Formal Charge
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Oxygen
0- 2 single bonds, 2 LP
+1- 3 single bonds , 1 LP
-1- 1 single bonds, 3 LP
Nitrogen
0- 3 single bonds, 1 LP
+1- 4 single bonds , 0 LP
-1- 2 single bonds, 2 LP
Carbon
0- 4 single bonds, 0 LP
+1- 3 single bonds , 0 LP
-1- 3 single bonds, 1 LP
Formal charge =
Valence e- - (bonds + LP)
cyclopropane
(triangle) c3h6
cyclobutane
Square C4H8
cyclohexane
C6H12 (hexagon)
cis bonds
same side, tight steric interactions
trans bonds
opposite sides, more stable, force is more spread out
Electronegativity pattern
increases up and to the right
Alkane
arrow with R group at the end
Cn H2n+2
Alkene
C=C
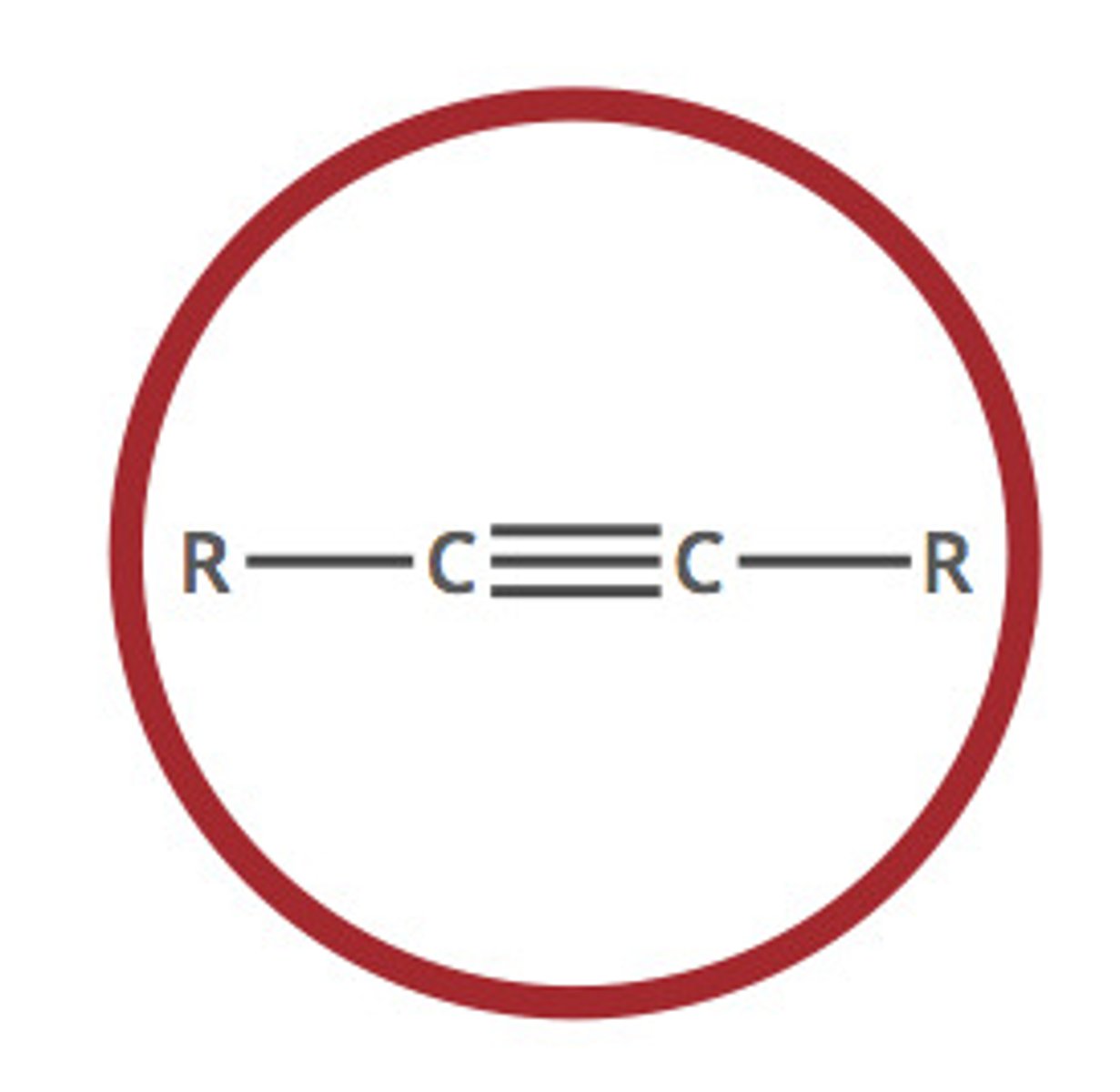
Alkyne
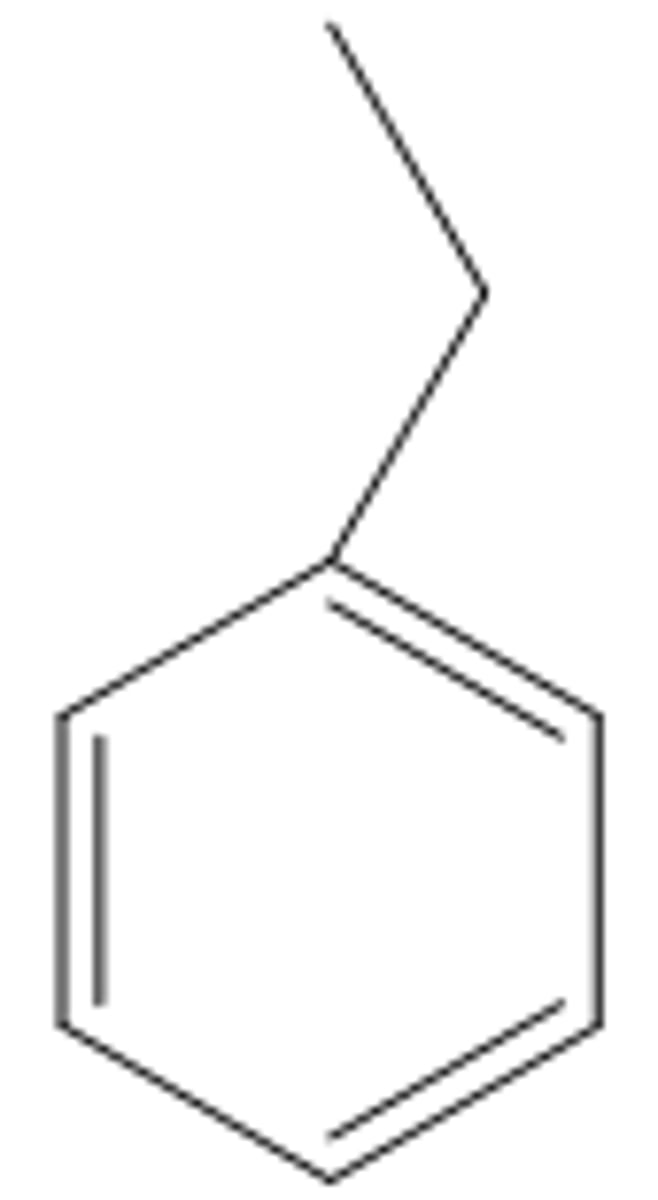
Benzene
Consists of a ring of six carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds.
Fluoro
Bromo
Chloro
Iodo
single bonded elements
Alcohol
R-OH
Ether
R-O-R
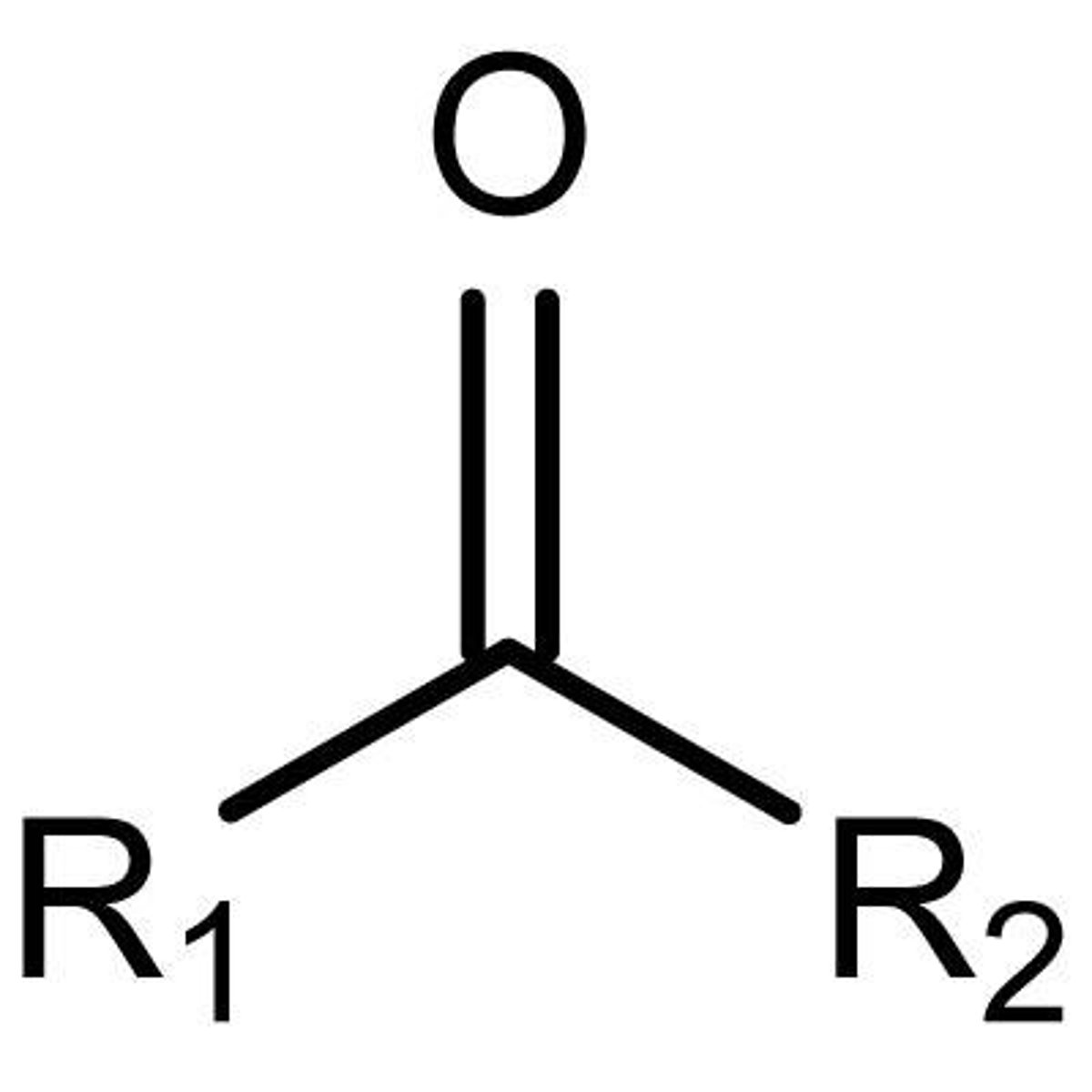
Ester
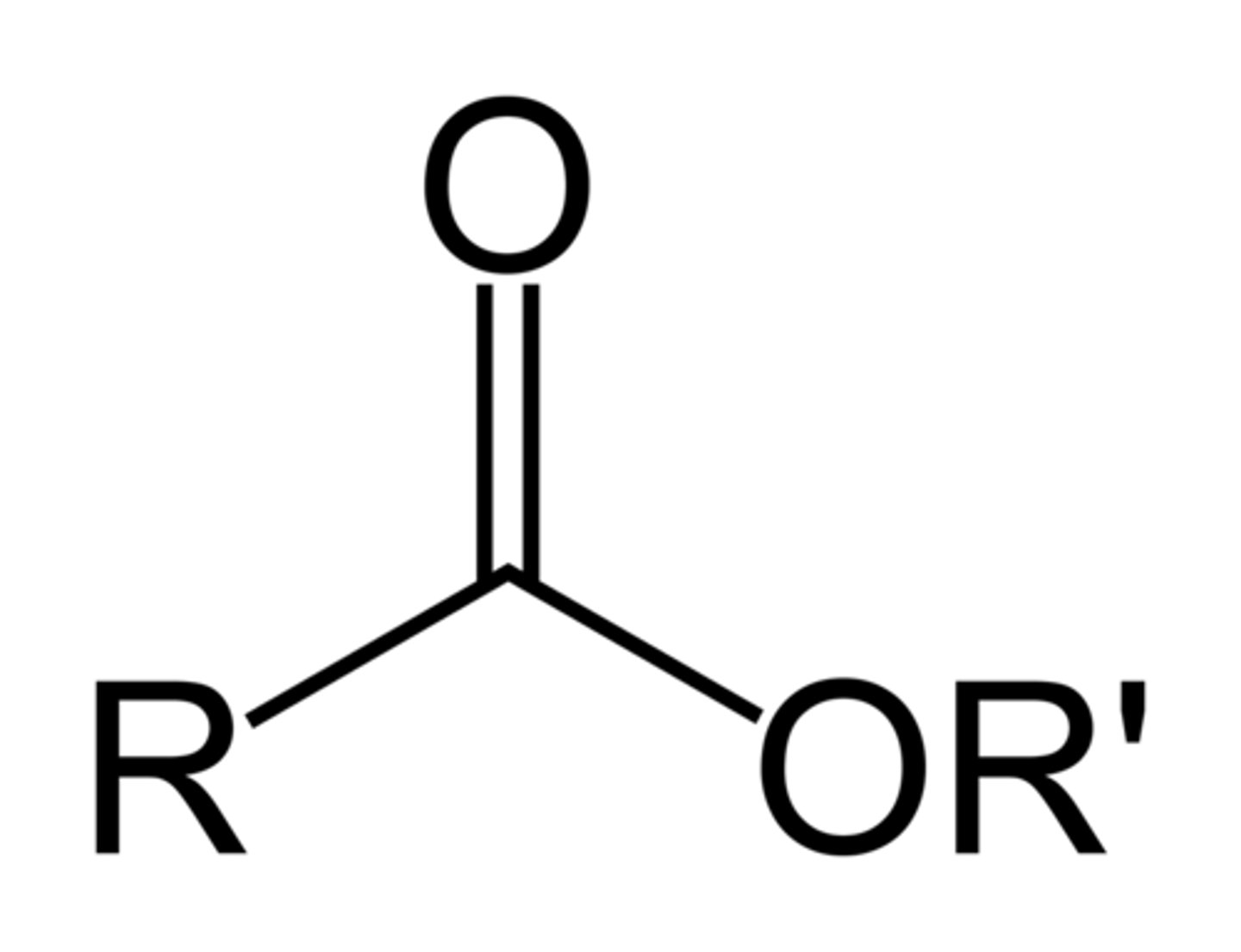
ketone
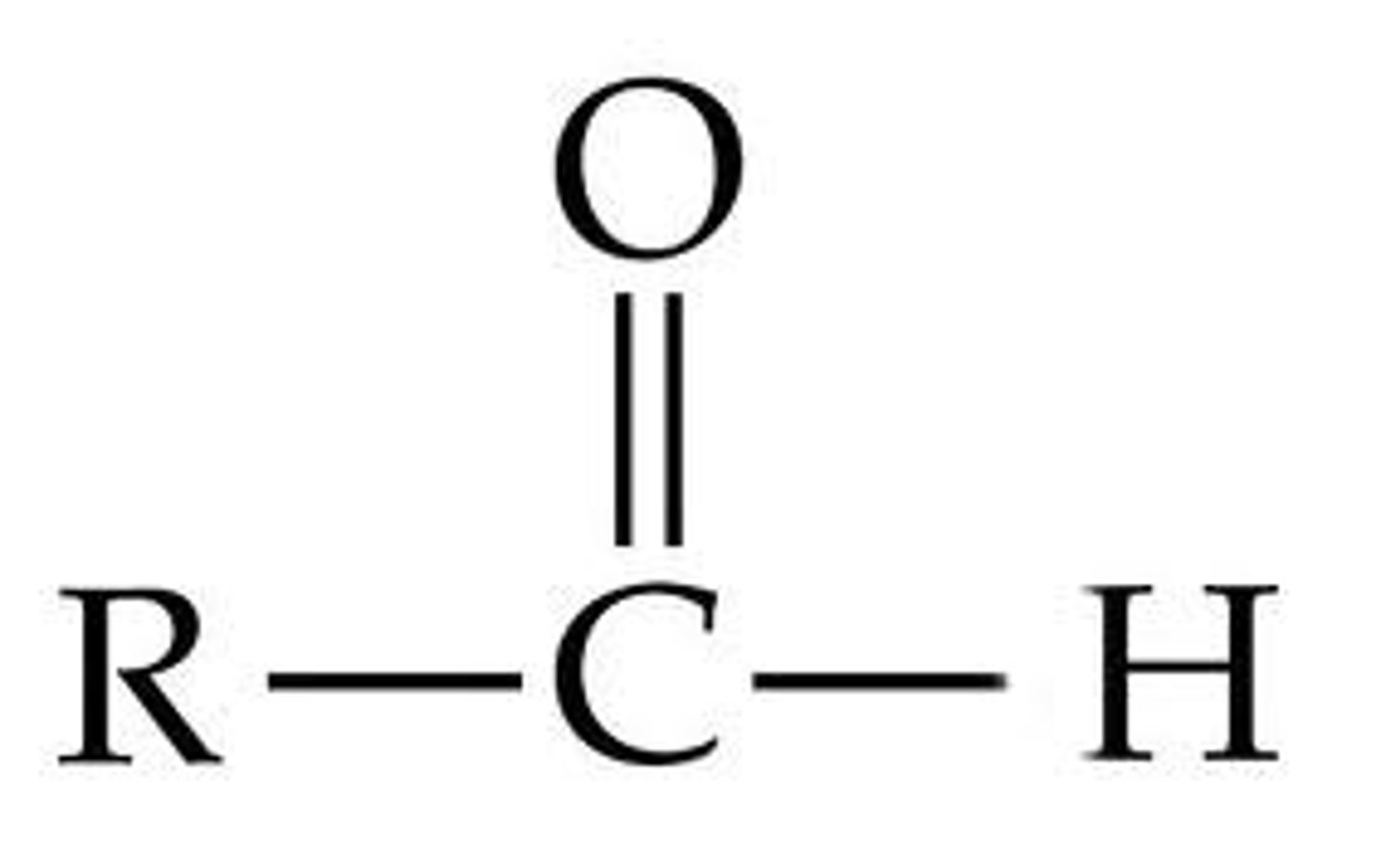
aldyhyde
Acid Chloride
R-C=O-Cl
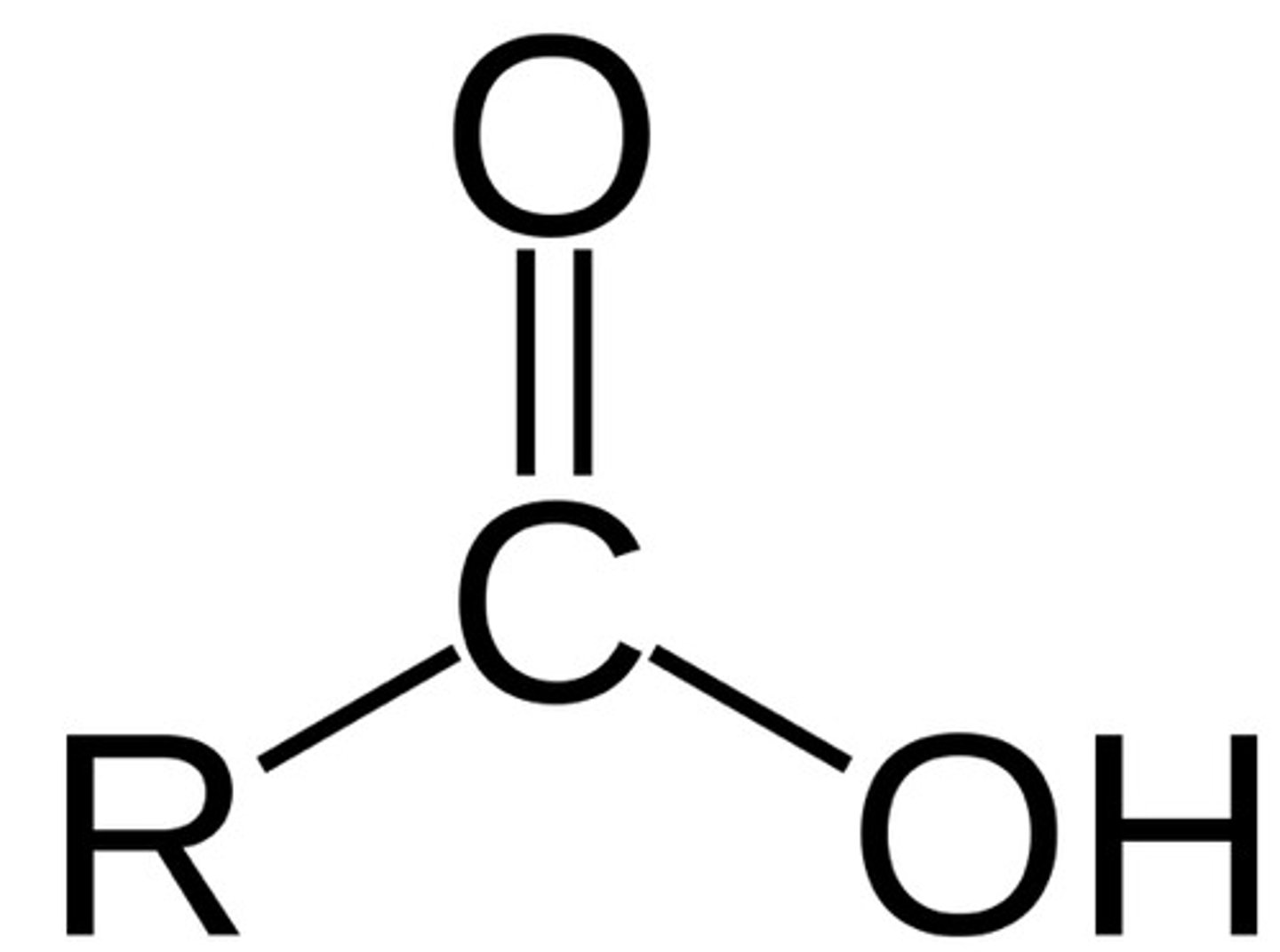
carboxylic acid
Thiol
R-SH
Thioether
R-S-R
Disulfide
R-S-S-R
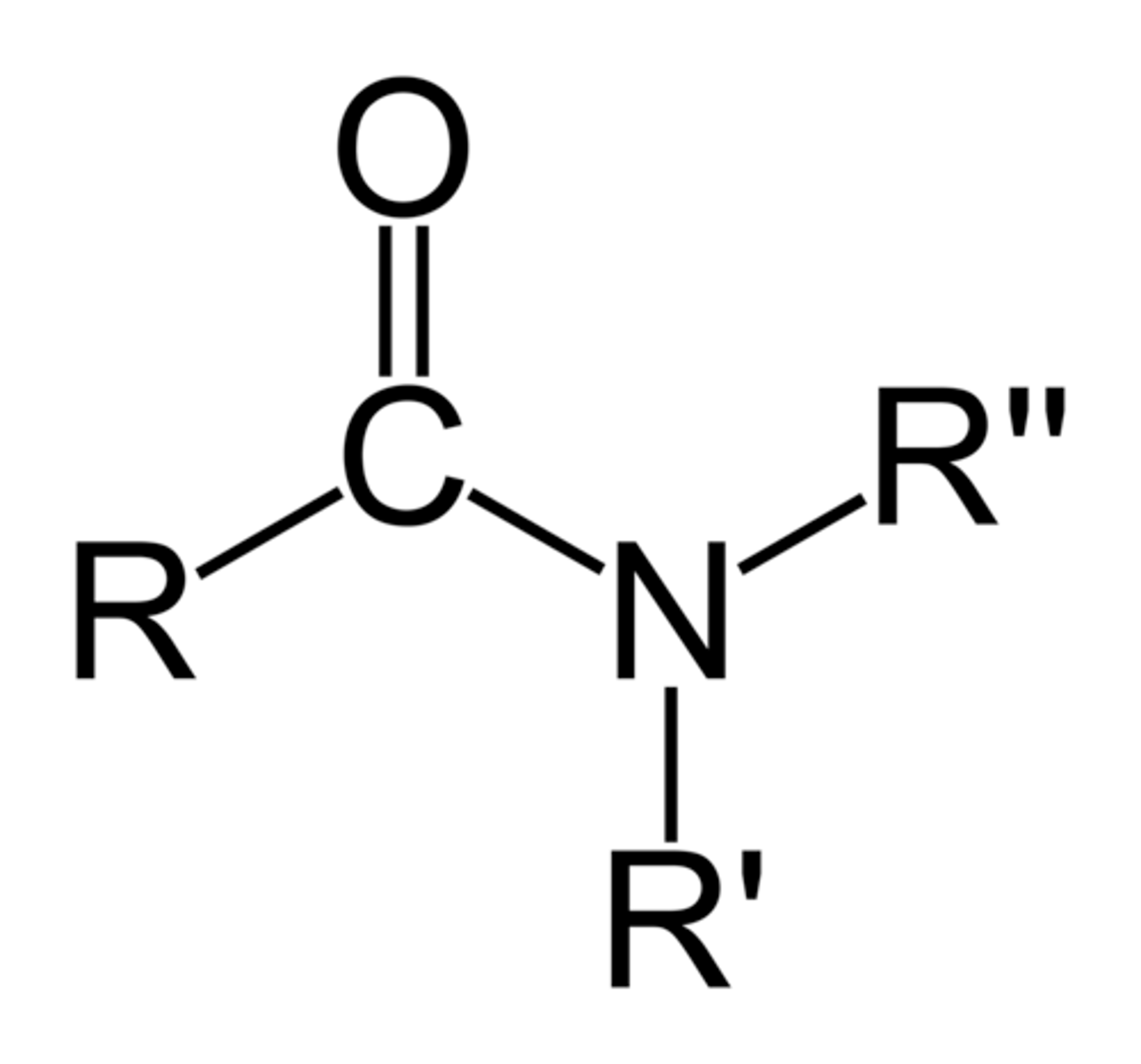
AMIDE
Primary Amine
Secondary
Tertiary
R-NH2
R-NH-H2
R-N-R (extra R below N)
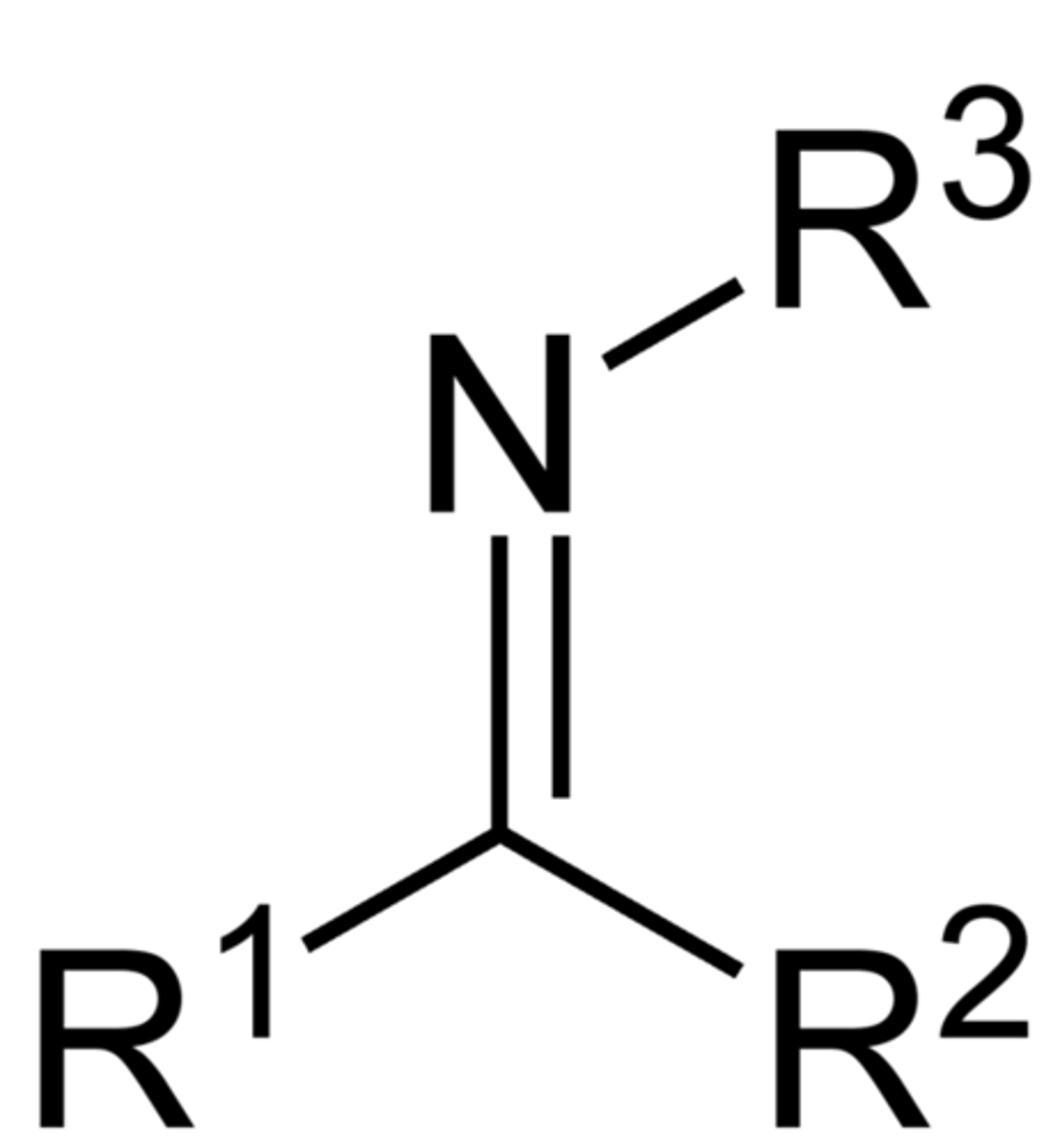
Secondary Imine
(primary)
primary has one less R
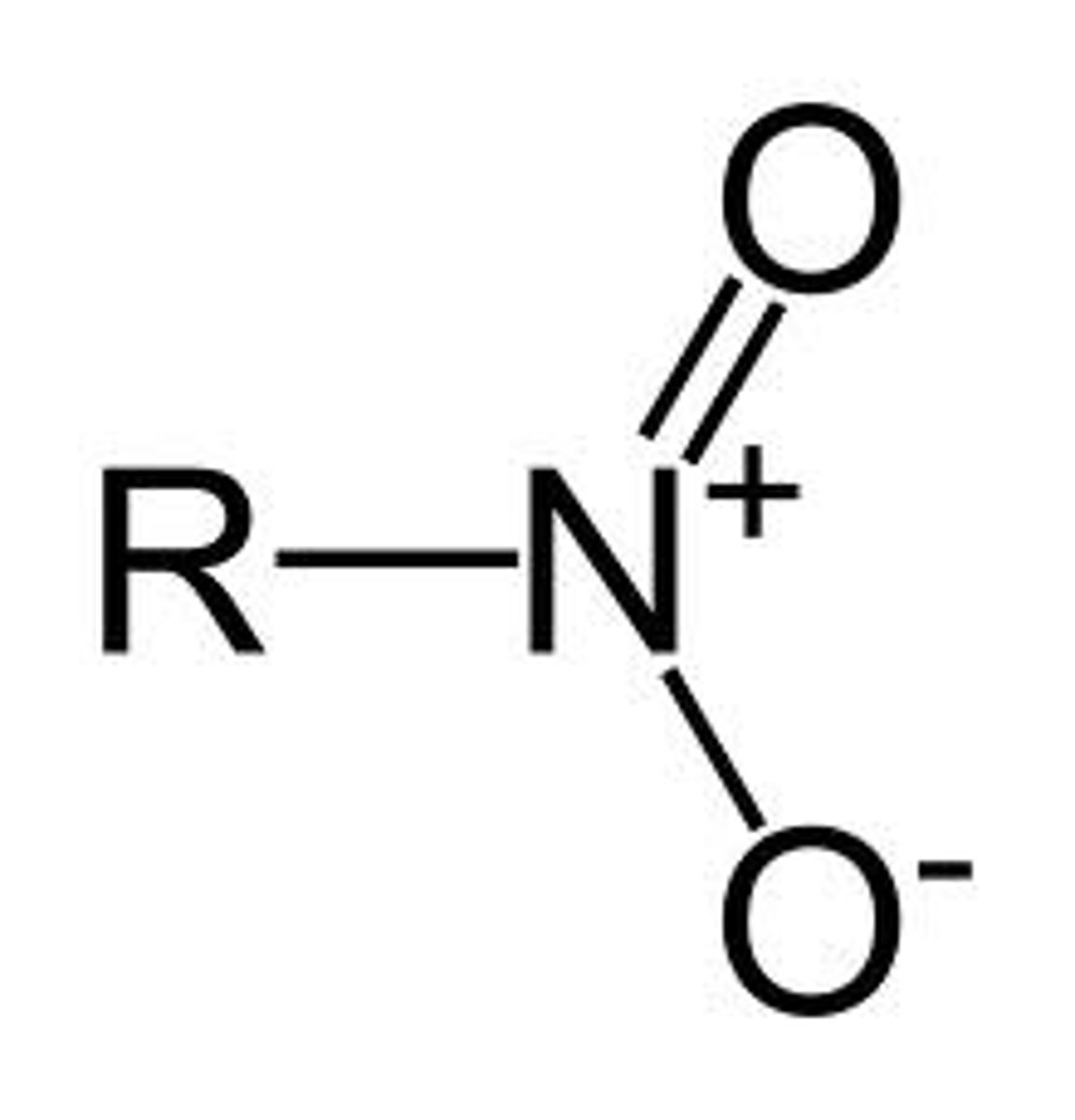
nitro
Nitride
carbon by numbers (chains)
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12
meth,eth,prop,but,pent,hex,hept,oct,non,dec,undec,dodec
Branched structures are called
Isomers
Constitutional isomers
same formula different structure
Primary carbon is bonded too
1C and 3 others
Secondary carbon
2 C and 2 other
Tertiary carbon
3 C and 1 other
quaternary carbon
4 carbons no other
propyl
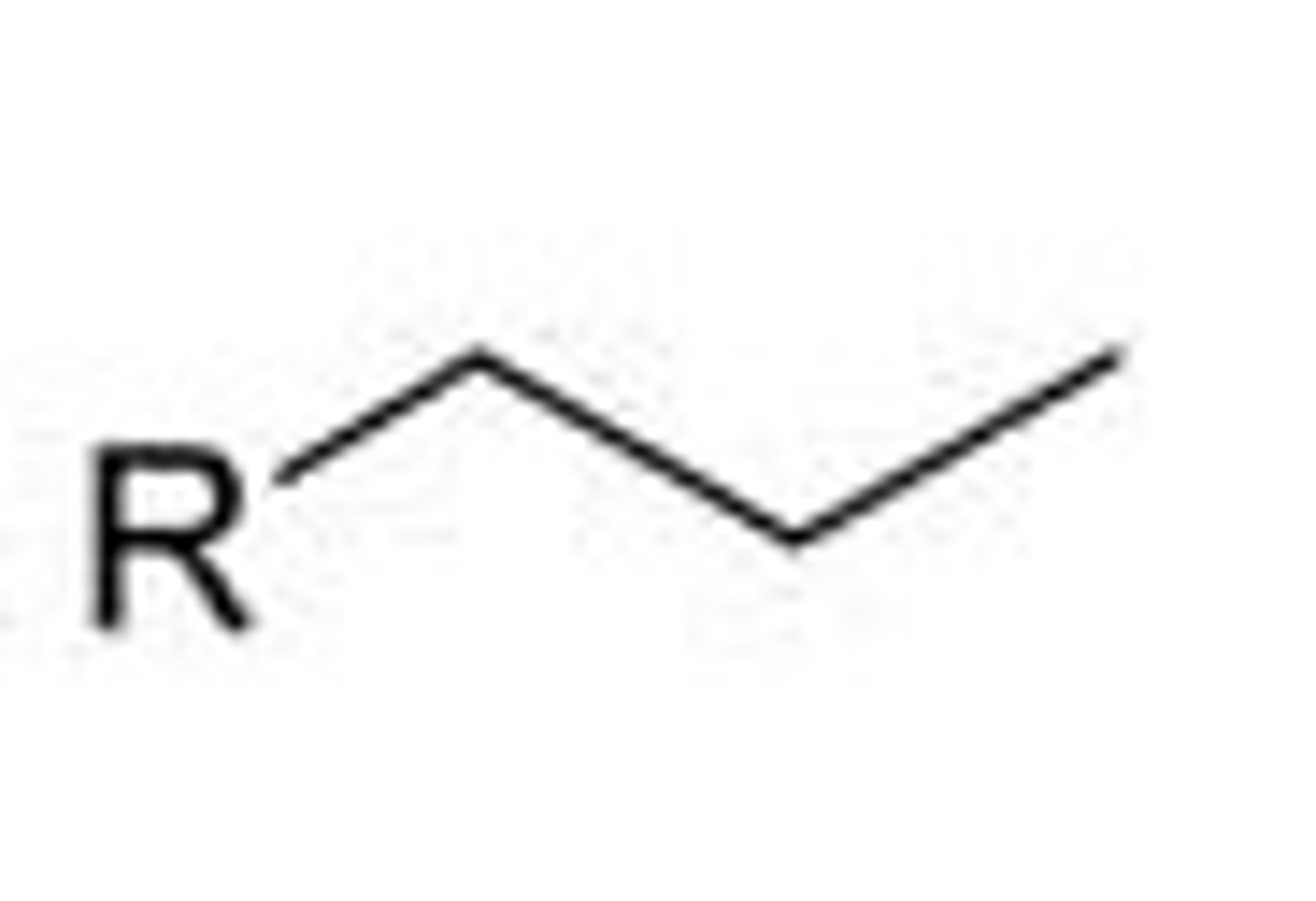
iso propyl
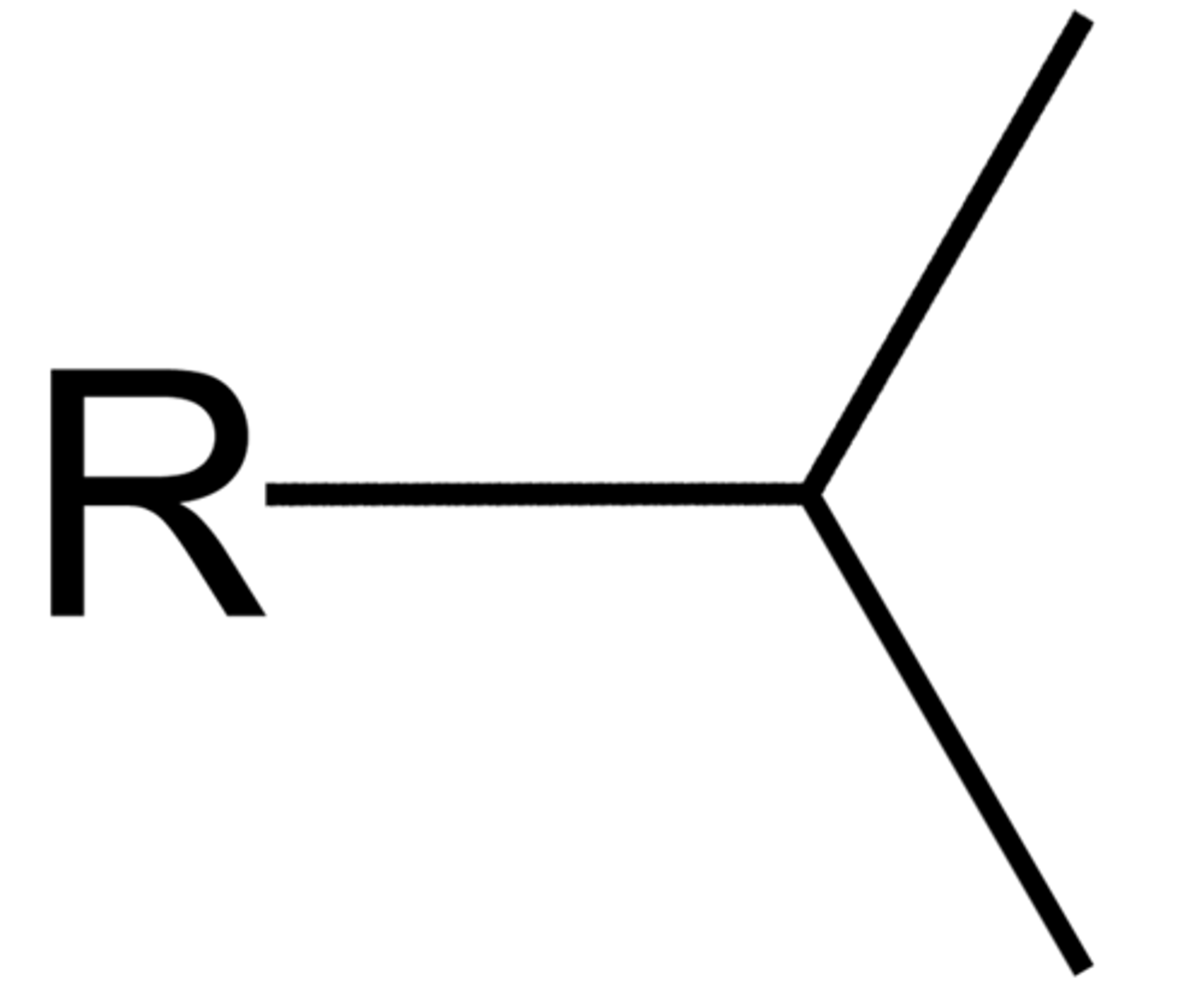
Butyl
-CH2CH2CH2CH3
iso butyl
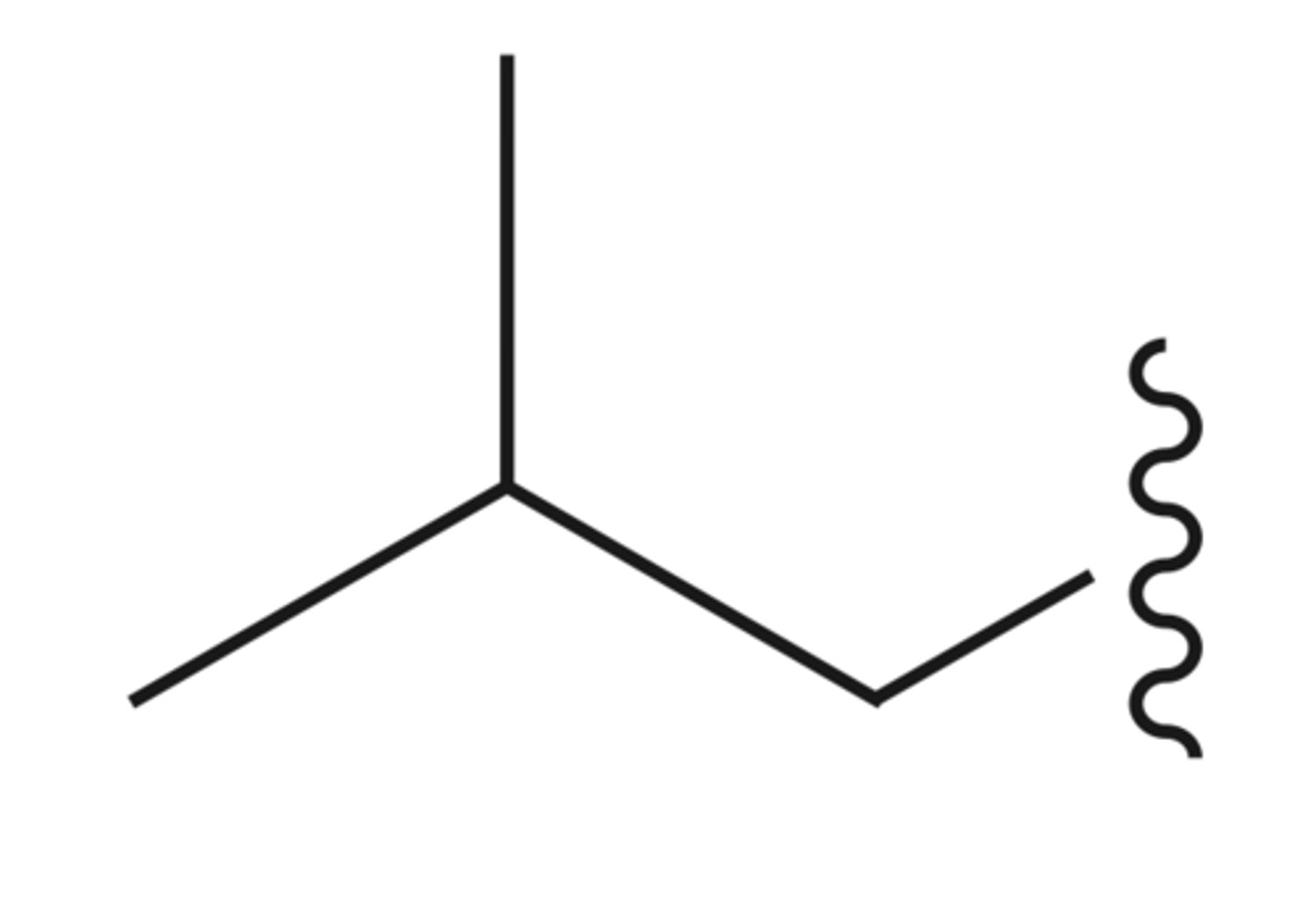
sec butyl
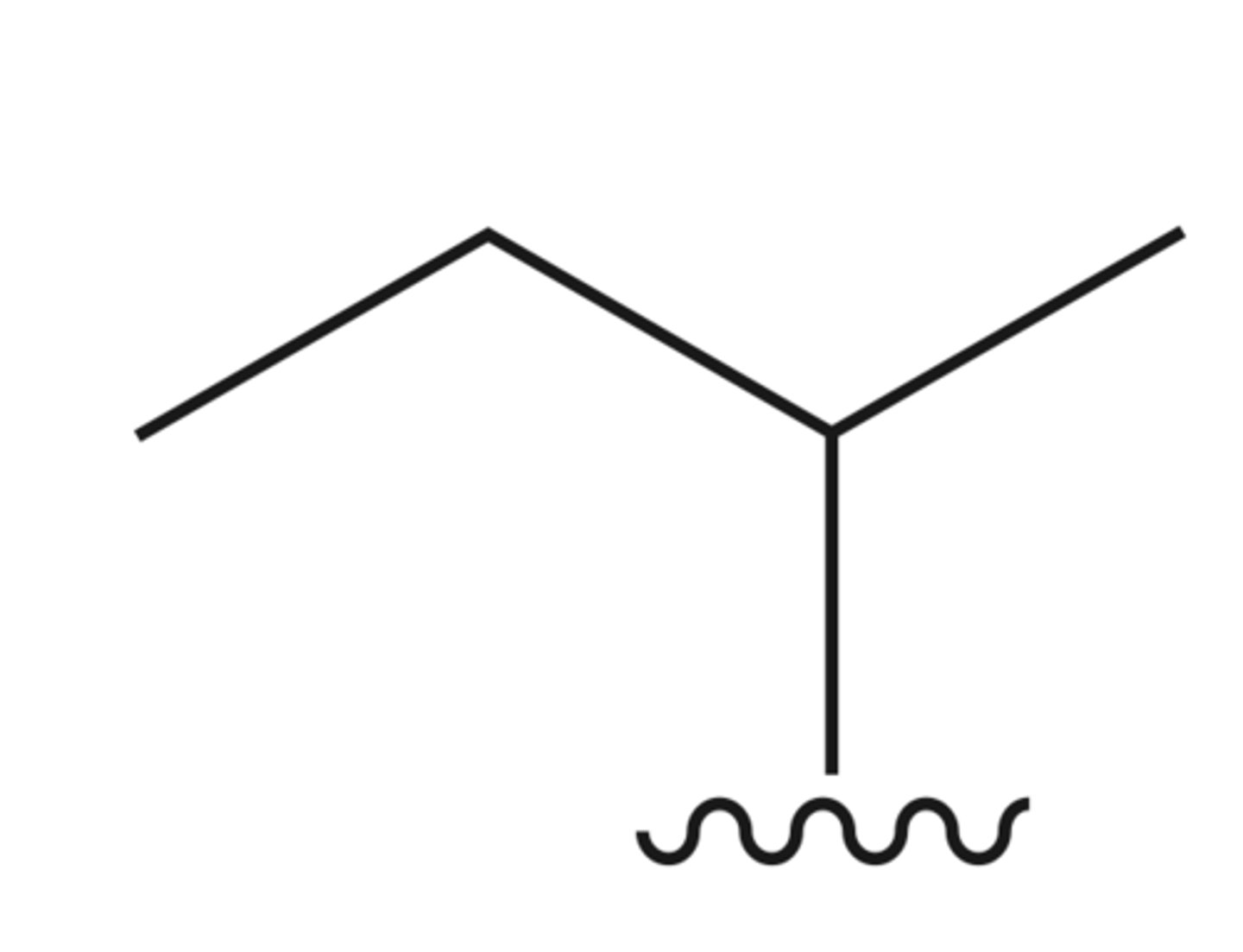
Tert Butyl
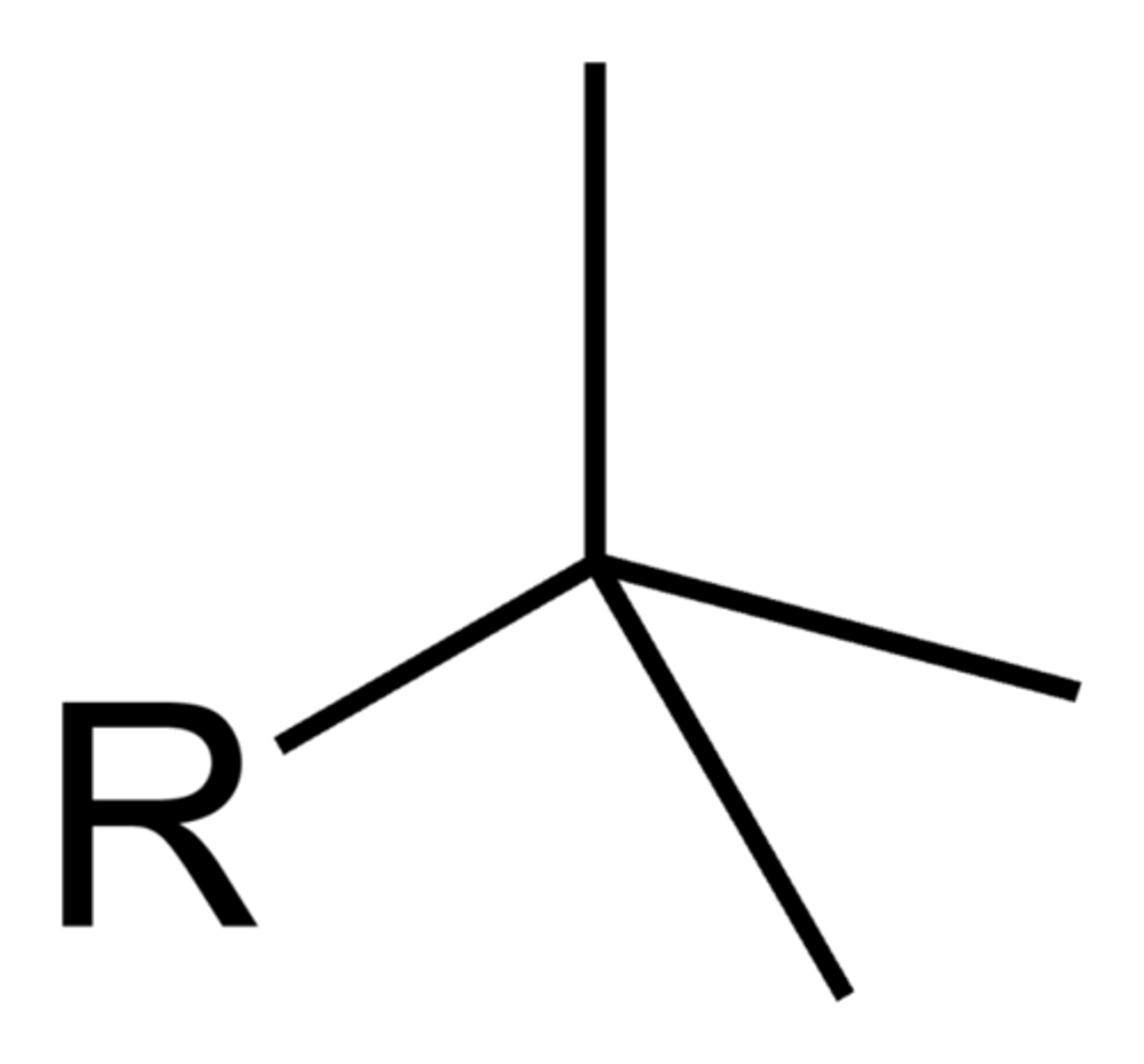
methyl
ch3 to ch to ch2 ch2
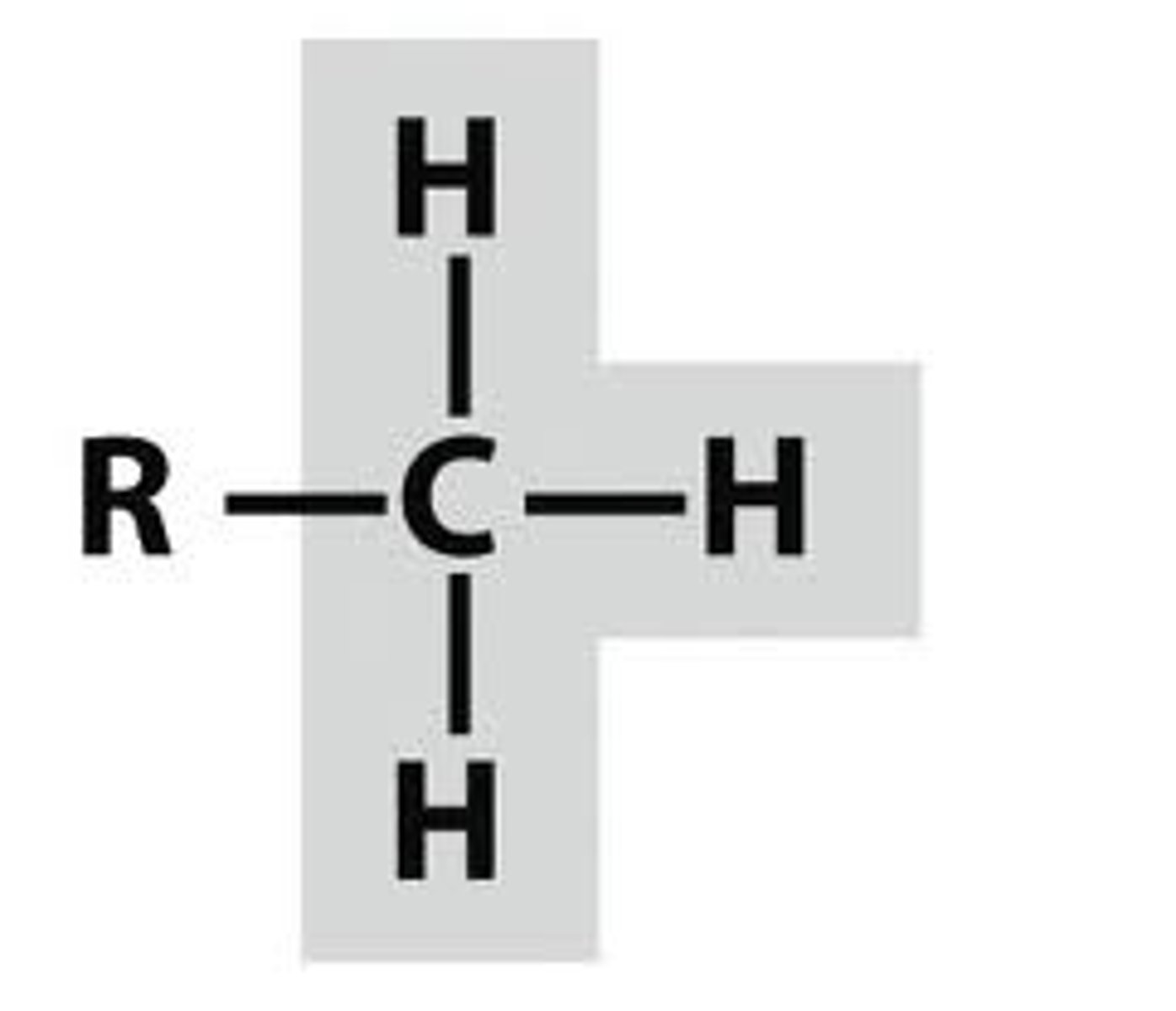
ethyl group
zig to branch
Rules for naming - ALKANES
1. identify longest C chain
2. number C so that the substituents get the lowest #, if same number is obtained, go by alphabet
3.write name with alphabet subs. seperate # and words with dash and # with comma. Chain name comes last
Rules for naming - Cyclic
1. # carbon ring
2.number sub. with lowest #, alphabet if 2, lowest # if 3
Functional priority groups rules
1. find c chain w/ highest priority group
2. #cahin/ring so highest FGgets lowest #
3. change ending pf parent name to suffix name of whatever FG is present.
Highest priority
Carboxylic acid - oic acid
lowest priority
Alkane - ane
eth/oxy
2 carbon chain on ether/ oxygen (o/\Ch3
meth/oxy
one carbon chain/ oxygen o-
prop/ oxy
3 carbon chain/ oxygen 0/\/
acid
contains the atom that is e- deficient. Positive/ partial positive, electrophile - likes e-, attracted to neg/partial neg charge.
base
contains atoms that are e- rich. Neg/ partial neg, nucleophile- likes nucleus, attracted to +/ partial +
Bronsted-Lowry acid
proton donor (H+)
Bronsted-Lowry base
proton acceptor
Lewis acid
electron pair acceptor
Lewis base
electron pair donor
conjugate acid
losses a proton (was formally an acid)
Conjugate Base
gains a proton (formally a base)