Anatomy Final Pregnancy
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
pregnancy
events that occur from fertilization until the infant is born
gestation period
last menstruation period to birth
-typically about 270 days
conceptus
the pregnant woman’s developing offspring (embryo or fetus)
-”the product of conception at any point between fertilization and birth”
embryonic period
fertilization through the 8th week
fetal period
9th week through birth
fertilization
oocyte & sperm
sperm fuses with an egg & forms a zygote
coitus
sexual intercourse
oocyte viability duration
12-24 hours
sperm viability duration
24-72 hours
for fertilization to occur
coitus must occur no more than 3 days before to 24 hours after ovulation
ovulated oocyte is encapsulated by
-corona radiata
-zona pellucida
corona radiata
-made of granulosa cells (secrete estrogen and progesterone)
zona pellucida
-coats the oocyte
-sperm secretes enzyme to penetrate
monospermy
only one sperm is allowed to penetrate the oocyte
mechanisms to ensure monospermy
-fast block to polyspermy
-slow block to polyspermy
fast block to polyspermy
plasma membrane depolarization
-makes oocyte more positive inside which repels more sperm from penetrating
slow block to polyspermy
cortical granules (oocytes) release enzymes destroying sperm receptors
monozygotic
identical twins
dizygotic
fraternal twins
identical twins
-develop from one zygote, which splits to form 2 embryos
-since identical twins develop from one zygote, they will be the same sex
-each twin develops from a separate egg and each egg is fertilized by its own sperm cell
-in very rare cases twins can have the same mother and different fathers
blastocyte implants in
the uterus
teratogen
harmful factors to the embryo
functions of the placenta
-nutrient and gas exchange
-endocrine function
encocrine function of the placenta
including human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), estrogen and progesterone
placenta is fully formed
by 3 months
formation of placenta
stimulated by implantation
extraembryonic tissues
-chorion
-amnion
-amnionic fluid
-yolk sac
-umbilical cord
chorion
-outermost membrane
-involved with implantation/attachment to endometrium
amnion
fluid-filled sac around embryo/fetus
amnionic fluid
-protection
-temperature regulation
-lung development
-nutrient and waste exchange
yolk sac
-contains very little yolk
-involved with blood cell production early on
-most of yolk sac gets incorporated into GI tract by 20 weeks
umbilical cord
-tube containing blood vessels (go in and out of fetus)
-connects fetus to placenta
human chorionic gonadotropin
hCG
hCG
-levels rise about 2 days after implantation and remain elevated for several months
-”saves” the corpus luteum
prosgesterone prevents
menstruation that would flush away the newly implanted embryo (blocks ovulation & decreases LH synthesis)
progesterone levels
high during pregnancy (except delivery)
progesterone
-prevents uterine shedding (as mentioned above)
-prevents uterine contractions
estrogen levels
stay high until birth happens
estrogen
-uterine/placental growth and development
-fetal development
uterine/placental growth and development with estrogen
promotes the enlargement of uterine muscles and blood vessels, ensuring adequate blood supply to the placenta and fetus
fetal developement with estrogen
estrogen influences the developement of various fetal organs and tissues
effects of pregnancy on the mother
-anatomical changes
-metabolic changes
anatomical changes
breasts enrlage, arola darkn, uterus expands, lordosis is likeley, pelivic ligaments & pubic symphysis relax, weight gain
avergae weight gain from pregnancy
about 30 poulnds
metabolic changes
placenta secretes hormones to stimulate breast maturation, increase maternal metabolism, (increase activation of vitamin D)
why is vitamin D important during pregnancy
helps formore calcium to provide growth of fetal skeleton
physiological changes effects of pregnancy
-GI tract
-urinary tract
-respiratory
-cardiovascular system
GI tract changes
morning sickness (increase estrogen & progesterone), constopation, gastroesophogeal reflux disease (GERD)
morning sickness cuased by
increase of estrogen and progesterone
Urinary tract changes
polyuria (increase urinary production) due to increase blood volume, increased metabolic wastes, bladder compression
respiratory changes
sometimes dyspnea (difficulty breathing: late term) due to enlarged uterus
cardiovascular system changes
increase blood volume (25-40%)
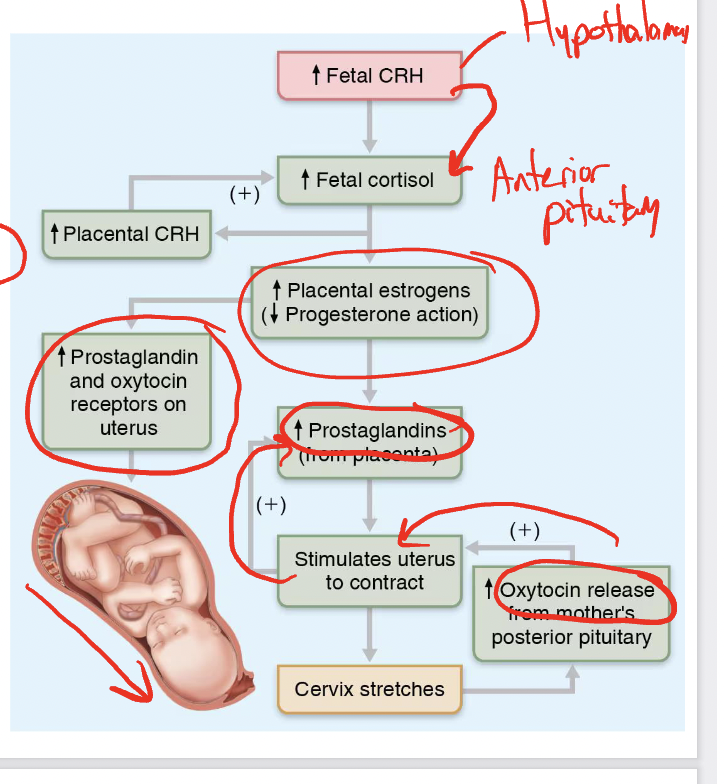
hormonal induction of labor
fetal CRH (hypothalamus) —> fetal cortisl (anteriror)—> increase estorgens (decrease progesterone)—>increase prostaglandins and ocytocin receptors—> increase prostaglandins—> stimulates contractions
pills for abortion
-mifepristone
-misoprostol
mifepristone
blocks progesterone receptors
misoprostol
synthetic prostaglandins
stages of labor
-dilation
-expulsion
-placental
dilation stage
– Time from labor’s onset until the cervix is fully dilated
by the baby’s head (about 10 cm in diameter).
– Typically lasts 6-12 hours
-eventually the ammonion ruptures, releasing ammniotic fluid, an event commonly referred to as the mother’s “water breaking”
early dilation
weak contractions
late dilation
contractions become more vigorous (oxytocin) and rapid
infant’s head is forced against the cervix with each contraction, the cervix softens, effaces (thins), and dilates
estrogen likely plays a role with this
expulsion
-vertex position
-breech position
expulsion
-lasts from full dilation to delivery of the infant
-typically lasts 50 minutes in a first birth and 20 minutes in subsequent births
-crowning occurs when the largest dimension of the baby’s head is visible through the vaginal opening
first birth expulsion is typically
50 min
crowning
occurs when the largest dimension of the baby’s head is visible through the vaginal opening
vertex position
head-first
-skull dilates cervix
breech position
buttock-first
-delivery more difficult; often forceps required, or C-section (delivery through abdominal and uterine wall incision)
placental stage
-delivery of placenta (aftebirth)
-usually accomplished within 30 minutes after birth of the infant
infant’s physical status is assessed within
1-5 minutes after birth
infant’s physical status is assessed based on
5 signs (0-2): heart rate, respiration, color, muscle tone, reflexes
-apgar score
apgar score
total score of above healthy scores (8-10 healthy)
umbilical arteries
carry deoxygenated blood from fetus to placenta
umbilical vein
carries oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
ductus venous
carries blood from umbilical vein to inferior vencava
ductus arteriosus
carries blood from the pulmonary trunk to the aorta
-allows blood to bypass the lungs
foramen ovale
flap covered hole between right and left atria
lactation
-rising hormone levels toward end of pregnancy prepare mammary glands
-colostrum —> then true milk
colustrum
1st 2-3 days (vitamin A, protein, minerals, & igA antiboies
no fat;little lactose
later turns to true milk
advantages of breast milk
-beneficial chemicals
-natural lacatives help cleanse bowels of meconium/feces
beneficial chemicals in breast milk
IgA (& other uimmunoglobins), other molecules involved with immunity (like complement)
meconium is composed of
materials ingested during the time the infant spends in the uterus (intestinal epithelial cells, lanugo, mucus, amniotic fluid, bile and water)
sticky, think, dark green