ARCC BU REVIEWER PART 2 (Electrical System)
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From recorded lecture video (2024)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Fossil fuel (Petroleum)
Source of energy for electric generation characterized by the burning of fuel in an internal combustion engine
Coal and Natural Gas
Source of energy for electric generation characterized by heating water and thus generating steam to start a turbine that initiates the electricity generation process
Nuclear energy
Source of energy for electric generation characterized by utilizing nuclear fission that releases a huge quantity of energy to produce steam which rotates a turbine with an alternator.
Hydroelectricity
Source of energy for electric generation characterized by the potential energy of dammed water driving a turbine and generator
Wind power
Source of energy for electric generation characterized by the conversion of wind energy into electricity through wind turbines.
Geothermal power
Source of energy for electric generation characterized by the use of geothermal heat for electricity generation
Solar energy
Source of energy for electric generation characterized by harvesting the energy of the sun by using collector panels and fields to gather enough power to charge small substations
Powerhouse
An independent building or integrated space (usually on the building’s second/third floor) that houses the transformer room, main electrical room, and generator room.
Transformer
A static alternating current (AC) device used to change voltage by increasing or reducing it
1 meter
The distance between the genset and the walls of the room’s walls
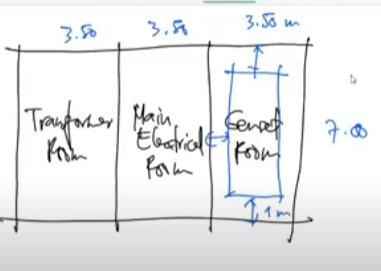
3.50 × 7.00 m
Usual size of the genset room
Electrical Room per floor
Room per floor in a multistory building that contains the feeder, conduits, and wiring for electricity
2 - 3.5 sq.mm.
Size of wires used in lighting applications if TW, THW, or THWN will be used
2 - 5.5 sq.mm.
Size of wires used in general purpose applications if TW, THW, or THWN will be used
2 - 2.00 sq.mm.
Size of wires used in lighting applications if THHN will be used
2 - 3.5 sq.mm.
Size of wires used in general purpose applications if THHN will be used
Conduit
A tube, pipe, or duct for enclosing and protecting electrical wires and cables
PVC Conduit
Usual conduit material
Rigid Steel Conduit
Abbreviated as RSC, these conduits are used for heavier wiring (e.g. main feeder wires, service entrance wires)
Electric Metallic Tubing
Abbreviated as EMT, it is a metal pipe conduit into which electrical conductors may be draw; has a thinner wall thickness than a rigid metal conduit.
Flexible metallic conduit
Known to the trade as Greenfield, these are non-rigid metal conduits used for motor connections and other locations where bibration is present, where movement is encountered, or where physical obstructions make its use necessary
Aluminum conduit
Abbreviated as AC, it is a type of conduit that is durable in outdoor and indoor uses, and non-magnetic, however limited in production due to costs.
Raceways
A channel expressly designed to hold and protect electrical wires and cables; can be opened up to accommodate new wiring installations as compared to enclosed conduits
Surface raceway
Type of raceway designed for exposed installation in dry, nonhazardous, noncorrosive locations, used for thin wall panels (e.g. hollow-core, precast walls) that don’t allow wiring inside the walls
Floor raceway
An arrangement of parallel rectangular metal or heavy plastic raceways laid on the structural slab and covered with concrete fill; can limit new wiring installations due to being embedded in the floor
Cellular metal floor raceway
A fully accessible floor raceway, provided by a cellular (metal) floor that is an integrated structural or electrical system
Wireways
Colloquially called gutter in the Philippines, it is a conduit to conceal electrical wires while rendering them permanently accessible
Busways
Also called bus duct, it is a rigid metal housing for a group of buses
Cable tray
Also called cablebus, it is an open metal framework for supporting insulated electrical wires
Full-access floor
Applicable to spaces with very heavy cabling, requirements particularly if frequent recabling and reconnection are required
Multichannel raceway
A surface-mounted raceway designed to house the electrical wires for a circuit and a series of receptacles; can be metallic or nonmetallic
Overcurrent
Any situation in which the current flow througha device or conductor exceeds the desired value is known as an over current. Both overload and short circuit can cause excessive current flow. Over currents may heat or damage the device
Panelboard
A single or group of panel units designed for assembly in the form of a single panel; including buses, automatic overcurrent devices, and equipped with or without switches for the control of light, heat, or power circuits
Circuit breaker
A device designed to open and close a circuit by nonautomatic means and to open the circuit automatically on a predetermined over-current without damage to itself when properly applied within its rating.
Ground-Fault Circuit-Interrupter (GFCI)
Type of circuit breaker that is used for wet areas (e.g. bathrooms); also helps protect individuals against shock, and detects even a very small current leak to a ground, which may not be detected by conventional circuit breakers
Fuse
An overcurrent protective device with a circuit opening fusible element which opens (break) when there is an overcurrent in the circuit