09.A BIO, C1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (PART A)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Inheritance
The process in which genetic material is passed from parents to their offspring
Genetics
The study of heredity

Trait
A specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another
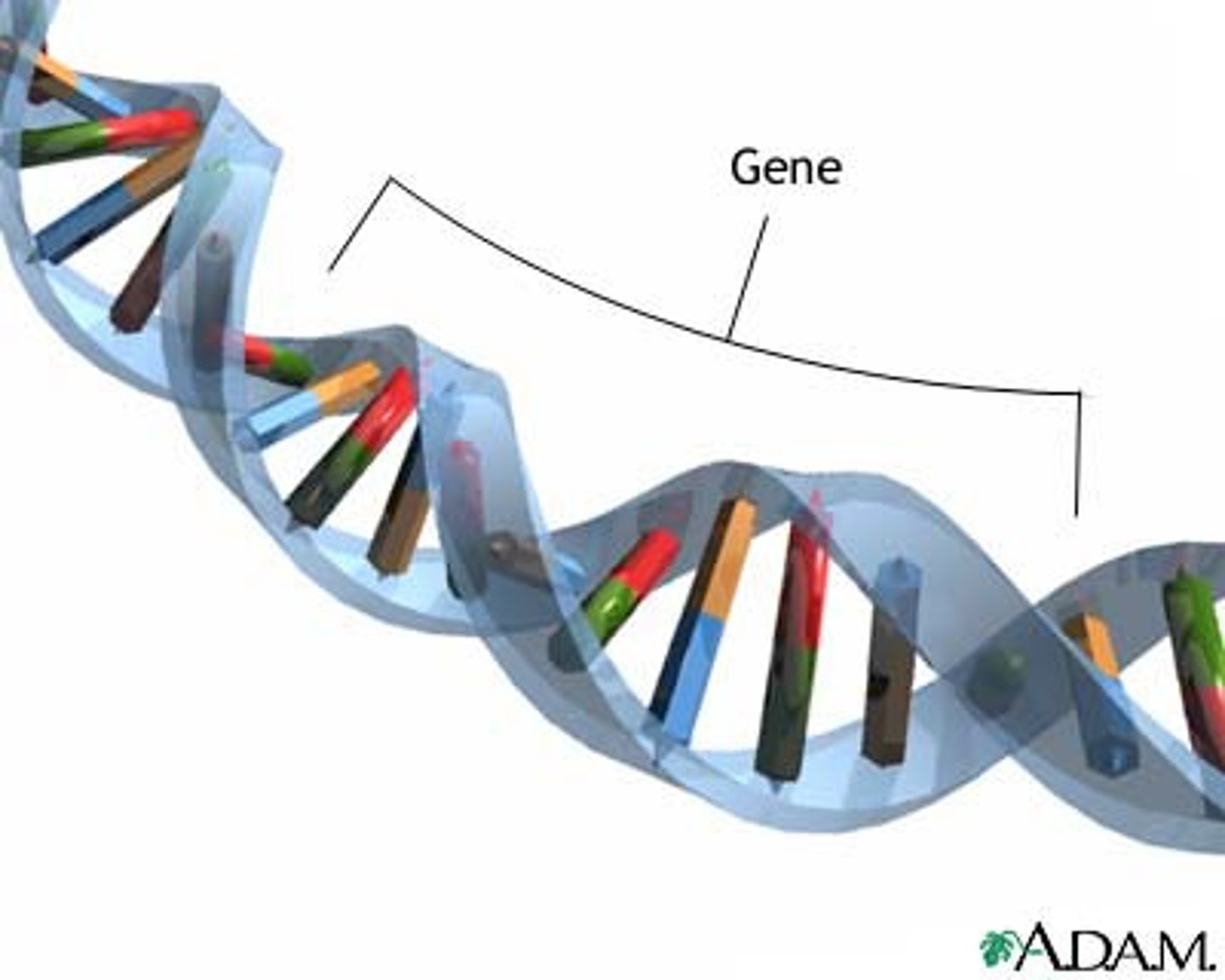
Gene
The sequence of nucleotides on a chromosome that codes for a protein and determines a trait
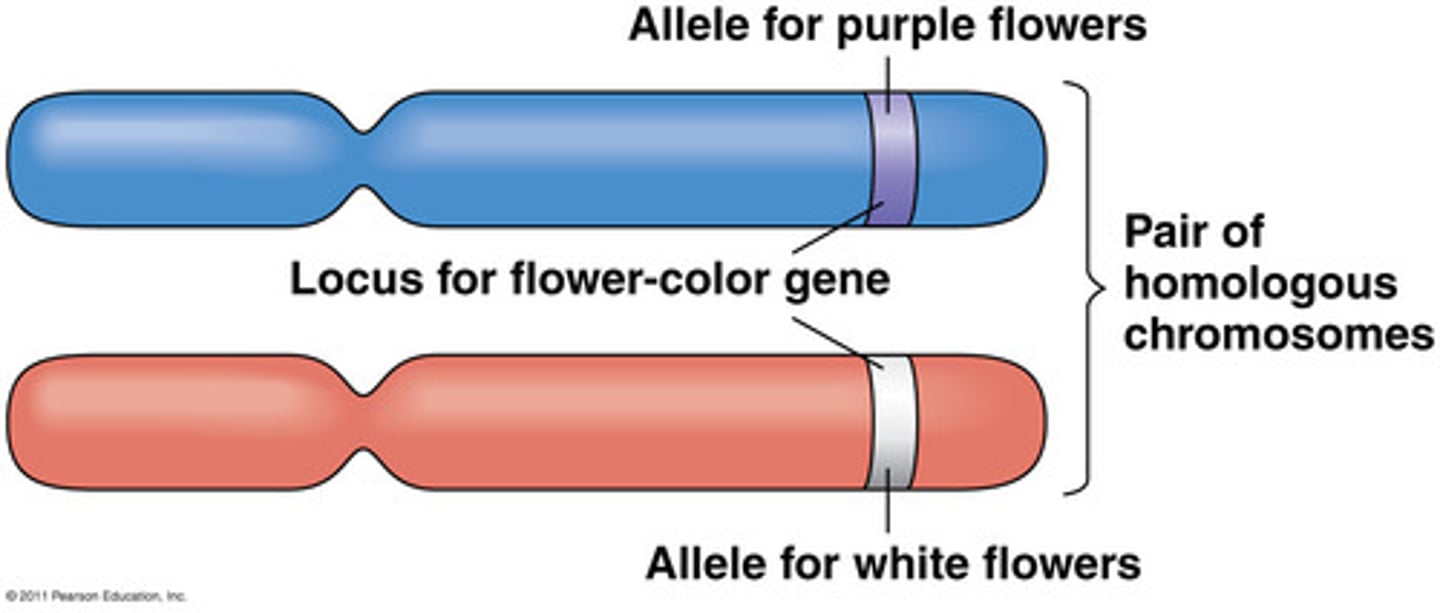
Allele
A form of a gene; for example, the gene for flower color could produce either purple flowers or white flowers
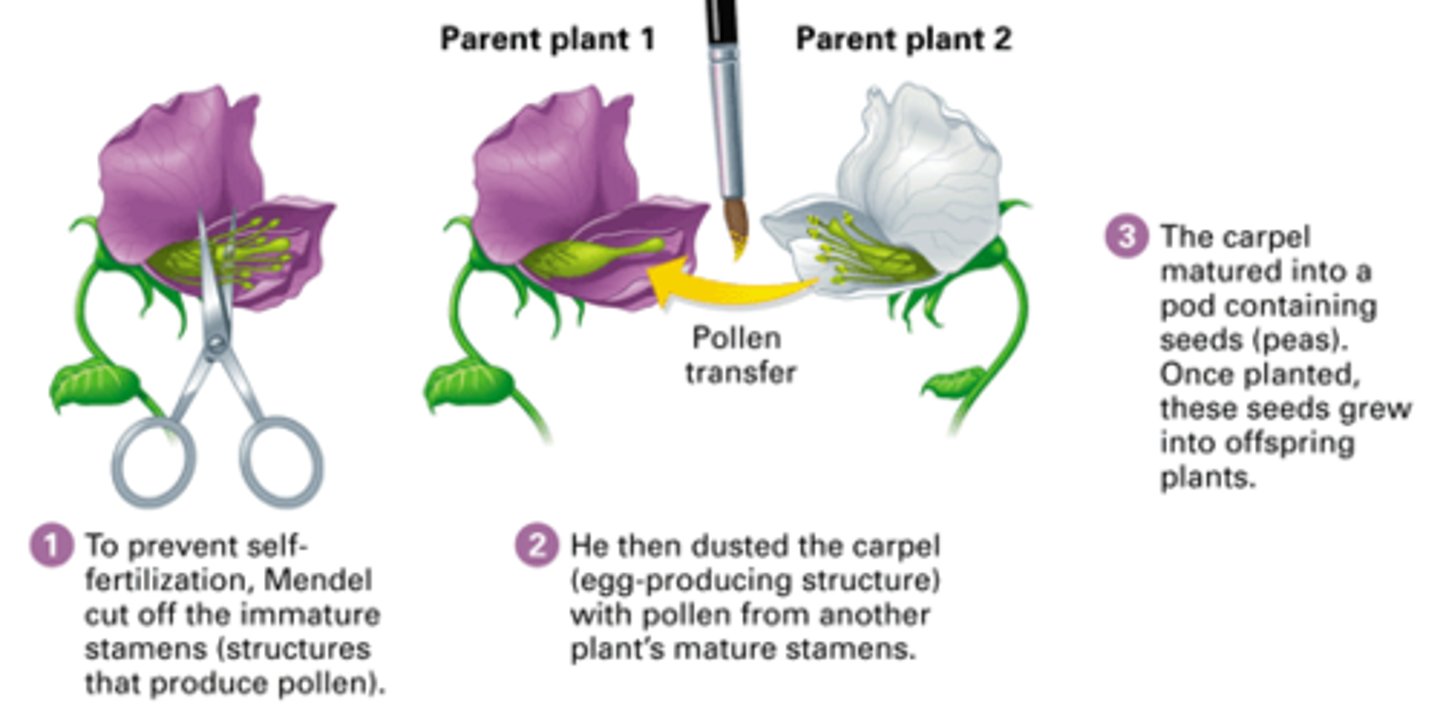
Self-pollination
The fusion of sperm and egg produced by the same individual organism
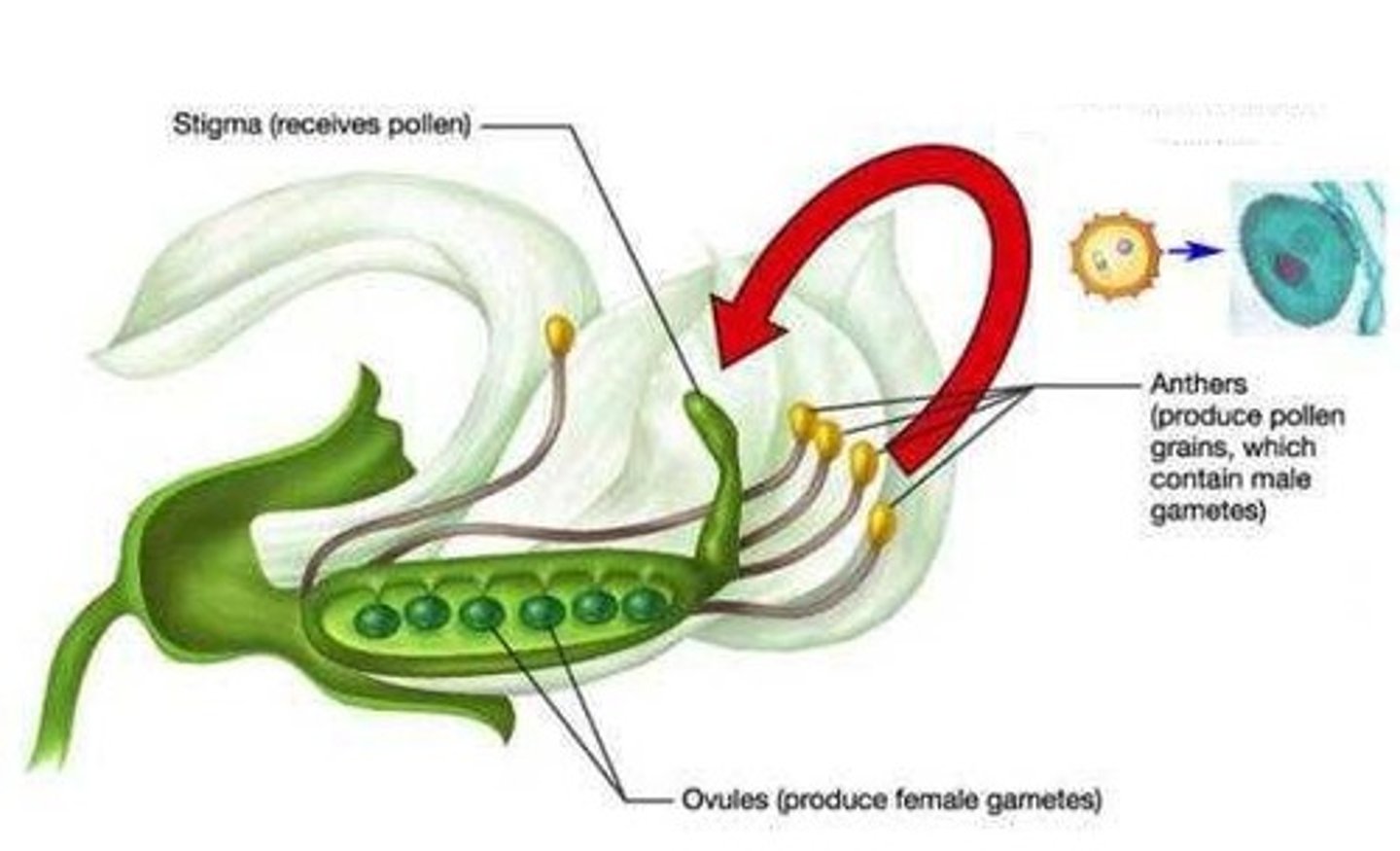
Cross-pollination
The process by which sperm from one flower's pollen fertilizes the eggs in a flower of a different plant; also known as cross-fertilization
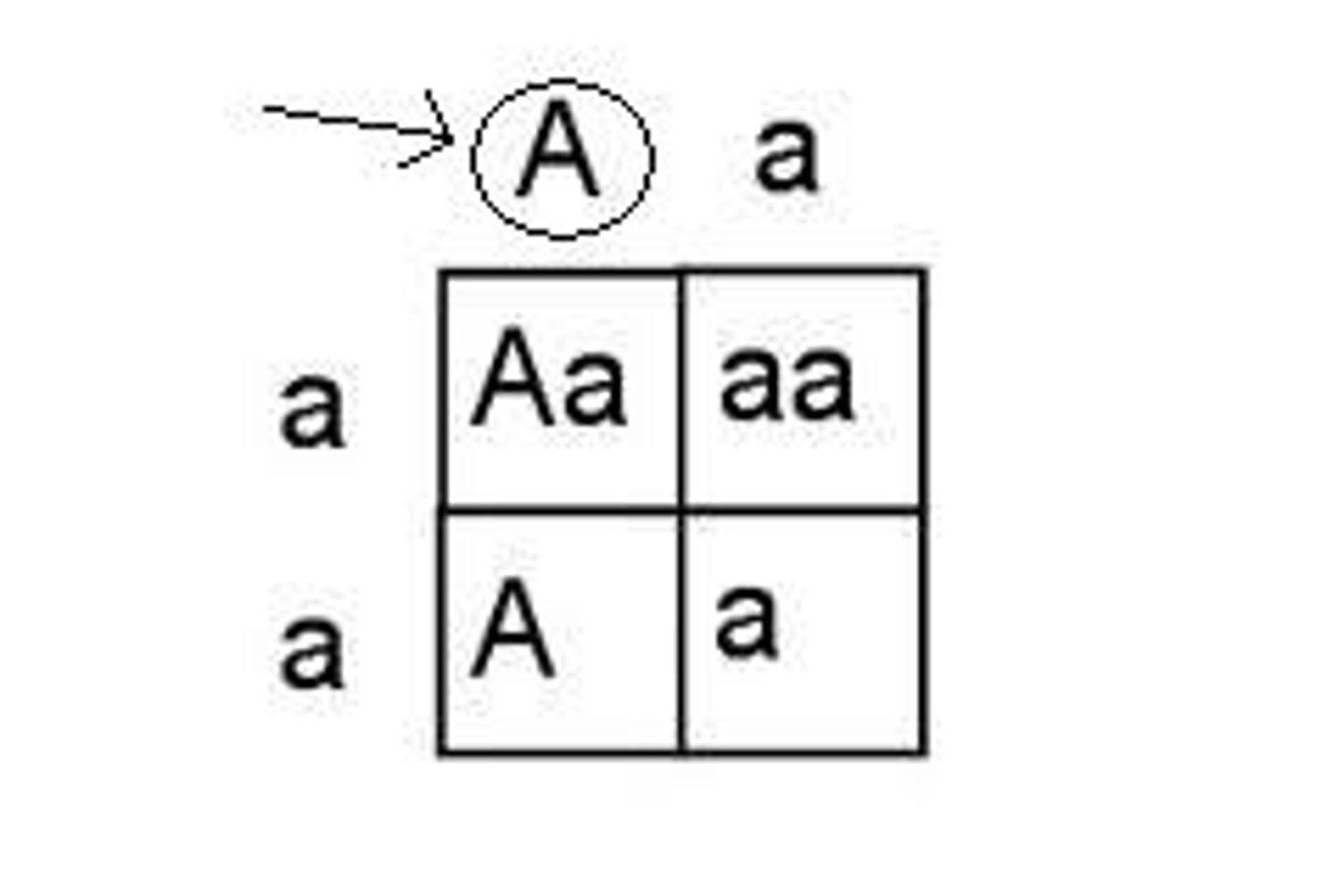
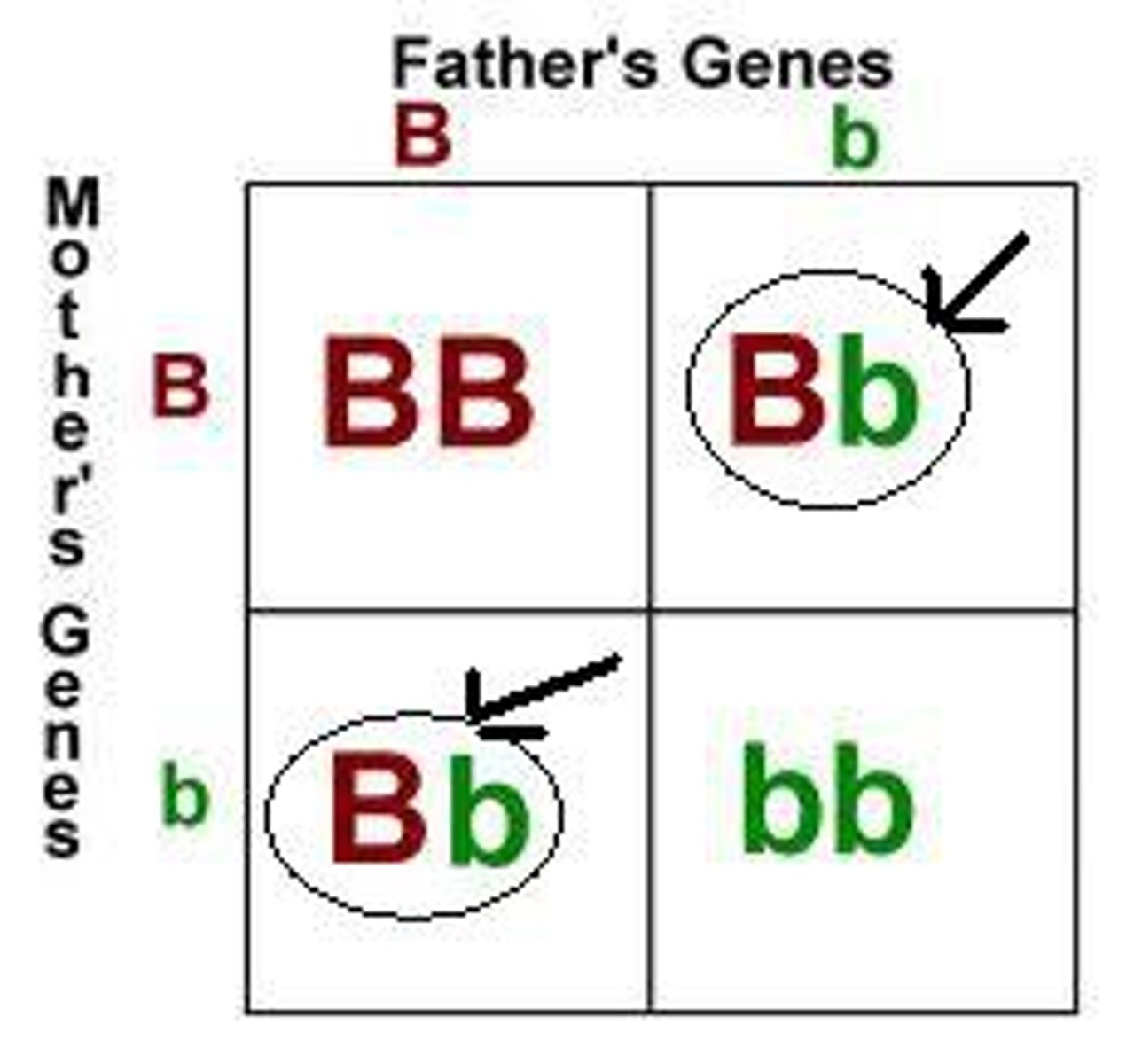
Dominant
A trait that will show up in an organism's phenotype if gene is present
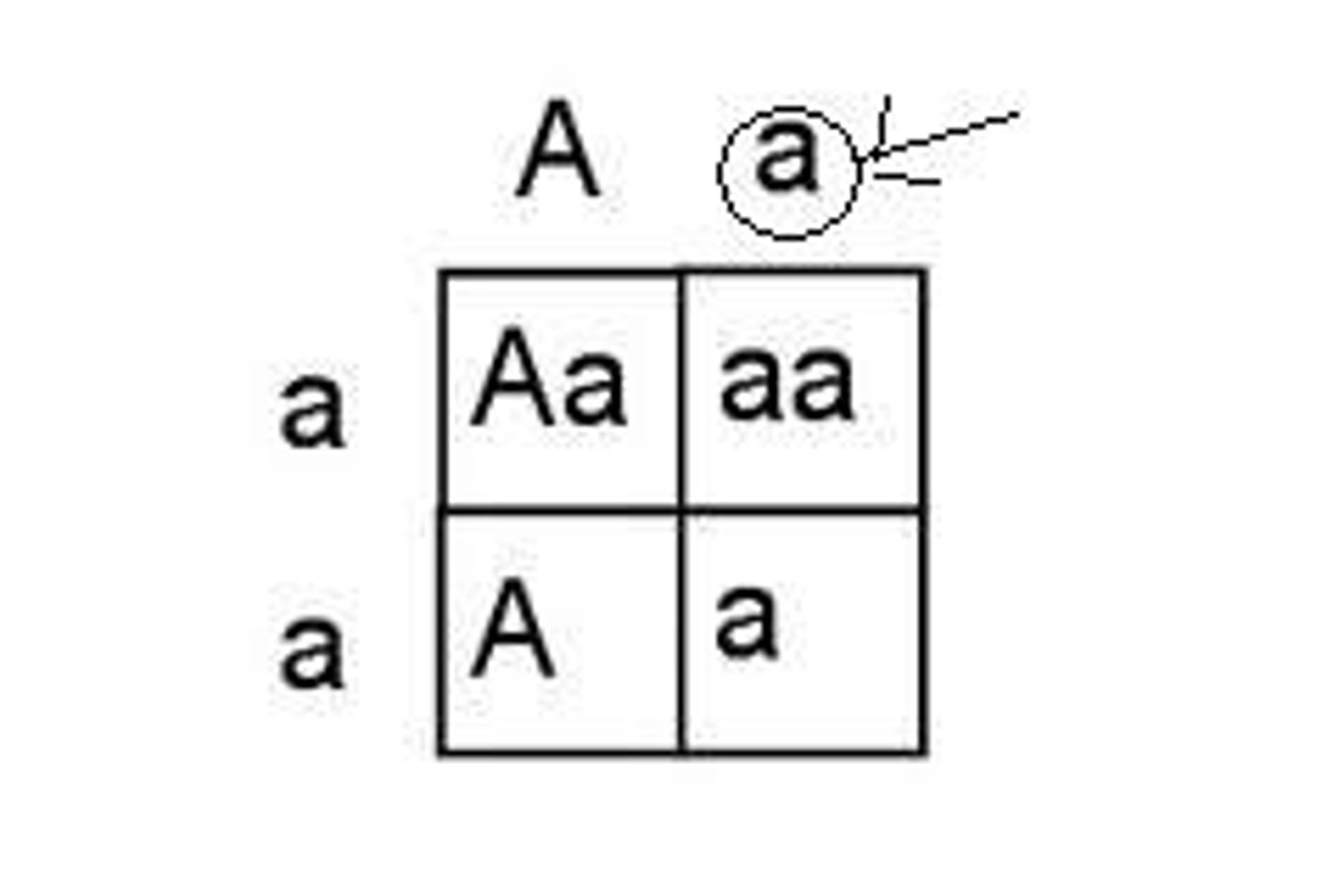
Recessive
A trait that will only appear in the phenotype if organism inherits two of them; covered up by the dominant gene
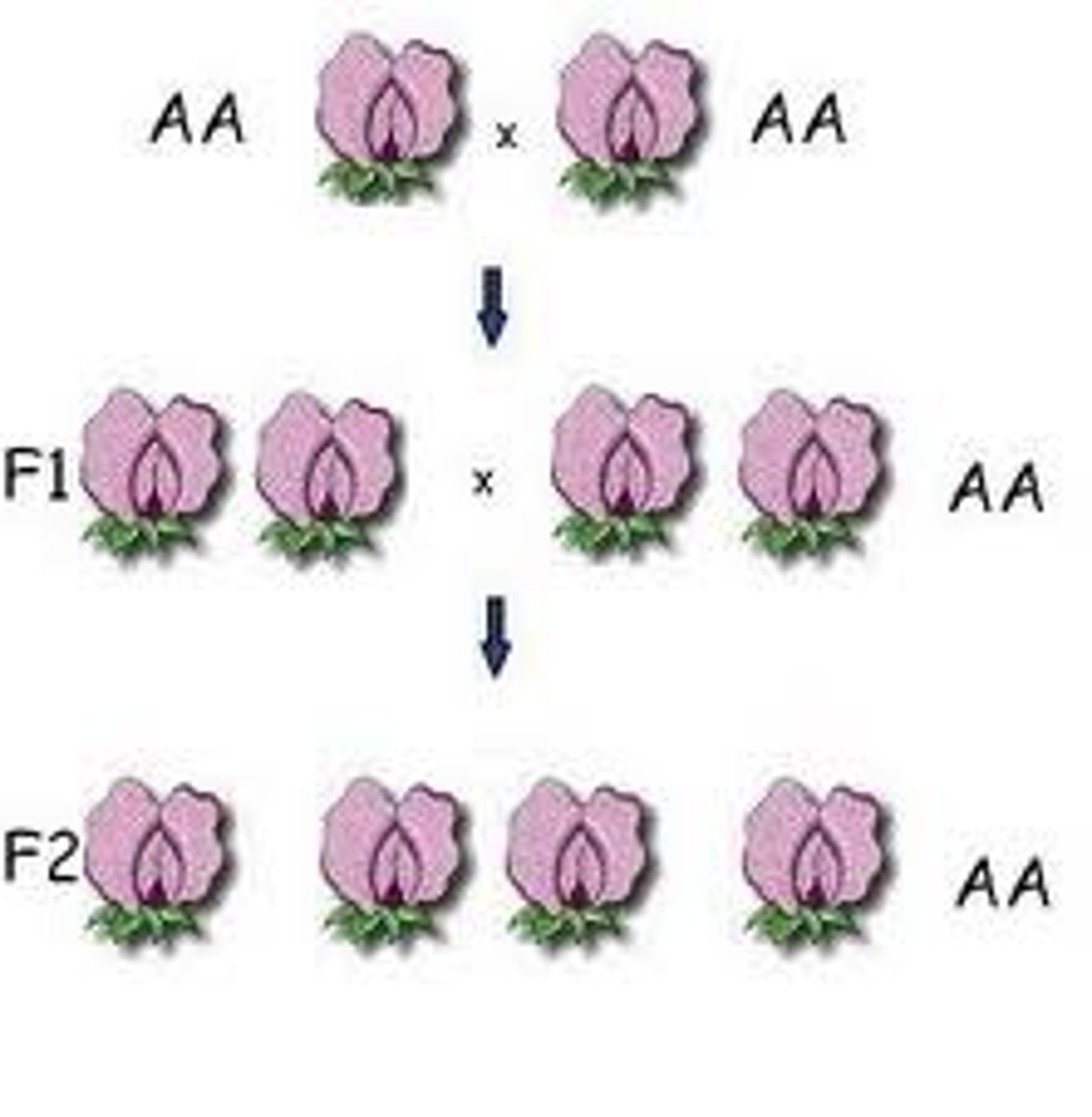
True-breeding
Inherited two identical alleles for a trait; homozygous or purebred
Segregation
The separation of alleles during meiosis or gamete formation
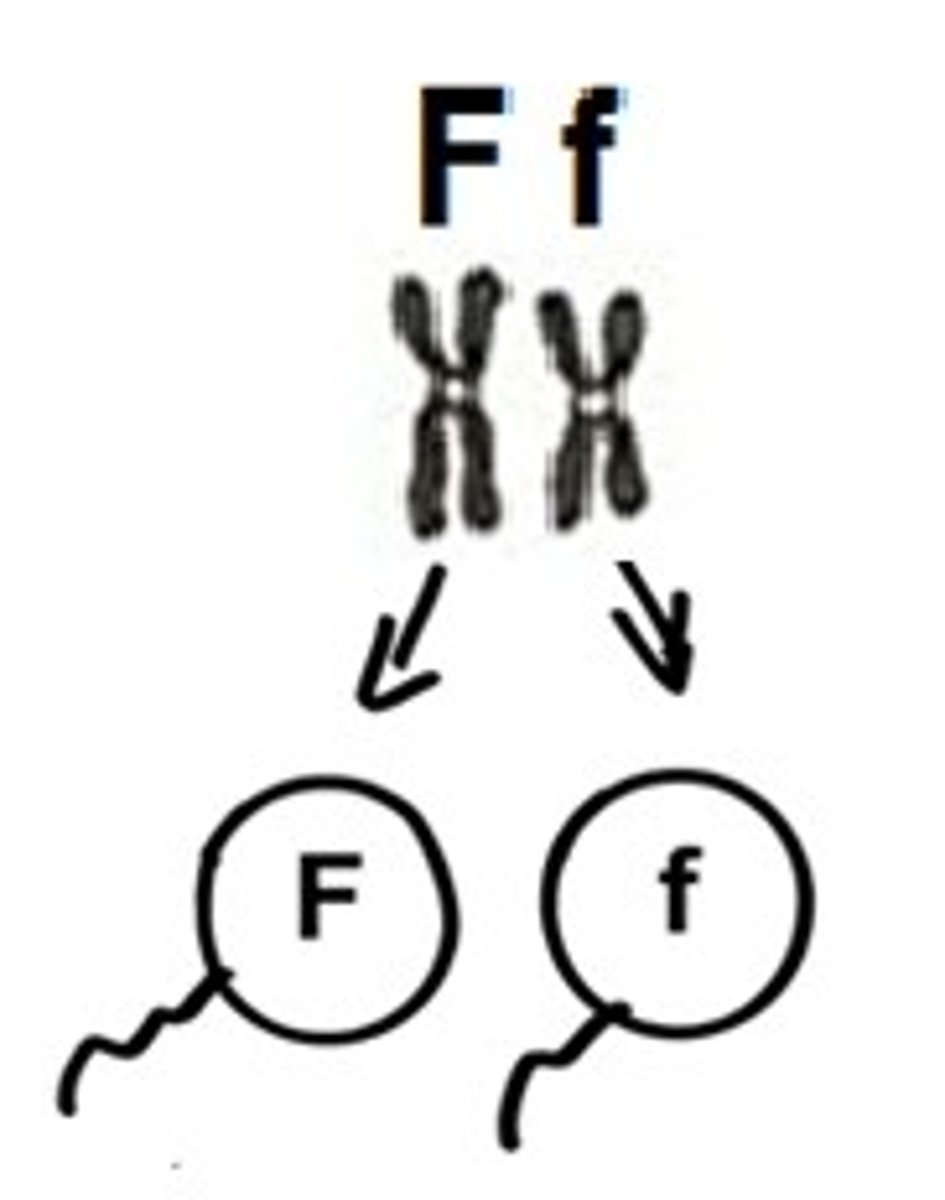
Gamete
Sex cell; sperm or egg
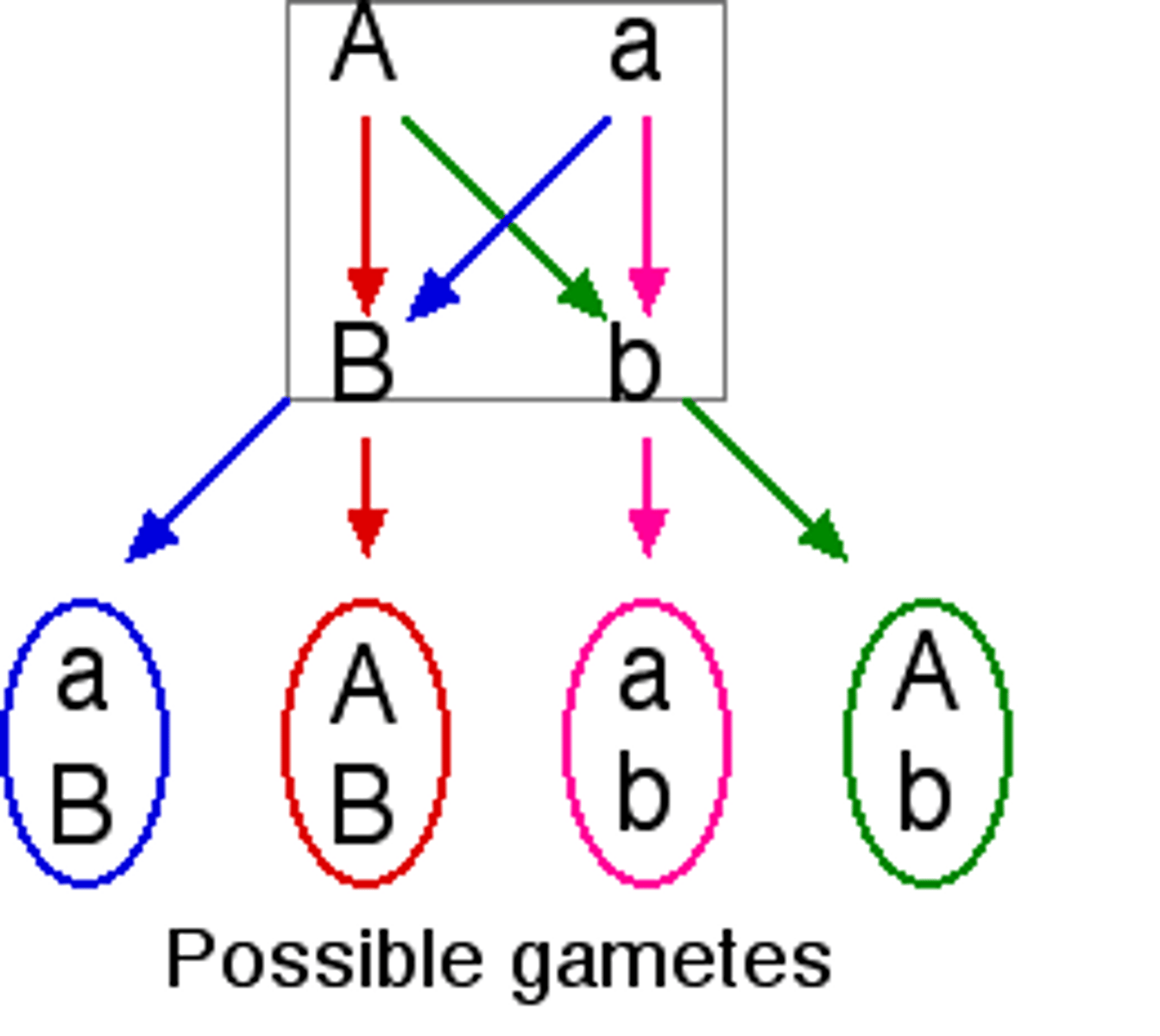
Independent assortment
Homologous chromosomes randomly line up and separate during meiosis
Hybrid
The offspring of a cross between parents with different traits; heterozygous
Principle of Dominance
Mendel's conclusion that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive and dominant alleles mask or cover up recessive alleles when present
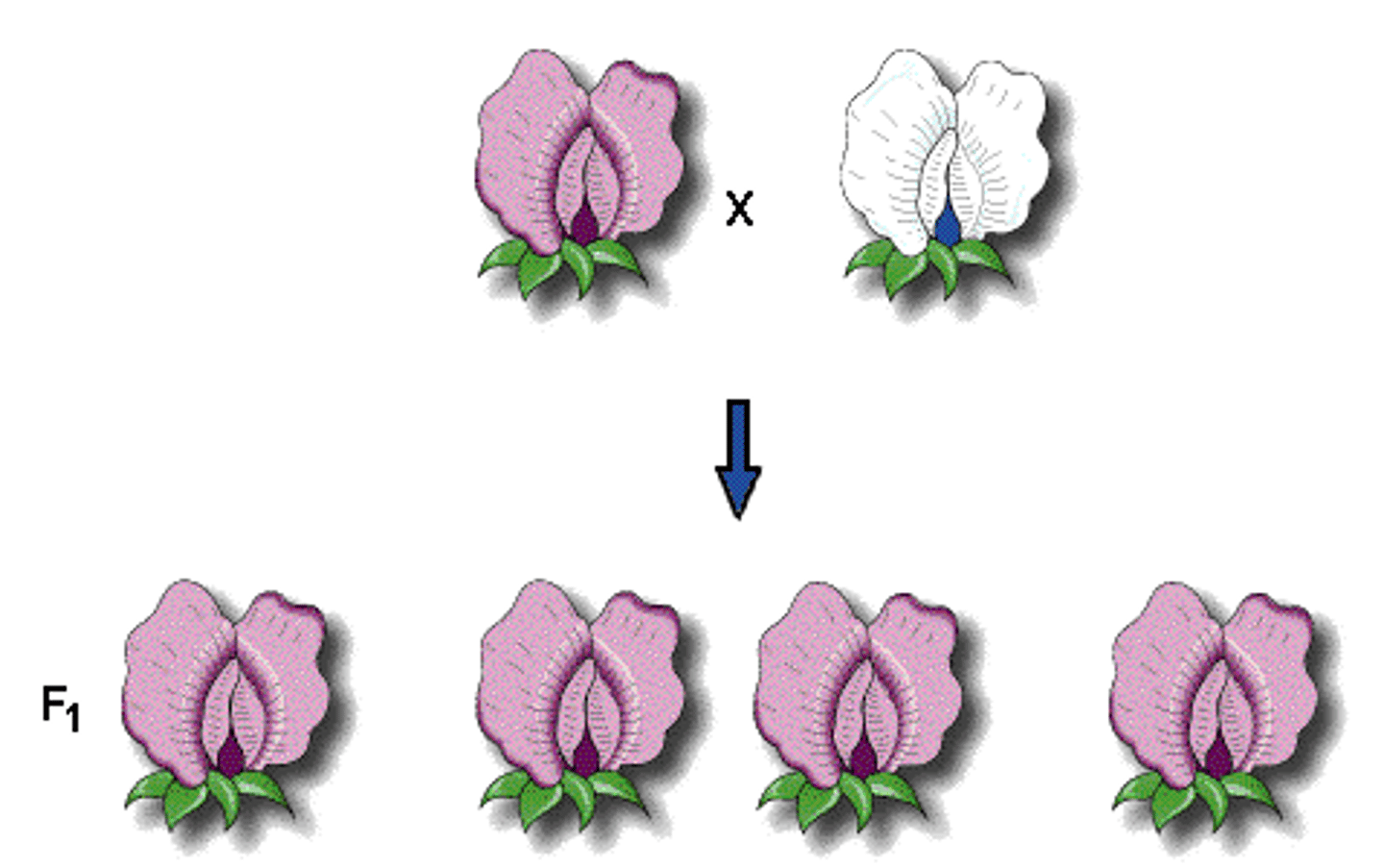
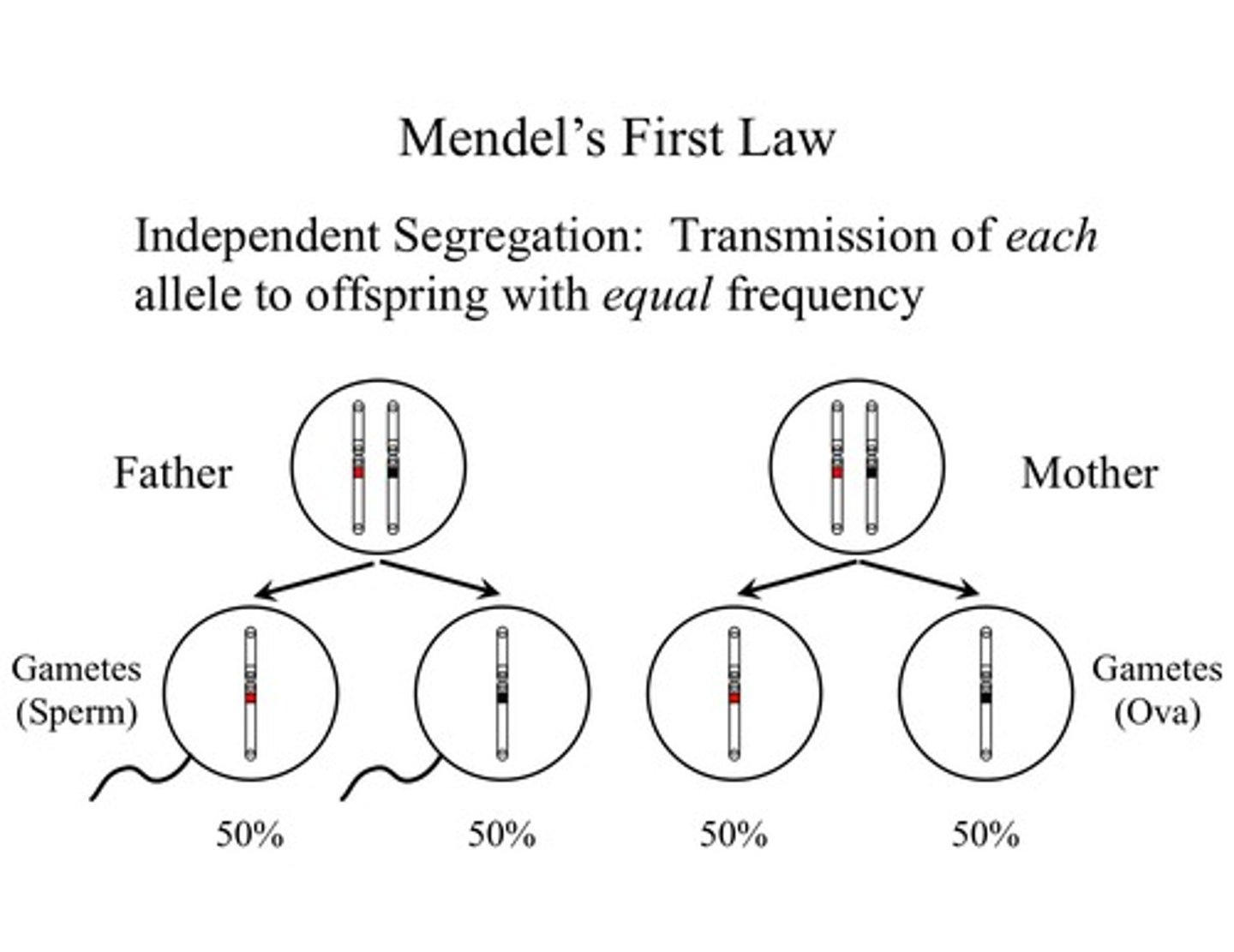
Law of Segregation
Mendel's Law that states that factors (alleles) for the same trait separate during gamete formation
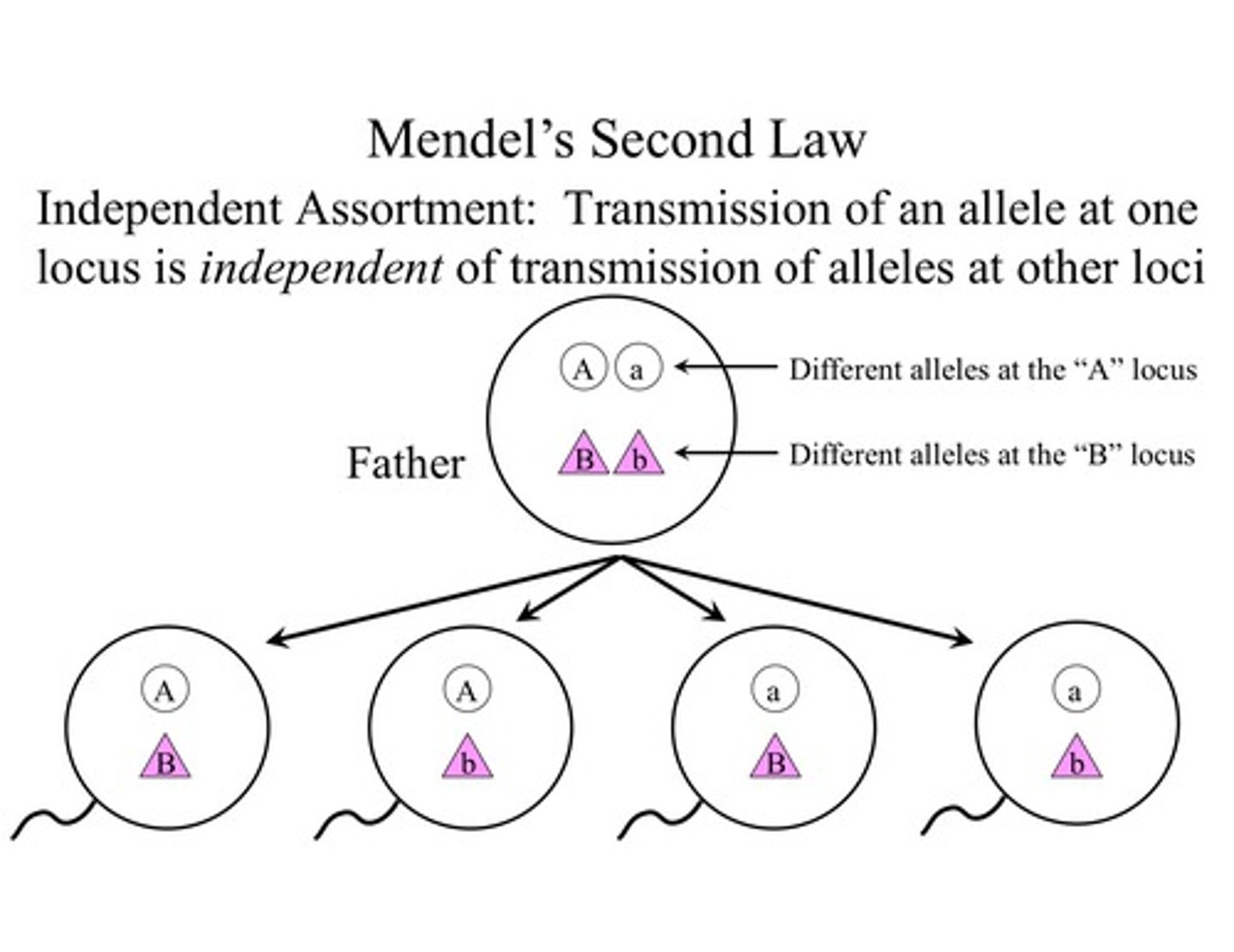
Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel's second law, stating that each allele pair segregates independently during gamete formation; applies when genes for two characteristics are located on different pairs of homologous chromosomes
Gregor Mendel
Austrian monk and botanist whose experiments in breeding garden peas led to his eventual recognition as founder of the science of genetics (1822-1884); experiments with pea plants led to the law of dominance, independent assortment, and segregation.

Flower
Reproductive structure of the plant
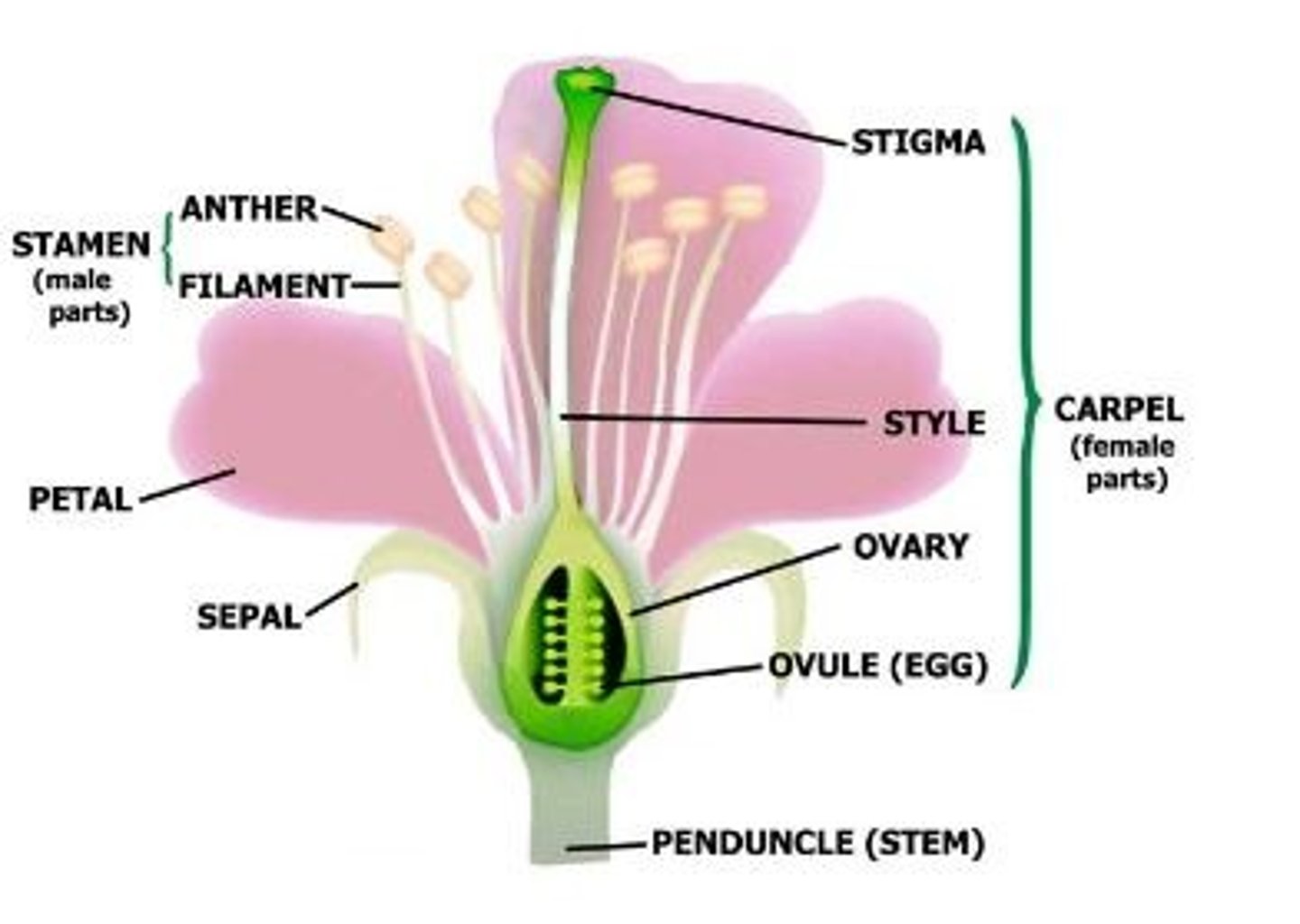
Stamen
Male parts of the plant that include the anther, filament and pollen

Carpel
Female parts of the plant that include the stigma, style, ovary, ovule

Pollen
A fine powdery substance, typically yellow, consisting of microscopic grains produced by the male part of a flower; each grain contains a male gamete that can fertilize the female ovule, when transported by the wind, insects, or other animals; male gamete

Ovule
A structure that develops within the ovary of a seed plant that contains the female germ cell and after fertilization becomes the seed; female gamete

P Generation
Parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
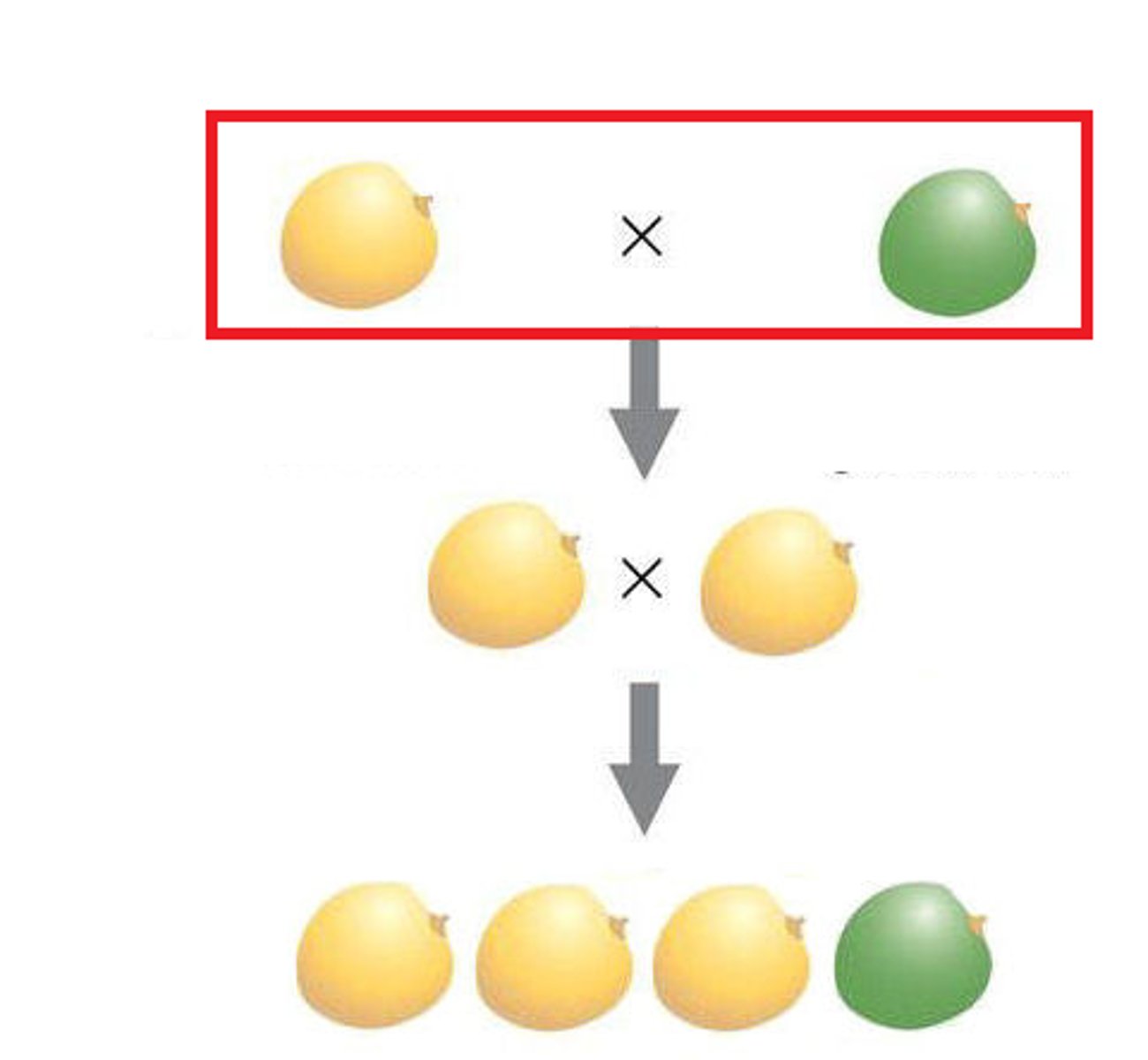
F1 Generation
The first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
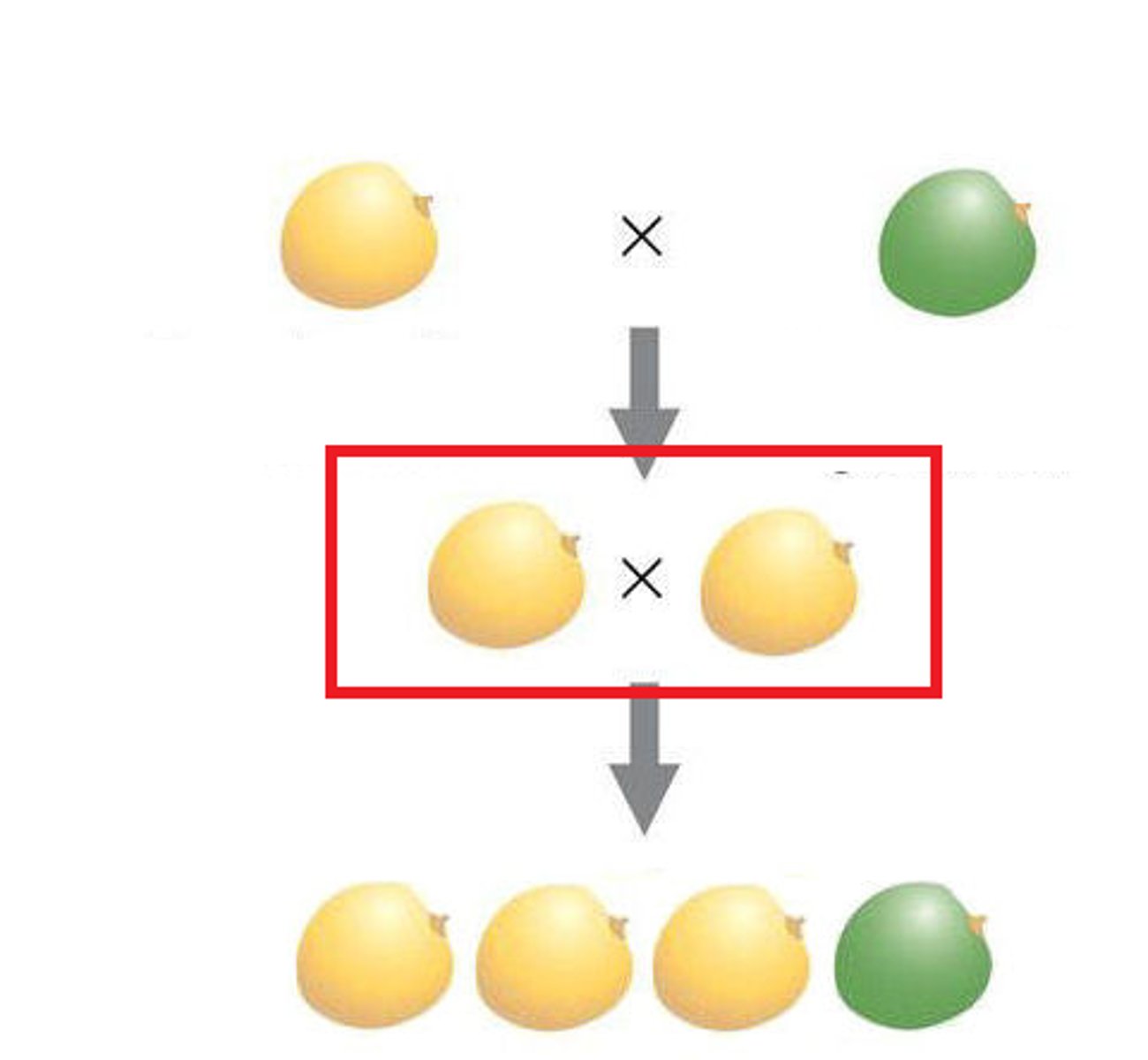
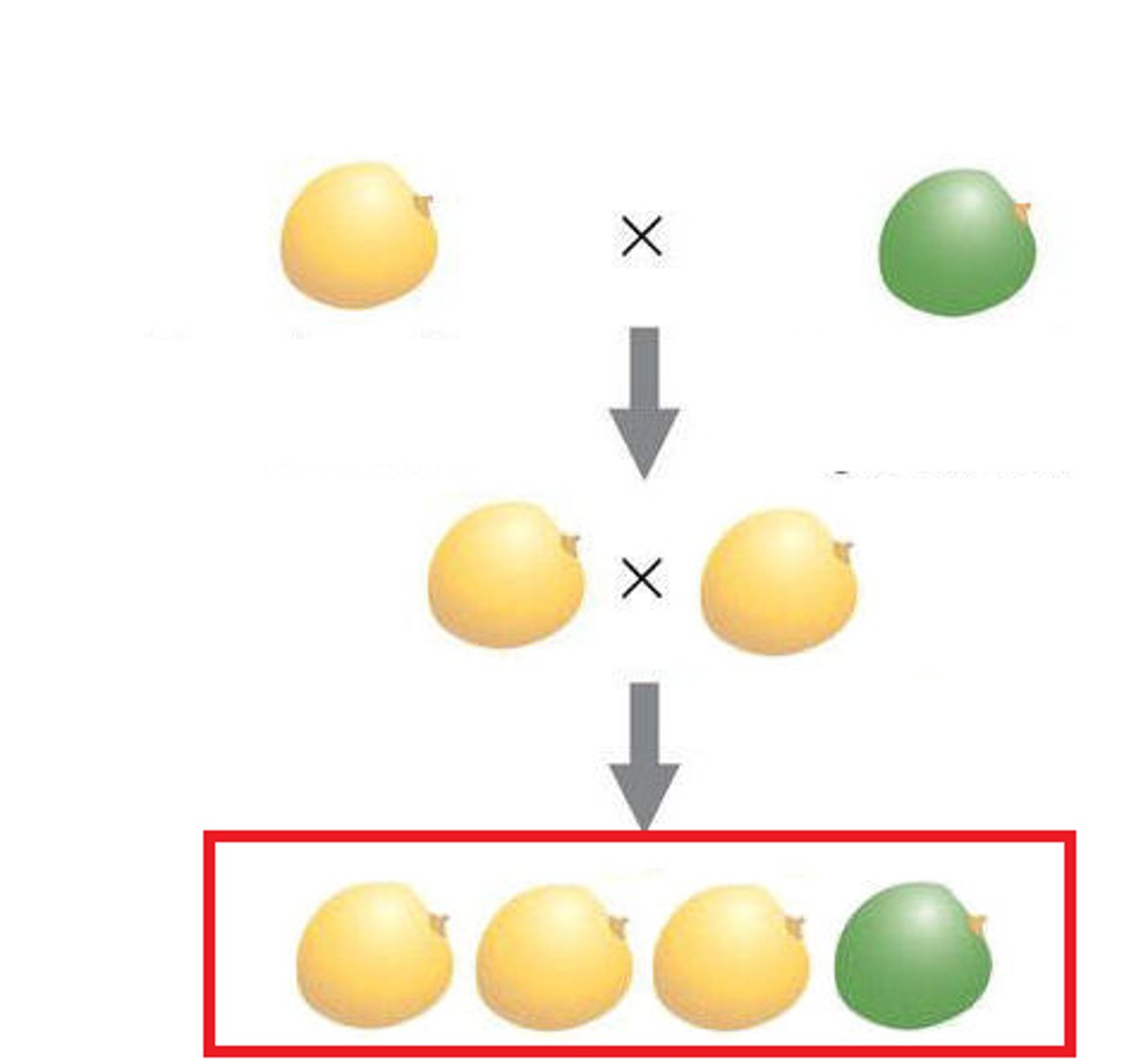
F2 Generation
The second generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two F1 organisms
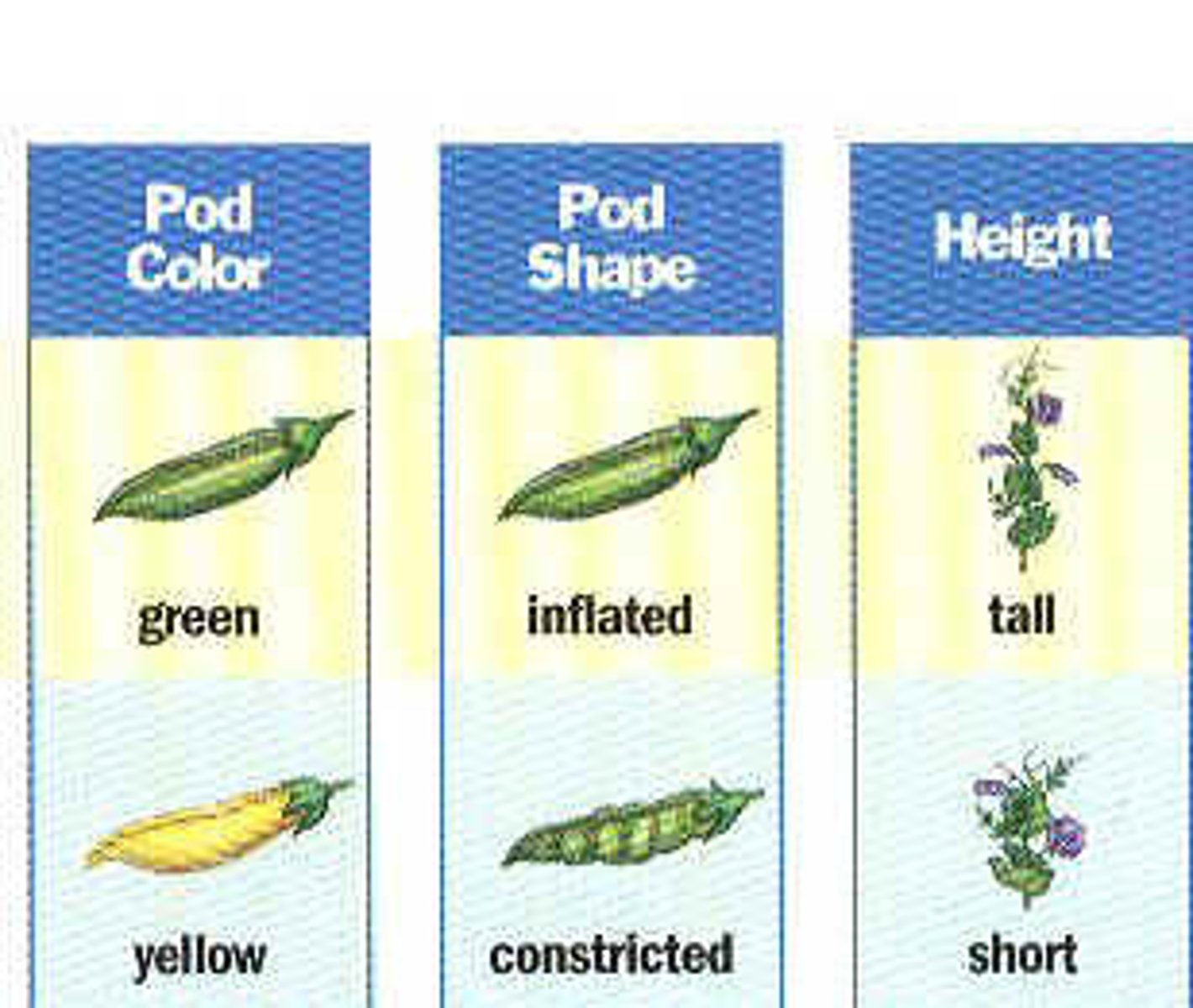
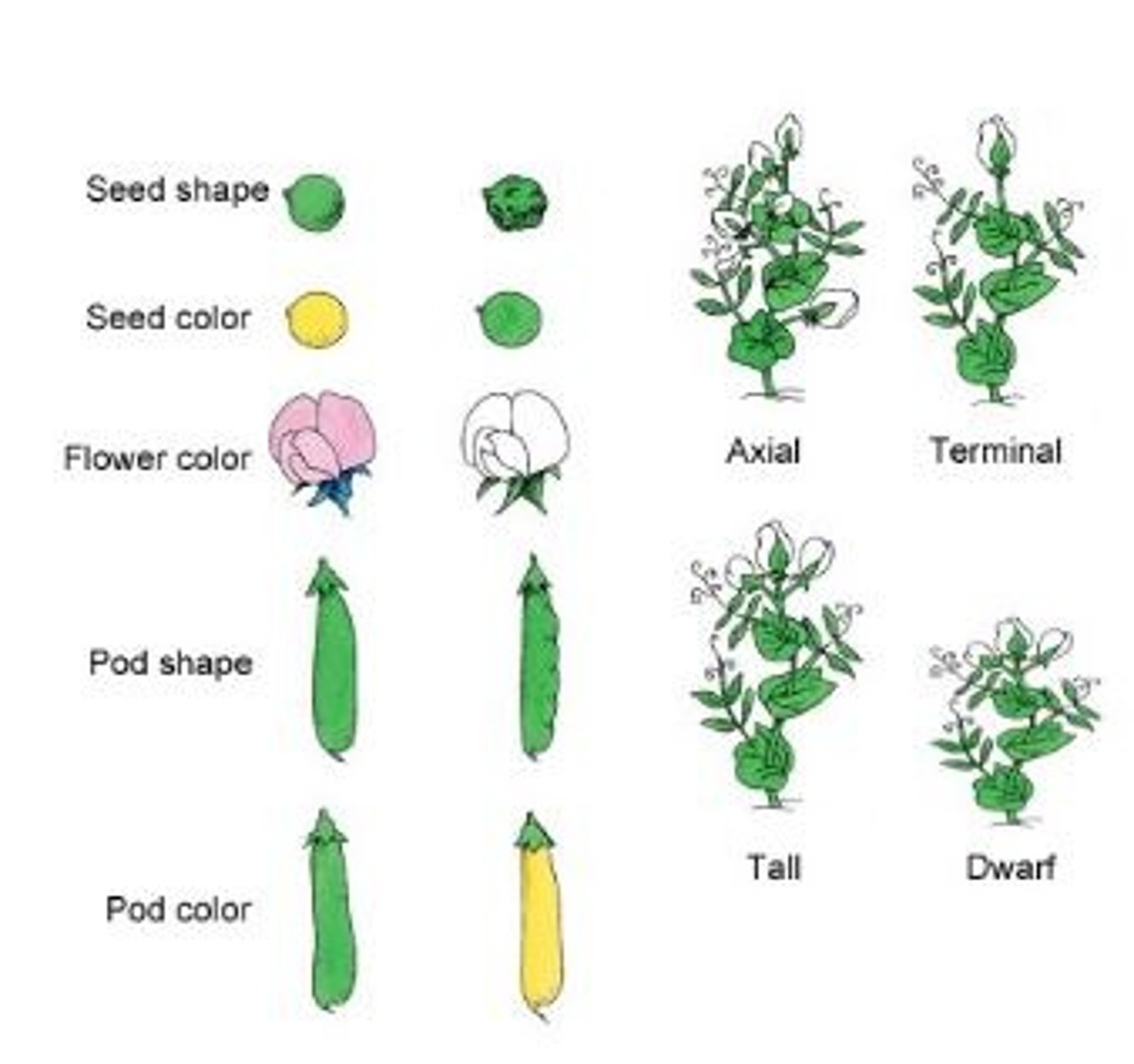
Pea Traits (Examples)
Seed shape
Seed color
Flower color
Pod shape
Pod color
Flower Location
Plant height
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations (i.e. TT, Tt, tt
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits (i.e. Tall/Short Plant, Purple/White Flowers)
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait (i.e. Tt, Rr, or Aa)
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
(i.e. TT/tt, RR/rr, or AA/aa)