eye movements
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
fovea centralis contains
sonly cone
macula lutea is temporal to
optic disc
optic disc contains NO
photoreceptors
what converge to form optic nerve?
retinal ganglion cell axons
Ophthalmoplegia
paralysis or weakness of eye muscles
ptosis
drooping eyelid
mydriasis
pupil dilated, loss of accommodation of lens
diplopia
double vision
eye movements muscles + CNs
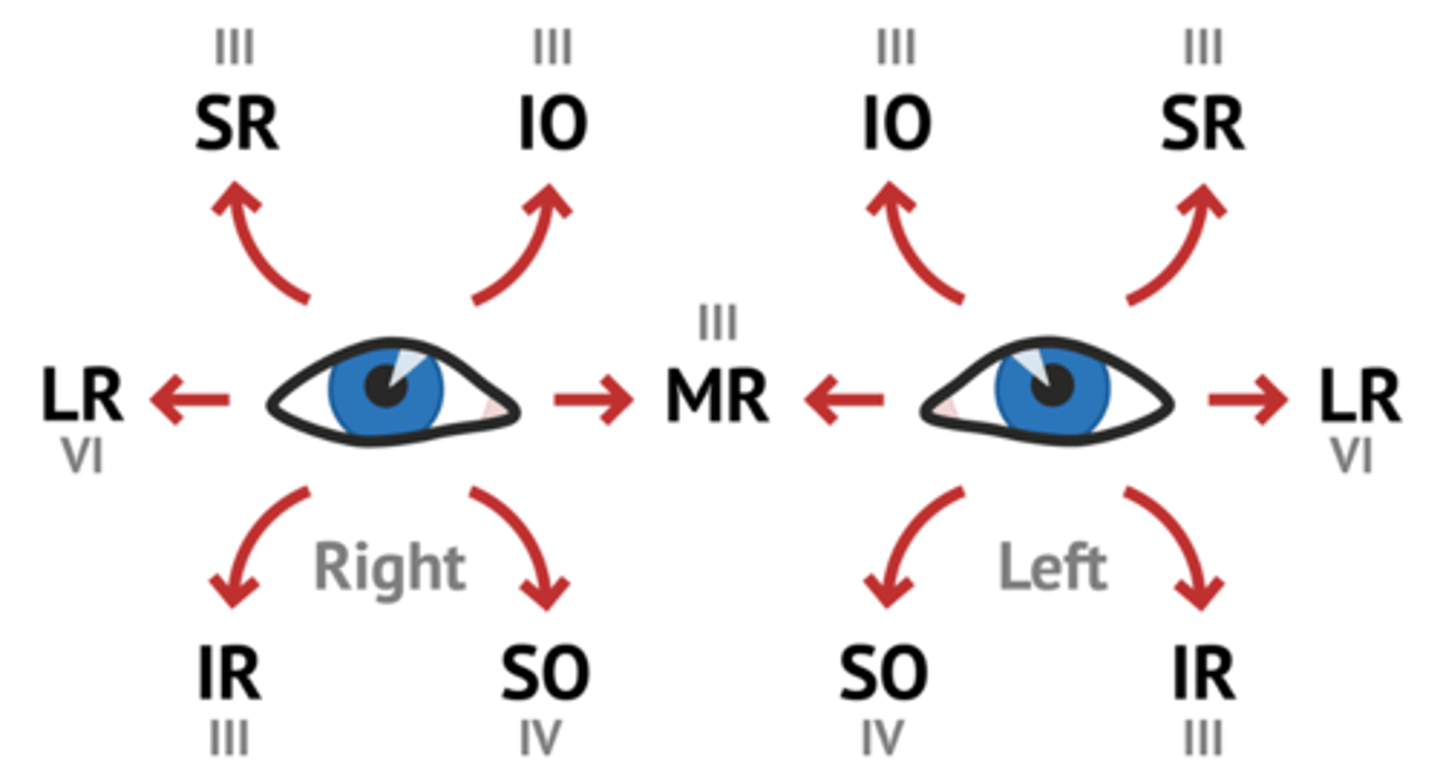
Conjugate movements include
- Saccadic
- Smooth pursuit
Conjugate movements
eyes move in same direction
saccadic movements
rapid, ballistic jerky eye movements
Reflexive conjugate movements include
- Optokinetic movements
- Vestibuloocular movements
Optokinetic movements
combination of slow-phase and fast-phase eye movements
what eye movement is used when an individual tracks (pursuit movement) a moving object with their eyes, which then moves out of the field of vision, a point at which their eyes move back to the initial position (saccade movement) when they first saw the object?
optokinetic movements
Vestibuloocular movements
the sensory signals encoding head movements are transformed into motor commands that generate compensatory eye movements in the opposite direction of the head movement, thus ensuring stable vision
Vergence movements occur when
eyes shifts between distant and near objects
Vergence movements
- converge
- diverge
converge eye movements
when the eyes move toward each other
diverge eye movements
when the eyes move away from each other
where is the horizontal gaze center located?
pons (some rostral medulla)
where is Vertical gaze center located?
midbrain
where is the vergence gaze center located?
midbrain
what is needed when both eyes look in the same directions? !!!!
horizontal gaze centers
Horizontal gaze center is in the
paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF)
(horizontal gaze center) Tonic timing signals generated by
nucleus prepositus hypoglossi
(horizontal gaze center) what allows eyes to maintain their position) ?
tonic timing signals generated by nucleus prepositus hypoglossi
(horizontal gaze center) phasic/burst signals from PPRF to
- Ipsilateral abducens nucleus (Ipsilateral lateral rectus muscles)
- Contralateral oculomotor nucleus •MLF at superior colliculus and Contralateral medial rectus muscle)
pontine lesions (CN VI nucleus) affects
horizontal gaze
(horizontal gaze stroke) Median aspect of the pons is supplied by
paramedian branch of the basilar artery
(horizontal gaze) what happens if the frontal eye field is damaged? !!!!!!!
Transient paralysis occurs when all or some muscle control comes and goes periodically
(horizontal gaze) what happens if the right PPRF (contralateral to the FEF) is damaged? !!!!!!!!
really nothing works as well, you won't be able to move either eye to the right
(horizontal gaze) what happens if the ipsilateral (left) side MLF is damaged? !!!!!!
right side is normal, but the left side will not be able to adduct
(horizontal gaze) what happens if the the level of the abducens nerve is damaged? !!!!!
left eye (ipsilateral in this case) is functioning fine but that the right eye will be unable to abduct or gaze to the right
horizontal gaze damage !!!!!!!!!
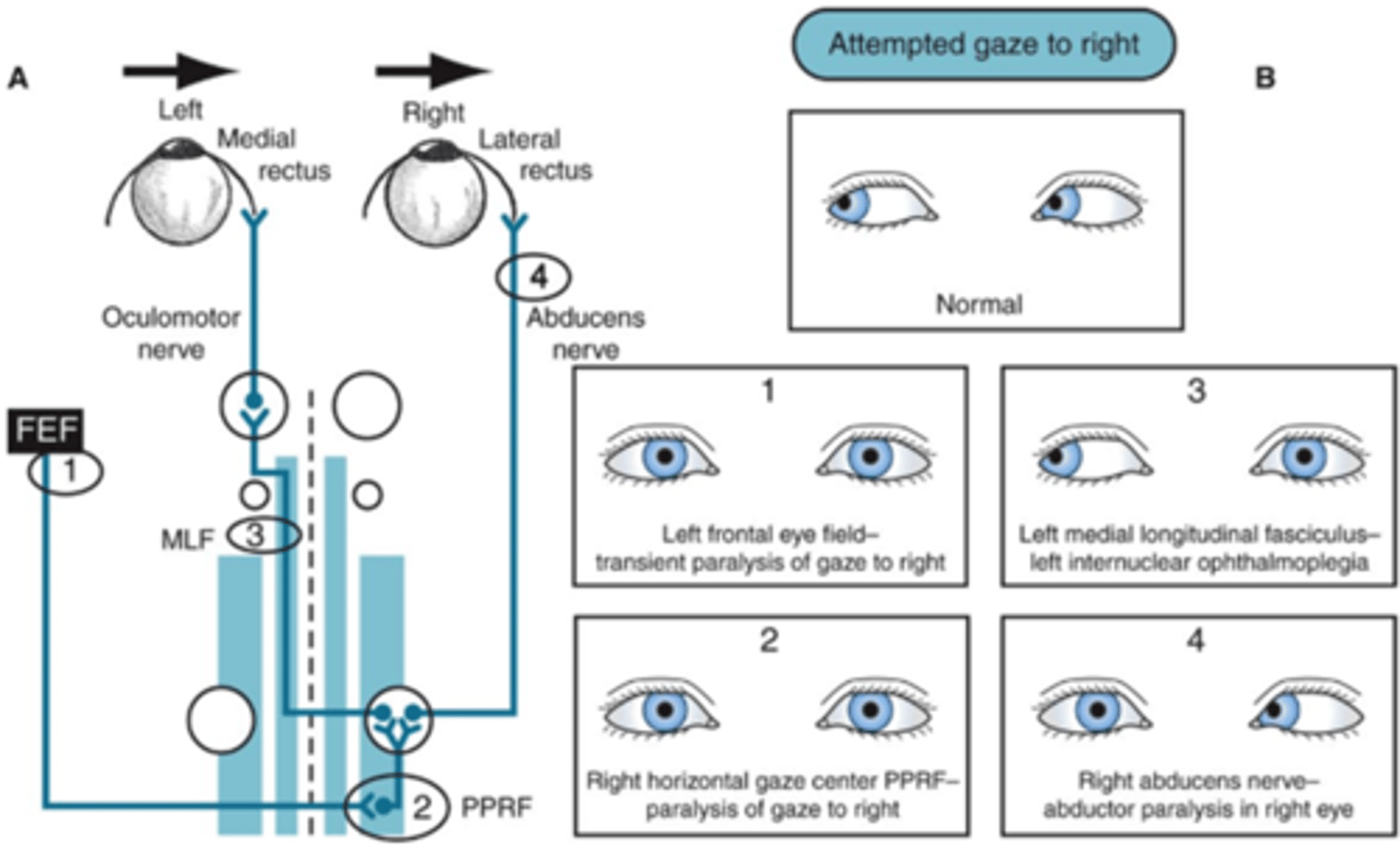
Unilateral lesion of MLF at or superior (rostral) to the abducens nucleus causes !!!!!!!
paralysis of eye adduction ipsilateral to lesion -- affected eye can adduct during convergence
most common causes of unilateral lesion of MLF
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brainstem infarction
internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) !!!!!!!
lesions in MLF-->conjugate horizontal gaze palsy
CN VI nucleus activates ipsilateral lateral rectus; contralateral CN III nucleus does not stimulate medial rectus to fire
abducting eye gets nystagmus
normal convergence
Vertical gaze center is in the
rostral interstitial nucleus of the MLF (riNMLF) of midbrain
(vertical gaze center) riNMLF phasic/burst signal acts
bilaterally
(vertical gaze center) within riNMLF
- upward movements (dorsal)
- downward movements (ventral)
(vertical gaze center) what is the role of medial accessory oculomotor nucleus?
tonic signal to keep eyes fixed
Vertical gaze palsy (VGP)
limitation of upward gaze and/or downward gaze
Vertical gaze palsy (VGP) results from
- Pineal gland tumor
- Dilation of cerebral aqueduct
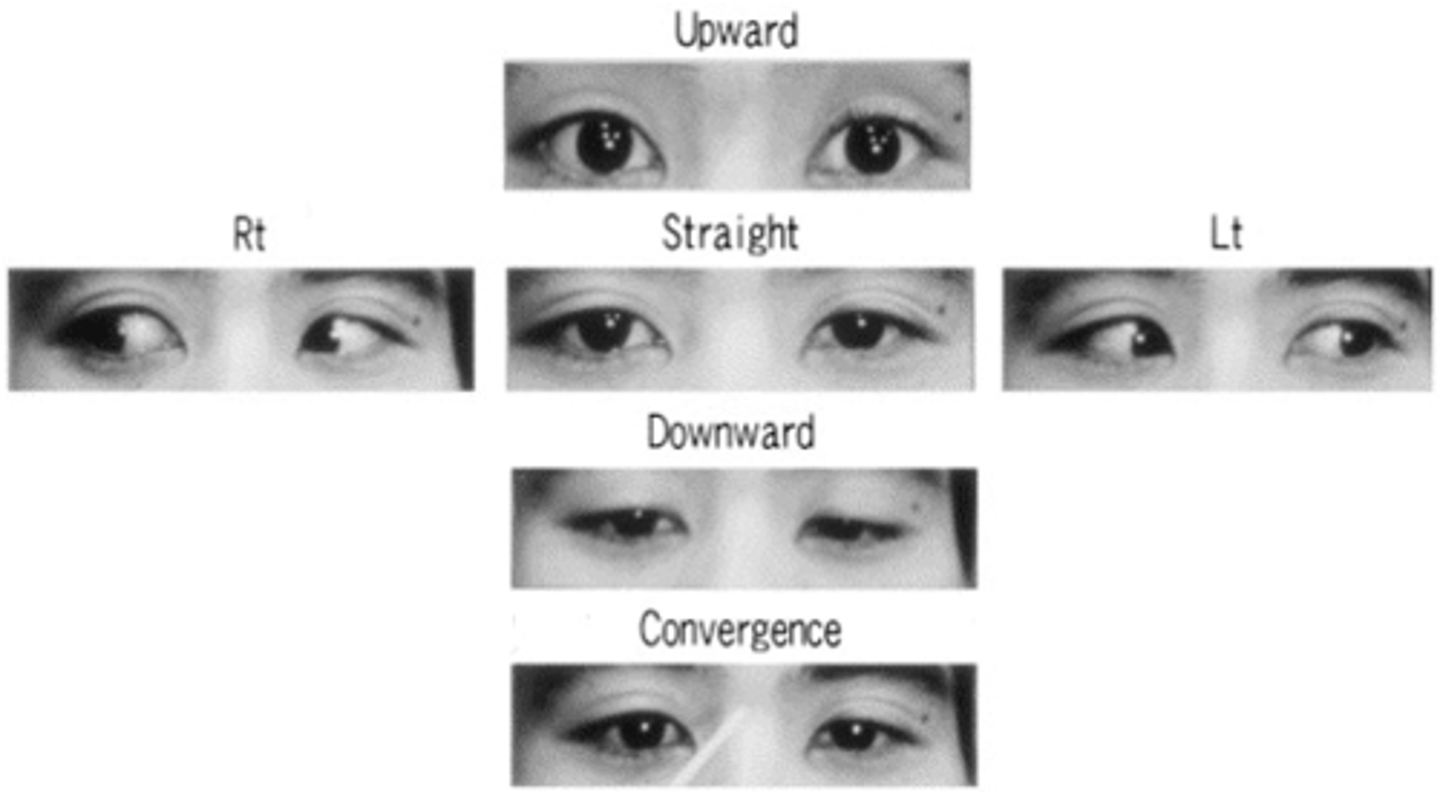
Paralysis of convergence with Vertical gaze palsy (VGP)
- L and R intact
- look up -- cant -- raise eyelids but eyes don't move
- look straight -- relax eyes
- downward -- look at you but relax eyelids
- can't cross their eyes

what is seen on radiograph with Vertical gaze palsy (VGP)?
- Hummingbird sign
- mickey mouse appearance
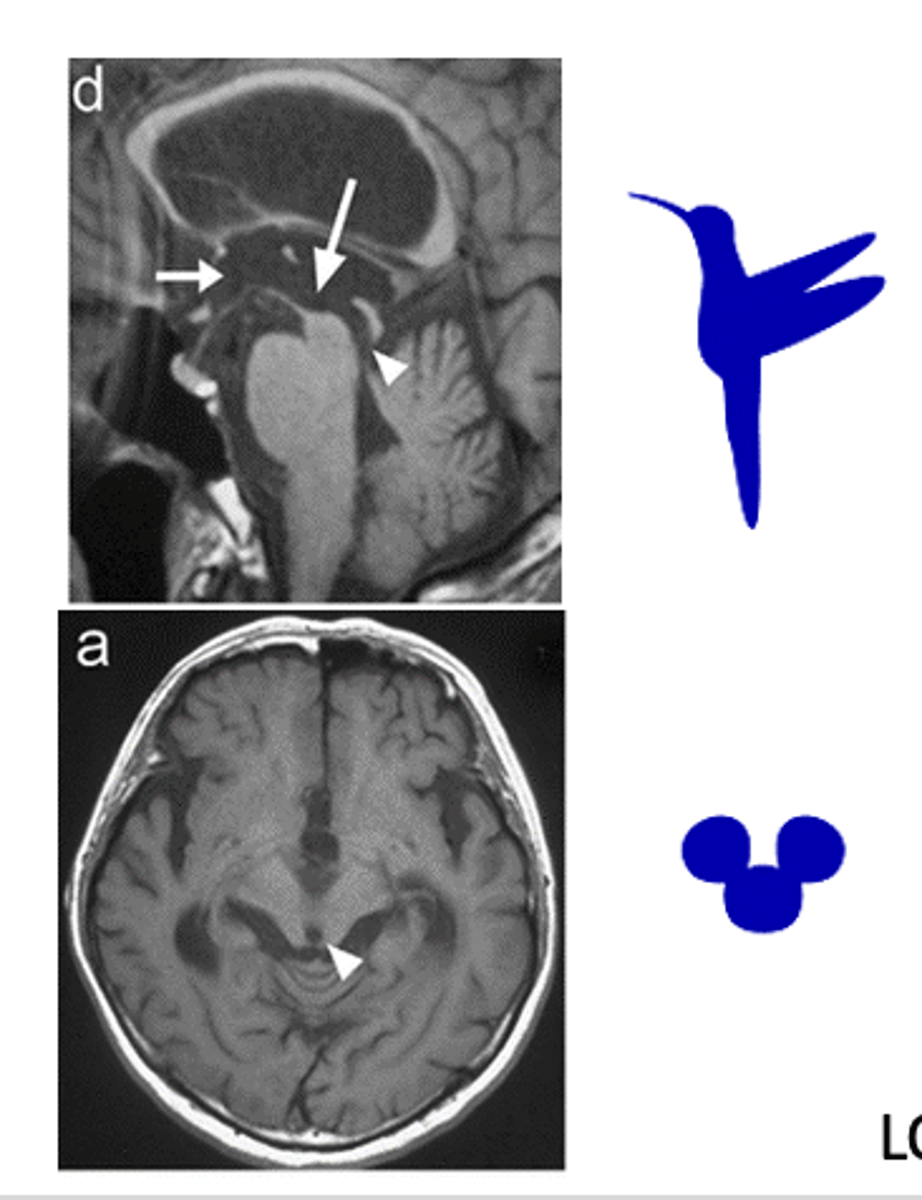
convergence is controlled by
supraoculomotor area (SOA)
supraoculomotor area (SOA) projects to
- Medial rectus and lateral rectus motor neurons
- Edinger-Westphal (accessory oculomotor nucleus) preganglionic nucleus (lens and pupil)
where is the rostral midbrain reticular formation located?
behind oculomotor nuclei
(convergence) Lens and pupil contraction via what innervation?
autonomic parasympathetic
what is the chief center for voluntary eye movements?
Frontal eye field (BA8)
Frontal eye field (BA8) projects to
- Vertical and horizontal gaze centers
- Superior colliculus
where is the Frontal eye field (BA8) located?
posterior part of middle frontal gyrus
Superior parietal lobule affects what type of eye movements?
saccadic movements
Superior parietal lobule has reciprocal connects with?
frontal eye field and superior colliculus
Superior parietal lobule plays a role in?
visual attention
lesions to superior parietal lobule cause
neglect of contralateral objects and difficulty with eye movements toward that side
posterior part of lateral temporal lobes are in charge of what eye movements?
smooth pursuit
Posterior part of lateral temporal lobes lesions result in
ipsilateral loss of smooth pursuit when targets are moving toward the side of the lesion
what forms the occipital eye field?
Primary visual and visual association areas
Primary visual and visual association areas controls what eye movements?
vergence movements
Primary visual and visual association areas afferent limb
normal visual pathway
Primary visual and visual association areas efferent limn
- Occipital lobe > superior colliculus > oculomotor nucleus
From oculomotor nucleus, eye accommodate for near vision
- Medial recti
- Ciliary muscles
- pupillary sphincters
Superior colliculus consists of
alternating gray and white layers
Superior colliculus plays a role as _______ _________ center
visuomotor integration
Superior colliculus control what eye movements?
reflex ocular
lesions of Superior colliculus
do not result in major eye movement abnormalities
input side of basal nuclei
Eye movement-related cortical areas > caudate nucleus > substantia nigra > superior colliculus and thalamus > modulates cortical output
output side of basal nuclei
modulation of the frontal and supplementary eye fields and superior colliculus by varying levels of inhibition (from SNr)
Substantia nigra !!!!
source of the striatal input of the neurotransmitter dopamine, plays a role in basal ganglia function
Parkinson's disease
Loss of dopaminergic neurons from compact part of substantia nigra
parkinson disease affects what basal ganglia pathways?
Decreased activity of direct pathway and increased activity of indirect pathway
Huntington's disease
Loss of excitatory subthalamic projections disinhibits the thalamus
Huntington's disease lead to a failure
suppress some cortical outputs
Eye movement-related areas of cerebral cortex project via pontine nuclei to the
oculomotor vermis
where is the oculomotor vermis located?
upper part of posterior lobe
what is the role of the oculomotor vermis?
regulated timing of muscles contractions during saccades
oculomotor vermis project to _________ nucleus then to _______ ________ _______ for eye movements
fastigial; brainstem pattern generator (BPF)
Flocculonodular lobe
receives inputs from eye movement-related areas of the cerebral cortex
how does the flocculus produce smooth pursuit movements of the eye?
suppresses vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR)
what happens if the flocculus is damaged?
- Impairment of smooth pursuit movements
- Loss of the ability to change the gain of the VOR
Which type of movement occurs when the eyes shift between distant and near objects? !!!!!
Converge or diverge movements
Which types of movements occur when the eyes move in the same direction? !!!
conjugate movements - smooth pursuit and saccadic
What is the horizontal gaze center called? !!!!
PPRF - paramedian pontine reticular formation
What is the vertical gaze center called? !!!!!
riNMLF - rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus
What is the brainstem center controlling convergence and divergence? !!!!!
Supraocular motor area
What is the chief cortical center for voluntary eye movements? !!!
frontal eye field
A patient complains of seeing two images of a single object (double vision or diplopia) whenever looking toward the right side. Examination shows that upon attempting to gaze to the right, the right eye abducts normally but the left eye fails to adduct. Both gaze to the left and convergence for near vision are normal. Which of the following structures has been affected?
Medial longitudinal fasciculus