Genes & Genomes: Structure, Regulation, and Human Genome Insights
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are the structural components of a typical gene?
A start and stop location, a binding site for RNA polymerase (promoter), and associated chromosomal regions that assist in regulation of expression.
What is the role of introns and exons in gene structure?
Introns are noncoding sequences that interrupt coding sequences (exons). The entire gene is transcribed into RNA, and introns are removed by splicing, leaving only exons in the mRNA.
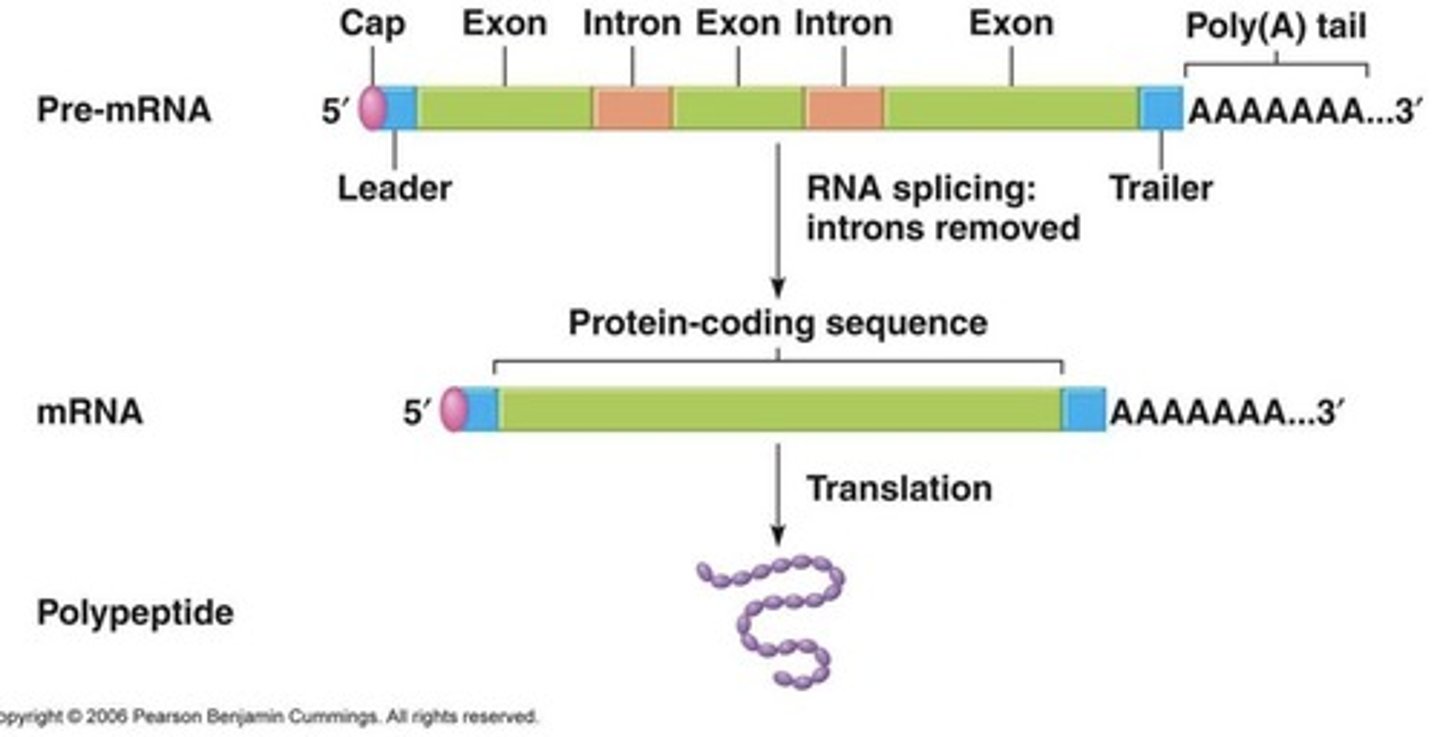
How many exons and introns does an average human gene contain?
An average human gene contains 9 exons and 8 introns.
What is alternative splicing?
Alternative splicing creates different combinations of exons, resulting in different proteins from the same gene.
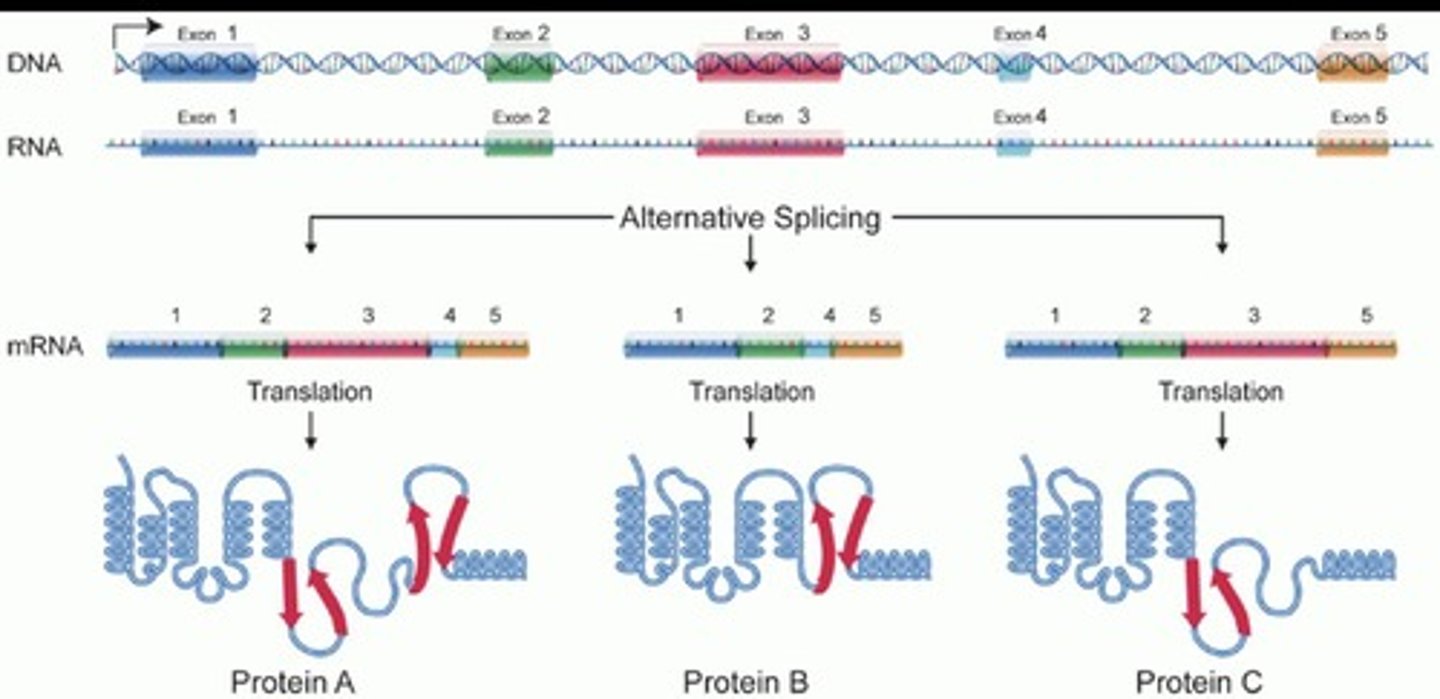
What is the significance of repetitive elements within the human genome?
Repetitive elements play a role in genome structure and function, although their specific significance is complex and varies.
How are transcription factors regulated?
Transcription factors are regulated by phosphorylation or dephosphorylation, often in response to growth factors, hormones, nutrients, and external stimuli.
What are pseudogenes?
Pseudogenes are genomic sequences that are highly similar to functional protein-coding genes and arise from duplication or retrotransposition events.
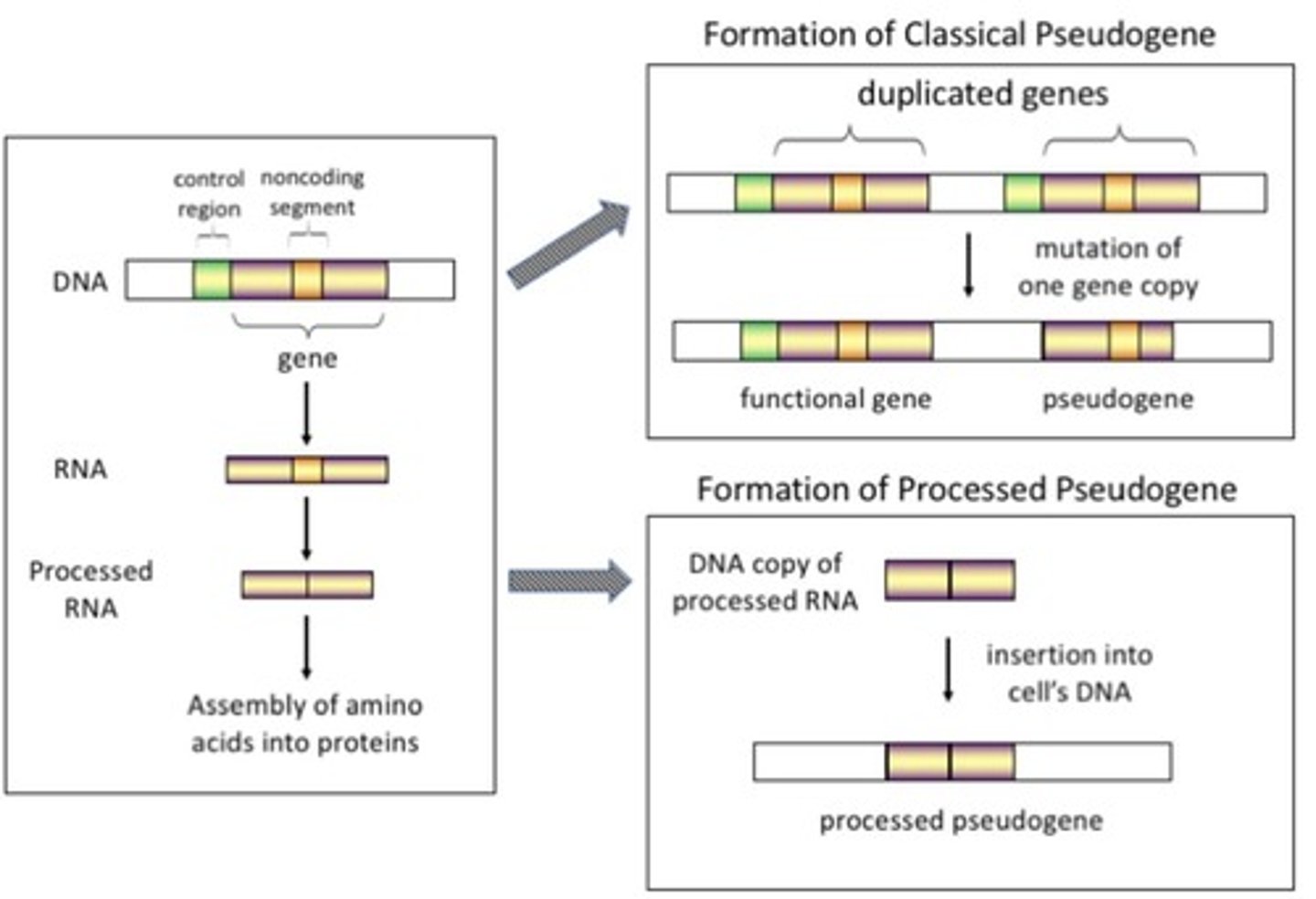
What association do oncogenic pseudogenes have with cancer?
The upregulation of oncogenic pseudogenes in cancer is associated with elevated growth and invasiveness.
What is the minimum requirement for a gene to be considered functional?
A gene must have a start and stop location and encode for a specific RNA.
What is the average size of a human gene in base pairs?
An average human gene is distributed over 30,000 base pairs (30 kilobases, or kb).
What is the role of DNA-binding proteins in gene expression?
Most DNA-binding proteins regulate gene expression.
What is the function of RNA polymerase in gene transcription?
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of a gene to initiate transcription of DNA into RNA.
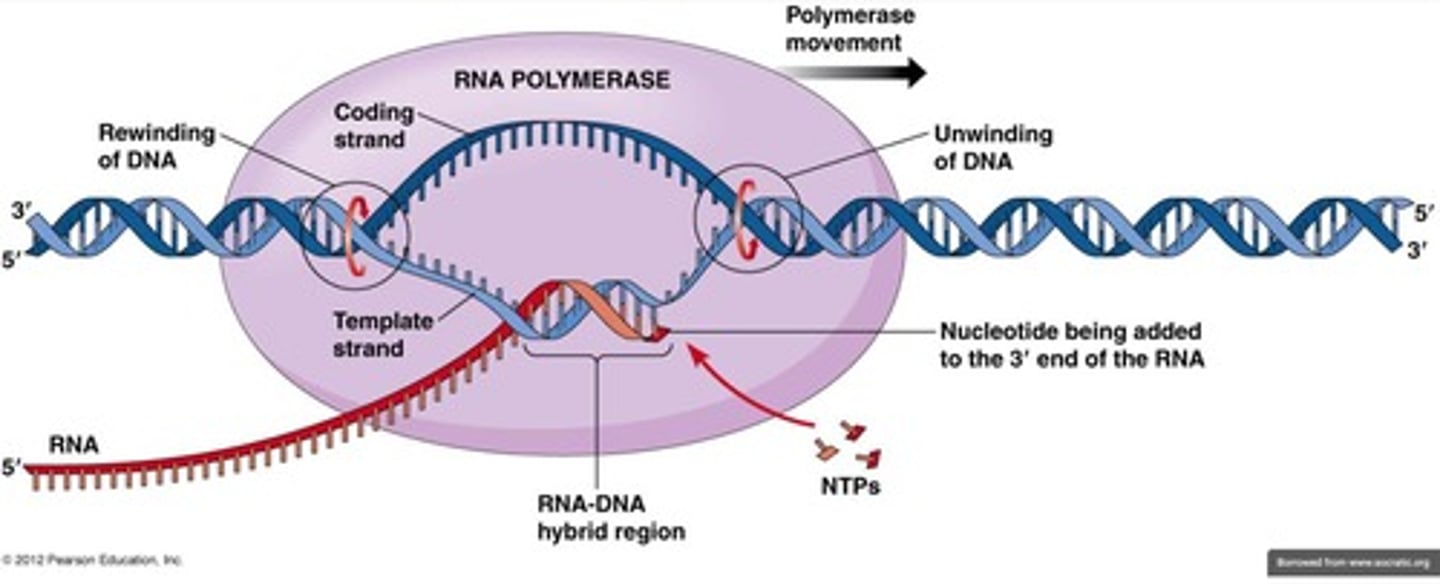
What happens to introns during RNA processing?
Introns are removed during RNA splicing, and only exons are included in the final mRNA.
What is the relationship between gene structure and gene expression regulation?
Gene structure, including the presence of promoters and regulatory regions, directly influences the regulation of gene expression.
How do protein kinases and phosphatases affect transcription factors?
They modify transcription factors through phosphorylation or dephosphorylation, impacting their activity.
In what context are pseudogenes particularly relevant?
Pseudogenes are particularly relevant in the context of cancer, where their upregulation can indicate increased growth and invasiveness.
What is the primary function of exons in a gene?
Exons code for the protein product of the gene.
What is the difference between coding and noncoding DNA in genes?
Coding DNA consists of exons that encode proteins, while noncoding DNA consists of introns that do not code for proteins.
What is the significance of Dr. Siddhartha Mukherjee's lecture mentioned in the notes?
It highlights the importance of understanding genes and genomes in the context of modern genomic research.
What is the impact of alternative splicing on protein diversity?
Alternative splicing increases protein diversity by allowing different combinations of exons to be included in the final mRNA.
What are Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)?
Single base pair polymorphisms that are spread throughout the genome, spaced about 1,000 bases apart, and cataloged in the HapMap database.
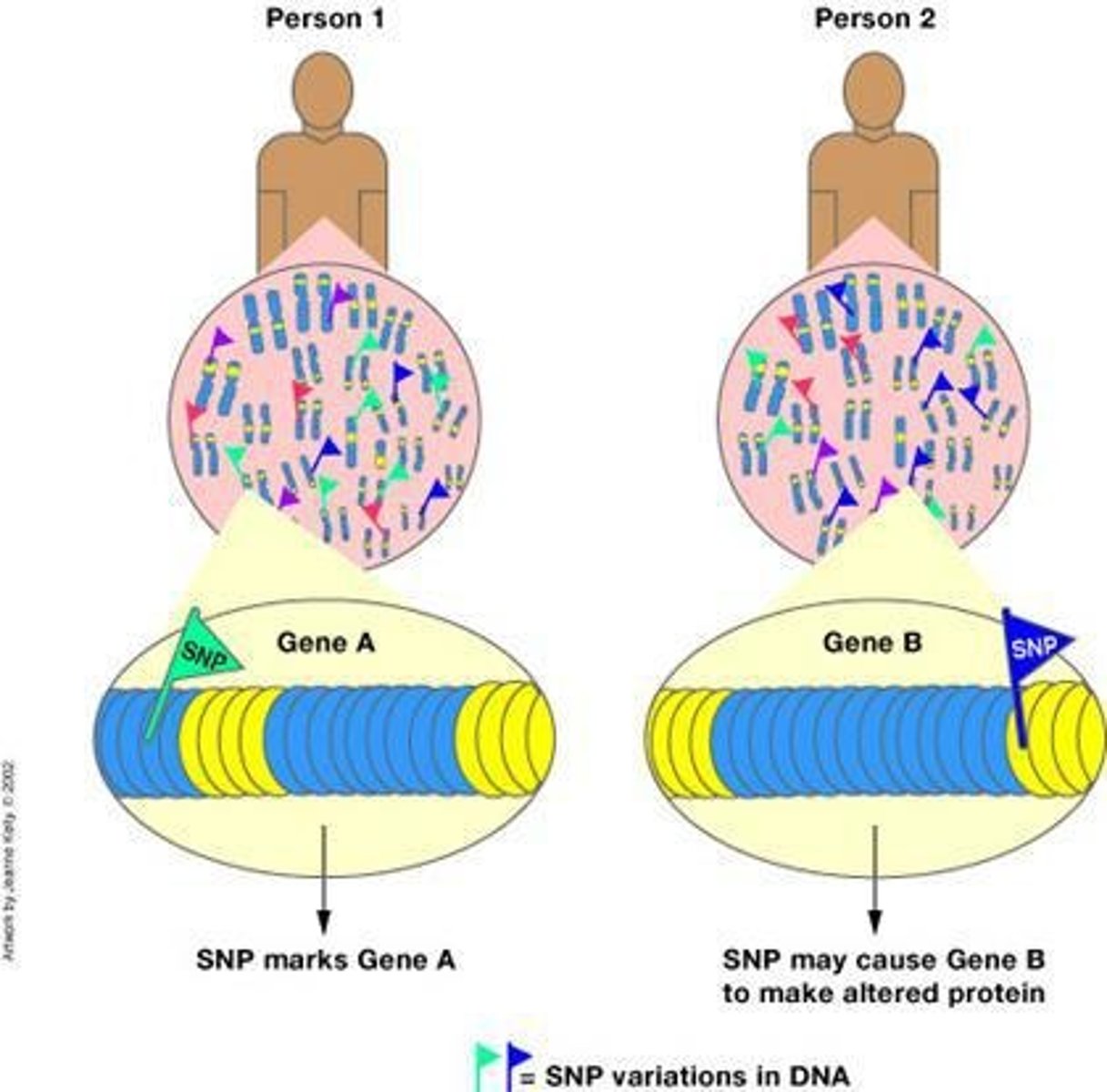
How many mapped human SNPs are there?
3.7 million mapped human SNPs.
What is the significance of characterizing SNPs in genetics?
Characterization of SNPs may help identify subsets of individuals at risk for specific diseases and predict drug responses/adverse reactions.
What percentage of mammalian DNA consists of highly repetitive sequences?
Approximately 50%.
What are simple-sequence repeats?
Tandem arrays of short sequences, ranging from 1 to 500 nucleotides.

What is minisatellite DNA?
DNA that consists of tandem repeats of 10-100 nucleotides, repeated 5-50 times.
What is microsatellite DNA?
Very short tandem repeat sequences of 2-9 nucleotides.
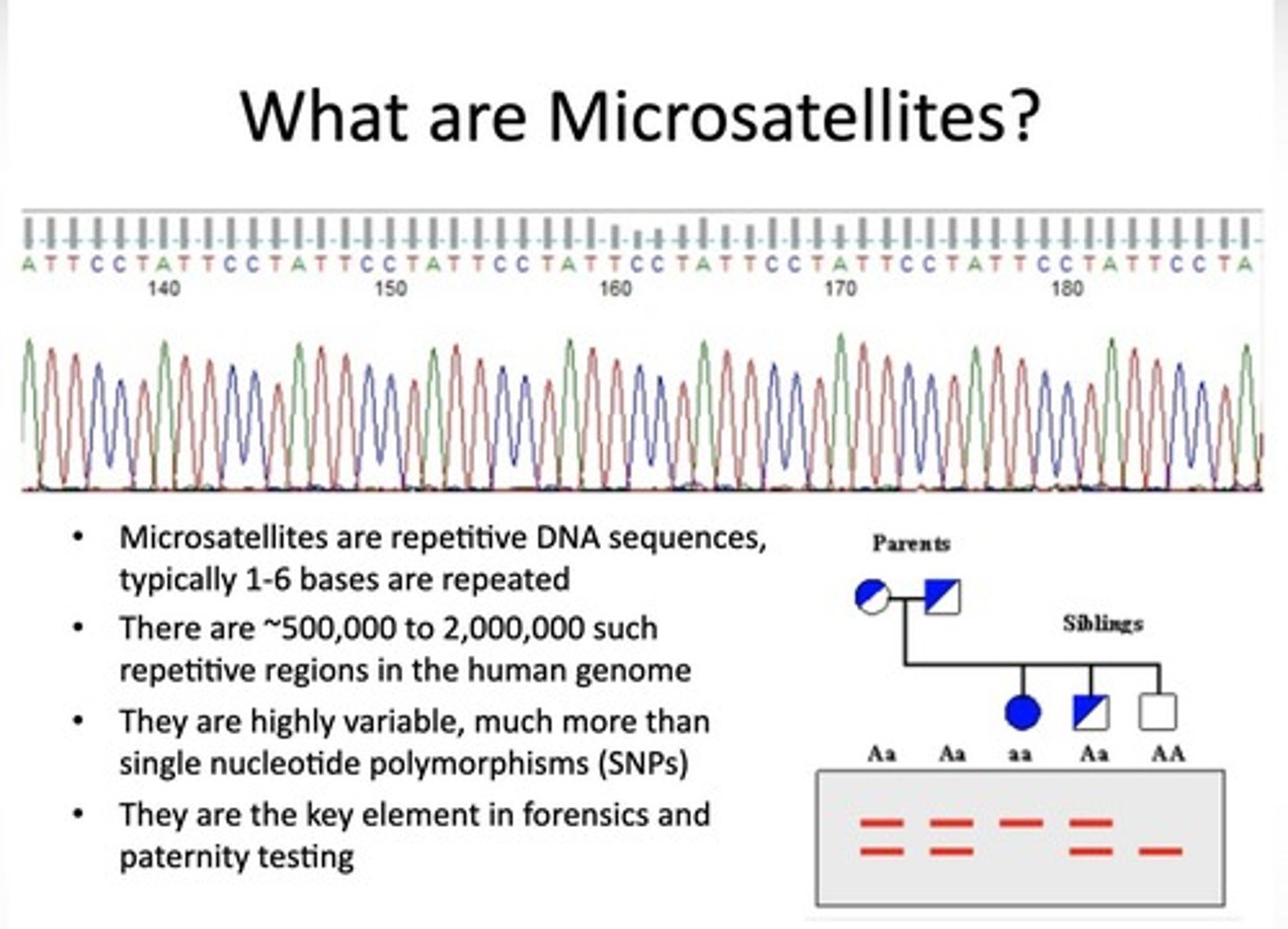
What is associated with the expansion of some trinucleotide repeats?
Disease.
What occurs in certain cancers related to microsatellites?
Instability in microsatellites.
What is the role of RNA in gene expression?
RNA is single-stranded and contains Uracil instead of Thymine, and is transcribed from one strand of DNA by RNA Polymerase.
What does the level of mRNA synthesis indicate?
Gene expression levels.
What are housekeeping genes?
Genes that are expressed nearly all the time.
What are developmental genes?
Genes that are only expressed at certain times.
How can environmental cues affect gene expression?
Some genes can be turned on and off in response to environmental cues, such as insulin.
What controls the levels of gene expression?
The promoter sequence.
What is the total size of the human genome?
6,200 Mbp total (diploid).
How many protein-coding genes are in the human genome?
At least 20,500 protein-coding genes, plus another 2,300 micro-RNA genes.
What is the function of most noncoding DNA in the genome?
Involved in regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and controlling epigenetic inheritance.
What fraction of the genome is made up of protein-coding sequences?
Approximately 1.5%.
What was the goal of the Human Genome Project (HGP)?
To completely map and understand all the genes of human beings.
What resource has the Human Genome Project provided?
Detailed information about the structure, organization, and function of the complete set of human genes.
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids?
Purines and pyrimidines.
What is the Watson-Crick model of DNA structure?
A 3-D model of DNA with two helical chains forming a right-handed double helix, where bases are stacked and perpendicular to the axis.

What is the main function of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
It catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs).
What is the significance of semiconservative DNA replication?
Each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
What are the roles of nucleotides in cellular functions?
They provide energy for metabolism (ATP, GTP), serve as enzyme cofactors (NAD+, FAD, CoA), and are involved in signal transduction (cAMP, cGMP).
What are the functions of nucleic acids?
Storage of genetic information (DNA), transmission of genetic information (mRNA), processing of genetic information (ribozymes), and protein synthesis (tRNA and rRNA).
What is the role of telomerase in DNA replication?
Telomerase extends telomeric DNA sequences, which protect chromosome ends from degradation.
What is the difference between the leading and lagging strands during DNA replication?
The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5′ to 3′ direction, while the lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous pieces called Okazaki fragments.
What is the function of primase in DNA replication?
Primase synthesizes short RNA fragments that serve as primers for DNA synthesis.
What is the role of DNA ligase in DNA replication?
DNA ligase joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
What is chromatin composed of?
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and histone proteins.
What are the two states of chromatin during the cell cycle?
Euchromatin (relaxed, transcriptionally active) and heterochromatin (condensed, transcriptionally inactive).
What is the significance of high titers of antibodies against histones?
It is diagnostic for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, an autoimmune disease.
What is the function of base analogs in cancer treatment?
They act as inhibitors of nucleotide biosynthesis or are incorporated into DNA or RNA to disrupt cancer cell replication.
How does 5-FU exert its anticancer effects?
By inhibiting thymidylate synthase and incorporating its metabolites into RNA and DNA.
What are origins of replication (ori)?
Binding sites for proteins that initiate the DNA replication process.
What is the role of exonuclease activity in DNA polymerases?
It allows the removal of incorrectly incorporated bases during DNA replication.
What is the significance of the year 1956 in DNA research?
It was the year DNA polymerase was first identified, providing a biochemical basis for DNA replication.
What is the difference between euchromatin and heterochromatin?
Euchromatin is relaxed and transcriptionally active, while heterochromatin is condensed and transcriptionally inactive.
What are Okazaki fragments?
Short pieces of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
What is the primary role of ribozymes?
Processing of genetic information.
What is the role of histones in chromatin structure?
Histones help package DNA into a compact, organized structure, facilitating gene regulation.
What happens to chromatin during cell division?
Chromatin condenses into highly organized structures called chromosomes.
What is euchromatin?
Euchromatin is a form of chromatin that is active in transcription.
What is heterochromatin?
Heterochromatin is transcriptionally inactive and contains highly repeated DNA sequences.
How does acetylation affect transcription?
Acetylation of lysine side chains in histones destabilizes chromatin structures and favors transcription by eliminating positive charges, weakening histone binding to DNA.
What is epigenetic inheritance?
Epigenetic inheritance refers to the transmission of DNA methylation patterns and histone modifications through cell generations.
What is the effect of methylation on histones?
Methylation of some lysine side chains in histones favors the formation of heterochromatin and reduces transcription, while methylation on other lysine and arginine side chains can have the opposite effect.
What percentage of cytosine in human DNA is methylated?
About 3% of the cytosine in human DNA is methylated.
What is the significance of CpG islands in gene regulation?
About 60% of human genes possess CpG islands near their promoters, and their methylation state varies across different tissues.
How does methylation suppress mobile elements?
CG sequences near mobile elements are kept in the methylated state to prevent their transcription.
What is X inactivation?
X inactivation is the process where the inactive second X chromosome in females, known as the Barr body, is kept in a condensed, heterochromatic state by widespread DNA methylation.
What is genomic imprinting?
Genomic imprinting is when a few dozen human genes become selectively methylated in the male or female germ line, leading to expression from only the maternally or paternally inherited chromosome.
What is gene silencing?
Gene silencing is a general term describing the epigenetic process of gene regulation through mechanisms like methylation.
What is the function of centromeres?
Centromeres connect sister chromatids and are composed of repetitive sequences; they are crucial for the formation of kinetochores.
What role do kinetochores play during mitosis?
Kinetochore proteins bind to spindle microtubules and act as molecular motors to drive the movement of chromosomes to daughter cells.
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
Humans have 23 pairs (total 46) of chromosomes, consisting of 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes (XX or XY).
What is the purpose of staining chromosomes?
Staining chromosomes reveals unique banding patterns that allow for analysis and arrangement in a karyotype, which is used for clinical diagnostics.
What are telomeres?
Telomeres are sequences at the ends of chromosomes required for the replication of linear DNA molecules and consist of repetitive sequences.
What is the repeat sequence of telomeres in humans?
The repeat sequence of telomeres in humans is TTAGGG.
What is the role of telomerase?
Telomerase replicates telomeric DNA sequences using reverse transcriptase activity, maintaining telomere length.
Why is telomere maintenance important?
Maintenance of telomeres is important for determining the lifespan and reproductive capacity of cells.
What happens to telomeres as somatic cells age?
Most somatic cells do not have enough telomerase to maintain telomere length, leading to gradual shortening and eventual cell death or senescence.
What is the relationship between telomeres and cancer?
Studies of telomeres and telomerase may provide insights into aging and cancer.
What is a chromatid?
A chromatid is one half of a duplicated chromosome, with identical DNA that separates during mitosis.
What is the structure of a normal human karyotype?
A normal human karyotype consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes, which can be studied using a light microscope during metaphase.