2 Money Demand, Interest Rates, Monetary Policy Transmission
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Why is there Demand for Money
For simplicity assume only assets are money and bonds
Money Provides: Liquidity and universally accepted
Bonds: Provide financial return through interest rate
What does demand for money depend on?
Depends on how frequently we transact
Nominal GDP used to approximate volume of transactions
What is used to approximate the volume of transactions
Nominal GDP
Nominal Money Demand is Proportional to
Real Money Demand is proportional to
Nominal GDP
Real GDP
How do interest rates affect the demand for money.
Higher interest rates mean higher opportunity costs of holding money
So demand is lower
Lower interests rates meran its cheaper to borrow
So demand is higher
Real Money (Purchasing Power) Demand
Increases with
Decreases with
Increase with higher Real Income
Decrease with higher interest rates
Money Market Equilibrium
When the demand for money equals the supply of money at a given interest rate.
Formula for Real Money Supply
Real Money Supply = Nominal Money Supply / Price Level
Central Bank’s influence on real money supply
Short-run
Long-run
Short-run (Prices are Fixed)
Can influence real money supply, because prices are fixed and they can change nominal money supply
Long-run (Prices are flexible)
Cannot directly control real money supply
It can only adjust real money supply through controlling inflation (rate of price increase)
Relationship between interest rates and consumption demand
If Interest is high, stocks and bonds go down in price so people feel poorer
This reduces consumption
If interest is lower, stocks and bond go up in price, so people feel richer
Increasing consumption
Relationship between Interest Rates and Investment
High Interest, increases cost of borrowing so Lower investment
Low Interest, decrease cost of borrowing so Higher Investment
What does monetary policy of CB’s usually target?
usually targets stable inflation rate (price stability)
Also output and employment
Expansionary vs Contractionary Monetary Policy
Expansionary
Used to boost output during recession or low inflation
Increases Money Supply (and Inflation) by lowering interest rates encouraging higher investment and consumption
Contractionary
Used to reduce output during high inflation
Reduces Money Supply (and Inflation) by raising interest rates to curb spending and borrowing.
What is the Transmission Mechanism (Chain Reaction) of Monetary Policy
And what does it depend on
Shows how a change in interest rates by the central bank affects the overall economy
Depends on long-term projected interest rates that drive consumption and Investment (Increase AD)
Steps
Monetary Policy
Affects short term interest rates impact the projected long-term interest rates
Long-term interest rates affect Aggregate Demand
Influences cost of borrowing, hence C and I, leading impact on AD and inflation.
Why do modern central banks generally use the interest rate as an instrument for monetary policy?
Interest rates influence borrowing, saving, and consumption
Fast and Predictable Transmission
Easy to Communicate and Manage Expectations
Model of Demand for Money
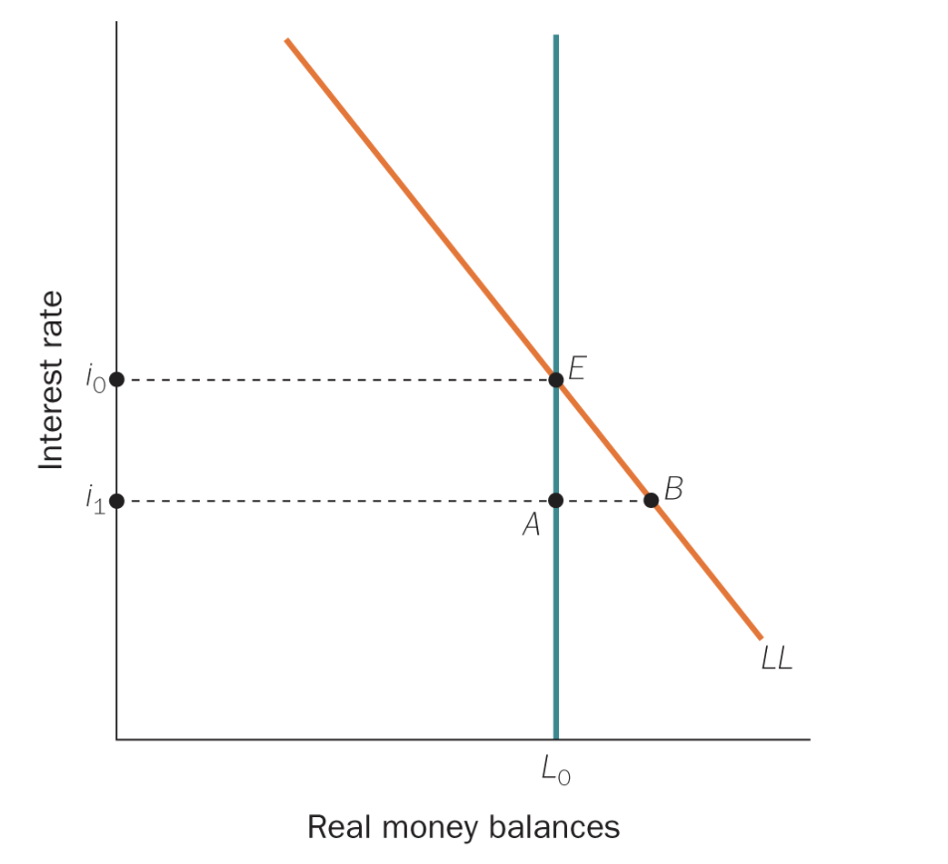
Vertical line (L₀):
Real money supply is fixed by the central bank (independent of interest rate).Downward sloping line (LL):
Demand for real money balances.
⤵ Interest rate ↑ → holding money is more costly → demand for money ↓Equilibrium at point E:
Interest rate i₀ where money demand equals supply (L₀).Point A (below E):
At lower interest rate i₁, people demand more money than is supplied → excess demand.Point B (off equilibrium):
Shows how demand would rise if interest rates fell, but supply (L₀) is fixed.
Intermediate Target meaning
Variable that Central Bank tries to control to help achieve inflation or employment goal
e.g. Money supply, interest rates, exchange rates
Quantitative Easing
A type of Non-traditional Monetary Policy
When a central bank creates new money to buy financial assets (like government bonds) to inject money into the economy and lower interest rates, especially when normal interest rate cuts aren't enough.
Money Illusion
When people focus on Nominal values instead of Real values