hnsc 1210 unit 7: the vitamins
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
vitamins
organic compounds that are vital to life ad indispensable to body functions
only needed in minute amounts, and are non-caloric, essential nutrients
2 classifications for vitamins
fat soluble
water soluble
what are the fat soluble vitamins
vitamin A
vitamin D
vitamin E
vitamin K
water-soluble vitamins
B vitamins
Thiamine (B1)
Riboflavin (B2)
Niacin (B3)
Folate
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B6
Biotin
Pantothenic acid
Vitamin C
fat soluble vitamins
dissolve in lipid and required bile for absorption
absorbed into the lymph and travel through the blood with protein carriers
stores in liver or with other lipids in fatty tissues and can build in toxic amounts - use with caution with fat soluble vitamin supplements
Vitamin A
first fat soluble vitamin recognized
three active forms of vitamin A
retinol is stored in the ivermectin and the body’s cells convert retinol to the other two active forms;
retinal and
retinoids acid as needed
b-carotene
found in plant based foods
can be converted to vitamin A
precursor to vitamin A
considered to be an antioxidant
takes approx 12ug b carotene to supply 1st of retinol
vitamin A functions
gene expression
vision
maintenance of epithelial tissue
immune defences
growth of bones
reproduction
vitamin a function: gene expression
regulates activities of genes, which direct the synthesis of proteins such as enzymes. vit a helps to activate or deactivate certain genes, thus affection the production of specific proteins

vitamin a functions with vision
plays 2 roles: a. process of light perception in the retina, b. maintenance of cornea
part of rhodopsin molecule (light sensitive pigment cells in the retina)
a. if deficient, night blindness can occur (lag before the eye can see again after a bright flash of light)
b. if deficient keratin (protein normally found in hair and nails) can accumulate and cloud the cornea, leading to a condition called keratinization
if vitamin a deficiency continues, it can lead to drying of the cornea (xerosis) and then progress to xerophthalmia (thickening of the coronet and permanent blindness)
vitamin a function: maintenance of epithelial tissue
involved in the cell differentiation and maturation process
each type of cells develops to perform a specific function
skin and al protective linings of the lungs, intestines, urinary tract, bladder, etc. all rely on vit a to ensure proper developed and replacement of cells
vitamin a: growth of bones
in children, old bone structures as dismantled by the body and remodeled into large bone parts
vitamin a plays important tole in the dismantling process - without it, bone growth cannot take place
vitamin a: reproduction
because of vitamin a’s role in cell differentiation and maturation
food sources
active vitamin A is in richest sources of animals
liver and fish oils
milk and fortified foods like cereal
plans contain no active vitamin a
deep orange and green plants have the precursor
precursor or provitamin, once inside the body can be converted into active vitamin a form - not that efficient
salad with carrots and cheese would be a good source
vitamin a and beta carotene snapshot
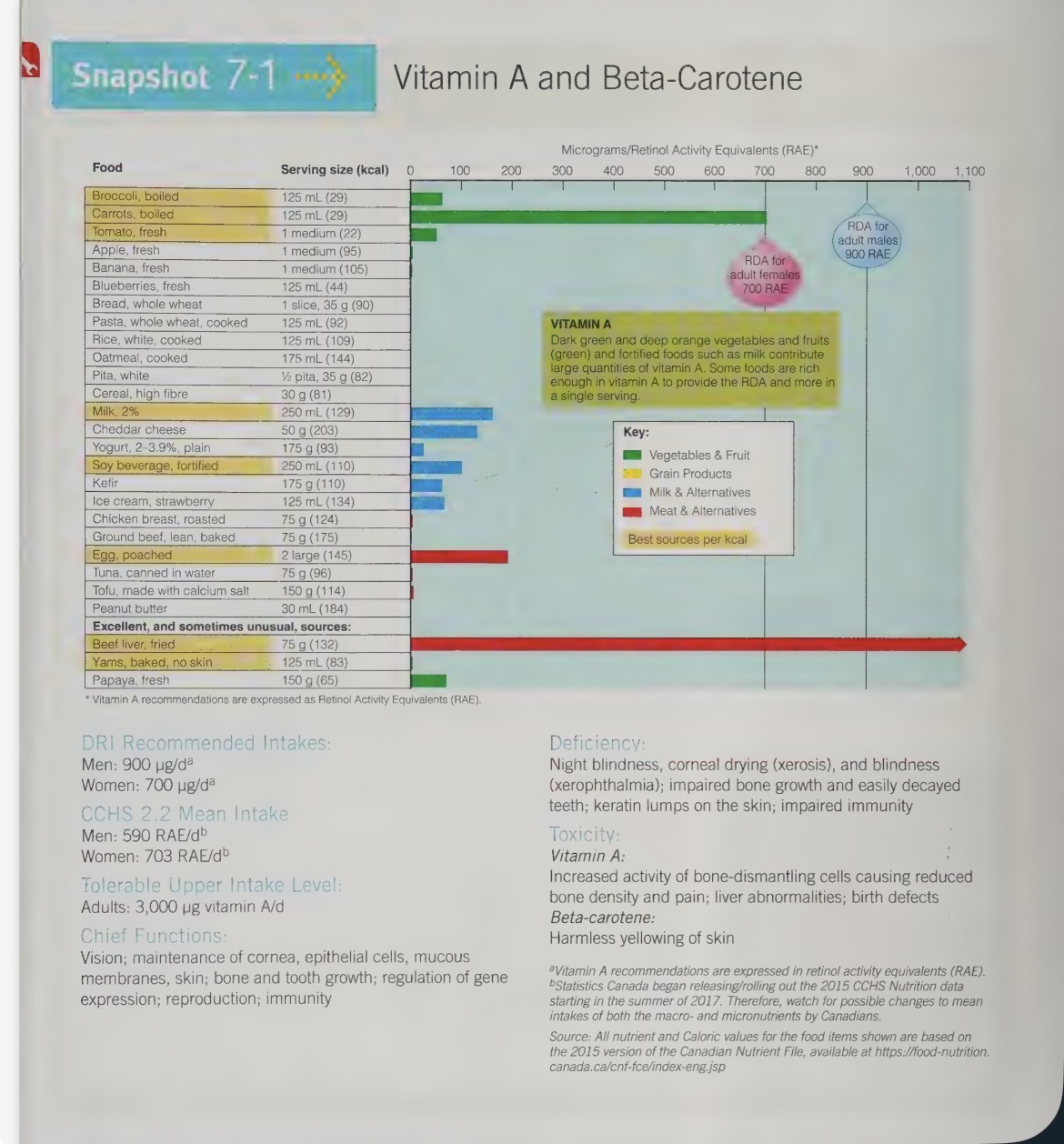
vitamin A deficiency
prevalent in devoting countries
b/w 3-10 million holders throughout the world suffer from signs of severe vitamin a deficiency
in countries were children receive vitamin a supplements, childhood death rates have been cut in half

symptoms of vitamin a deficiency
blindness, night blindness, xerosis
impaired bone growth, easily decayed teeth
lowered immune function
keratin lumps on skin: because cells do not mature – instead, they die off and secrete keratin.
vitamin A toxicity
seen from supplements and fortified foods
only food that is a natural source of vitamin a can cause toxicity is liver; including fish livers, and the liver of animals that eat whole fish (e.g polar bears)
chronic intake of even small excesses of vitamin a can weaken the bones and contribute to hip fractures

why should pregnant women be cautious with vitamin A
chronic use of vitamin A supplements at high doses can cause malformations of the fetus
vitamin A toxicity symptoms
stunted growth, muscle/bone pain, edges
fatigue, blurred vision, headaches, loss of menstration
abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, diarrhea
skin disorders, rashes, itching, hair loss
liver damage, enlargement of spleen
beta carotene not converted efficiently enough to retinal to cause toxicity symptoms
it has been known to turn people’s skin bright orange/yellow
beta carotene builds up in the fat beneath the skin
this looks alarming, however is harmless
concentrated beta carotene supplements may have adverse effects however, such as increased risk of lung cancer in those who smoke

other forms of vitamin A
retinoids acid can be used as a dug, directly applied to the skin resulting in rapid turnover of skin cells
retin-A: used for acne; renova: used as anti-wrinkle product
supplementing vitamin A does not help acne. accurate is derived from vitamin A, but is chemically altered and given in controlled doses
all of these forms are highly toxic and at risk for causing serous brith defects if taken using pregnancy
vitamin D
chemical name is cholecalciferol
vitamin D functions
plays a role (along with a number of other nutrients and hormones) in regulating blood calcium and phosphorus levels - thereby maintaining bone integrity
when blood calcium levels are low, vitamin D acts on the skeleton, the digestive tract and the kidneys to raise blood calcium levels
functions as a hormone and plays roles in the workings of the brain, heart, stomach, pancreas, skin, cells of the immune system, and reproductive organs by stimulating cell maturation
vitamin D food sources
Fortified milk and margarine, eggs, butter, and fish. More foods are starting to be fortified with Vitamin D (e.g., yogurt).
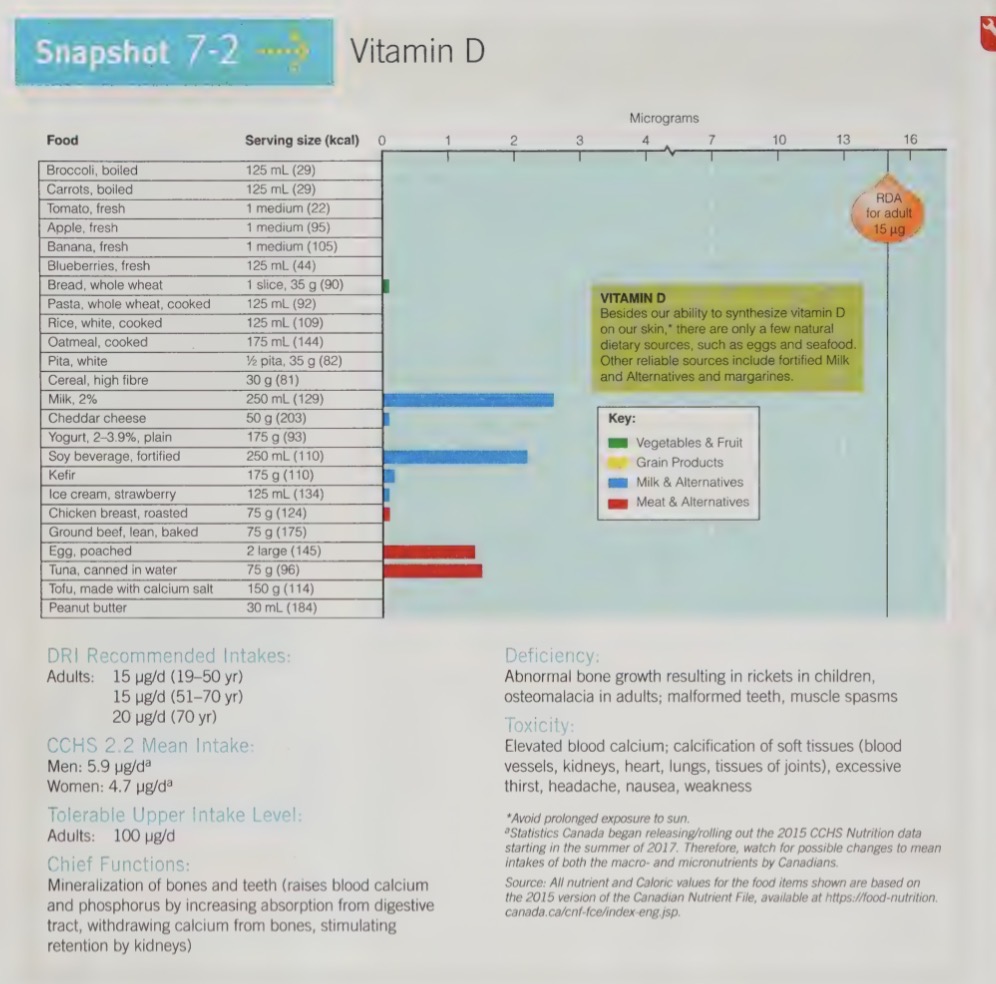
sunlight
UV light from the sun inverts cholesterol compounds in human skin into a vitamin D precursor and is directly absorbed into the blood
liver and kidneys then finish converting the precursor to active vitamin D
the duration of UV light exposure is needed is specific to race
fair skinned individuals may need exposure of facial area for 10-15 minutes 3-7 days per week to synthesize required levels of vitamin D, whereas darker-skinned individuals may need upwards of 3 hours.
Latitude also plays a role: in Manitoba, we typically only have the strength of the sun needed to synthesize vitamin D between April and October.
During the winter months, we rely on our liver stores.
factors effecting sun exposure
affects sun exposure and vitamin D synthesis: UV rays cannot penetrate clouds, smog, heavy clothing, window glass, window screens
some screens prevent sun rays exposure
time of day - mid day gives us maximum direct sun exposure
lifestyle - working indoors, older adults are homebound
use sun screen - limit exposure
go outdoor for 15 mins then put on sunscreen after to get adequate vitamin D synthesis
too much exposure does not affect vitamin D synthesis but can result in skin cancer
vitamin D deficiency
two forms: rickets and osteomalacia (bone disease in children and adults, respectively)
vitamin d deficiency: rickets
children developed bowed legs due to weakened bones to support body weight
develop knobs/beads on the ribs
condition is fairly uncommon in developed countries today, however is sometimes seen if a child is not provided with adequate dietary vitamin D (e.g fed soy/rice beverage hat is not fortified with vitamin D o replace cow’s milk which is fortified), and in children in developing countries
vitamin d: osteomalacia
adult form of vitamin D deficiency
can occur in women with repeated pregnancies who have low calcium intake, little sun exposure and breast feed multiple children
calcium is withdrawn from the bones, as a result he bones in the legs and spine soften and the person becomes bowlegged and stooped
research is hinting that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to many problems such as high blood pressure, some type of cancer, diabetes, heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, even multiple sclerosis
well established problems concern impairment of calcium and the bones
the risk of vitamin D deficiency increases with age due to a number of factors
lower intake, housebound (so little UV light exposure), decreased ability to activate vitamin D, and our need for vitamin D increases after the age of 50
vitamin D toxicity
out of all the vitamin, vitamin D is the most potentially toxic
toxicity is squally seen from supplements
vitamin D toxicity symptoms
appetite loss, nausea/vomiting, increased thirst & urination, severe psychological depression (because of the effects on the central nervous system)
vitamin D long term toxicity
Vitamin D raises the blood mineral levels dangerously high, resulting in calcium deposits in the soft tissues of the heart, blood vessels, lungs and kidneys, which can lead to serious malfunctions and even death.
There is a case discussed in your textbook where two people died after drinking milk from a dairy that accidentally over fortified the milk with 500 times the usual dose of Vitamin D.
vitamin E
active form s tocopherol
alpha is the gold standard, therefore DRI is expressed as alpha-tocopherol
vitamin E function
acts as an antioxidant, serves as the body main defenders against oxidative agents.
important in red blood cells because they are exposed to high levels of oxygen
white blood cells depend on vitamin e - therefore may play a role in immunity
previous research as shown hope that supplements help heart diseases, but recent studies don’t show this
too much vitamin e intake can be harmful to health
free radical damage and antioxidant protection
vitamin E food sources
Vitamin E is found wide-spread in foods (e.g., vegetable oils [canola, safflower, sunflower], vegetables and fruits, fortified cereals/grains, meat and alternatives, and milk products). Heat processing destroys Vitamin E, so most processed, fast foods, deep fried foods and convenience foods retain little intact vitamin E.
![<ul><li><p>Vitamin E is found wide-spread in foods (e.g., vegetable oils [canola, safflower, sunflower], vegetables and fruits, fortified cereals/grains, meat and alternatives, and milk products). Heat processing destroys Vitamin E, so most processed, fast foods, deep fried foods and convenience foods retain little intact vitamin E.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e83a3397-be1f-4831-bbdd-307853cec227.jpg)
vitamin E deficiency
Vitamin E deficiency is rare because of three things:
Vitamin E is widespread through foods.
The body stores enough vitamin E in fatty tissue to last a long time.
The cells recycle their working supply of vitamin E, using the same molecules over and over again.
vitamin e deficiency increases premature infants
may occur in premature infants born before transfer of vitamin e from mother to baby (thought to occur in the last quarter of pregnancy, from 30 weeks on). without sufficing vitamin E, the infants’ red blood cells rupture (erythrocyte hemolysis) and the infant becomes anemic
vitamin e deficiency increases adults
may be associated with diseases that cause fat malabsorption (e.g., injury/disease of the liver, the gallbladder or the pancreas). The symptoms sometimes seen in adults (weakness, impaired reflexes, impaired vision/speech) are caused by oxidative damage. Vitamin E treatment corrects them.
Sometimes, Vitamin E deficiency can be seen if an extremely low fat diet is being followed long term (over a few years).
Research is hinting that chronic low intake of vitamin E may play a role in disease development.
vitamins e toxicity
rare
no adverse effects have been reported from naturally occurring vitamin e in foods
toxicity is more s seen from supplements and fortified foods
supplements doses up to the DRI are generally safe, doses beyond are risky. research shows an increased risk death from all cases, compared to those taking smaller doses
supplements also increase the effects of anticoagulant medications used to prevent unwanted blood clotting. this means the potential for an increased risk of uncontrollable bleeding
symptoms of vitamin e toxicity
nausea
fatigue
Gi distress
blurred vision
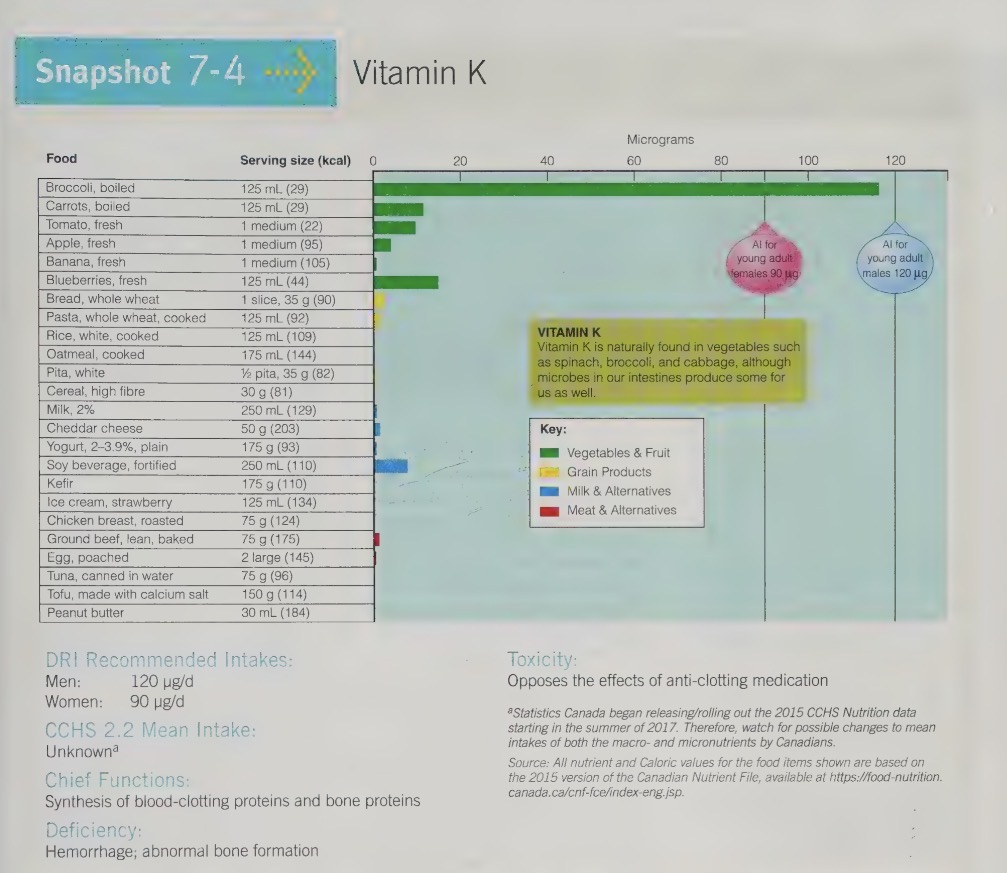
vitamin k functions
main function is to help synthesize proteins that j help clot the blood
anticoagulant medications (e.g warfarin/ coumadin) interfere with the action of the vitamin k in promoting clotting
vitamin K needed for synthesis of key bone proteins
without vitamin k, the bones produce an abnormal protein that cannot bind to bone minerals, resulting is low bone density
adequate vitamin k may reduce the risk of hip fractures that those with lower intakes
vitamin k sources
like vitamin d, vitamin k can be derived from a non-food source - this time by our intestinal bacteria
we normally have billions of bacteria residing in our colon, some which synthesize vitamin k, this production if affected by:
absorption problems/illness
antibiotic use
both affect the bacteria residing in our colon, so we can result in decreased vitamin k production
vitamin k food sources
richest plant food sources include dark leafy green veggies, spinach and coloured green, cabbage family
vegetable oil like canola and vegetable
beans and legumes
fortified cereal
reaches animal sure is liver, milk and eggs contribute small amounts
vitamin k deficiency
few north american adults experience, exception may be people who have taken antibiotics that have killed harmful and the beneficial bacteria in their intestinal tract
another exception is if a person has problems with fat absorption
vitamin k supplementation would be requires, as vitamin k deficiency can b fatal.
symptoms include: easy bruising and hemorrhaging
vitamin k deficiency is infants
newborn infants are born with sterile intestinal tract, and the vitamin k producing bacteria take weeks to establish themselves
therefore, to prevent hemorrhage the newborn is given a dose of vitamin k at birth
vitamin k toxicity
rare reports in healthy adults, DRI no UL
sometimes seen in infants and pregnant women, toxicity occurs when vitamin k supplements are given too eagerly
toxicity causes the breakage of RBC and release of their pigment (bilirubin). the liver then releases the bilirubin into the blood instead of excreting it into the bile and this leads to jaundice. if bilirubin invades an infant’s brain this can lead to brain damage, even death
water soluble vitamins
are the vitamin C and vitamin Bs
dissolve in water, so they are absorbed directly into the blood stream where they travel freely
most are not stored in the tissue to any great extent and excesses are excreted in the urine. therefore, there is less risk of immediate toxicities
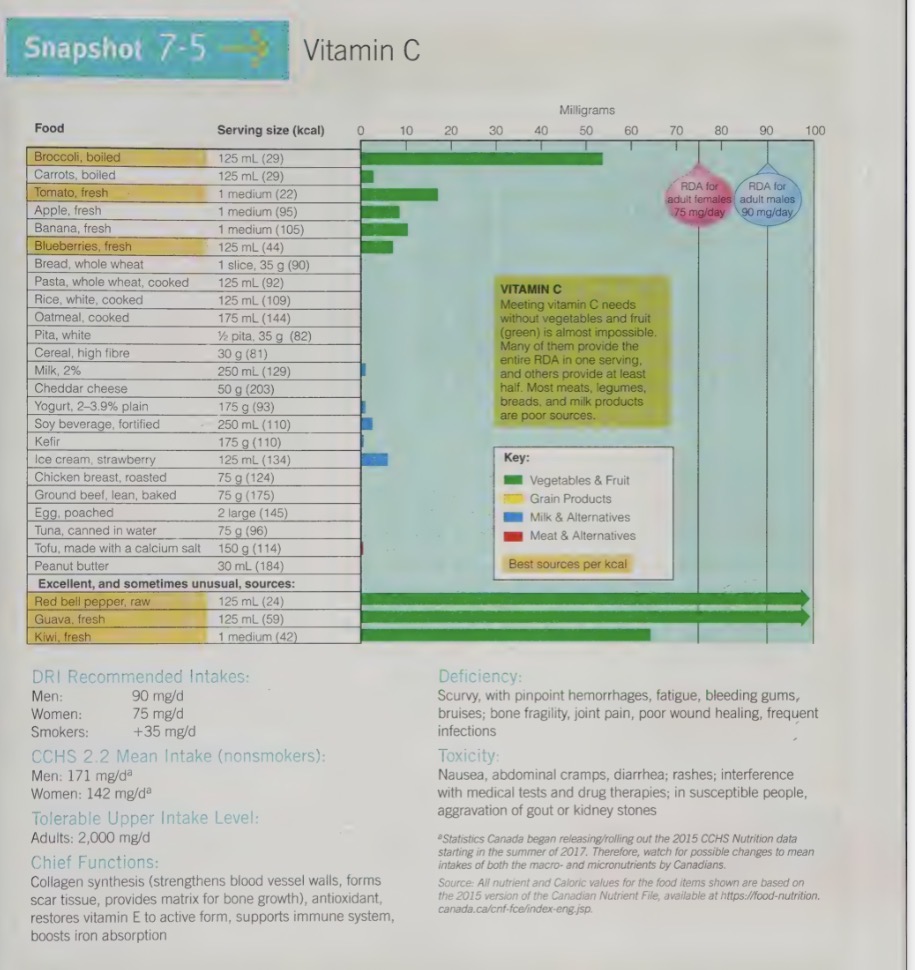
vitamin c requirements
not that much because if the vitamin c in our body is recycled back into the active form for reuse
body’s pool of vitamin c overflows at around 100mg/d (meaning we will typically urinate out the rest)
smoking and vitamin c
Smoking/tobacco introduces oxidants to our body that deplete the body’s vitamin C. Therefore, smokers need more vitamin C to maintain blood vitamin C levels similar to a non smoker (an additional 35 mg/d). Even being around second hand smoke can increase a person’s need for Vitamin C.
vitamin c functions
best known for maintaining the connective tissue and as an antioxidant
vitamin c functions: maintenance of collagen/connective tissue
collagen forms the base of all connective tissues including our bones, teeth, skin, and tendons
it forms scar tissue to heal wounds, forms the reinforcing structure that mends fractures, and forms the supporting material of capillaries that prevent bruises
vitamin c assists several enzymes in performing their task
enzymes novices in the formation and maintenance of collagen (a tissue protein) rely on vitamin c for their activity
vitamin c function: antioxidant protection and immune function
Vitamin C protects cells from oxidation by becoming oxidized itself (e.g., immune cells maintain high vitamin C levels to protect themselves from free radical damage when fighting bacteria and other invaders).
vitamin c functions: promotes iron absorption
In the intestines, vitamin C protects iron from oxidation, therefore promoting its absorption.
vitamin c functions: assist with vitamin E recycling
Vitamin C also helps to protect sensitive blood constituents from oxidation and helps to protect and recycle vitamin E to its active form.
vitamin c’s role as an antioxidant, research done to see if it can play a role in disease prevention
however, research is finding the vitamin c appears useless against diseases such as heart disease and cancer unless there is a deficiency in vitamin C
vitamin c and the common cold
no study to the current date has shown that vitamin c can prevent cold or reduce their severity
some research showing that taking a therapeutic dose of vitamin c at the onset of a cold can reduce the length by a half day and the symptoms by 40%
1g of vitamin c a day is a therapeutic dose
these effects may be greater in children than adults, they need close to UL 2.g
placebo affect, one study gave participants half vitamin c and half a placebo, told each group they gave them opposite group, placebo group reported less colds than the ones who did get vitamin c
if pearson things product it will treat them, it might
vitamin c food sources
Fruits and vegetables are the key sources of vitamin C.
The best sources are fresh, raw, and quickly cooked fruits, vegetables and juices, as vitamin C is vulnerable to heat and destroyed by oxygen.
Therefore, foods should be properly stored and consumed promptly after purchase to maximize vitamin C content.
vitamin c deficiency
200 years ago people who went long seagoing ship only had 50% chance of survival because of scurvy. this is due to the cook using fresh veggies and fruits first of the voyage, leaving only grains and animals meats to survive on for the rest of the voyage. once discovered that citrus juice could cure scurvy, british navy required al vessels to provide lime juice to each sailor daily
absorbing acid literally means “no scurvy acid”
deficiency is now rare. sometimes seen in elderly (if lower food intake), alcohol/drug addicts, and in infants fed not cow’s milk as their fluid (no vitamin c fortified formula or juice. breast milk and formula provide vitamin c
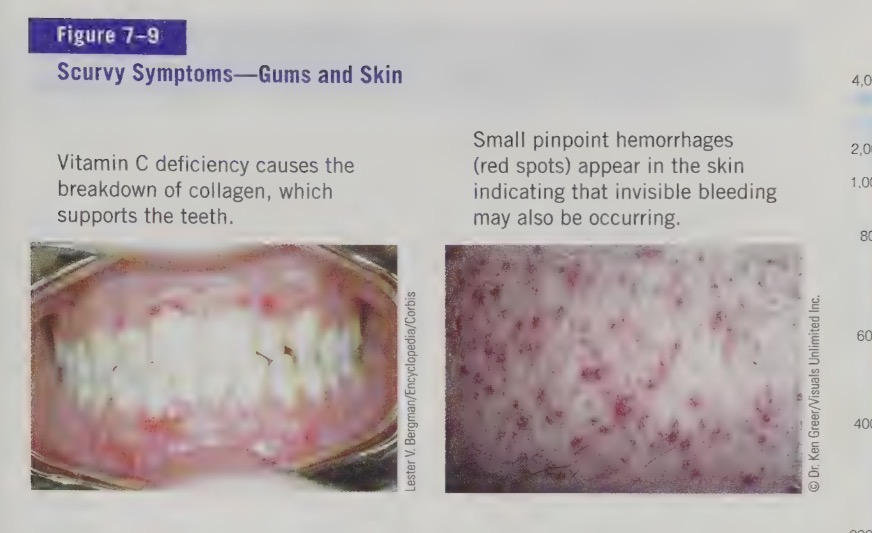
Most of the symptoms of scurvy are caused by the breakdown of collagen in the absence of vitamin C. We can also see anemia develop, because of vitamin C’s role in helping the body use and absorb iron. Vitamin C deficiency causes the breakdown of collagen, which supports the teeth.
vitamin c deficiency: hemorrhages
Tiny hemorrhages (red spots) the size of appear in the skin, an indication that internal bleeding may also be occurring. Other symptoms include loss of appetite, growth cessation, weakness, frequent infections, bleeding gums, loose teeth, and swelling in wrists and ankles.
vitamin c toxicity
vitamin c as a nutraceutical (marketing a nutrient as having pharmacological effects) have led thousand of people to take huge doses of vitamin c
recommended 4,000mg per day
one effect observed when 2 grams of vitamin c are consumed daily is altered insulin response to CHO in people with otherwise normal glucose tolerance
other adverse effects include nausea, abdominal cramping, gas, diarrhea, and the development of kidney stones
massive doses of vitamin c may also interfere with blood clotting medication and may be dangerous for individuals with iron overload (hemochromatosis) because of the role that vitamin c plays in enhancing iron absorption
the B vitamins
thiamin
riboflavin
niacin
folate
vitamin B12
vitamin B6
biotin
pantothenic acid
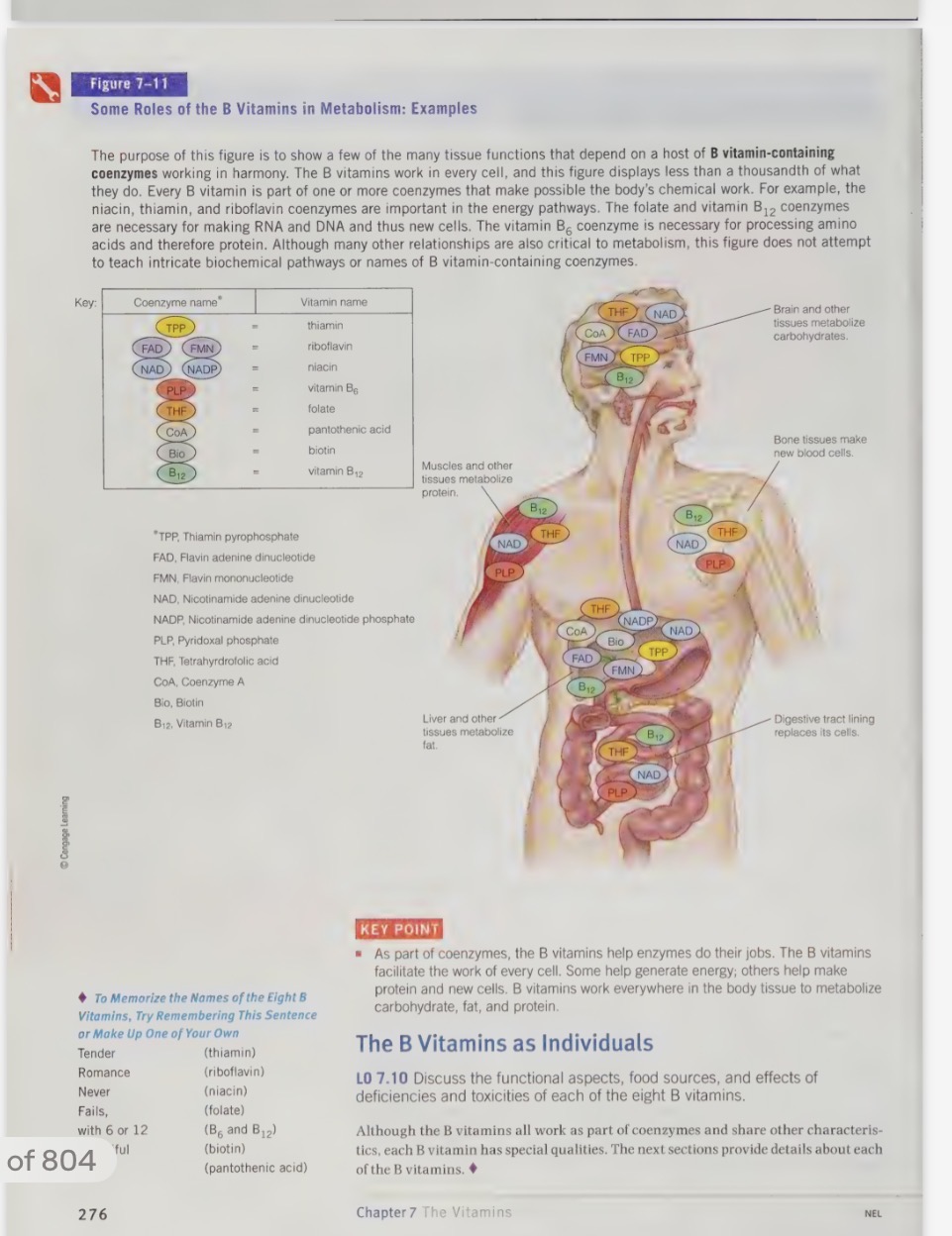
the B vitamins act as coenzymes
coenzymes are small molecules that combine with enzymes to activate the enzyme
without the coenzyme, the enzyme would be as useless as a car without wheels

the B vitamins are also involved in energy metabolism
help body to metabolize CHO, fats, and amino acids
they do not supply the body with energy directly, but rather hep the body to use the fuel from the energy providing nutrients
thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, and biotin participate in the release of energy from CHO, fat, and protein
vitamin B6 help the body use amino aids to make protein, while folate and vitamin B12 help cells to multiply, including the cells that deliver energy to all other cells
therefore al of the B vitamin are directly or indirectly involved in energy metabolism
thiamin functions
critical role in energy metabolism of all cels
also occupies a site on nerve cell membranes
therefore, nerve processes and muscles deepen heavily on thiamin
thiamin food sources
small amounts of thiamin occur in many nutritious foods, such as legumes, enriched/whole grain cereals, sunflower seeds and pork
by choosing nutrient dense foods, one can easily achieve their thiamin recommendation
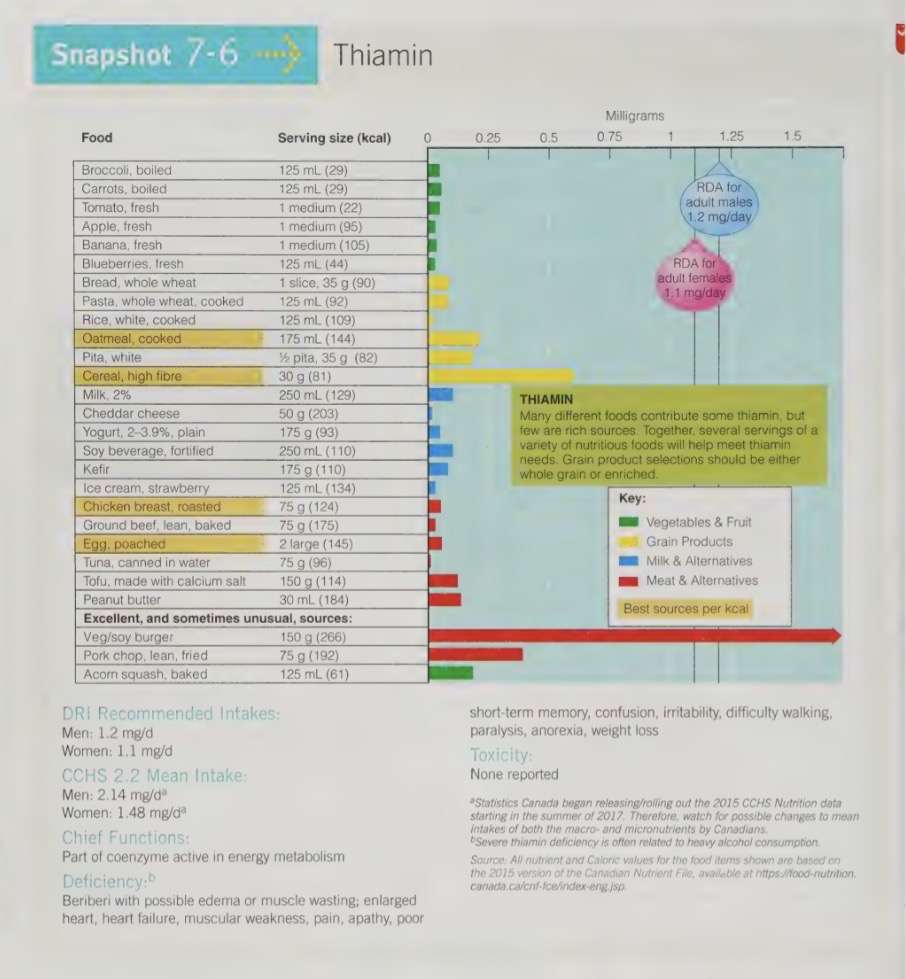
thiamin deficiency
is called beriberi
characterization by loss of sensation in he hands and feet, muscular weakness, advancing paralysis and abnormal heart action
can be wet (accompanied by edema) or dry (no edema)
thumb print remains in the skin (wet beriberi) - a sign of edema
serve thiamin deficiency called Vernickle-Korsakoff syndrome, in those who abuse alcohol
not only does alcohol often displace foods for alcohol abusers, it also impairs the absorption of thiamin from the digestive tract, and speeds up its excretion in the urine
Verniicke-Korsakoff characterized
apathy
irritability
mental confusion
disorientation
memory loss
jerky eye movement
staggering gait
beriberi first observed
first observed in east asia where rice is a staple food
polishing rice became popular, removing the brown outer coat, the thiamin
swept through the population like an epidemic
scientist is took a long time to realize it wasn’t a microorganism causing this but something lacking in the diet
riboflavin functions
like thiamin, riboflavin plays a role in the energy metabolism of all cells. It also helps to support vision and skin health.
riboflavin food sources
Enriched breads, cereals, pastas and other grain products contribute about 25% of our riboflavin intake, with the rest coming from milk products, eggs, meats and some vegetables (e.g., spinach, mushrooms).
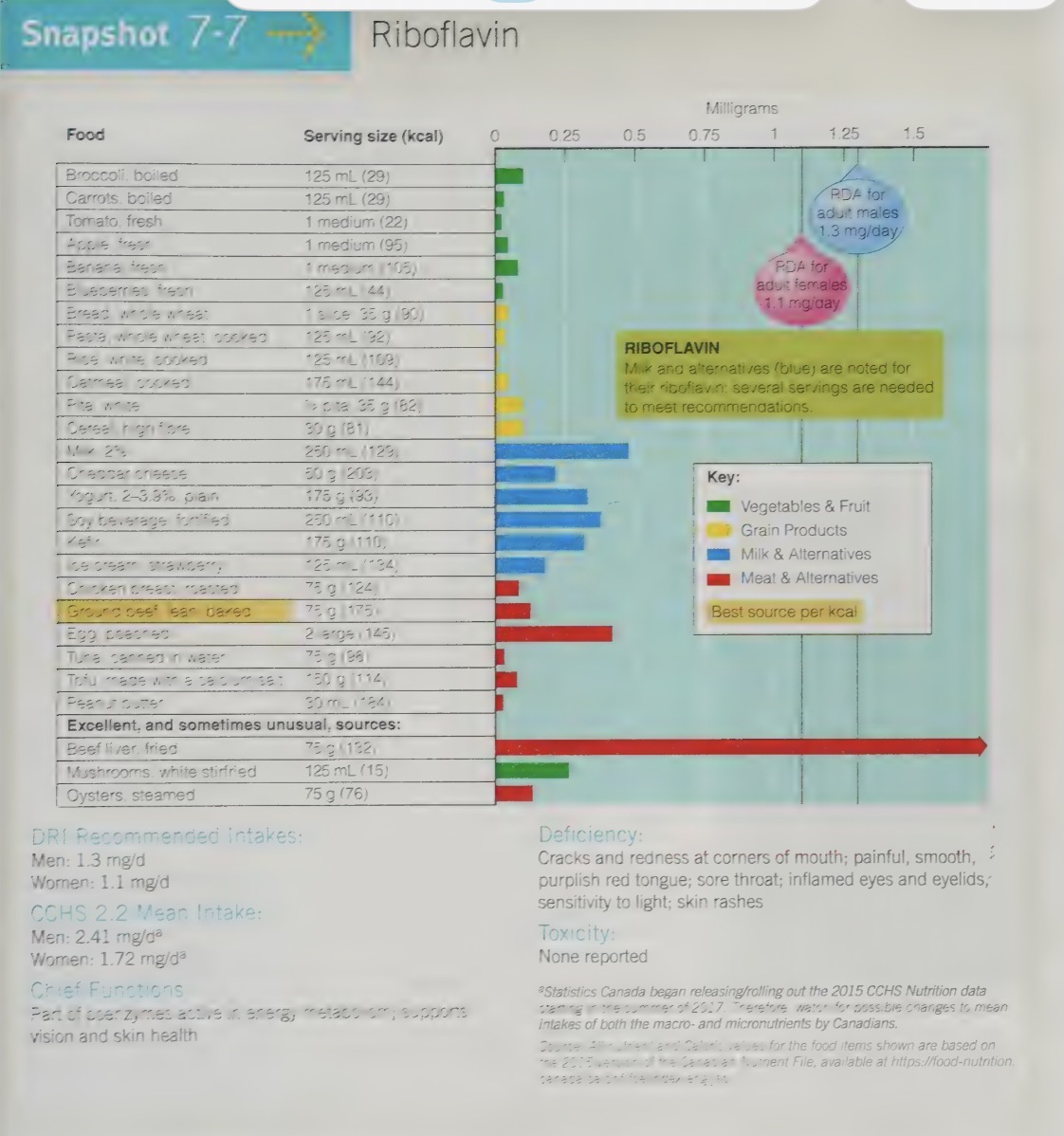
riboflavin deficiency
ariboflavinosis is the deficiency disease of riboflavin characterized by cracks and redness at the corners of the mouth (these cracks can actually start to spread down the sides of the face)
smooth magenta coloured tongue, sore throat, inflamed eyes and eyelids, hypersensitivity to light, as well as skin rashes
when diet is deficient in thiamin, it may be deficient in riboflavin (similar food sources)
riboflavin deficiency often goes infected because the symptoms of thiamin deficiency are some severe
riboflavin toxicity
there are no reported symptoms of toxicity
no UL set at this time
niacin functions
participates in the energy metabolism of all cells
tryptophan (an amino acid found in almost all proteins) can be converted to niacin in the body. therefore, person eating adequate amounts of protein will not be deficient in niacin
niacin equivalents are the amounts of niacin present in food and take not account the niacin that can be created from the tryptophan present in food
niacin food sources
enriched (added back to the natural level) & whole grains; cereals and baked products
*legumes
leafy green vegetables, mushrooms
*meat, fish, eggs
*milk & milk products
Almost all protein containing foods are a source of niacin and tryptophan. The only protein that is limited in tryptophan is the protein of corn.
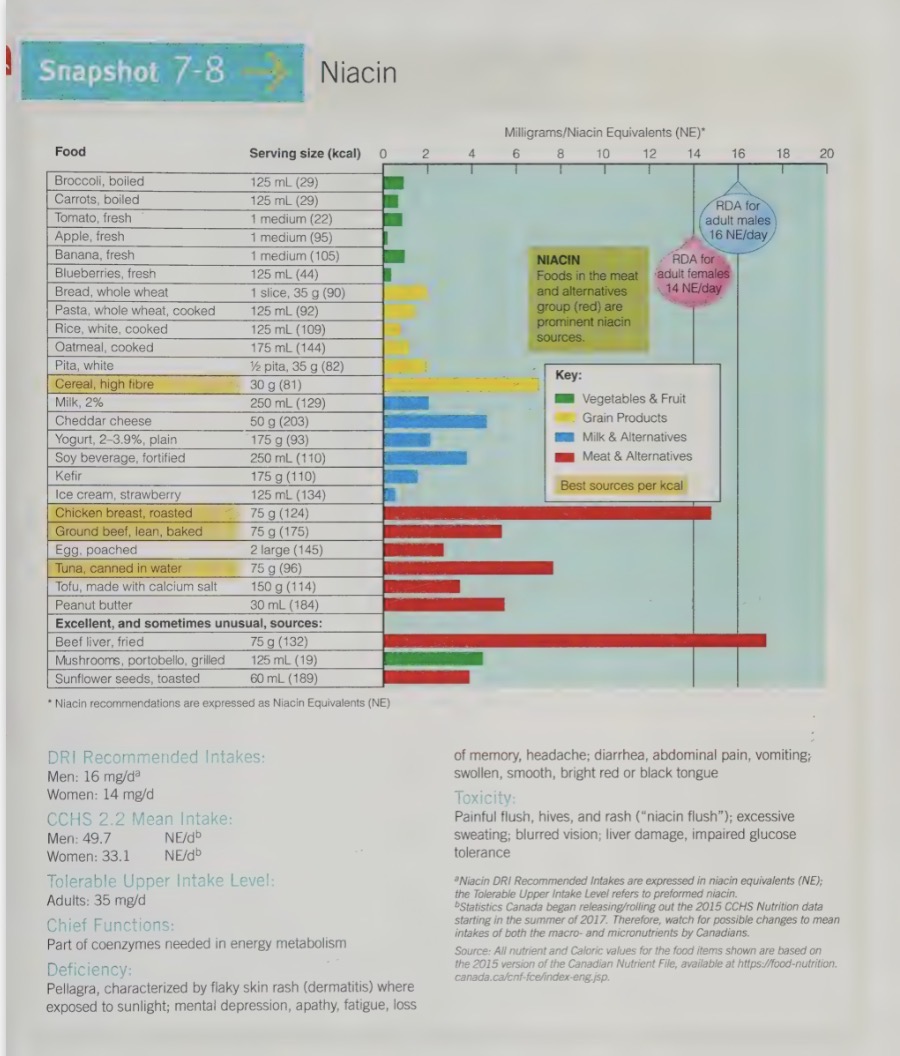
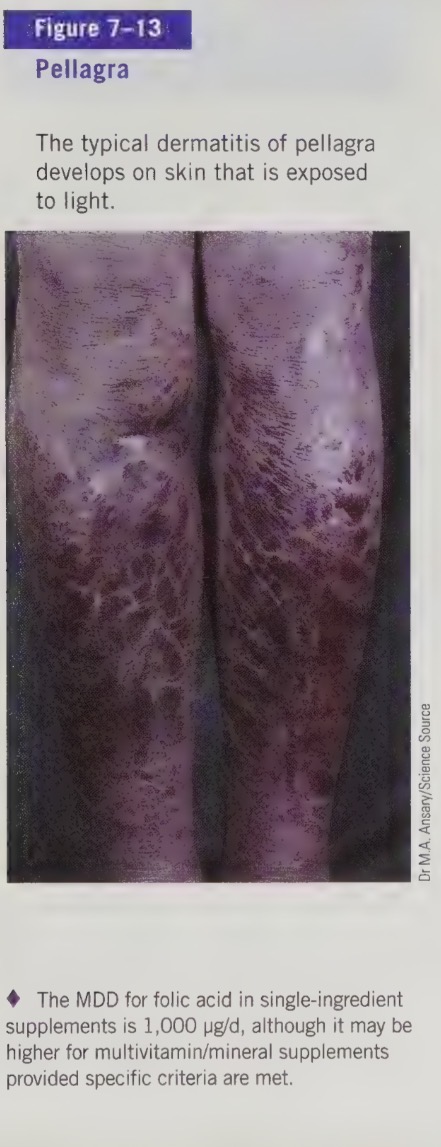
niacin deficiency
called pellagra
symptoms include 4 D’s: diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia, and ultimately death
also see headaches, abdominal pain, vomiting, and the tongue can become smooth, swollen and red or black in colour
Pellagra appeared in Europe in the 1700’s when corn became a staple food (corn protein is limited in tryptophan). It is still common in parts of Africa and Asia.
niacin toxicity
typically linked to supplements intake, rather than food intake
niacin toxicity can cause ‘niacin flush’ - a dilation of capillaries of the skin with tingling sensation that can be painful
hives also occur, as well as excessive sweating, blurred vision, liver damage, and impaired glucose tolerance
other symptoms include: stomach pain, nausea, and diarrhea
overtime the body adapts to high doses and many symptoms resolve, however it is important to monitor for liver damage, which can silently occur
niacin supplementation
physicians may adminters a dose of niacin to lower blood lipid levels
use as a drug
self doses not advised
rage doses cause damage to liver, peptic ulcers, and extreme conditions, vision loss
folate requirements
folate supplement ion occurs before refinance occurs
dri recommend pregnant women to consume 400 mg of folate a day form supplements or enriched foods addition to in natural foods
form of folate is better absorbed in our body from supplements and enriched foods that naturally occurring (weird)
folate (folic acid) functions
in order for new cells to be made, tissues must have folate
each new cell must have copies f parents cell’s DNA and folate helps to synthesize this DNA
cells that divide rapidly are most vulnerable to deficiency
folate very important for early embryonic growth to prevent neural tube defects (abnormalities of the brain and spinal cord apparent at birth), as well as for tissues with fast turnover rates (e.d intestine, skin, RBC)
critical for the normal metabolism of a number of amino acids
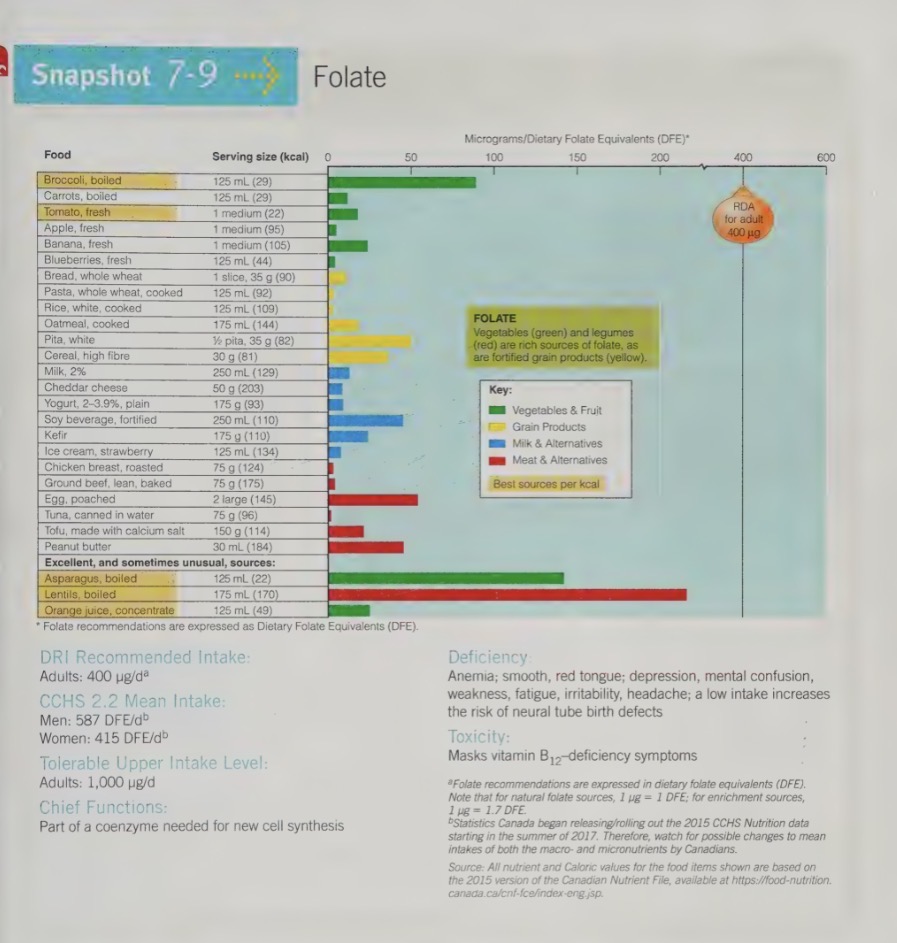
folate (folic acid) food sources
deprived from latino word foliage, giving us an idea what foods are good sources
leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and turnips greens are great source
other vegetables such as broccoli and asparagus, fruit such as organs and organs juice, legumes, seeds, and liver also contain folate
fresh uncooked vegetables and fruits are a good source of folate - heat and oxidation both destroy folate
consuming milk with a mela may enhance folate absorption
white flour, enriched pasta, and corn meal all have been fortified with folic acid in Canada. this was done as a public health strategy to increase dietary folate intakes and lower the incidence of neural tube defects, which we discuss further in this section.
White flour is fortified with 0.15mg folic acid per 100g flour (about twice the amount found naturally in whole grain flour). Enriched pasta is fortified with 0.2mg per 100g. The amounts of folate added to foods was kept low because of concerns that higher levels may mask vitamin B12 deficiency (we will look at this with vitamin B12).

folate deficiency
causes anemia (large cell-type), lowered immunity, and abnormal digestive function
anemia is caused related to the anemia of vitamin B12, because both of these B vitamins work together to produce RBC
large, immature RBC become present as a result
other symptoms include smooth red tongue, depression, mental confusion, fatigue, irritability, and headaches
folate deficiency: neural tube effects
also associated with neural tube defects (abnormalities of the brain and spinal cord apparent at birth)
neural tubes occur the first days to weeks of pregnancy, before woman knows she’s pregnant
neural tubes occur in 1/1,000 briths and are the second most common birth defect
food surveys show us that most canadians do not eat enough vegetables and fruits each day to supply them with the needed folate, DRI recommends synthetic folate for all women of childbearing years
between 2006 and 2020 1,832 cases of neural tube defects were reported in Canada
those at risk of folate deficiency include
pregnant women
elderly (many medications interact with folate absorption, e.g., antacids, aspirin, oral contraceptives, and anticonvulsant medications. The elderly may also may have lowered food intake)
alcoholics (decreased folate absorption, also may have lowered food intake)
smokers (folate inactivation in lungs occurs, increasing the need for folate)
Research suggests that a diet deficient in folate may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, colon cancer and increase a woman’s risk of cervical cancer
folate toxicity
The UL for synthetic folate is 1,000 ug /day for adults. The concern is that folate can mask Vitamin B12 deficiency by resolving the macrocytic anemia seen in both folate and B12 deficiency.
Vitamin B12 functions
Vitamin B12 helps to maintain the myelin sheath that surround and protect nerve fibres.
Without sufficient vitamin B12, nerves become damaged.
It also acts as a coenzyme in energy and amino acid metabolism.
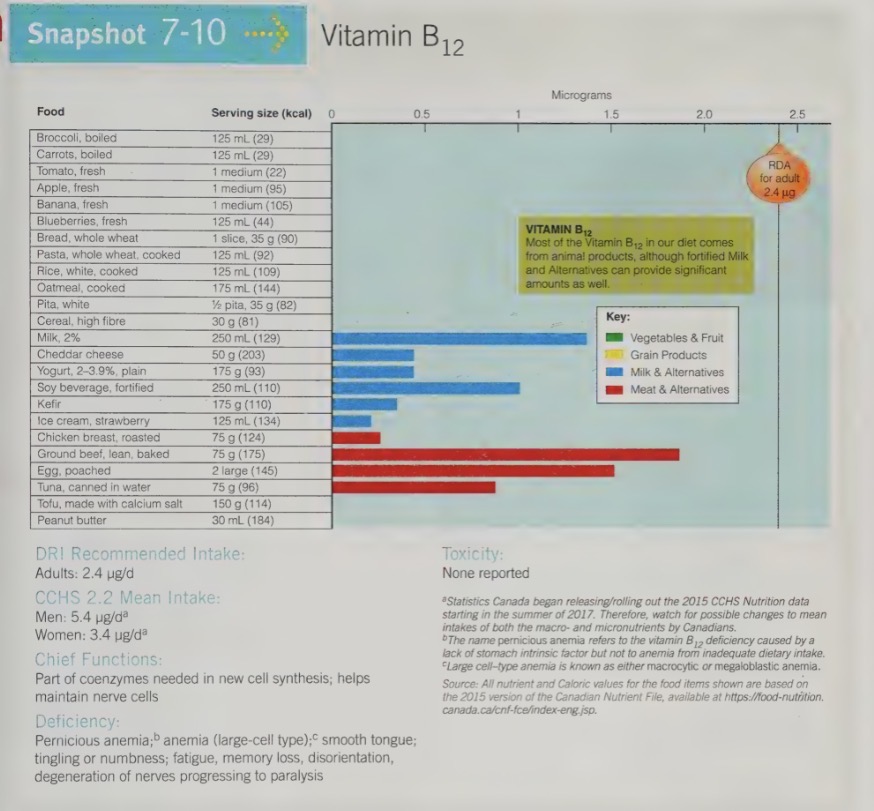
vitamin B12 food sources
only present in foods of animal origin, not in foods from plants.
However, many vegetarian foods are being fortified with vitamin B12 (soy beverages, soy meat alternatives)
Algae are an exception of a plant food where we do find vitamin B12, and another vegetarian source of vitamin B12 is Red Star Yeast.
Some fermented products contain this vitamin however it is typically not in its active form.
vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 and folate are closely related, each relies on the other for activation.
Without sufficient vitamin B12, folate fails to do its red blood cell building work so vitamin B12 deficiency causes an identical anemia as folate deficiency does.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can also cause neuromuscular dysfunction such as creeping paralysis and general malfunctioning of nerves and muscles.
Administering folate often clears up the anemia, but allows the vitamin B12 deficiency (and corresponding neuromuscular dysfunction) to continue undetected.
vitamin B12 absorption
requires intrusion tic factor, compound made in the stomach
gastric acid liberates vitamin B12 from the food protein that binds it and the intrinsic factor attached to B12
it is then absorbed into look stream in small intestine
as we age, we do not produce enough gastric acids and instruct factor, not being able to absorbed enough vitamin B12
some people have an inherited defect in the gene for intestine factor making absorption for vitamin B12 abnormal, this begins in mid adult hood
if here is no intrinsic factor or reduce intrinsic factor, the individual typically needs vitamin B12 injections or high dose supplements
a change in diet alone may not correct vitamin B12 deficiency
vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) functions
Vitamin B6 participates in over 100 reactions in body tissues and is needed to convert over abundant amino acids into other, non-essential amino acids the cells lack
other functions of vitamin B6 include
Energy metabolism
Synthesis of hemoglobin and neurotransmitters
Conversion of tryptophan to niacin
Releasing stored glucose from glycogen – thus contributes the regulation of normal blood glucose levels
Immune function and steroid hormone activity
Critical to the developing brain and nervous system in a fetus. Deficiency at this stage can cause behavioral problems later on.
Because vitamin B6 plays so many roles in protein metabolism, the requirements for vitamin B6 were created to be proportionate to protein recommendations
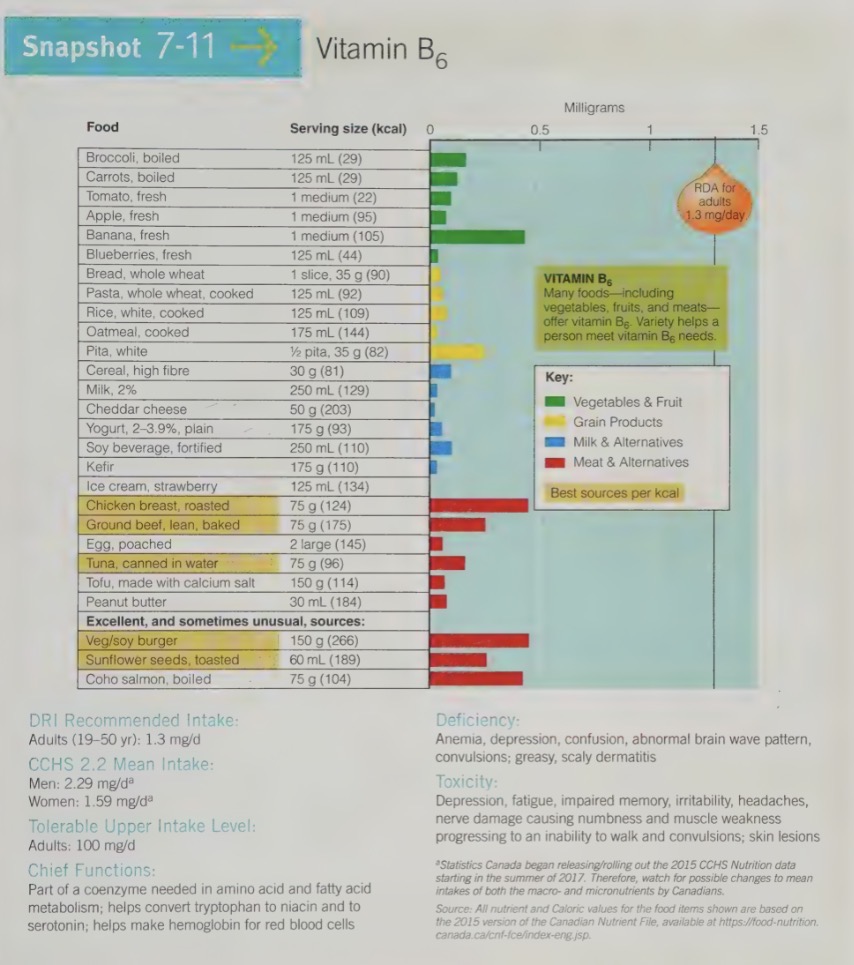
vitamin B6 food sources
Meats, fish and poultry are good sources, along with potatoes, leafy green vegetables, and some fruits. Legumes and peanuts contain smaller amounts of vitamin B6
vitamin B6 deficiency
cause weakness, psychological depression, confusion, irritability, insomnia, anemia (small-celled), and greasy dermatitis
may also causes convulsions, and may weaken the immune system
some evidence suggest that low vitamin B6 intakes may be related to an increased incidence of heart disease

vitamin B6 toxicity
large doses from supplements can be dangerously
reported symptoms in a women taking more than 2g for 2 months to relived PMS symptoms, she got numbness of hands and feet and couldn’t walked. this went away after she stopped the supplements
other toxicity symptoms include: depression, fatigue, impaired memory, irrationality, headaches, restless, conflucsions
only seen with supplements
would need over 3,000 bananas or 38,000 chicken breast to get 2g a day - hard to go over limit on natural foods
sometimes supplements are used to treat carpal tunnel, sleep disorders, or PMS syndromes
research shows vitamin b6 supplements are ineffective to resolve any of those conditions
biotin function
Biotin plays a role as a cofactor in energy metabolism