Chapter 19: Hypothesis Testing for Proportions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a null hypothesis (H0)?
A statement of no effect or no difference; it assumes the status quo (e.g., H0: p = 0.5).
What is an alternative hypothesis (HA)?
A claim we test against the null; it represents the effect we’re looking for (e.g., HA: p > 0.5).
What is a p-value?
The probability of observing a statistic as extreme as the one obtained, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
What does a small p-value indicate?
Strong evidence against the null hypothesis — the result is unlikely by chance alone.
What is the general form of the test statistic for a proportion?
Where p0 is the null value.
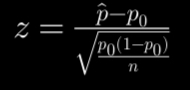
What conditions are needed for a valid hypothesis test about a proportion?
Random sample
10% Condition (independence)
Success/Failure: np0 >=10 and n(1 - p0) >= 10
What is a one-proportion z-test?
A statistical test used to test claims about population proportions using z-scores.
What are the steps of a hypothesis test?
State H0 and HA
Check conditions
Calculate test statistic
Compute p-value
Make a conclusion (reject/fail to reject H0)
What does it mean to “fail to reject” H0?
There is not enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
How is the conclusion of a test written?
Use context. Example: “There is sufficient evidence to suggest the proportion of voters is greater than 50%.”
Why do we never say “accept” the null?
Because the test only checks if data is inconsistent with H0, not proof that H0 is true.
When do you use the Normal model in a proportion test?
Only if the sample meets the Success/Failure and 10% conditions.