Cell Structure Exam 3
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Cellular respiration
harvests the energy remaining in pyruvate and NADH from glycolysis, it uses an external electron acceptor to oxidize substrates completely to CO2
Stages of aerobic respiration
Glycolytic pathway
Pyruvate is oxidized to generate acetyl CoA
The Citric Acid Cycle
Electron transport
Oxidative phosphorylation
Mitochondrial myopathies
human diseases caused by defects in mitochondrial functions
Oxygen
The terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration
Water
the reduced form in aerobic respiration
Which type of respiration yieldsmore energy
Aerobic respiration
Where are mitochondria frequently clustered?
in regions of cells with the greatest need for ATP (ex. muscle cells)
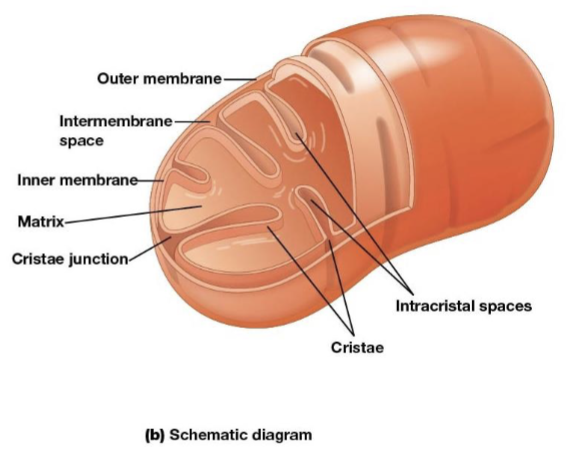
Mitochondria outer membrane
contains porins that allow passage of solutes with molecular weights up to 5000
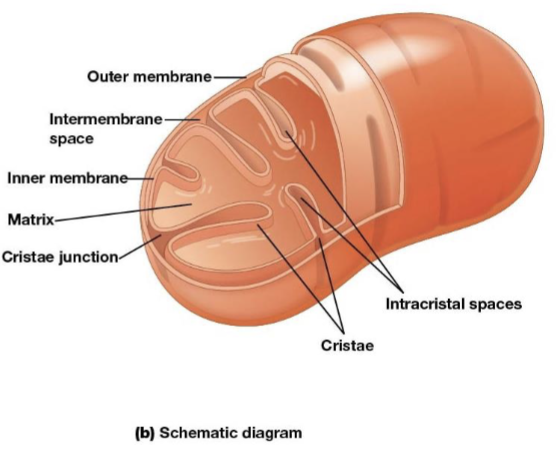
Mitochondria intermembrane space
the space between the inner and outer membranes
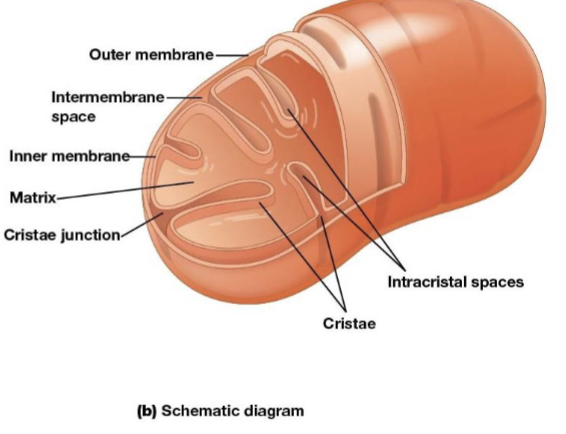
Mitochondria inner membrane
the most permeable to most solutes, partitioning the mitochondrion into two separate compartments, the intermembrane and the mitochondrial matrix
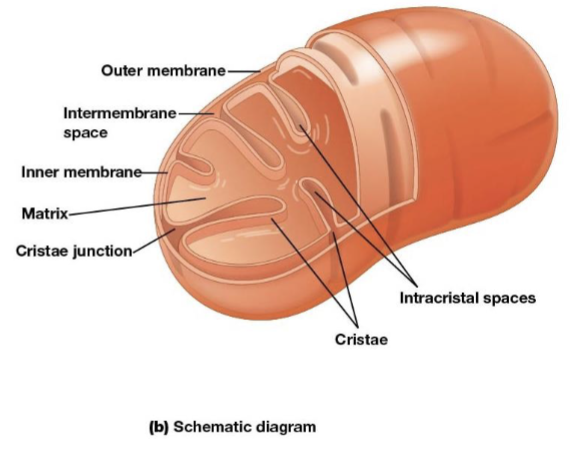
Cristae
infoldings on the inner membrane of the mitochondria, increase surface area of the inner membrane and provide more space for electron transport to take place
Transit sequences
targeting signals located on the N-terminal of a polypeptide
Transit peptidase
enzymes that remove the transit sequence once the polypeptide has arrived
Special transport complexes
located on the outer and inner membrane of the mitochondria and allow for uptake of polypeptide chains
Pores for transport
TOM (translocase of the outer membrane)
TIM (translocase of the inner membrane)
Transit sequence receptors
component of transport complex that recognizes transit sequences
Chaperone proteins
bind polypeptides targeted to the mitochondria to help maintain the unfolded state
Mechanism of import of polypeptides into the mitochondrial matrix
Hsp70 chaperone proteins bind to the polypeptide and help with unfolding
TOM transit sequence receptor binds to the N-terminus of the polypeptide
Chaperone proteins are released, and ATP is hydrolyzed as the polypeptide moves through the TOM and TIM pores
Transit sequence is removed by transit peptidase in the matrix as soon as the transit sequence enters the matrix
Mitochondrial Hsp70 chaperone proteins bind polypeptide as it enters the matrix
Often, mitochondrial Hsp60 chaperone proteins bind the polypeptide and assist in proper folding
Citric Acid Cycle/TCA Cycle/Krebs cycle
Each round involves the entry of two carbons, the release of two CO2, and the regeneration of oxaloacetate, pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A—bridging the reaction
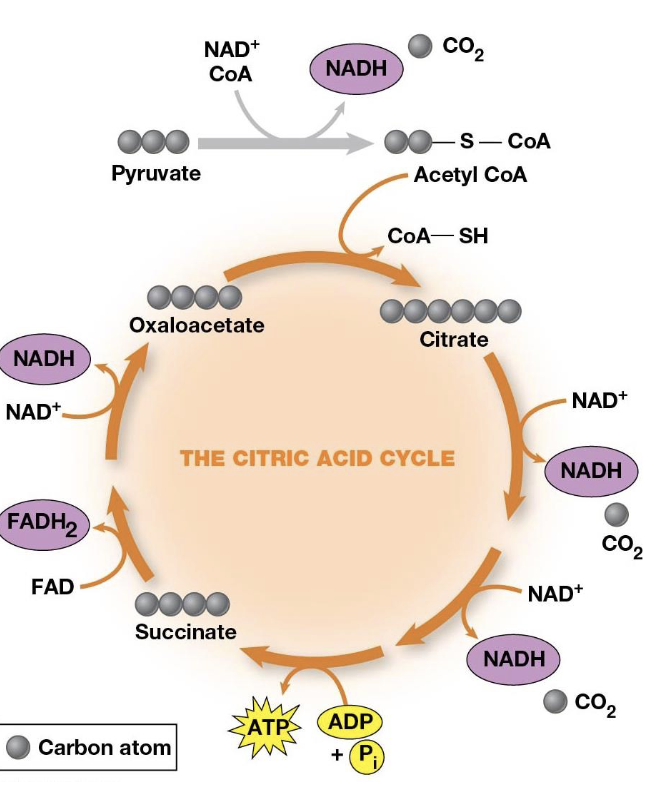
How is pyruvate converted to acetyl CoA
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH)
Substrates of TCA
CoA, NAD+, FAD, and ADP
Products of TCA
NADH, FADH2, CO2, and ATP
Allosteric inhibitors of TCA
NADH, ATP, and acetyl CoA
These activate at least one regulator enzyme in the cycle
NAD+, ADP, and AMP
Electron transport
transfer of electrons from reduced cofactors (NADH, FADH2) to oxygen
Electron transport chain (ETC)
a multistep process involving an ordered series of reversibly oxidized electron carriers functioning together to carry out electron transfer (contains a number of integral membrane proteins that are found in the inner mitochondrial membrane)
Which complexes are found in the inner mitochondrial membrane?
Complexes I, III, and IV
Complex I (NADH coenzyme Q oxidation complex/NADH dehydrogenase)
transfers electrons from NADH to CoQ, when 2 electrons are transferred, 4 protons are pumped across the membrane
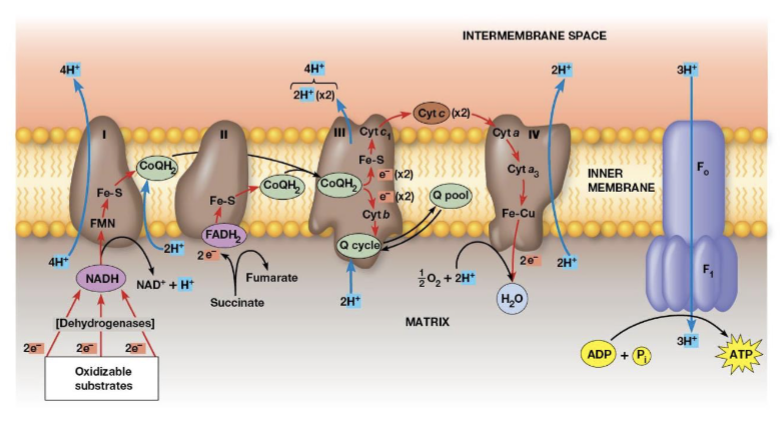
Complex II (succinate—coenzyme Q oxidoreductase complex/succinate dehydrogenase)
transfers electrons from succinate to FAD (generating FADH2; this is reaction CAC-6), the electrons are transferred through 3 Fe-S centers to CoQ, no protons are pumped during this reaction
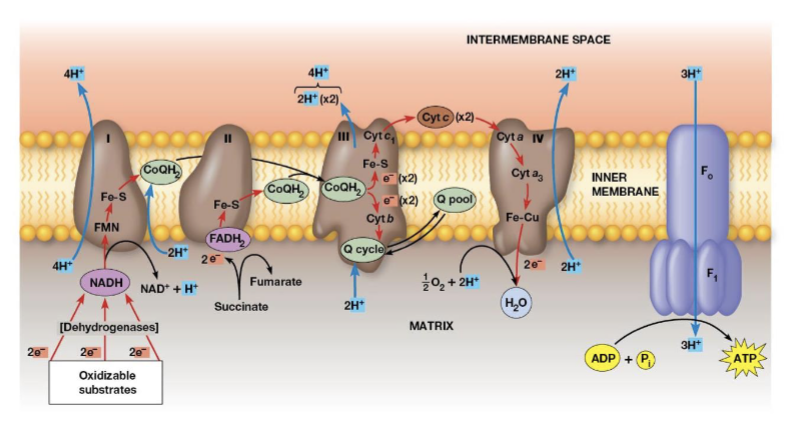
Complex III (cytochrome complex/ coenzyme Q—cytochrome c oxidoreductase complex)
accepts electrons from CoQ and transfers them to cytochrome c, two cytochromes are prominent components, when 2 electrons are transferred, 4 protons are pumped across the membrane
Complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase)
electrons transfer from cytochrome c to an Fe atom in the heme A cofactor of cytochrome a then to cytochrome a3, there are 2 copper atoms which receive one electron, 4 electrons are needed to reduce O2 to H2O, 2 protons are pumped across the membrane for each electron pair
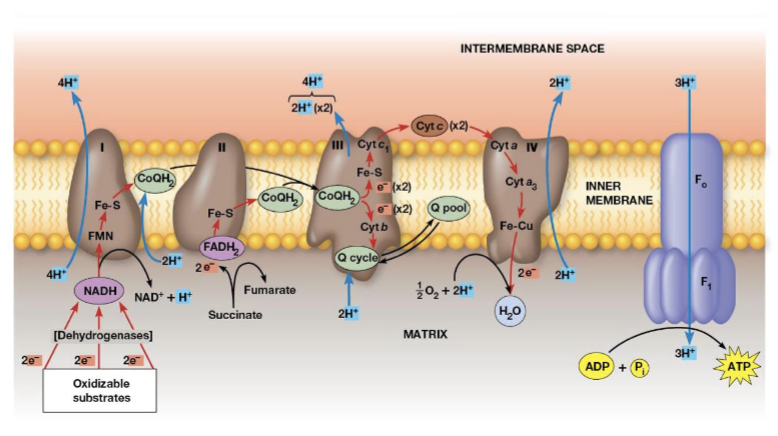
Which complex is the terminal oxidase?
complex IV transfers electrons directly to oxygen
What are the genes encoded by mitochondrial DNA
Complex I, II, III, and IV proteins, tRNAs, mitochondrial rRNA
Which compounds contribute to cellular aging?
Superoxide anion (O2-)
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
antioxidants
soak up highly reactive oxidants and prevent cellular damage
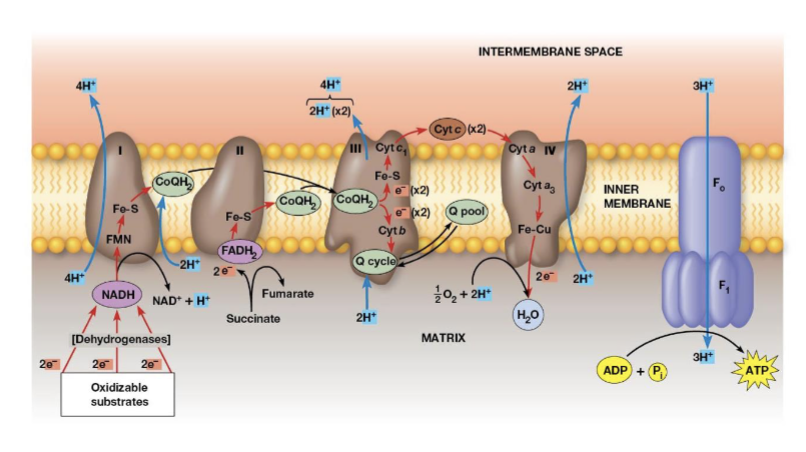
Electrochemical proton gradient
the crucial link between electron transport and ATP production, drives ATP synthesis, ATP synthesis is coupled to electron transport
Chemiosmotic coupling model
the essential feature is that the link between electron transport and ATP formation is the electrochemical potential across a membrane, the electrochemical potential is created by pumping protons across a membrane as electrons transferred through the respiratory complexes
Proton translocator
the channel through which protons flow across the membrane (F0)
F0
provides a channel for exergonic flow of protons across the membrane, acts as a proton translocator, has 2 b subunits and 10 c subunits
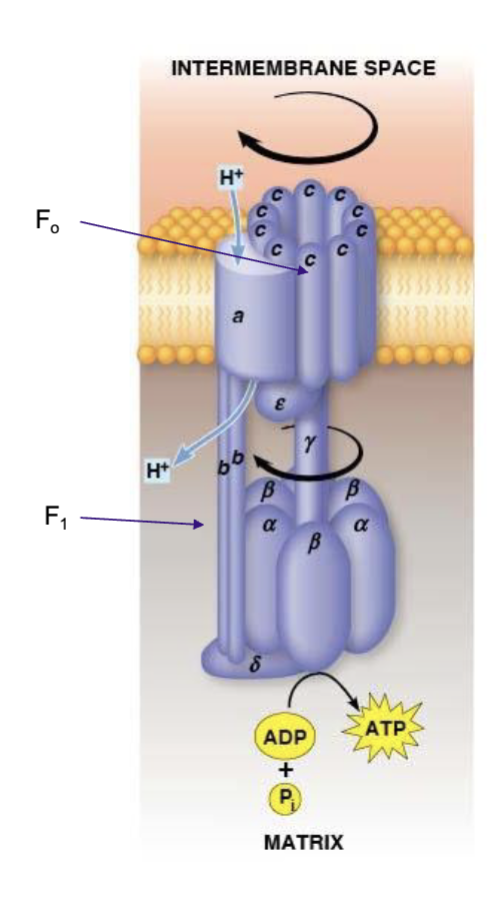
F1
carries out the ATP synthesis, driven by the energy of the proton gradient, has 3 alpha and 3 beta subunits plus 1 delta, 1 gamma, and one sigma subunit
ATP synthase
F0 and F1
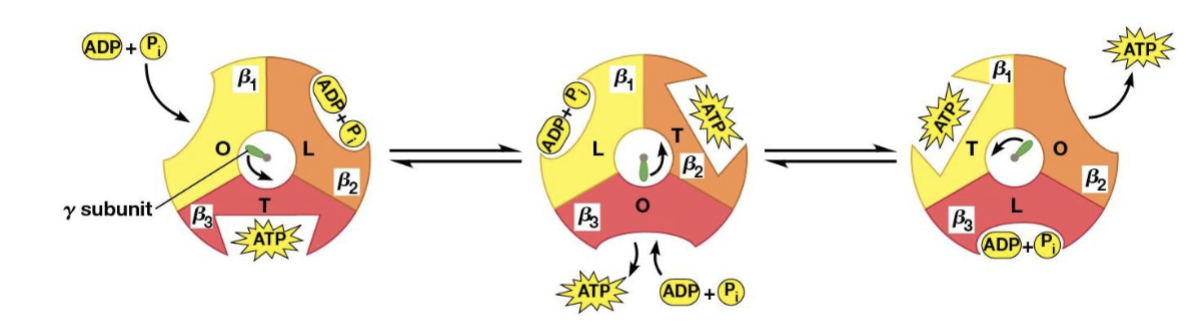
Binding change model (Paul Boyer)
proposed that each of the 3 beta subunits of the F1 complex progresses through 3 different conformations
Conformations of the model
L (for loose), which binds ADP and Pi loosely
T (for tight), which binds ADP and Pi tightly and catalyzes the formation of ATP
O (for open), with little affinity for either substrates or product
Components of the endomembrane system
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi complex
Endosomes
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
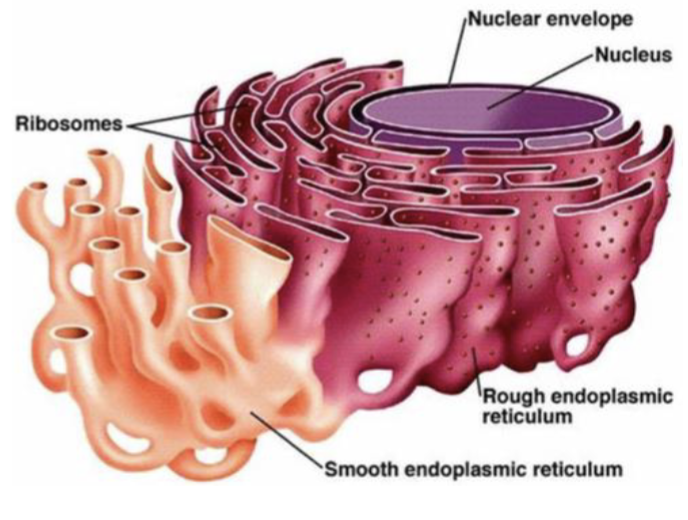
Endoplasmic reticulum
involved in protein synthesis and sorting
Rough ER
characterized by ribosomes on the cytosolic side of the membrane (form large flattened sheets)
the site for membrane synthesis, the folding of polypeptides, recognition and removal of misfolded proteins, assembly of multimeric proteins, and the initial steps of addition of carbohydrates to glycoproteins
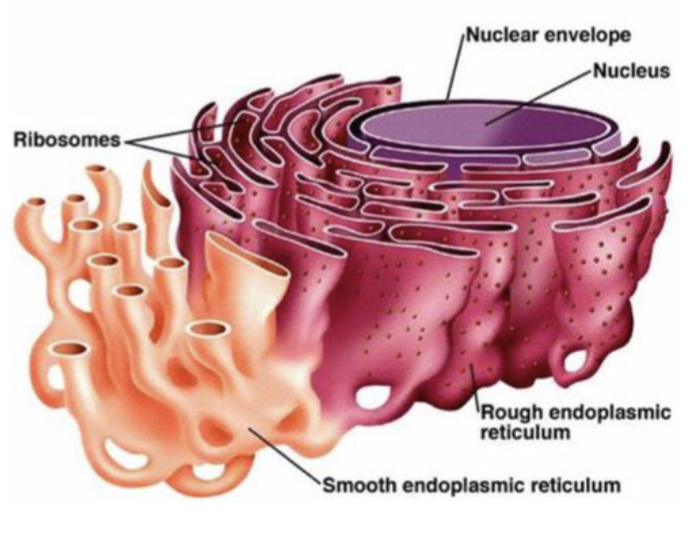
Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes and has other roles in the cell involving the processing and storage of nonproteins (form tubular structures)
its functions include drug detoxification, glycogen breakdown, calcium storage, and steroid biosynthesis
Hydroxylation
adding hydroxyl groups to hydrophobic drugs to increase their solubility, making them easier to excrete from the body
Cytochrome P-450
catalyzes hydroxylation
How does hydroxylation occur?
via electron transport
Pharmacogenetics
investigates how inherited differences in genes, like P-450 can lead to differential responses to drugs and medications
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
a part of the smooth ER that specializes in calcium storage
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMG-CoA reductase
the committed step in cholesterol biosynthesis, founded in the smooth ER of liver cell
Statins
drugs that lower cholesterol, target HMG-CoA
What synthesizes phosphatidylethanolamine?
Mitochondria
What synthesizes cholesterol?
Peroxisomes
Phospholipid translocators (flippases)
transfer fatty acids for membrane proteins to the lumenal side of the bilyaer
Phospholipid exchange proteins
convey specific phospholipids to the mitochondria, chloroplasts, or peroxisomes
protein tags
target the proteins to a transport vesicle that will take it to the correct location
What is the first step in the pathway for delivering proteins to various locations in the endomembrane system?
Cotranslational import
Signal hypothesis
for polypeptides destined for the ER, the N-terminus contains an ER signal sequence that directs ribosome-mRNA-polypeptide complexes to the surface of the RER, then as the polypeptide chain elongates, it progressively crosses the ER membrane and enters the ER lumen
Components of amino acid sequences
15-30 amino acids long
positively charged N-terminal region
central hydrophobic region
polar region next to the cleavage site
Sorting signals
a linear sequence of amino acids that direct proteins to specific locations in the cell
Signal recognition particle (SRP)
recognizes and binds to the ER signal sequence and the binds to the ER membrane
The SRP Mechanism of Cotranslational import
mRNA binds to a free ribosome. The polypeptide is synthesizd until the ER signal sequence has been formed
SRP binds the ER signal sequence and blocks translation
The SRP binds to the ribosome to a translocon in the ER membrane
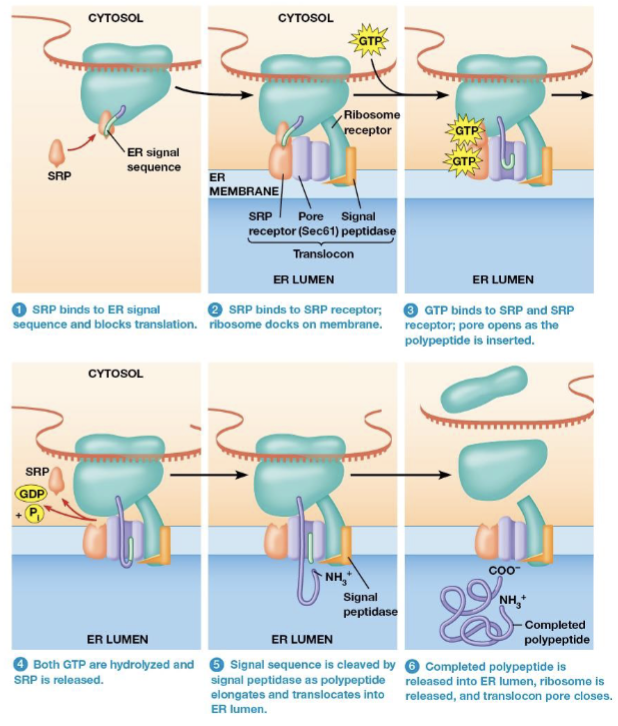
What is the translocon composed of?
SRP receptor
Ribosome receptor
Pore protein
Signal peptidase
SRP receptor
binding site for the SRP
Ribosome receptor
holds the ribosome in place
Pore protein
forms a channel for the growing polypeptide to enter the ER lumen
Signal peptidase
an enzyme to remove the ER signal sequence
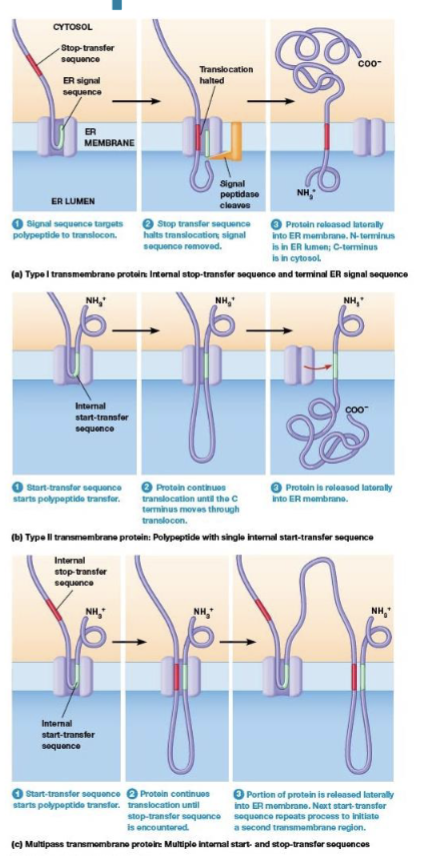
Stop transfer sequence
halts translocation of the polypeptide through the ER membrane and the rest of the polypeptide stays on the cytosolic side of the ER membrane, moves laterally forming a permanent transmembrane segment
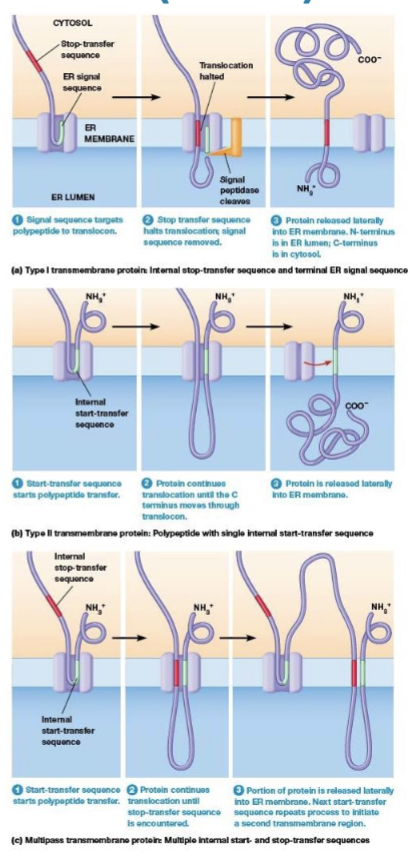
Start transfer sequence
the SRP binds and targets to the ER membrane, its hydrophobic region functions as a membrane anchor
Molecular chaperones
facilitate folding and assembly of polypeptides into multisubunit proteins
BiP
an Hsp70 chaperone protein, binds the hydrophobic region of a polypeptide which prevents aggregation
Golgi complex
involved in processing and sorting
Endosomes
carry and sort material brought into the cell
Lysosomes
digest ingested material and unneeded cellular components
Peroxisomes
involved in lipid metabolism and scavenging of reactive oxygen species