MEC316 Renewable Energy: Hydroelectric and Other Sources
1/339
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
340 Terms
What are the three types of renewable energy sources mentioned in the notes?
Hydroelectric, geothermal and heat pump, traditional and modern biomass.
What percentage of the world's electricity supply is provided by hydroelectric power?
About 20%.
In how many countries is hydroelectric power the principal source of electricity?
About 30 countries.
What is the formula for calculating the available pressure head in hydroelectric power generation?
∆𝑝 = 𝜌𝑔ℎ, where ∆𝑝 is the pressure head, 𝜌 is the density of water, 𝑔 is gravitational acceleration, and ℎ is height above datum.
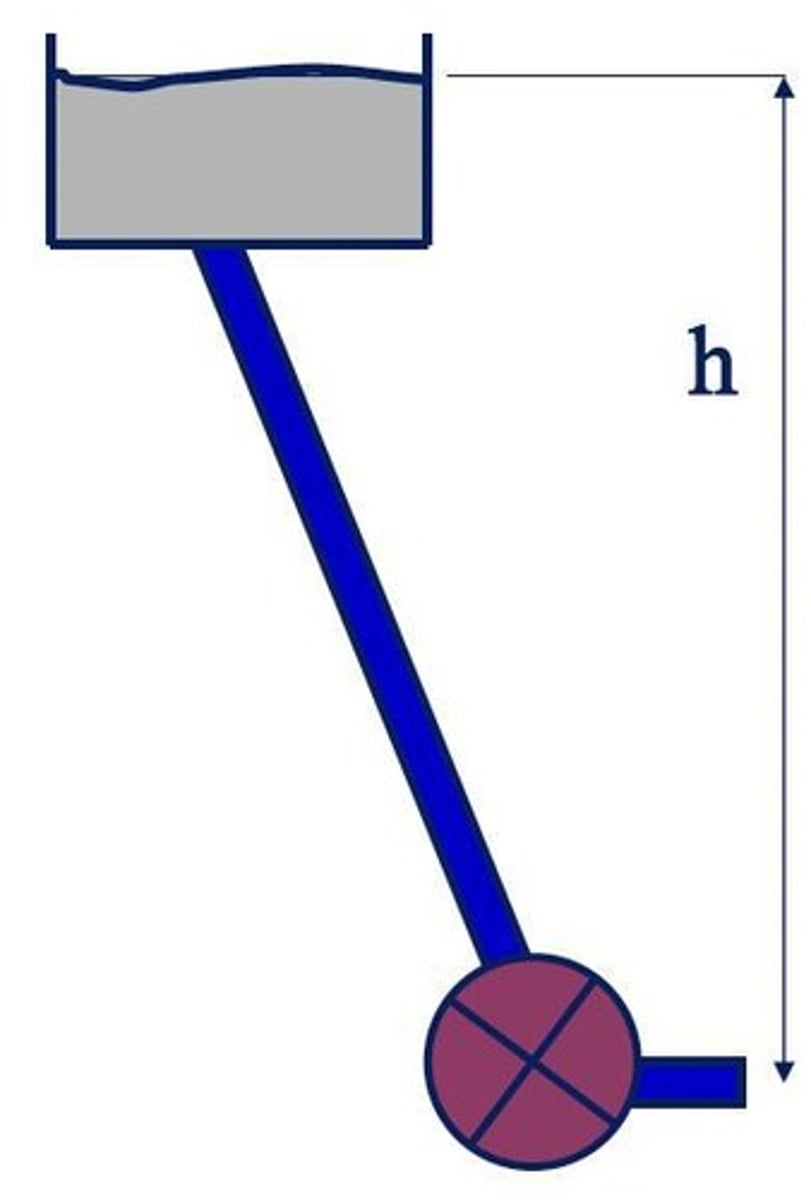
What is the relationship between pressure head and fluid velocity in hydroelectric systems?
Fluid velocity can be calculated as 𝑣 = √(2∆𝑝/𝜌) = √(2𝑔ℎ).
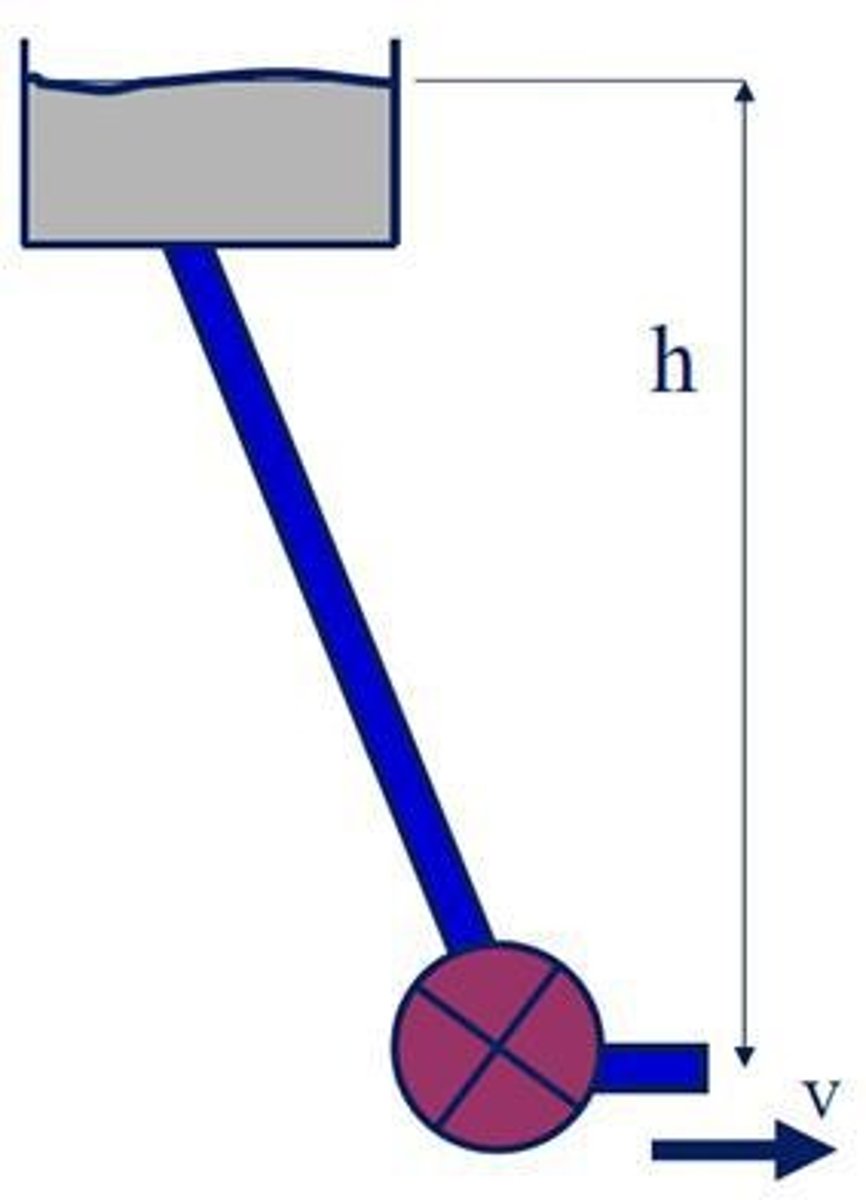
What does the power generated by a hydroelectric system depend on?
Power = pressure head x volumetric flow rate (P = ∆𝑝𝑄).
What factors are accounted for when calculating the effective power output of a hydroelectric system?
Head efficiency coefficient (𝜂ℎ) and mechanical efficiency (𝜂𝑓).
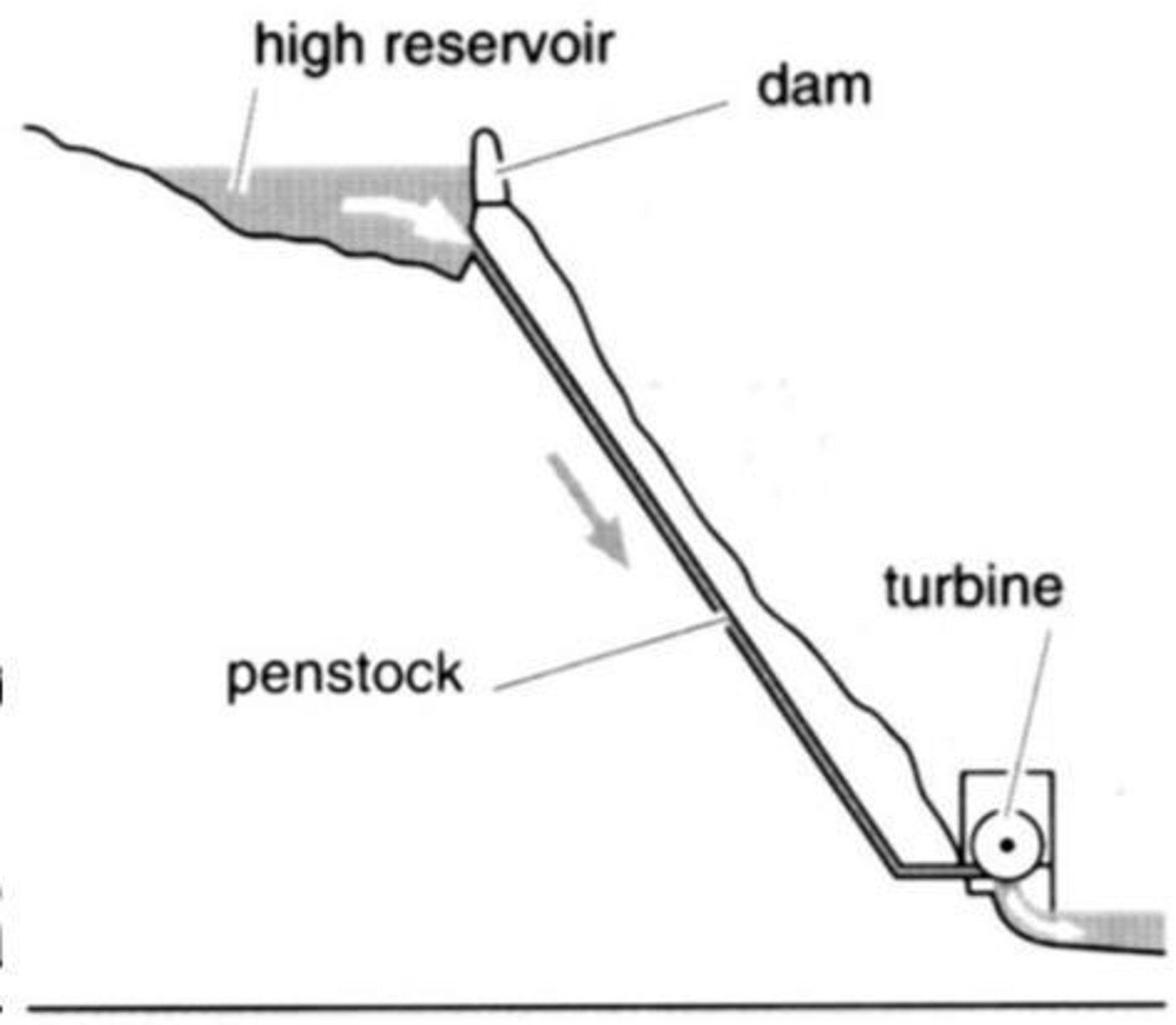
How are hydroelectric plants classified based on effective head?
High head (ℎ > 100m), medium head, and low head (ℎ < 10m).
What are the three basic types of turbines used in hydroelectric plants?
Francis turbine, propellers, and impulse turbine.
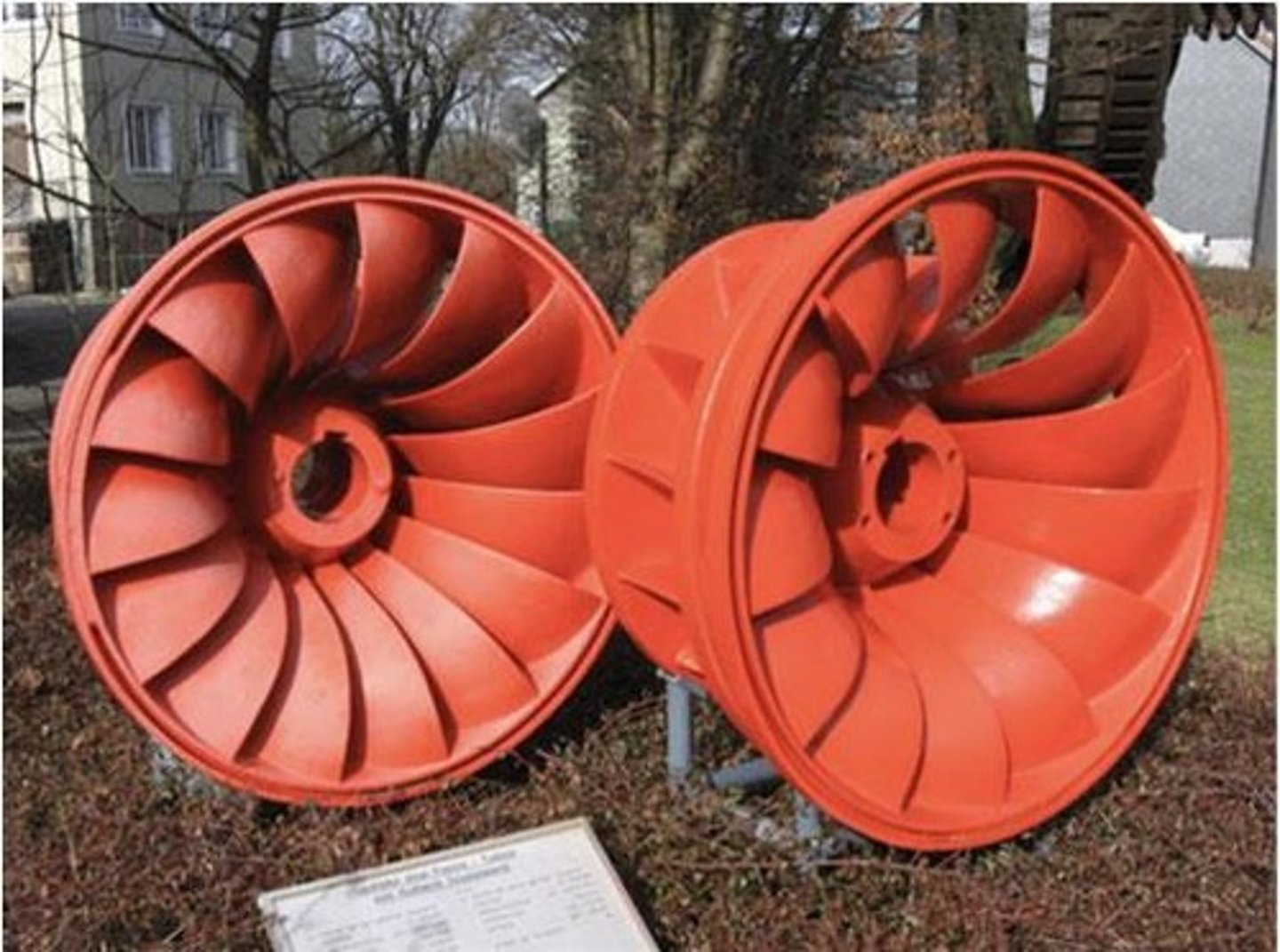

What is a Francis turbine and its efficiency?
Most common turbine for hydroelectric applications with an efficiency of up to 95%.
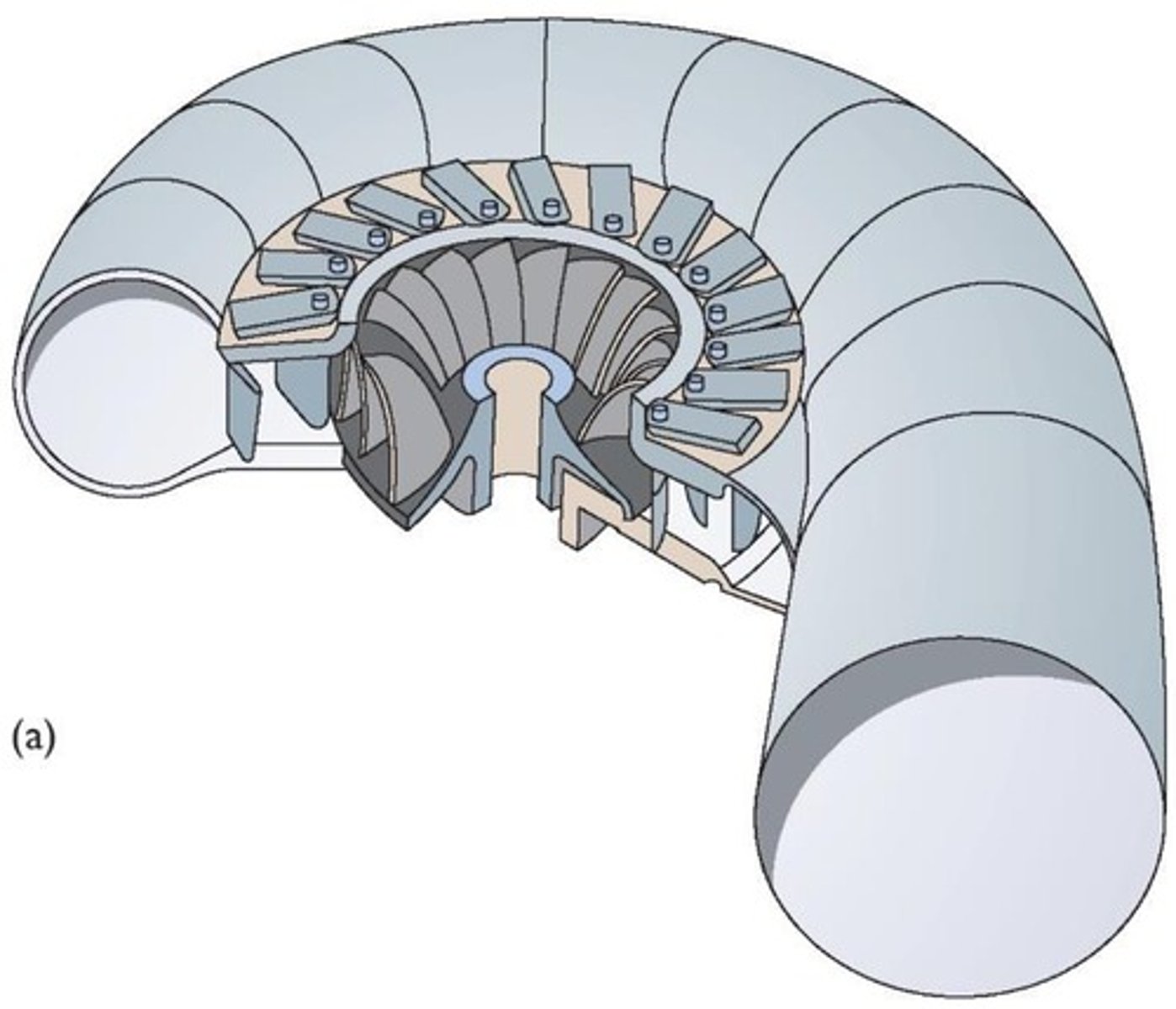
What is a key limitation of Francis turbines?
They are limited at low heads and are a poor choice for high heads/speeds.
What type of turbine is normally used in low head applications?
Propeller turbines.
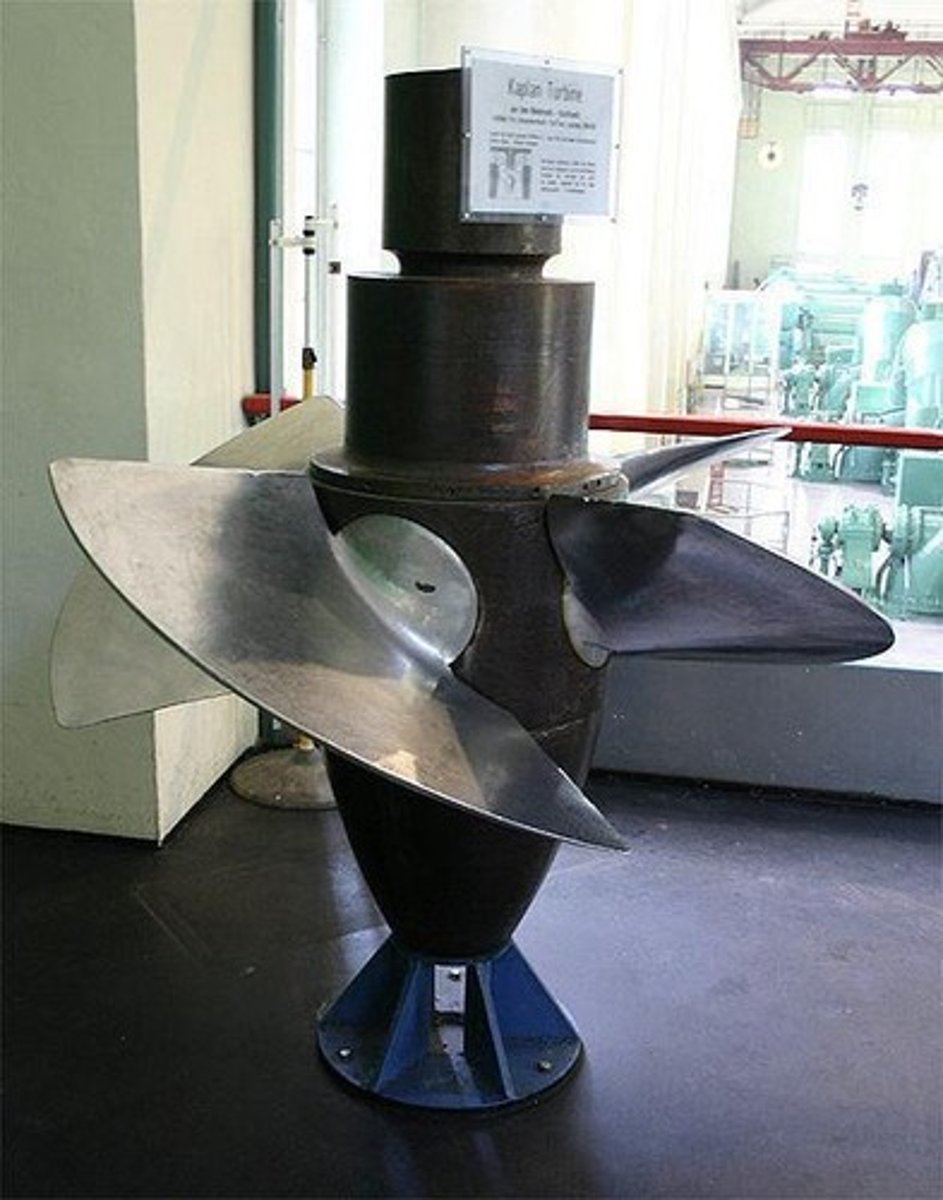
What is a Kaplan turbine?
A type of axial flow turbine where blade angles can be altered to control flow and output.

What is an impulse turbine and its simplest example?
An impulse turbine uses jets of water to drive the turbine; the simplest example is the Pelton Wheel.
What is the efficiency characteristic of impulse turbines?
They have very high efficiency, giving up almost all kinetic energy.
For what head situations are impulse turbines typically used?
High head situations, specifically greater than 250m.
What is the optimal speed for cups in a Pelton Wheel to achieve maximum energy extraction?
Cups should move at half the speed of the water jet.
What is the role of the sun's energy in the hydropower cycle?
About 25% of the sun's energy contributes to the evaporation of water, which is essential for hydropower schemes.
What is a significant factor limiting the potential energy available for hydropower?
Only a fraction of the potential energy from evaporated water is available for use.
What is the volumetric flow rate in hydroelectric systems represented by?
Q = vA, where v is fluid velocity and A is the outlet cross-sectional area.
What is the significance of guide vanes and runner blades in Francis turbines?
Their design is important for the performance of the turbine.
What is the primary function of turbines in hydroelectric plants?
To convert the energy from flowing water into mechanical energy for electricity generation.
What is the typical diameter range for turbines used in hydroelectric plants?
About 0.3 to 6 meters.
What is the height of the Three Gorges Dam in China?
181 m
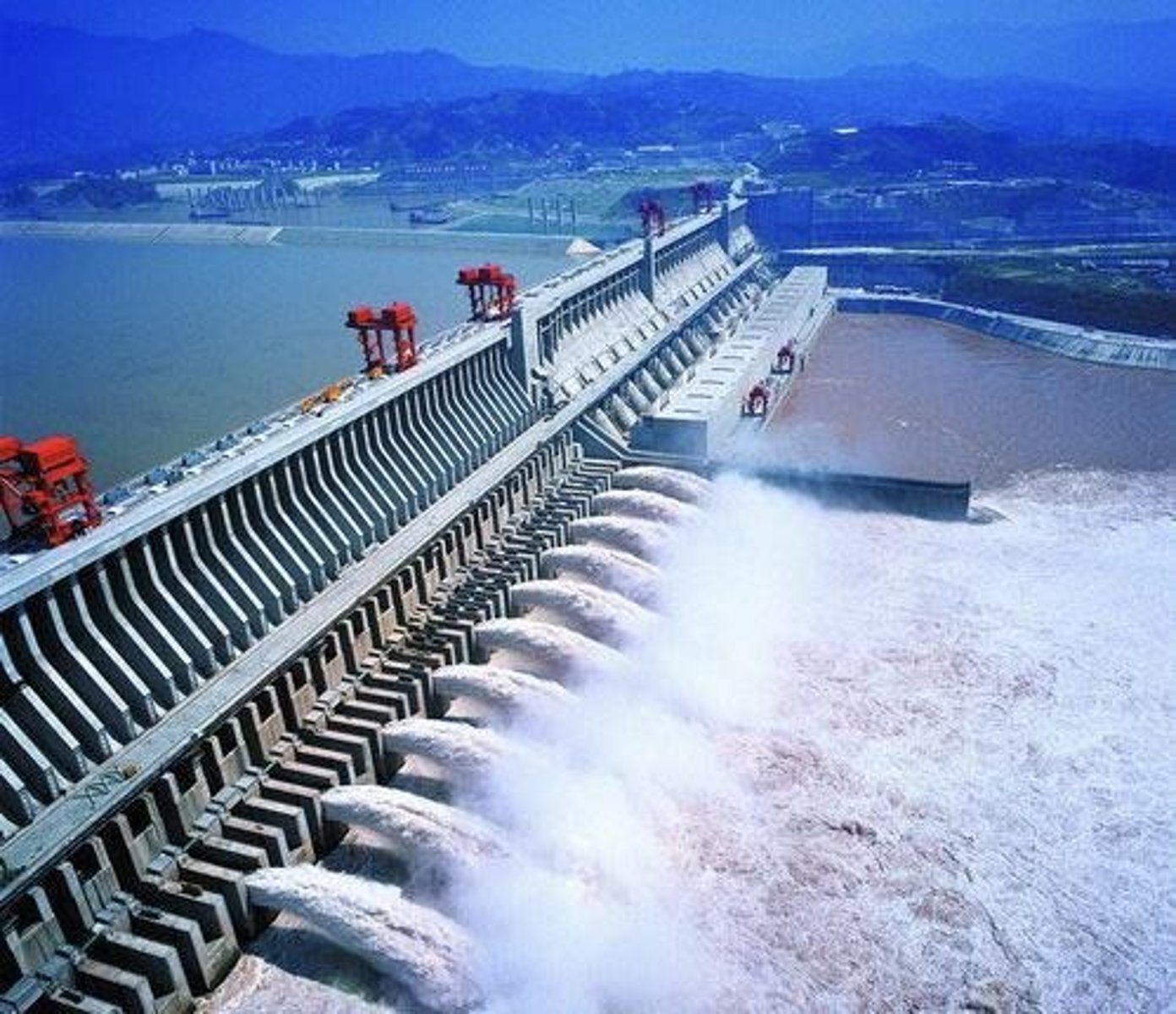

What is the total installed capacity of the Three Gorges Dam?
22.5 GW
What is the annual generation of the Three Gorges Dam as of 2014?
~100 TWh
What is tidal power primarily caused by?
The gravitational pull of the moon.
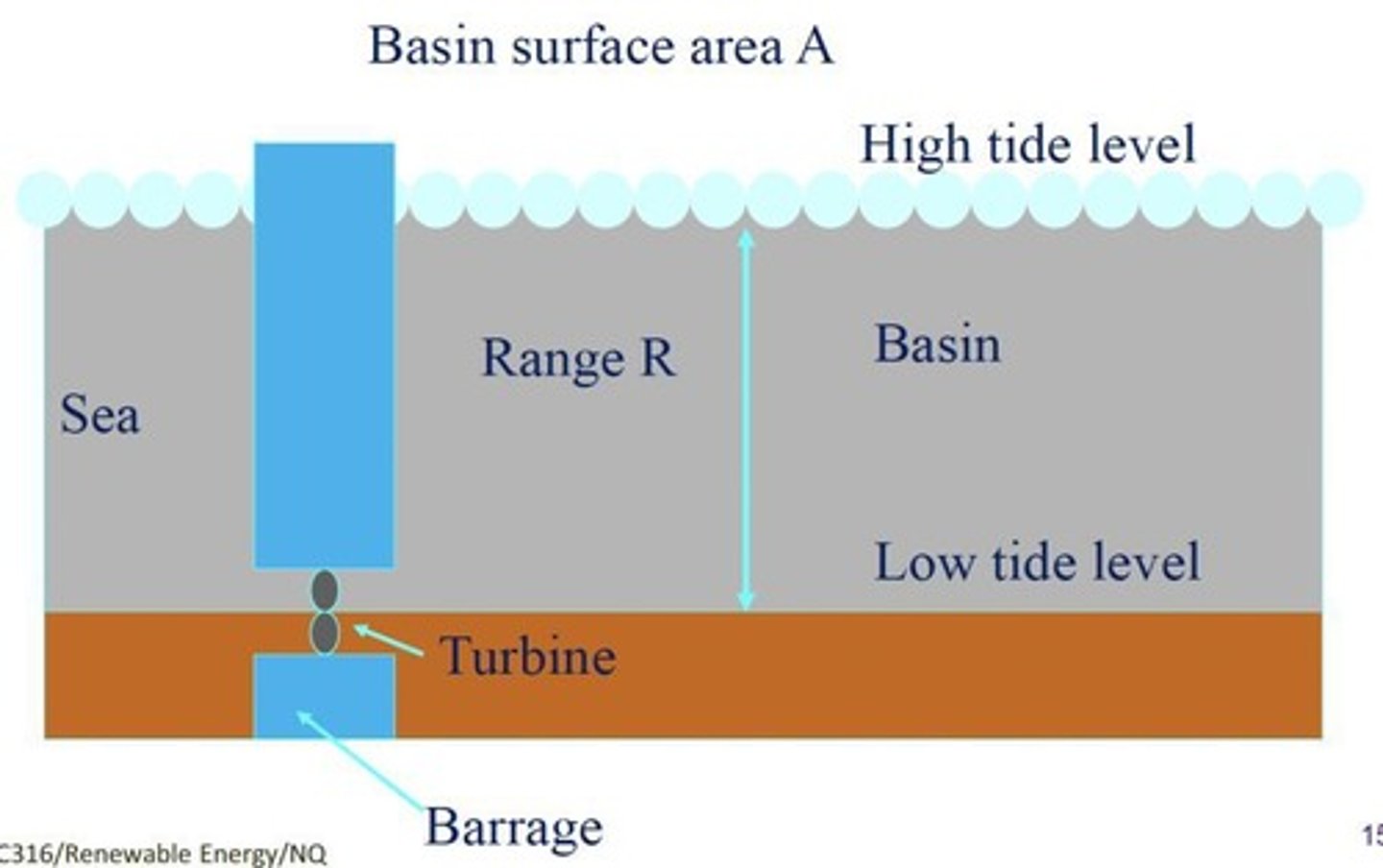
What is the minimum tidal range considered useful for tidal power exploitation?
Approximately 5 m.
What is the world's first tidal power station and when was it completed?
La Rance Estuary Power Station, completed in 1966.
How long is the La Rance Estuary Power Station barrage?
740 m.
What is the installed capacity of the La Rance Estuary Power Station?
240 MW.
What is the capacity factor of the La Rance Estuary Power Station?
28%.
What is one of the best sites for tidal power in the UK?
The Severn Estuary.
What is a key technical consideration for tidal power generation?
Power generation can occur on ebb or flow tides, or both.
What is the typical turbine speed range for tidal power systems?
50 - 100 rpm.
What is the purpose of flood pumping in tidal power systems?
To increase the energy recovered per cycle by pumping seawater into the basin near high tide.
How do tidal stream turbines operate?
They utilize water flow caused by tides and resemble horizontal axis wind turbines.
What is the typical current speed range for tidal turbines?
Between 2 and 3 m/s (4 to 6 knots).
What is the primary cause of sea waves?
Wind over the surface of water.
How does wave energy relate to solar energy?
Wave energy can be viewed as a form of solar energy since wind is caused by differential solar heating.
What are the two main types of wave power generator devices?
Fixed devices and floating devices.
What is the challenge in extracting power from waves?
The physics of power extraction are challenging.
What does the idealized equation for power extraction from waves depend on?
Wave height, wave period, and water density.
What is the density of water compared to air, which affects tidal turbines?
Water is approximately 800 times denser than air.
What is the annual generation of the La Rance Estuary Power Station?
500 GWh.
What is a disadvantage of simple one-directional tidal systems?
They generate power only 3 - 6 hours at each tide, resulting in short bursts of power not matched to demand.
What is a benefit of two-way operational tidal systems?
They provide more continuous output using reversible pitch turbines.
What are the main types of wave generators?
Fixed devices and floating devices.
What are the characteristics of fixed wave generators?
They are either attached to the seabed, attached to the shore, or constructed near the shore for waves to enter.
What are the two main types of floating wave generators?
1. A high mass vessel that allows waves to pass through, changing the volume and pushing air through a turbine. 2. A float that moves with the waves and is attached to an electrical generator.
What is the Tapered Channel (TAPCHAN) and where is it located?
It is a wave power technology located near Bergen, Norway, featuring 10m high channel walls and a length of 170m.
How does the Tapered Channel (TAPCHAN) work?
It amplifies wave height, spilling over into a reservoir that is 3m above mean sea level.
What is the Islay LIMPET?
The world's first commercial wave power station located in Scotland, designed to operate on exposed shores for local power generation.
What is the output capacity of the Islay LIMPET?
0.5 MW.
What is the Wells turbine used for?
It is designed to spin in the same direction regardless of the air flow direction, making it suitable for oscillatory flow produced by waves.
What is the maximum rotation rate of the Wells turbine?
Up to about 3000 RPM.
Who developed the Salter Duck and what is its power generation method?
Developed by Stephen Salter, it generates power through a gyroscopic electrical motor.
What is the size of the central spine of the Salter Duck?
14 meters in diameter.
How does the Pelamis wave generator orient itself?
It self-orientates into the direction of the oncoming waves.
What mechanism does the Pelamis wave generator use to produce power?
Relative motion of its sections forces hydraulic fluid through generators.
What distinguishes deep geothermal energy from other renewable sources?
It is constantly available and independent of the sun.
What are the three essential features of geothermal sites?
1. An aquifer containing water accessible by drilling. 2. A cap rock to contain geothermal fluid. 3. A heat source, such as crystalline granite.
What is the significance of the Lardarello geothermal plant?
It is a notable example of geothermal energy utilization.
What is the typical heat flow at boundaries between tectonic plates?
It can reach approximately 300 mW/m2.
How does the extraction rate of deep geothermal energy compare to thermal recharge?
Extraction rates are typically 10 to 100 times greater than thermal recharge from the Earth.
What is the temperature of the Earth's core?
Approximately 7000°C.
What is the difference between natural and engineered geothermal extraction?
Natural extraction involves using existing geothermal resources, while engineered extraction involves creating conditions for geothermal fluid flow for power generation.
What does Darcy's law describe in the context of aquifers?
Darcy's law describes the flow of fluid through aquifers, governed by the equation v = KW(H/L), where v is fluid velocity, H is effective head, K is hydraulic conductivity, and L is distance.
What is the volumetric flow equation for aquifers according to Darcy's law?
The volumetric flow equation is Q = A * KW(H/L), where Q is volumetric flow, A is cross-sectional area, KW is hydraulic conductivity, and H/L is the hydraulic gradient.
What are high enthalpy regions in geothermal energy?
High enthalpy regions are areas with temperatures greater than 180°C, primarily sourced from volcanic heat.
What are low enthalpy regions in geothermal energy?
Low enthalpy regions are areas with temperatures less than 100°C, such as deep sedimentary basins that can carry water to depths with exploitable heat.
What is the concept of 'hot dry rocks' in geothermal energy?
'Hot dry rocks' refer to areas without natural aquifers where artificial aquifers can be created by enhancing rock fractures to allow geothermal fluid flow.
What is the heat conduction equation relevant to geothermal energy?
The heat conduction equation is q = KT(ΔT/z), where q is one-dimensional vertical heat flow, KT is thermal conductivity, ΔT is the change in temperature, and z is the depth.
What is a dry steam power plant in geothermal energy?
A dry steam power plant is a simple system where hot steam is passed directly through a turbine, requiring reinjection of fluid.
What is the single flash power plant process in geothermal energy?
The single flash process involves steam production through pressure reduction, keeping the well under pressure to avoid scaling/blockage.
What is the organic Rankine cycle in geothermal energy?
The organic Rankine cycle uses a secondary working fluid, like butane, to utilize lower temperature resources and chemically impure geothermal fluids.
What is the double flash power plant process in geothermal energy?
The double flash process increases power output by including a second flashing process using unflashed liquid from the first stage.
What is the purpose of ground source heat pumps (GSHPs)?
Ground source heat pumps utilize the ground's thermal energy for heating and cooling by transferring heat between the ground and a building.
What are the four main steps in the operation of heat pumps?
1) Refrigerant vaporizes in the evaporator, 2) Cold vapor is compressed, raising temperature and pressure, 3) Hot vapor condenses in the condenser, releasing heat, 4) Warm liquid expands, dropping pressure and temperature.
What does the coefficient of performance (COP) measure in heat pumps?
The COP measures the efficiency of a heat pump, calculated as COP = Useful heat / Work input.
What are good COP values for heat pumps?
COP values in the range of 3-5 are considered 'good' for heat pumps.
What is the significance of seasonal CoP (SCOP) in heat pumps?
SCOP is more useful than instantaneous CoP as it reflects the performance of heat pumps over a season, often calculated based on controlled tests.
What is the role of vertical ground heat exchangers in GSHP systems?
Vertical ground heat exchangers are used when surface area is limited relative to the required heat exchange capacity.
What is hydraulic conductivity in the context of aquifers?
Hydraulic conductivity (KW) is a measure of a material's ability to transmit water, crucial for determining flow rates in aquifers.
What is the hydraulic gradient in aquifers?
The hydraulic gradient (H/L or h/l) is the change in head per meter of distance along the flow direction, influencing fluid velocity.
What is the relationship between effective head and fluid velocity in aquifers?
Fluid velocity is directly proportional to effective head; as effective head increases, fluid velocity also increases.
What is the significance of enhancing rock fractures in geothermal systems?
Enhancing rock fractures allows for the creation of artificial aquifers, facilitating geothermal fluid flow in areas lacking natural aquifers.
What are the challenges associated with using geothermal fluids in power plants?
Geothermal fluids can be chemically impure, requiring systems like the organic Rankine cycle to manage lower temperature resources.
How does pressure management affect steam production in geothermal power plants?
Keeping the well under pressure ensures that flashing occurs only in the power plant, preventing scaling and blockage in the well.
What is the primary heat source for geothermal energy in volcanic regions?
Volcanic heat is the principal source of geothermal energy in high enthalpy regions.
What is shallow geothermal energy?
Heat extracted from the earth through vertical boreholes.
What materials are typically used in borehole heat exchangers?
Plastic pipes made of polyethylene or polypropylene.
How should multiple borehole heat exchangers be connected?
They should be connected to ensure equal distribution of flow in different channels.
What is the formula for sizing boreholes based on heat extraction?
Length (m) = Heat evaporator capacity (W) / Specific heat extraction rate (W/m).
What is the typical range for specific heat extraction rates in boreholes?
40-70 W/m, depending on factors like geology and heat pump operation.
How can the performance of borehole heat exchangers be improved?
By reinjecting heat from summer cooling loads.
What is the preferred method for ground heat collectors in regions with cheaper land?
A wide pattern (loop) with pipes laid in shallow trenches.
What is the process for installing ground heat collectors with a dense pipe pattern?
Remove the top earth layer, lay the pipes, and distribute soil back over the pipes.
What primarily drives thermal recharge in ground arrays?
Solar energy.
How does the time constant affect heat transfer in ground arrays?
There is a long time constant between heat input and output, allowing for averaging over months.