Introduction to Kinetics
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEE1008: Mechanics of Materials - Lecture 15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Kinematics
Study of motion without reference to the forces which cause the motion.
Kinetics
Relates the action of forces on bodies to the resulting motion.
Inertia
The resistance to the rate of change of velocity
m = F/a
Direction of acceleration
Always in the direction of the applied force.
Force unit
Newton (kg m/s2)
Weight equation
mass x gravity
Choice of coordinate system
Depends on the type of motion
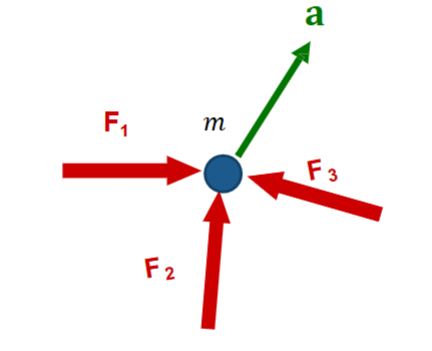
Vector sum of ΣF
ΣF = ma
Rectilinear motion of particle

Curvilinear motion of particle
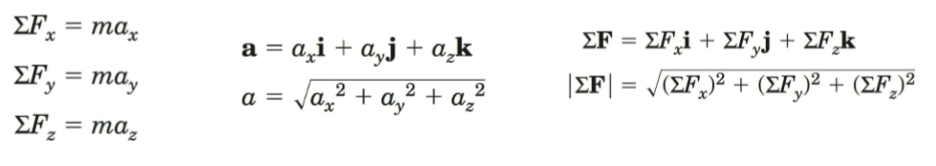
Law of sines

Law of cosines
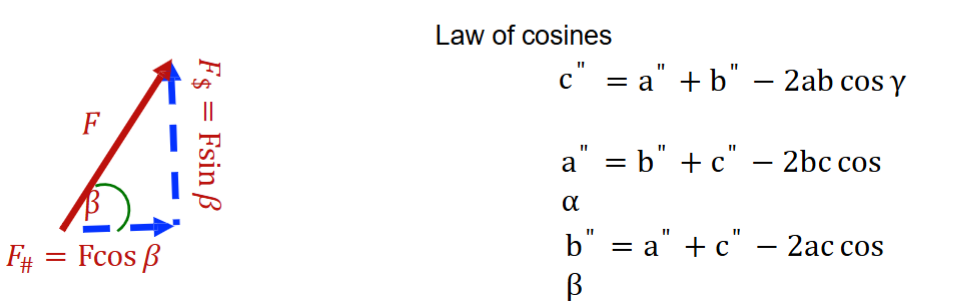
Force of a spring
A compressed spring exerts a pushing force and a stretched spring exerts a pulling force.

Hooke’s Law
Used to calculate force of spring
F = kx
where F is the spring force, k is the spring constant and x is the distance displaced.
Friction
Occurs when the unlubricated surfaces of two solids are in contact under a condition of sliding or a tendency to slide.
Static friction
No motion
Fmax = μsN and F < μsN
where μs is the coefficient of static friction and N is the normal force.
Kinetic friction
Motion
Fk = μkN
where μk is the coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the normal force.
Steps to construct a free body diagram
Decide which system to isolate.
Isolate the system and draw its external boundary.
Identify all forces acting on the system.
Add the coordinate system on the diagram.