Qual 2 Qualitative data analysis
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
4 qualities of qualitative data analysis
systematic, inductive, describes and interprets data, complex
What does transcription involve?
Transcribing speech verbatim using standard spelling conventions or more complex methods
What is the Jefferson system of transcription?
It includes prosody, paralinguistics, and extralinguistic elements
What is prosody
phonemic aspects of spoken language e.g. intonation
What is paralinguistics
non-phonemic aspects of langue e.g. serious
What is extralinguistic
non-linguistic aspects e.g. gesture
What is the aim of content analysis
use qualitative data to examine patterns in communication in a replicable and systematic manner
What is the aim of grounded theory
to generate theories from data collected
2 qualities of grounded theory
systematic methodology and theoretical sampling
What is the aim of discourse of conversation analysis
to identify rules of conversational organisation
3 concepts explored by discourse analysis
utilisation of language, social contexts and meaning/perception shaped by language
What is the aim of interpretative phenomenological analysis
to understand how a given person makes sense of their experiences
2 processes within interpretative phenomenological analysis
detailed analysis (of personal accounts) and researcher’s role (in interpreting data)
How does Braun and Clarke define thematic analysis?
A method for identifying, analysing, and reporting patterns (themes) within data.
What 3 ways makes TA flexible?
It can be semantic or latent, inductive or deductive, essentialist or constructionist.
Thematic analysis is relatively __ and __ to learn and do
easy, quick
Thematic analysis is accessible to __
novice researchers
Thematic analysis ___ key features of a large body of data
summarises
Across a data set, thematic analysis highlights ___
similarities and differences
Thematic analysis can generate __ insights
unanticipated
Thematic analysis allows for social and psychological ___ of data
interpretations
Who are results of thematic analysis accessible to
educated general public
What are the six phases of TA, according to Braun and Clarke?
(1) Data familiarisation, (2) Generating codes, (3) Searching for themes, (4) Reviewing themes, (5) Defining and naming themes, (6) Producing a report
What is the inductive approach
whereby codes and themes are derived from the data, rather than using pre-defined set of concepts and assumptions
4 key processes in data familiarisation
re-reading data, keep research question in mind, data immersion and not rushing
Why is it important not to rush initial impressions into themes?
To avoid being anecdotal and ensure systematic analysis.
What are codes in qualitative analysis?
Concise labels that identify features of the data, either semantic (descriptive) or latent (interpretative).
What does codes in qualitative analysis refer to
the most basic segment of raw data
What is the distinction between 1st-order and 2nd-order codes?
1st-order codes are Descriptive/semantic (surface level), 2nd-order codes are abstract/latent (underlying meanings).
How does Braun and Clarke define a theme?
A theme captures something important about the data related to the research question and represents some level of patterned response or meaning
What concept do themes provide to bring codes together
central organising concept
What does "searching for themes" involve?
Actively shaping codes into a coherent story by grouping them into categories or candidate themes.
4 key questions to consider when reviewing themes
(1) evident across multiple data items, (2) is there any overlap, (3) do the themes answer the research question, (4) do themes capture most codes
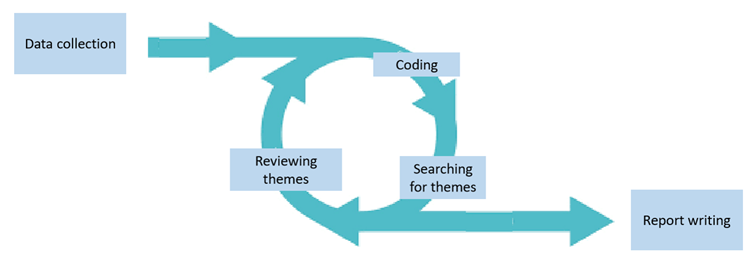
Why is qualitative analysis an iterative process?
Progress often involves returning to earlier phases, like coding or searching for themes.
3 qualities of theme names
concise, informative and catchy
What is a thematic map?
A tool to visualize the overall structure of the analysis, showing how themes form a cohesive story.
4 aspects in theme writing
analytic narrative (story), interpretation of data, theme definition, theme names