Uterine Disorders
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what makes up the majority of the uterus by size and weight?
the uterine corpus
what are leiomyoma?
benign growths of smooth muscle class on the uterine wall "fibroids"
most common tumor of the uterine wall
who are leiomyomas more common in?
African Americans
what do s/sxs depend on with a leiomyoma?
size and location
what are main sxs of leiomyoma?
AUB, heavy menstrual bleeding, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia with deep penetration, pelvic pressure, infertility, and recurrent pregnancy loss
what are risk factors for leiomyoma?
age, African america, 1º relative, early menarche, late menopause, obesity
what are protective factors against leiomyoma?
smoking, exercise, increased parity, late menarche, early menopause, OC use
what is leiomyoma thought to arise from?
poorly understood, but thought to arise from an alteration in a single cell
what is bulf of the fibroid due to?
expansion of the extracellular matrix
what is used to classify fibroids?
FIGO classification system
(international federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics)
classifies myomas by location
what do tx options of fibroids depend on?
vary greatly depending on the size and location of myxomas, therefore, continued efforts to improve classification modalities are vital
what are the different types of fibroids?
submucosal, intramural, subserosal, interligamentous
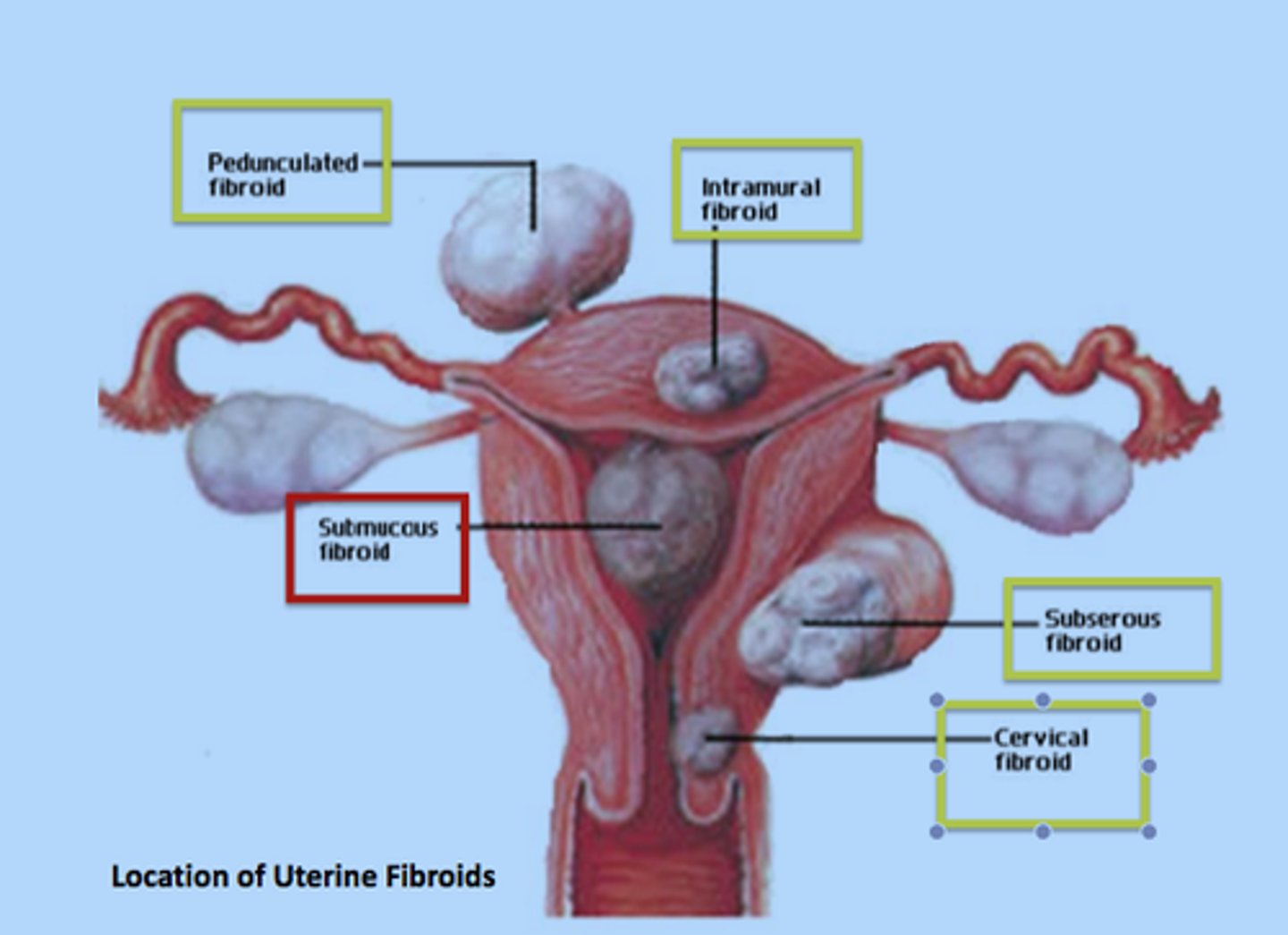
what is the danger of submucosal fibroids?
they create a change in the architecture of the uterine cavity
where do intramural fibroids lie and what is their danger?
lie within the myometrium
depending on their size and positioning can protrude outward to the abdominal cavity or inward which creates defects in the uterine cavity
where do subserosal myomas lie?
under the peritoneal layer covering the uterus and protrude outward to the abdominal cavity but can also alter the myometrium
where do interligamentous myomas lie?
within the broad ligament
what are parasitic or metastatic myomas?
myomas that move beyond the uterus
on gross exam, what do fibroids look like after removal?
white-grey or yellow appearance
contained within a pseudocapsule
what is the main differential for leiomyomas? why?
ovarian and colonic masses because they can mimic the appearance of uterine myomas on imaging
what do uterine related differentials of leiomyomas include?
adenomyosis, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, polyps, grossly proliferative endometrium, endometrial hyperplasia or malignancy, ovarian malignancy, or leiomyosarcoma
what are the clinical findings of leiomyomas?
they can be asymptomatic!
if symptomatic: there is notable decrease in qoL
most common presenting symptoms are AUB (abnormal uterine bleeding), HMB, pelvic pressure and pain, infertility and spontaneous abortion
what is the most common presenting complaint of myomas? which myoma is it most associated with?
AUB
pts often present with heavy or prolonged menses
most frequently seen in submucosal fibroids
fixed retroverted uterus******* endometriosis
what is myoma related pelvic pain and pressure related to?
directly related to size and location
myomas >5cm are associated with increased pain
how do myomas create pain?
- through infarction and increasing local inflammatory response ~ (local ischemia creates pain and can even present as an acute abdomen )
- they also cause increased production of cytokines, resulting in increased inflammatory response that contributes to pain ~ (especially in those with dysmenorrhea 2º fibroids)
- submucosal myomas can create HMB and clots that create worsening dysmenorrhea
what causes fibroids to mess with fertility?
structural problem
- submucosal or intramural disrupt the endometrial cavity
-cant really undertsand 15
what will physical exam findings reveal in myomas?
vary depending on size and location
- can present as distended abdomen like pt w advanced gestation