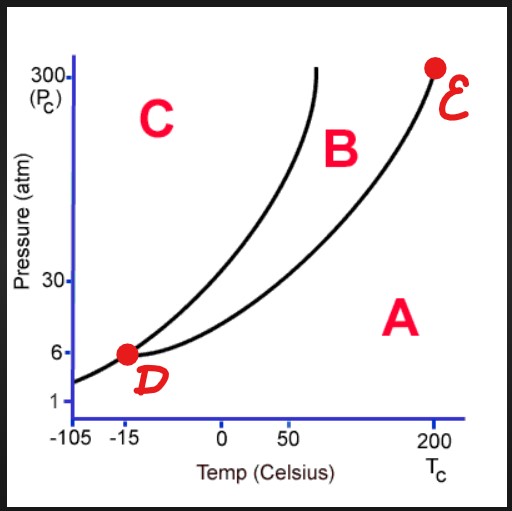
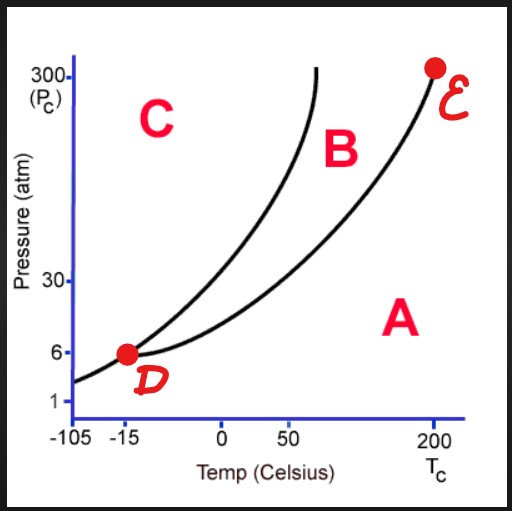
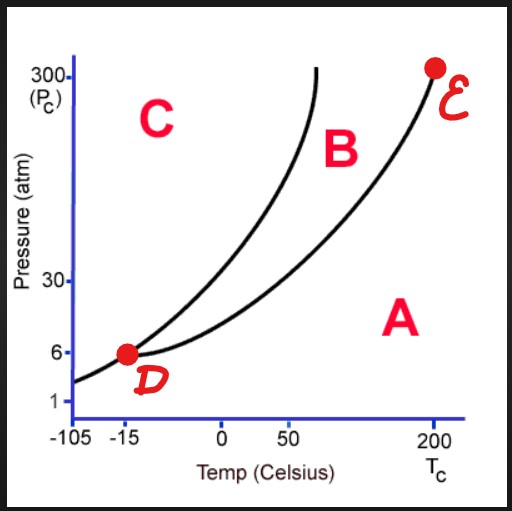
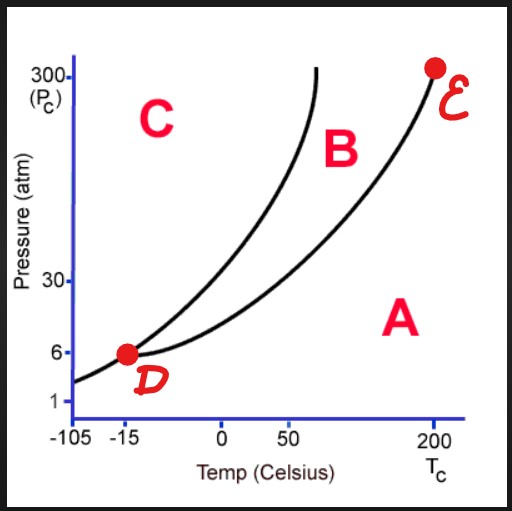
A
Gas
41
New cards
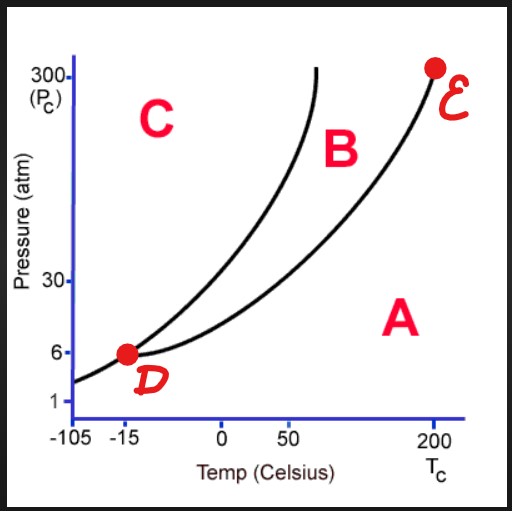
B
Liquid
42
New cards
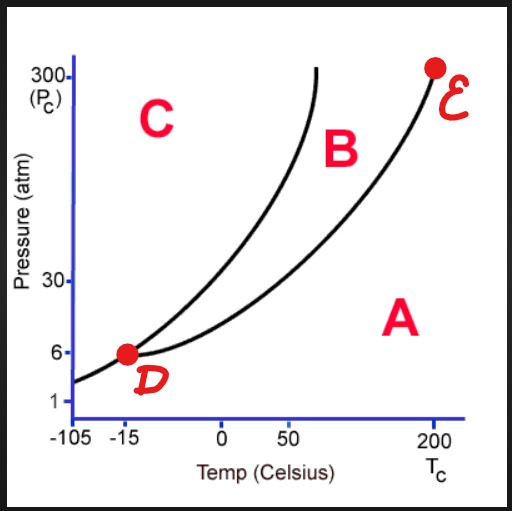
C
Solid
43
New cards
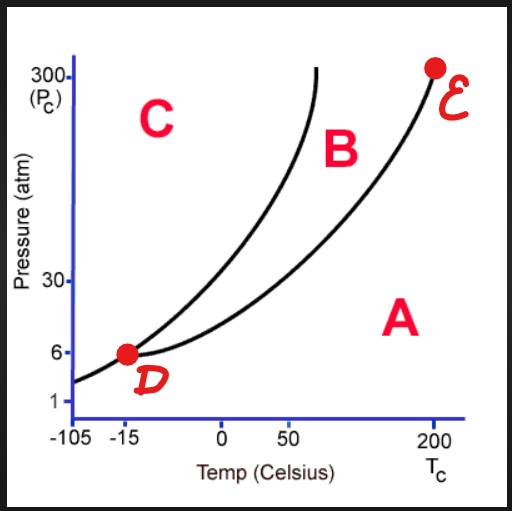
D
Triple Point
44
New cards
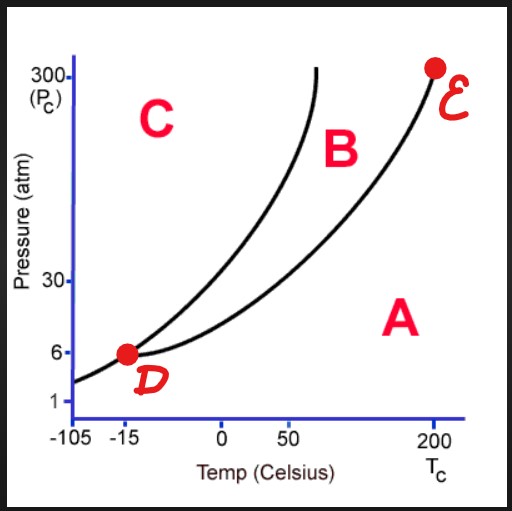
E
Critical Point