BY 124- Ch 37 Gibbons
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Why do plants need minerals from the soil?
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other minerals are essential for plant growth
They play important roles in both cell structure and cell function
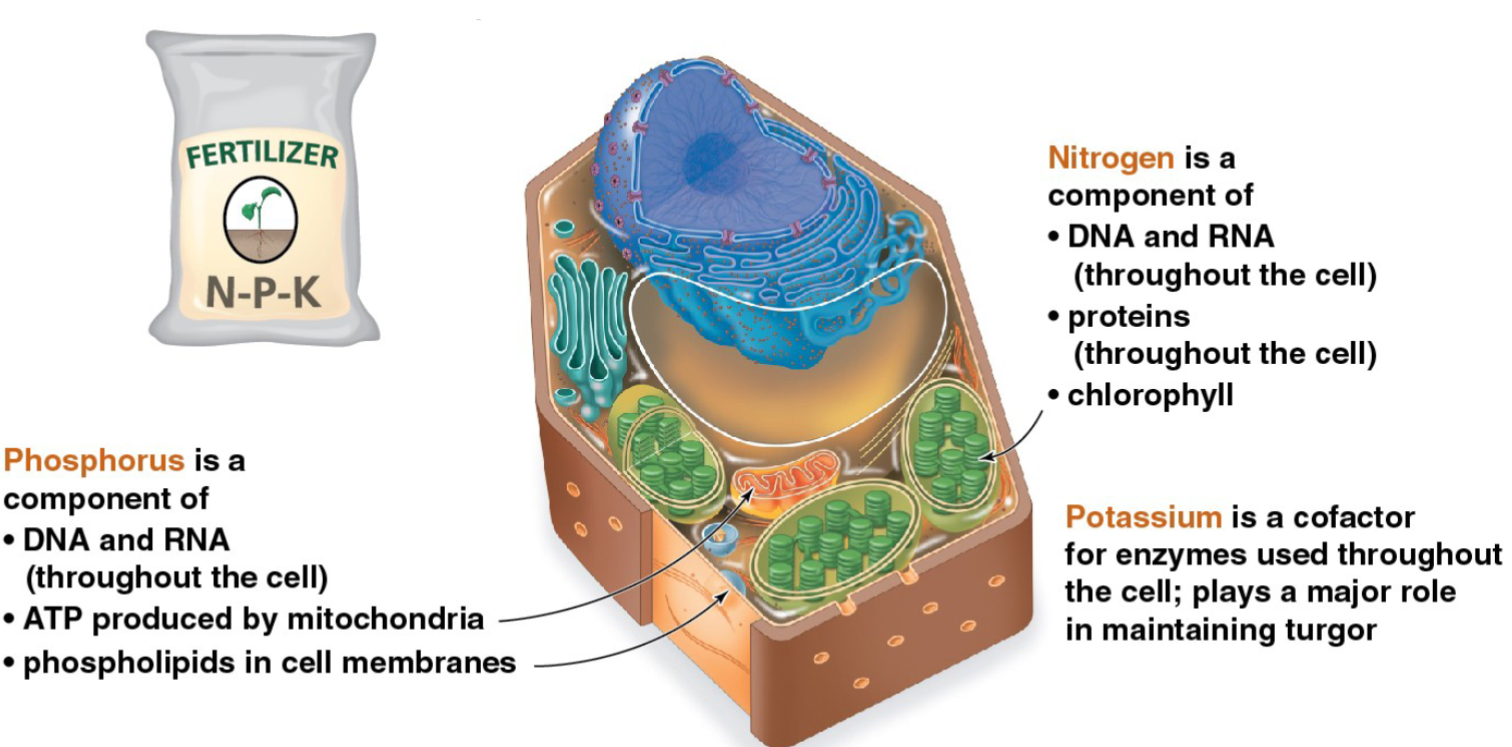
Water, air, and soil minerals all contribute to plant growth
80–90% of a plant’s fresh mass is water
96% of a plant’s dry mass is from CO2 assimilated into carbohydrates during photosynthesis
4% of a plant’s dry mass is inorganic substances
from soil
Essential Elements
Definition: Chemical elements that are required for reproduction and completion of life cycle
There are 17 essential elements for plants
Researchers use hydroponic culture to determine which chemical elements are essential
Nine essential macronutrients
Nine of the essential elements are macronutrients (plants require them in relatively large amounts)
carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, calcium, and magnesium
Nitrogen contributes the most to plant growth and crop yields
Eight essential micronutrients
Eight essential elements for plants are micronutrients (required only in very small amounts)
chlorine, iron, boron, manganese, zinc, copper, nickel, and molybdenum
Micronutrients function as cofactors, nonprotein helpers in enzymatic reactions
Where does the majority of the dry mass of a plant come from?
A. Nutrients, like nitrogen, from the soil
B. Water from the soil
C. CO2 from the air
D. There’s no way to know.
C. CO2 from the air
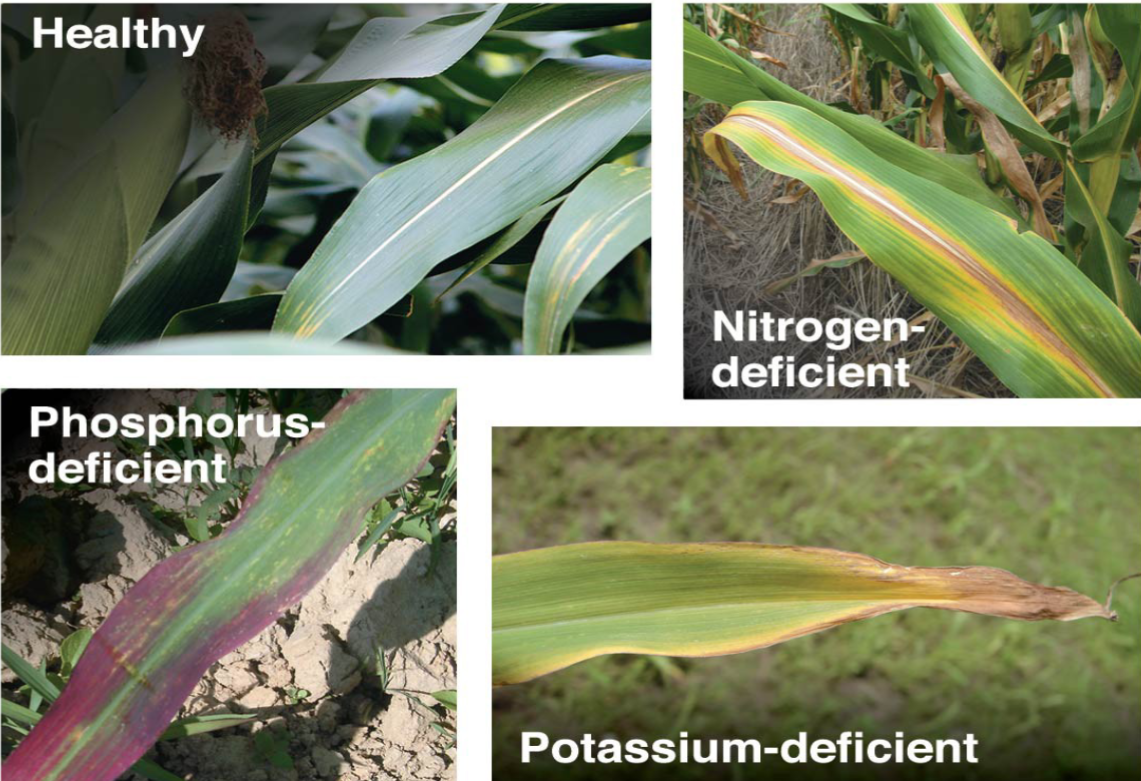
Mineral deficiency
Depend on the nutrient’s function and mobility
within the plant
The most common deficiencies are those of
nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus

Global Climate Change and Food Quality effect on plants
Climate change (increased CO2 and rising temps)
is predicted to cause (or is causing):
Increase in Global food production but only in certain parts of the world
Decline in the nutritional quality of wild and crop plants, possibly due to insufficient uptake of nutrients by plants
Decline in pollinators, maybe from declining quality of their food source
The difference between macronutrients and micronutrients is that _____.
A. the molecules of macronutrients are larger than those of micronutrients
B. macronutrients are essential for physiological function of plants, while micronutrients amplify plant growth if they are available
C. macronutrients are needed for growth, while micronutrients are needed only for reproduction
D. macronutrients are required by plants in larger quantities than are micronutrients
D. macronutrients are required by plants in larger quantities than are micronutrients
Symbiosis with both species benefitting from close interactions
Mutualisms
Plants-Bacteria Mutualism
Plants have mutualistic relationships with soil bacteria
Dead plants provide energy needed by soil-dwelling microorganisms
Secretions from living roots support a wide variety of microbes in the near-root environment
Fungus-Bacterium Mutualism
Lichen- mutualistic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic partner
The cyanobacterium provides food (through photosynthesis); the fungus provides anchorage, protection, minerals, and water
Animal-Bacterium Mutualism
Puffer fish form a mutualism with a bacterium that produces a nerve toxin called tetrodotoxin
The fish gains a chemical defense, the bacteria live in a
high nutrient, low competition environment
Animal-Fungus Mutualism
Leaf-cutter ants harvest leaves which they feed to
fungal gardens in their nests
The ants are able to eat part of the fungus
Plant/Algae–Bacterium Mutualism
Aquatic fern Azolla forms mutualisms with nitrogen-fixing
cyanobacteria
The cyanobacterium provides the fern with nitrogen, while
the fern provides it with food (sugars)
Plant-Fungus Mutualism
Most plant species have mutualisms with mycorrhizal fungi
The fungus absorbs food (sugars); the fungus expands the
absorptive surface of the plant roots for uptake of water and minerals
Plant–Animal Mutualism
Acacia plants provide carbohydrate–rich nectar to ants; ants protect them from predators and competitors
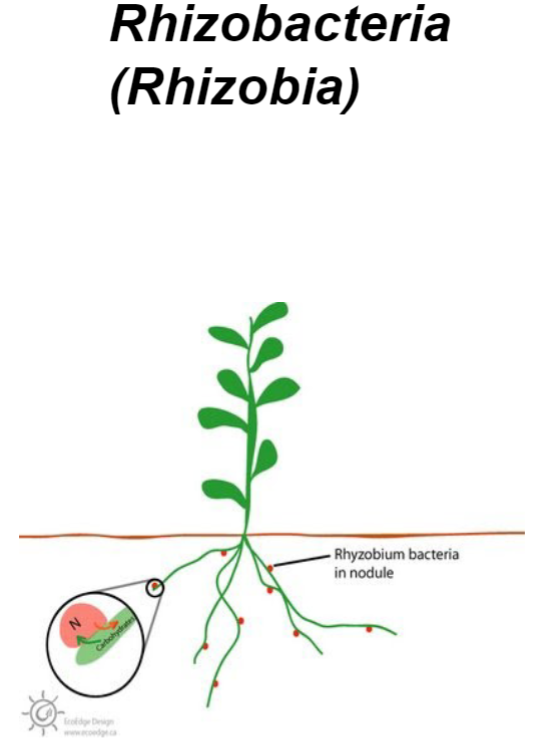
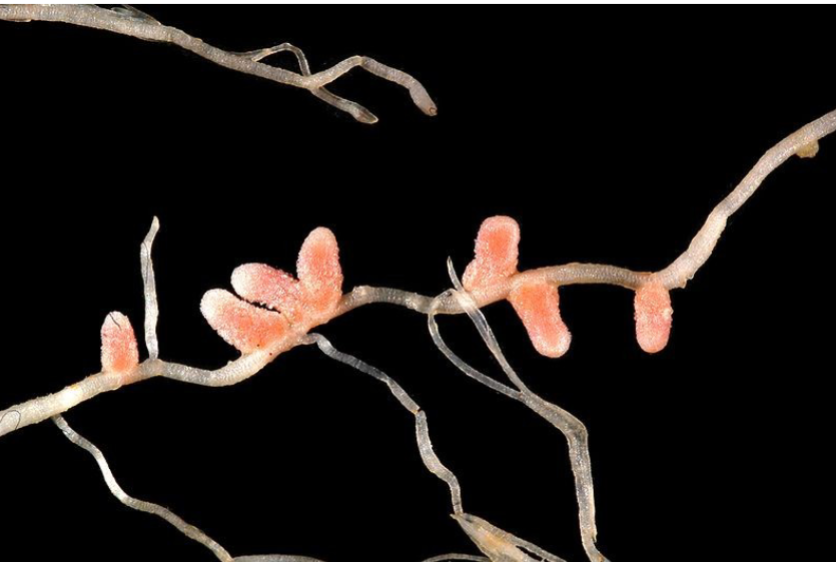
Rhizobacteria
Rhizobacteria- mutualistic bacteria that live in close association with plant roots
Plants provide food (sugars); rhizobacteria help the plant in many ways
producing antibiotics that protect roots from disease
absorbing toxic metals or increasing nutrient availability
converting nitrogen gas into forms usable by the plant
producing chemicals that stimulate plant growth
Bacteria in the Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen is required in large amounts by plants, and is abundant in the atmosphere as N2
Nitrogen deficiency usually the most limiting nutrient to plant growth
Plants can only absorb nitrogen as NO3– or NH4+
Some soil nitrogen derives from inorganic sources, but most comes from the activity of soil bacteria
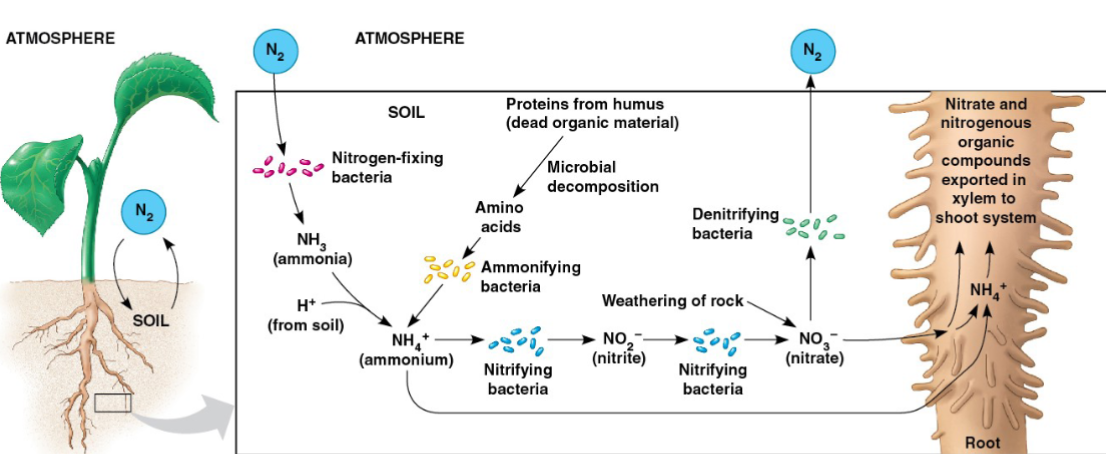
Nitrogen cycle
natural processes that transform nitrogen and nitrogen-containing compounds
Nitrification
Soil NO3– is formed in a two-step process called nitrification
Nitrifying bacteria oxidize ammonia (NH3) to nitrate to NO3–
Plant enzymes convert NO3– to ammonium (NH4+), which is incorporated into organic compounds
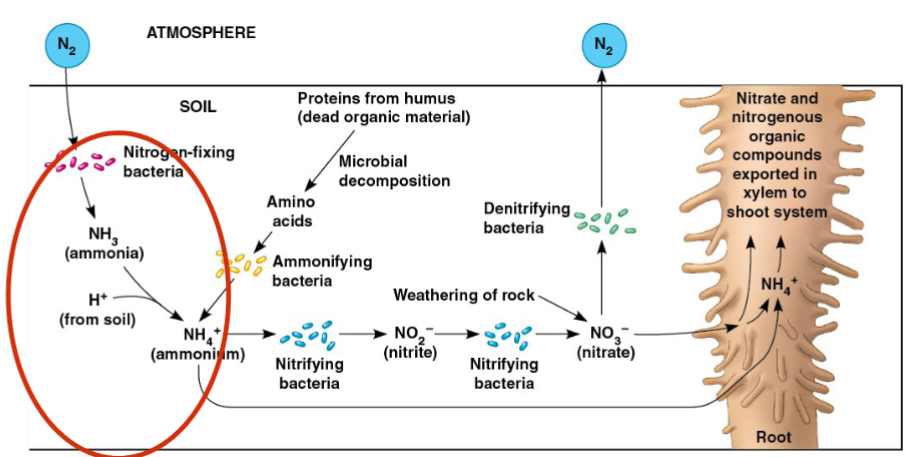
How do plants acquire N in a usable form? (NH4+)
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert N2 into NH3 (ammonia); NH3 picks up an H+ in the soil solution and forms NH4+
Ammonifying bacteria break down dead organic
compounds and release NH4+
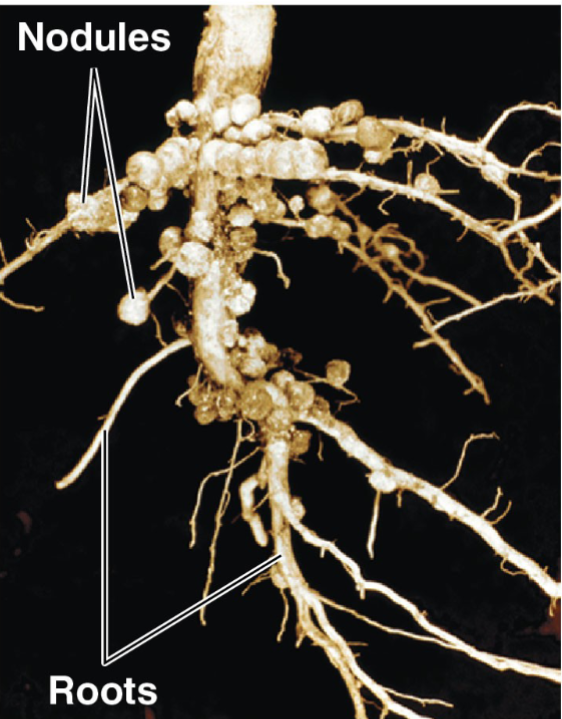
Bacteria and Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen is abundant in the atmosphere but unavailable to plants because of the triple bond between atoms in N2
Nitrogen fixation by bacteria (like Rhizobium) make atmospheric Nitrogen available to plants
The rhizobia form nodules on the roots of legumes in a mutualistic relationship.
Nitrogen Fixation and Agriculture
Crop rotation takes advantage of the agricultural benefits of symbiotic nitrogen fixation
When legumes (with Rhizobia) are rotated with non-legumes (like corn), you can recover fixed nitrogen that was depleted by a nitrogen depleting crop.
Fungi and Plant Nutrition
Mycorrhizae are mutualistic associations of fungi and roots
The host plant provides the fungus with sugar
The fungus increases the surface area for water and mineral uptake by the host plant by promoting root branching
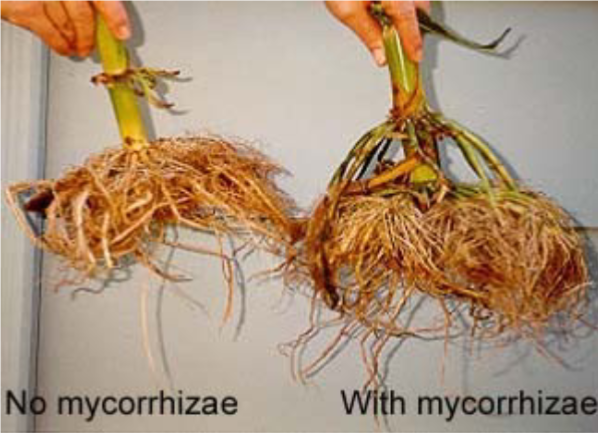

Mycorrhizae and Plant Evolution
Early land plant fossils show associations with mutualistic fungi (from about 400 to 500 million years ago, which would be a very harsh environment)
Early plants lacked the ability to extract essential nutrients from the soil, while fungi were unable to produce carbohydrates
The mycorrhizal association between early land plants and fungi allowed both to exploit the terrestrial environment
The most limiting nutrient for plants is usually
A. Nitrogen
B. Carbon
C. Phosphorous
D. Potassium
E. Sodium
A. Nitrogen
Agricultural and Ecological Importance of Mycorrhizae
Farmers inoculate seeds to promote mycorrhizal mutualisms with their crops
Garlic mustard (invasive exotic plant) disrupts interactions between native plants and their mycorrhizal fungi, by inhibiting growth of mycorrhizae
Legumes (such as soybeans) commonly obtain their nitrogen through a mutualistic association with _____.
A. nitrifying bacteria, which oxidize ammonium to nitrite
B. ammonifying bacteria, which convert organic nitrogen to ammonium
C. denitrifying bacteria, which convert organic nitrite to ammonium
D. nitrifying bacteria, which extract nitrogen from decomposing animals
E. nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which convert gaseous nitrogen to ammonium
F. Mycorrhizae, which increase the mass of their roots
E. nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which convert gaseous nitrogen to ammonium
Other Nutritional Adaptations in Plants:
Some plants have nutritional adaptations that use other organisms in nonmutualistic ways
Epiphytes, parasitic plants, and carnivorous plants
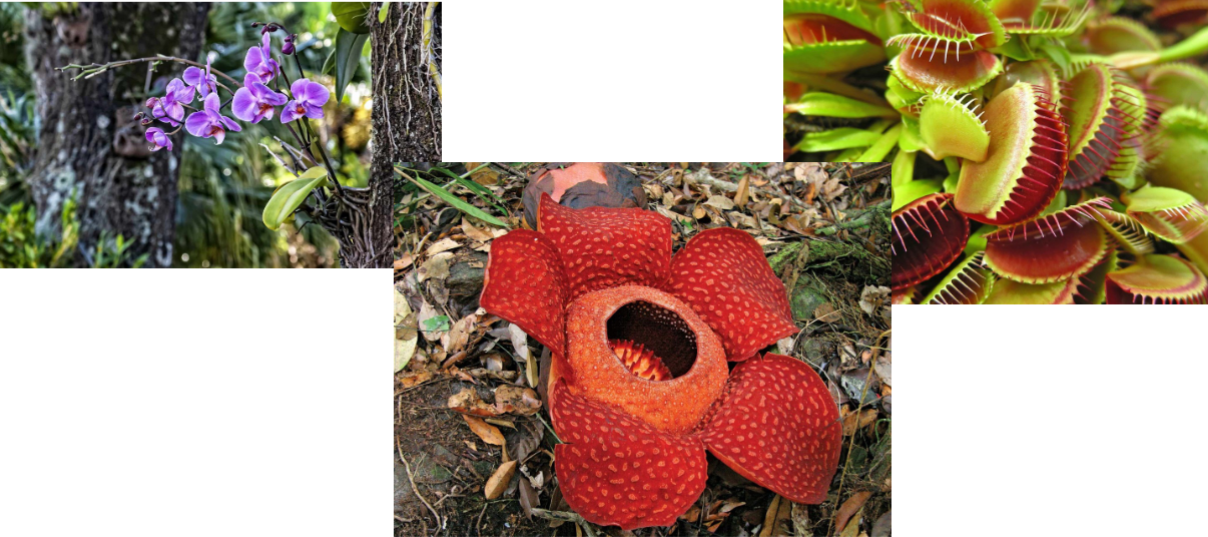

Epiphyte
An epiphyte grows on another plant and obtains water and minerals from rain
Epiphytes do not tap into hosts for sustenance
Examples include staghorn ferns, bromeliads, and many orchids

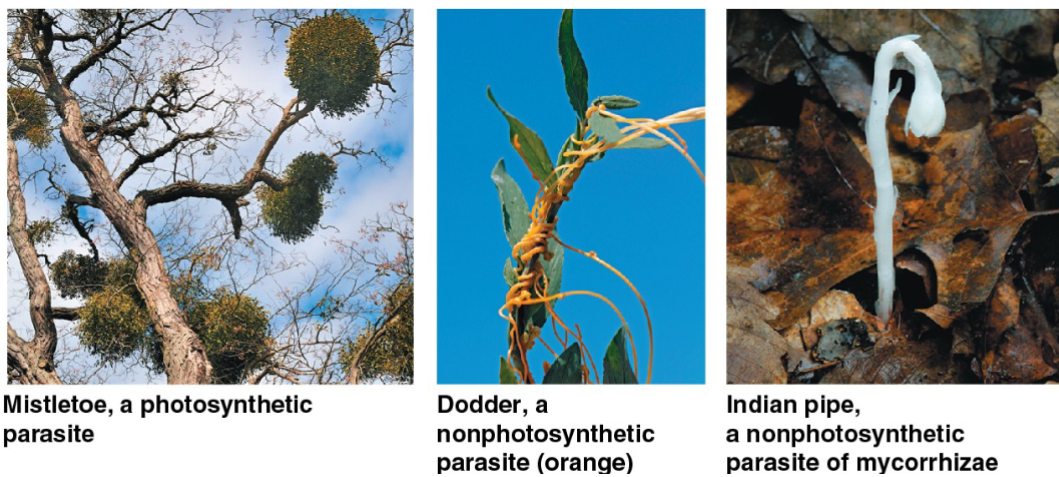
Parasitic plants
Parasitic plants absorb water, minerals, and sugars from their living host plant
Some species photosynthesize, but others rely entirely on the host plant for sustenance
Some species parasitize the mycorrhizal hyphae of other plants

Carnivorous Plants
Carnivorous plants have adaptations for trapping insects and other small animals
They are photosynthetic, but obtain nitrogen by killing and digesting mostly insects
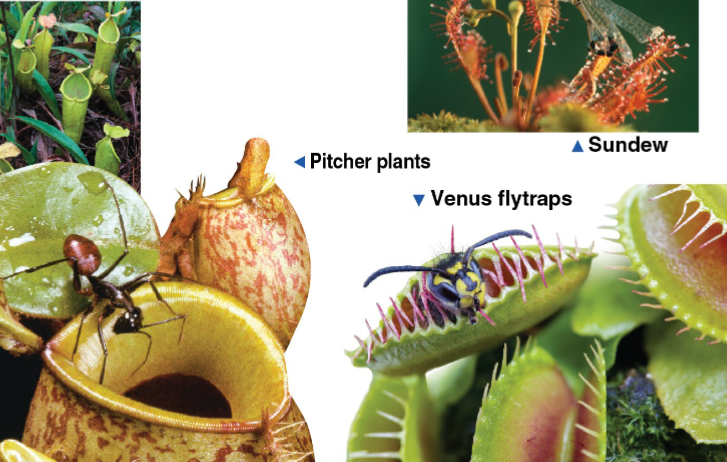
True or False: Parasitic plants and carnivorous plants are non-photosynthetic
A. True
B. False
B. False
By trapping insects, carnivorous plants obtain __________, which they need __________.
sugars; because they can't make enough in photosynthesis
nitrogen; to make protein
nitrogen; to make sugar
phosphorus; to make protein
water; because they live in dry soil
nitrogen; to make protein
Which of the following nutrient-deficiency symptoms is correctly matched with the deficient nutrient?
poor growth; nitrogen
wilting; boron
general chlorosis in young leaves; carbon
mottling of older leaves, with drying of leaf edges; calcium
reduced internode length; zinc
reduced internode length; zinc
A cattle farmer is forced to use antibiotics to treat an outbreak of bacterial infections in his herd of cattle. The antibiotic is excreted by the cattle in their urine and feces and ends up in an irrigation ditch that provides water for a nearby soybean (a legume) farmer. The soybean farmer begins to notice that his soybean crop is not growing as well as usual.
What might be the cause of this change in the growth of the soybeans?
None of the listed responses is correct.
The antibiotic is toxic to the soybean plants and stunts their growth.
Bacteria in the water that contained the urine and feces affects soybean growth.
The antibiotic got into the soil and killed many of the bacteria that provide usable phosphorous to the soybeans.
The antibiotic got into the soil and killed many of the bacteria that provide usable nitrogen to the soybeans.
The antibiotic got into the soil and killed many of the bacteria that provide usable nitrogen to the soybeans.
Which of the following statements is correct regarding mycorrhizae?
Arbuscular mycorrhizae form a dense sheath over the surface of a plant’s roots.
Arbuscular mycorrhizae are less common than ectomycorrhizae.
Ectomycorrhizae penetrate the cell walls of a plant’s root cells.
Ectomycorrhizae form a dense sheath over the surface of a plant’s roots.
Ectomycorrhizae are the most common type of mycorrhizae.
Ectomycorrhizae form a dense sheath over the surface of a plant’s roots.
Soil can easily become deficient in ________, because these ions are negatively charged and do not stick to negatively charged soil particles.
magnesium
potassium
nitrate
calcium
ammonium
nitrate
Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship between plants and the mutualistic bacteria associated with them?
Endophytes and rhizobacteria both depend on plants for various nutrients.
Endophytes live between cells within a plant.
Endophytes and rhizobacteria both can enhance plant growth.
All of the listed responses are correct.
Rhizobacteria live in the rhizosphere, the soil surrounding a plant’s roots.
All of the listed responses are correct.
Crop rotation benefits agriculture by __________.
restoring the concentration of fixed nitrogen in the soil
using up all the fixed nitrogen in the soil
None of the listed responses is correct.
replenishing the concentration of magnesium in the soil
replenishing the concentration of phosphorous in the soil
restoring the concentration of fixed nitrogen in the soil
Nitrogen fixation is __________.
using nitrogen to build molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids
converting nitrogen in the air to a form usable by plants
performed by fungus inhabiting root nodules
recycling nitrogen from organic matter in the soil
absorbing N2 from the soil
converting nitrogen in the air to a form usable by plants
Fertilizers are usually enriched in __________.
iron, manganese, and zinc
calcium and boron
all essential nutrients
nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
molybdenum, copper, and magnesium
nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
Which of the following statements correctly describes macronutrients?
Examples of macronutrients are iron, zinc, and copper.
Plants require macronutrients in relatively small amounts.
Plants require macronutrients in relatively large amounts.
Macronutrients function in plants mainly as cofactors.
The macronutrient nitrogen contributes the least to crop growth and yield.
Plants require macronutrients in relatively large amounts.
All of the following statements regarding soil pH are correct except ________.
Soil pH below 5 allows toxic aluminum ions to be absorbed by plants.
Plants prefer basic soil pH.
Soil pH should be matched to a crop’s mineral needs.
Soil pH influences mineral availability.
Plants prefer slightly acidic soil pH.
Plants prefer basic soil pH.
Which of the following processes occurs in the nodules of legume roots?
pH regulation
cation exchange
nitrogen fixation
All of the listed responses are correct.
carbon fixation
nitrogen fixation
Which is true regarding mineral deficiency symptoms in plants?
Deficiency symptoms of immobile nutrients will show up first in older organs.
Deficiency symptoms of freely moving nutrients will show up first in younger organs.
Symptoms of mineral deficiency always show up in older leaves first.
Growing tissues would show signs of mineral deficiency of mobile nutrients after older tissues.
Symptoms always show up in younger leaves first.
Growing tissues would show signs of mineral deficiency of mobile nutrients after older tissues.
Which of the following nutrient-deficiency symptoms is correctly matched with the deficient mineral?
chlorosis at the tips of older leaves; nitrogen
chlorosis between veins; carbon
reduced internode length; iron
None of the listed pairs is matched correctly.
very slow development; magnesium
poor growth; calcium
chlorosis at the tips of older leaves; nitrogen
“Smart plants” are genetically engineered plants that can _________.
fix gaseous nitrogen into nitrogen usable by a plant
eat insects and small animals to supplement their diets
None of the listed responses is correct.
signal, only after damage to the plant has occurred, when a nutrient deficiency is imminent
increase the surface area for absorption by a plant’s roots
signal, before any damage to the plant has occurred, when a nutrient deficiency is imminent
signal, before any damage to the plant has occurred, when a nutrient deficiency is imminent
Cation exchange is the process in which _________.
humus develops from dead organisms
mineral nutrients are added to the soil
anions enter the soil solution by being displaced by other anions
cations enter the soil solution by being displaced by other cations, particularly H+
soil is carried away from different areas by wind and rain
cations enter the soil solution by being displaced by other cations, particularly H+
Many people add various types of fertilizers to their plants to facilitate growth. What does fertilizer contain that facilitates plant growth?
Fertilizer contains amino acids, which facilitate plant growth.
Fertilizer contains organic carbon, which plants can use for growth.
All of the listed responses are correct.
Fertilizer contains minerals that are essential for healthy plant growth.
Fertilizer contains water, which plants need for growth.
Fertilizer contains minerals that are essential for healthy plant growth.
The biological process that produces 96% of the dry mass of a plant is called __________.
photosynthesis
cation exchange
oxidation
transpiration
respiration
photosynthesis
The relationship between mycorrhizae and plants benefits both organisms because _________.
the host plant depletes the fungus of sugar, and the fungus reduces the surface area of the plant’s roots for nutrient absorption
the host plant provides the fungus with a steady supply of minerals, and the fungus has no effect on the plant
the host fungus provides the plant with a steady supply of sugar, and the plant increases the surface area of the fungus for nutrient absorption
All of the listed responses are correct.
the host plant provides the fungus with a steady supply of sugar, and the fungus increases the surface area of the plant’s roots for nutrient absorption
the host plant provides the fungus with a steady supply of sugar, and the fungus increases the surface area of the plant’s roots for nutrient absorption
If a plant's leaves are yellowing, it may be that the plant is deficient in the elements needed to make chlorophyll, one of which is __________.
copper
phosphorus
molybdenum
magnesium
sulfur
magnesium
If a plant is deficient in __________, it will not be able to make DNA.
iron
phosphorus
magnesium
sulfur
manganese
phosphorus
Legumes (members of the pea family) have roots with swellings called nodules that __________.
increase the surface area for water uptake
produce antibiotics that protect the plant from soil bacteria
contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria
provide a steady supply of sugar to the host plant
form fungal hyphae
contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria
The most abundant gas in our atmosphere cannot be used by plants directly in its atmospheric form and is, therefore, captured by certain bacteria that live symbiotically in their roots.
What is this gas?
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Iron
Carbon dioxide
Nitrogen
The topsoil and other soil layers are referred to as _________.
cations
soil horizons
loams
humus
None of the listed responses is correct.
soil horizons
Which of the following substances does a plant obtain from the air?
Water
Nitrogen
Carbon
All of the listed responses are correct.
Magnesium
Carbon
At low soil pH levels (5 or less), what can happen?
Absorption of calcium is enhanced, but iron is unavailable.
Absorption of negatively charged ions is enhanced, causing the plants to grow faster.
Toxic aluminum ions become more available, stunting the plant's growth.
Cation exchange will be enhanced, causing the plants to grow faster.
Plant roots are eaten away by the acidic soil.
Toxic aluminum ions become more available, stunting the plant's growth.
Epiphytes are a type of plant that ________.
increases the surface area for nutrient absorption by other plants
fixes gaseous nitrogen into usable nitrogen in the soil
grows on other plants without using the host plants for nutrients
grows on other plants and absorbs nutrients from its hosts
captures insects and small animals to supplement its diet
grows on other plants without using the host plants for nutrients
What is the goal of phytoremediation?
To replace lost minerals in soil.
To clean contaminated sites by using plants that have the ability to extract and store soil pollutants.
To test whether an element is essential to a certain species of plant.
To grow crops such as alfalfa and wheat that provide good ground cover.
To increase resistance to aluminum toxicity
To clean contaminated sites by using plants that have the ability to extract and store soil pollutants.
Mycorrhizae develop __________.
when nutrients are required by plants in relatively large amounts
when soil is too compact and lacks sufficient air spaces
to control the evaporation of water from leaves
when nutrients are required by plants in relatively small amounts
between roots and beneficial fungi
between roots and beneficial fungi