Biol 1406 Final Exam
1/442
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
443 Terms
endonuclease
an enzyme that cleaves DNA at specific sites, leaves sticky complementary tails
gel electrophoresis
Procedure used to separate and analyze DNA or protein fragment by size and charge
gel electrophoresis uses
forensics, compare DNA at crime scene
Reverse transcriptase PCR
a modification of PCR in which the first round of replication involves the use of RNA and reverse transcriptase to make a complementary strand of DNA. Use to make cDNA
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
labels DNA
Ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the DNA molecule.
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that links together the growing chain of ribonucleotides during transcription to form mRNA
Taq polymerase
Heat-tolerant enzyme used to copy DNA in PCR
reverse transcriptase
Needed to form cDNA libraries
This organism is genetically engineered to make insulin
bacteria
How can bacteria make insulin?
Gene for human insulin protein is inserted into bacteria by plasmids
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
is used to copy and amplify small quantities of DNA
PCR steps
denaturation, annealing, synthesis
knockout genes
genes that take the place of normal genes. Results in failure to produce the specific protein produced by the normal genes
knockin gene
Gene is replaced by another gene so new protein is produced.
genetic engineering uses
Bioremediation, glyphosate resistant crops, Golden Rice
CRISPR
a collection of DNA sequences that tells Cas9 exactly where to cut. For treatment of genetic diseases.
Is CRISPR used to treat chromosomal disorders?
No, genetic only. Not trisomies or monosomies
restriction map
diagram that shows the lengths of fragments between restriction sites in the strand of DNA
restriction map use
Remove DNA fragment from one plasmid vector to another
Proteome
the entire set of proteins expressed by a given cell or group of cells
Genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
DNA microarray
research tool used to study gene expression
protein microarrays
can be used to analyze protein-protein interactions
STRs (short tandem repeats)
sections in between chromosome in which DNA sequences are repeated
STR usefulness
forensics, paternity
Why more mRNA than genes?
Alternative splicing, removal of introns
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Natural selection acts on
phenotypes in a population, allele frequency in a population
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
condition that occurs when the frequency of alleles in a particular gene pool remain constant over time
bottleneck effect
A change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population
founder effect
change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population
genetic drift
A change in the allele frequency of a population as a result of chance events rather than natural selection.
Mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information
Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment, longer life then more babies
sickle cell anemia
a genetic disorder that causes abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in some red blood cells assuming an abnormal sickle shape, recessive trait so both parents are heterozygous.
directional selection
Form of natural selection in which the entire curve moves; occurs when individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve
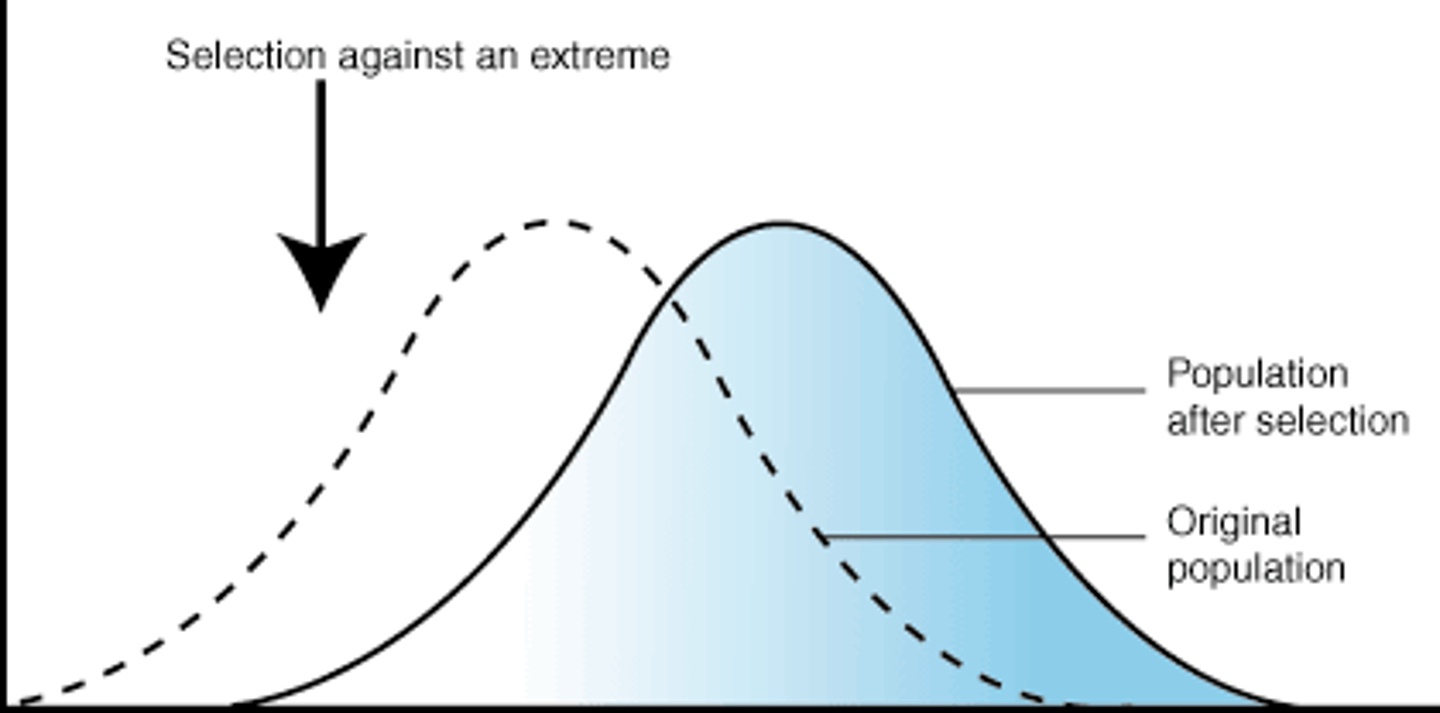
stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
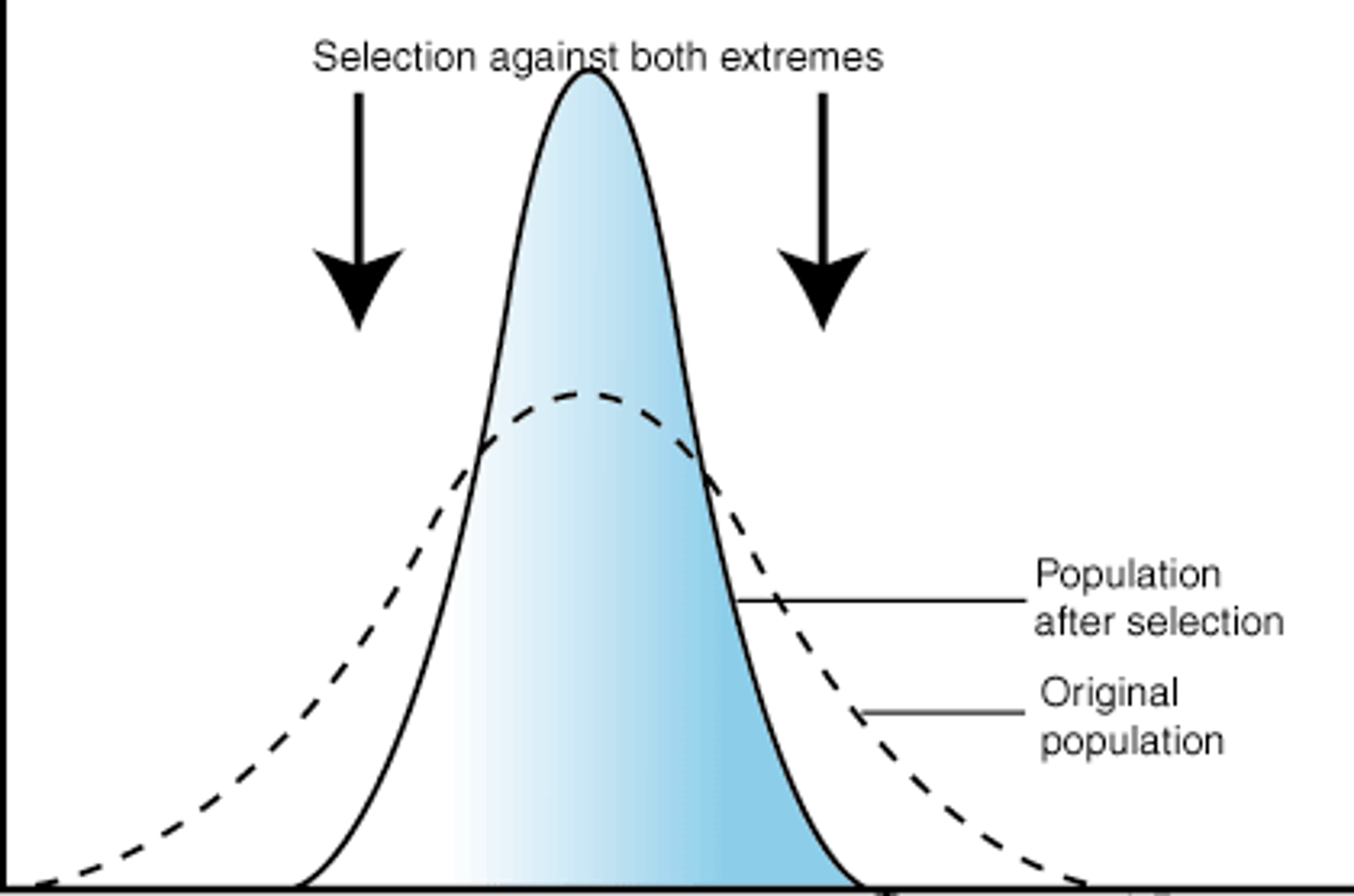
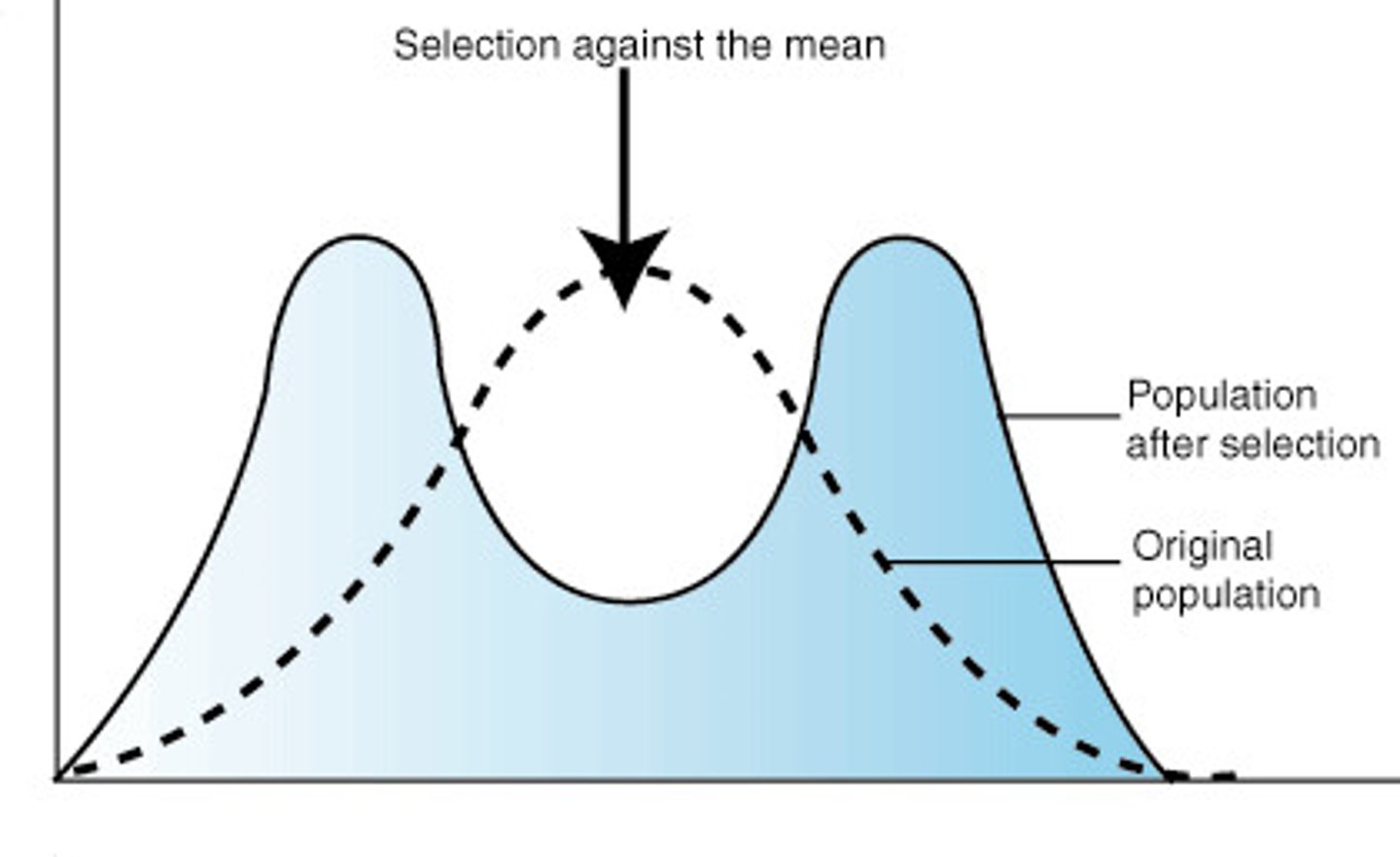
disruptive selection
form of natural selection in which a single curve splits into two; occurs when individuals at the upper and lower ends of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments, skeleton of fish, shark, dolphin (all have fins and streamlined)
homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry. Ex: human hand & whale fins
artificial selection vs natural selection
AS- humans breed for certain traits, occurs quickly and more change is seen
NS- inherited beneficial adaptations
measure radioactive decay
to date rocks or fossils
vestigial structures
A structure that is present in an organism but no longer serves its original purpose, whale pelvis, human appendix
Biogeography
Study of past and present distribution of organisms, oceanic island inhabitants resemble organisms of nearest mainland with some differences.
Evidence to support evolution
Fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, molecular record, vestigial structures, homologous structures
transgenic organism
organism that is genetically engineered by inserting a gene from another organism
DNA introduced into plants by
-Electroporation
-physical bombardment (coat nanoparticles with recombinant DNA and fire particles into plant tissue)
-chemical treatment
-bacterial transfer (plasmid)
RNA interference (RNAi)
introduction of double-stranded RNA into a cell to inhibit gene expression (protein synthesis)
What are the 4 classes or groups of biomolecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Monomers or building blocks of carbohydrates are ____.
Monosaccharides
(such as glucose)
Monomers or building blocks of lipids are ____.
Fatty Acids and Glycerol
Monomers or building blocks of proteins are ____.
Amino Acids
Monomers or building blocks of nucleic acids are ____.
Nucleotides
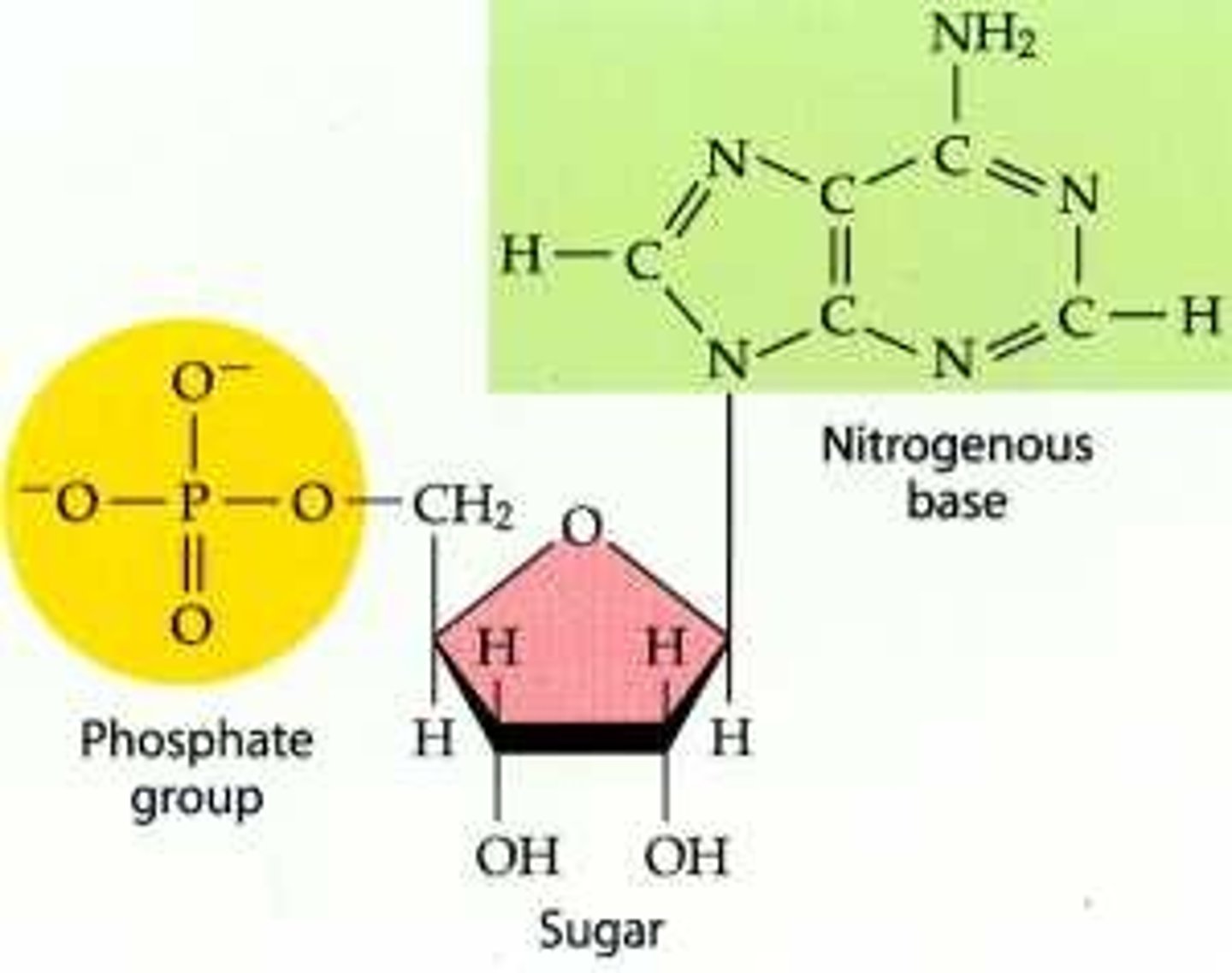
What 3 parts or subunits make up a nucleotide?
5-Carbon sugar
Phosphate Group
Nitrogenous Base
What 5-carbon sugars would you expect to find in a nucleotide?
Deoxyribose (in DNA)
OR
Ribose (in RNA and ATP)
Carbohydrates that are sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides) often end in the suffix.
-ose
What nitrogenous bases would you expect to find in a nucleotide?
Any one of these:
Adenine (DNA, RNA, & ATP)
Guanine (DNA & RNA)
Cytosine (DNA & RNA)
Thymine (only DNA)
Uracil (only RNA)
___ make up polymers. They are like building blocks.
Monomers
Monomers join together to make up ___.
Polymers
Which group of biomolecules have this structure?
Carbohydrates
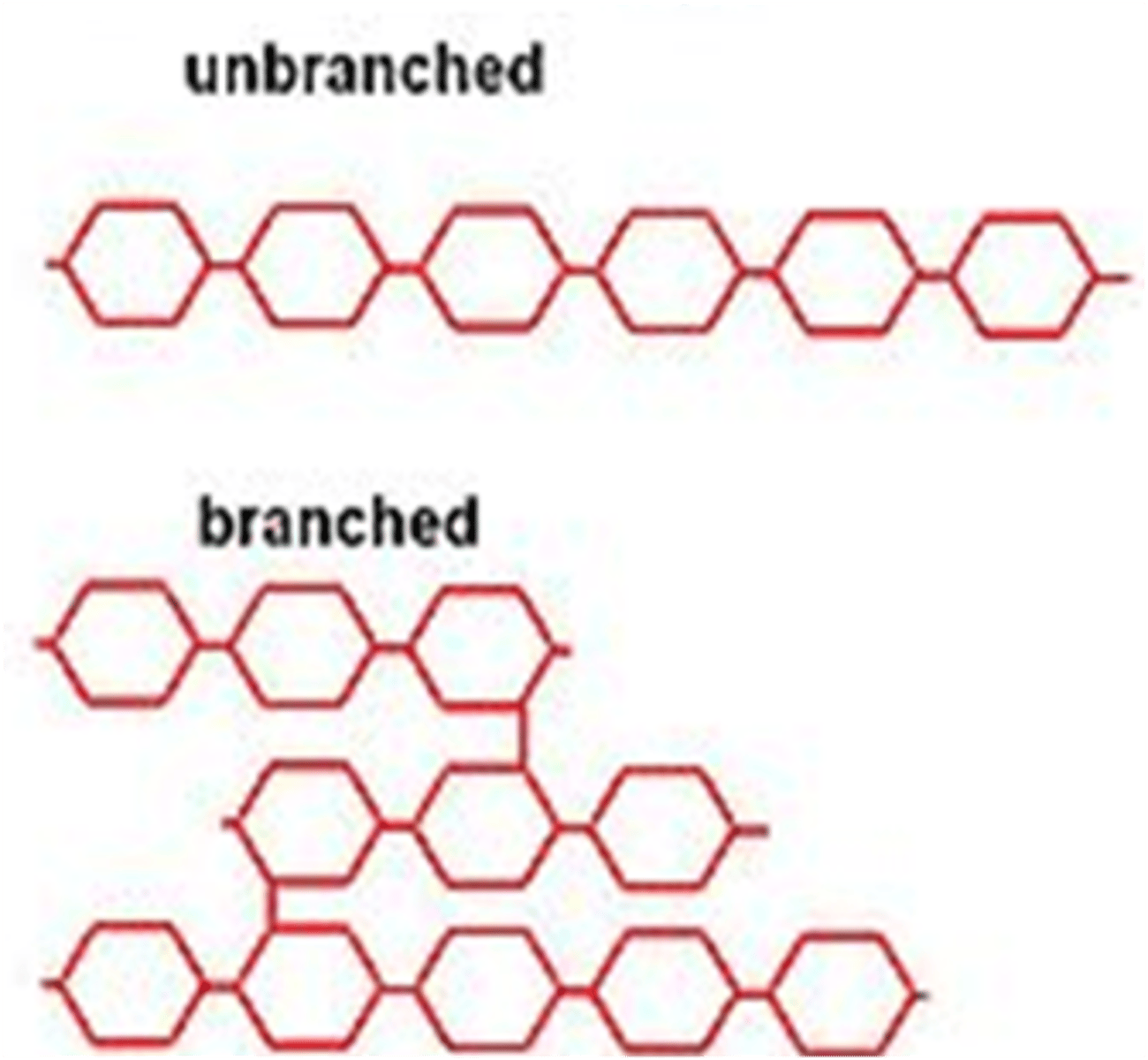
Carbohydrates can be classified into 3 groups based on size. What are they?
Monosaccharides (1 sugar big such as glucose)
Disaccharides (2 sugars big, such as sucrose)
Polysaccharides (many sugars big, such as starch or cellulose)
Identify this molecule.
What class of biomolecules does it belong?
Glucose
Carbohydrate
(simple sugar or monosaccharide)
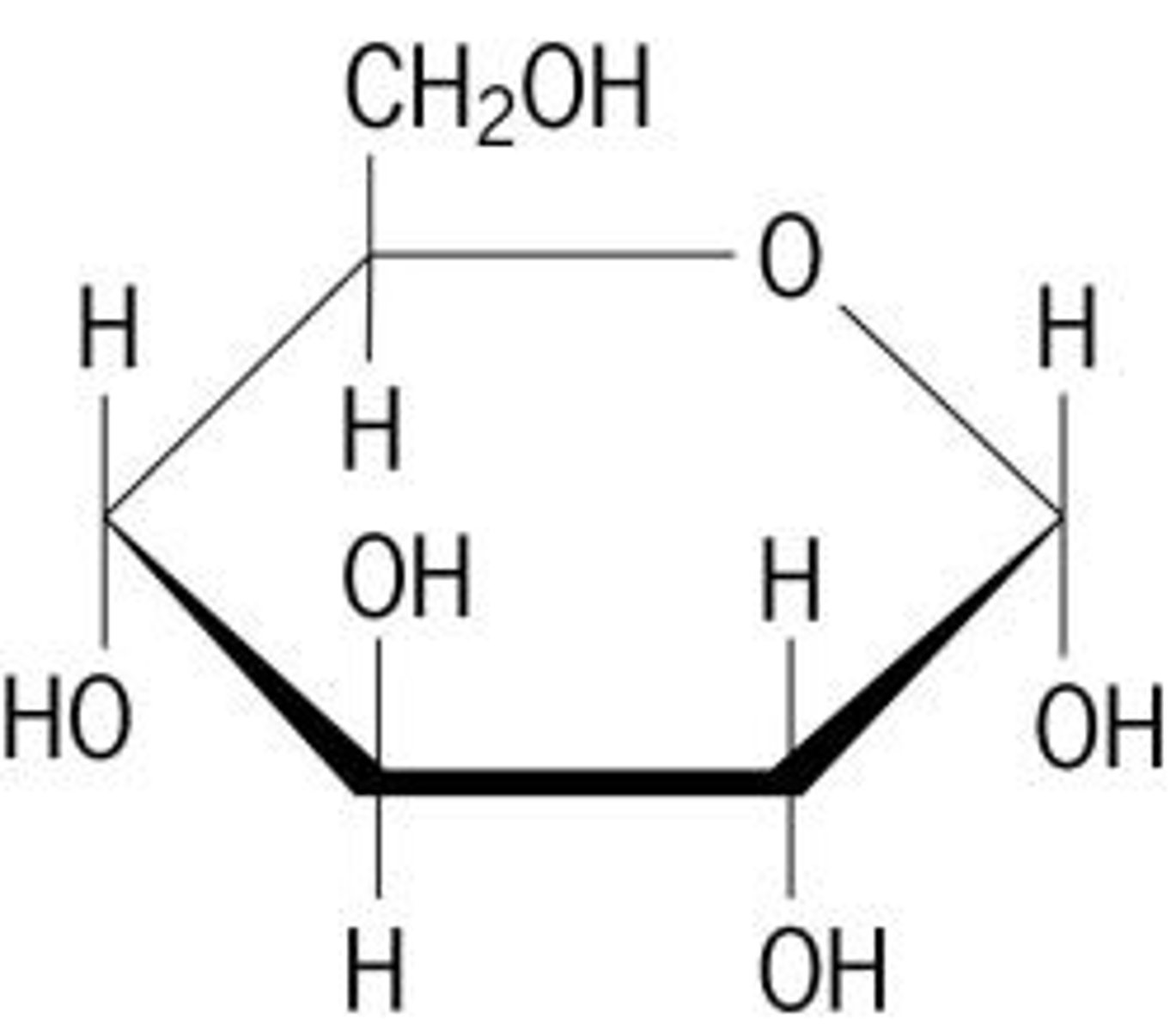
How does this molecule function in cells?
Basic energy or fuel source
(This molecule is converted to ATP so the cell can do work)
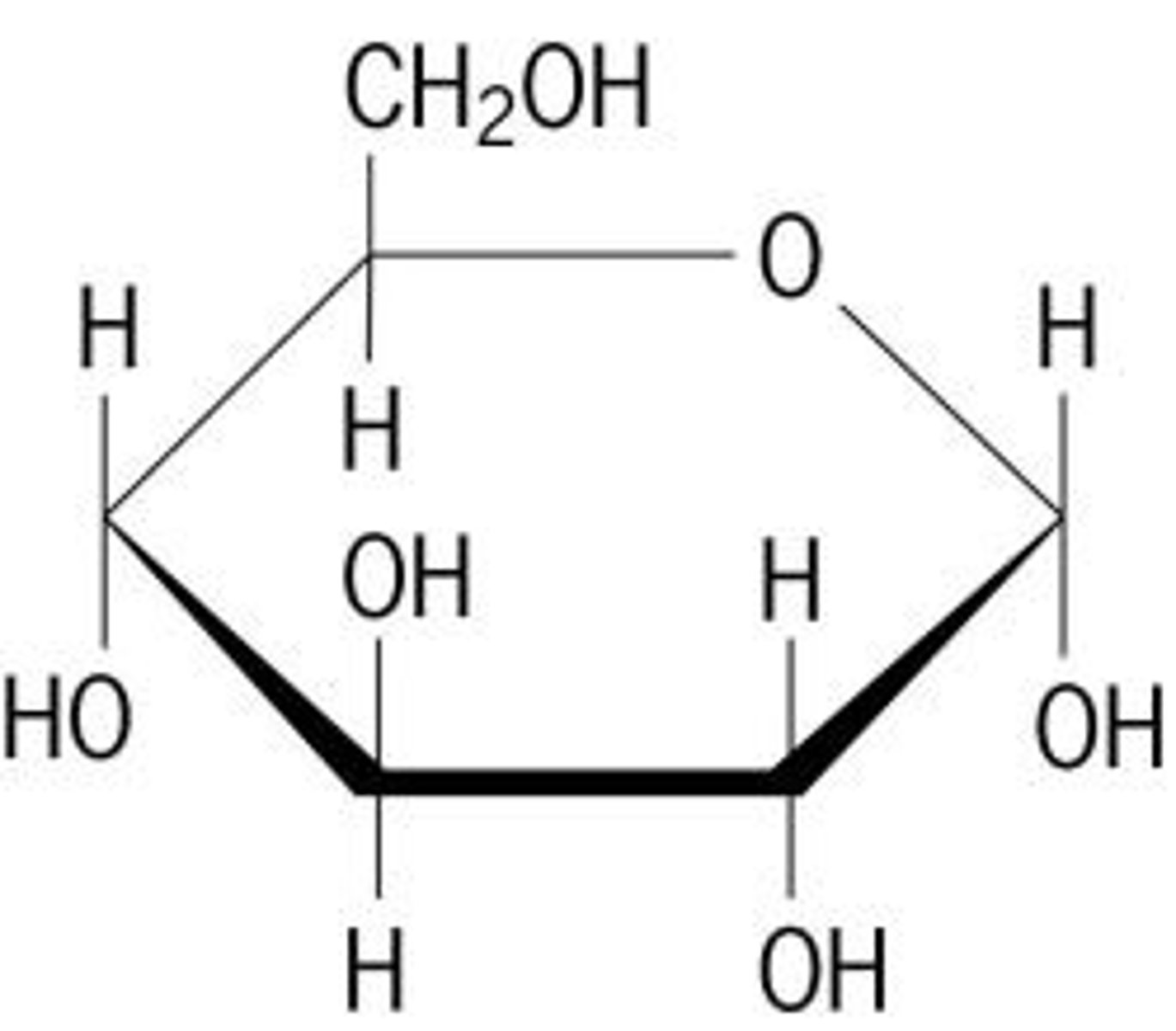
1. Where in the cell is this molecule produced?
2. Where in the cell is this molecule converted to cellular energy or ATP?
1. Chloroplasts (plant cells)
2. Mitochondria (all cells)
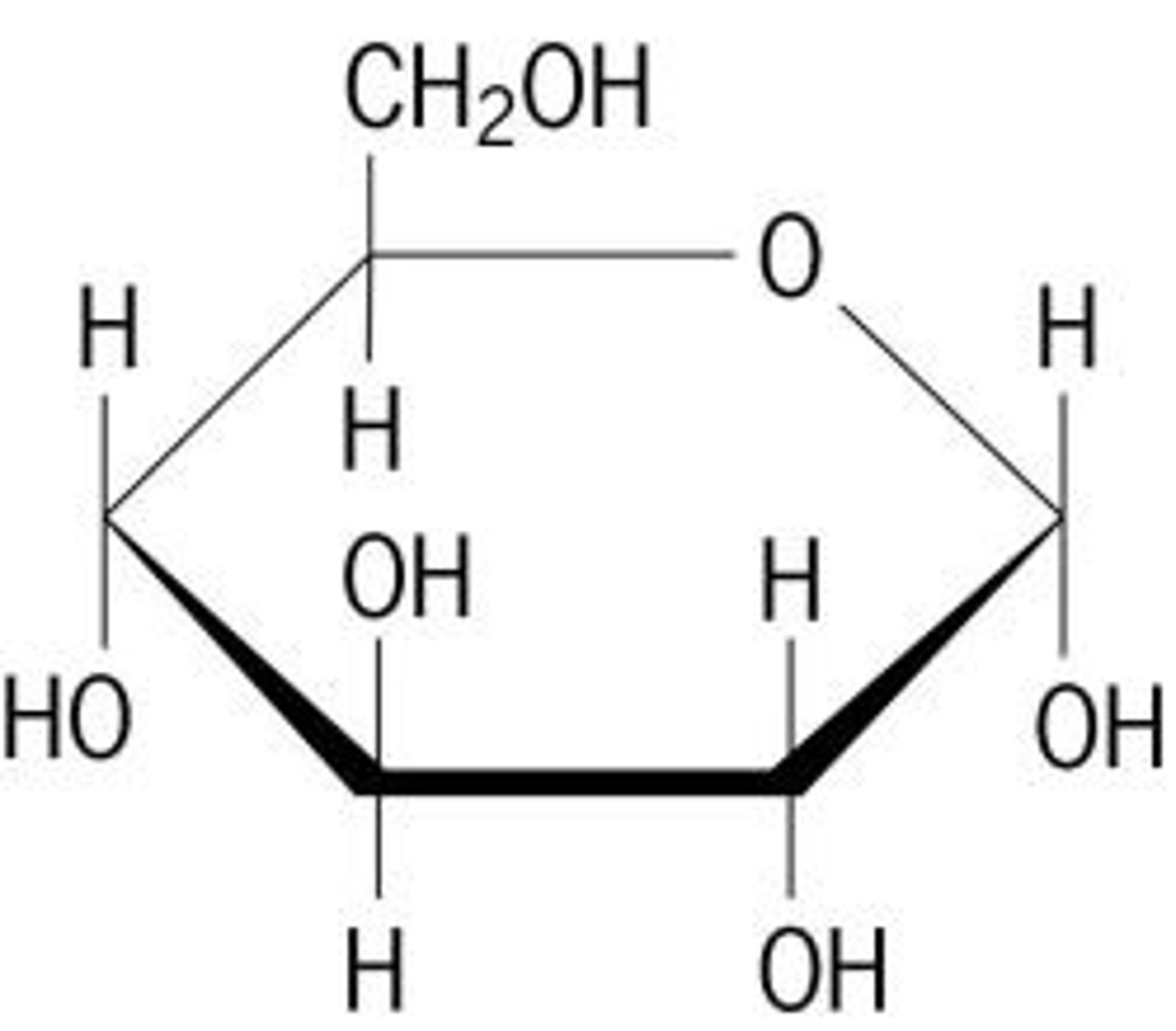
1. What must be removed for two or monomers to join together to make a larger molecule (polymer)?
2. What is this called?
1. Water
2. Dehydration synthesis ("building larger by taking away water")
1. What must be added to a polymer to break it down into smaller pieces?
2. What is this called?
1. Water
2. Hydrolysis ("breaking by adding water"
How do carbohydrates function?
1. Primary energy source (glucose)
2. Structure (cellulose)
3. Short-term storage (starch, glycogen)
Identify this molecule.
Amino Acid
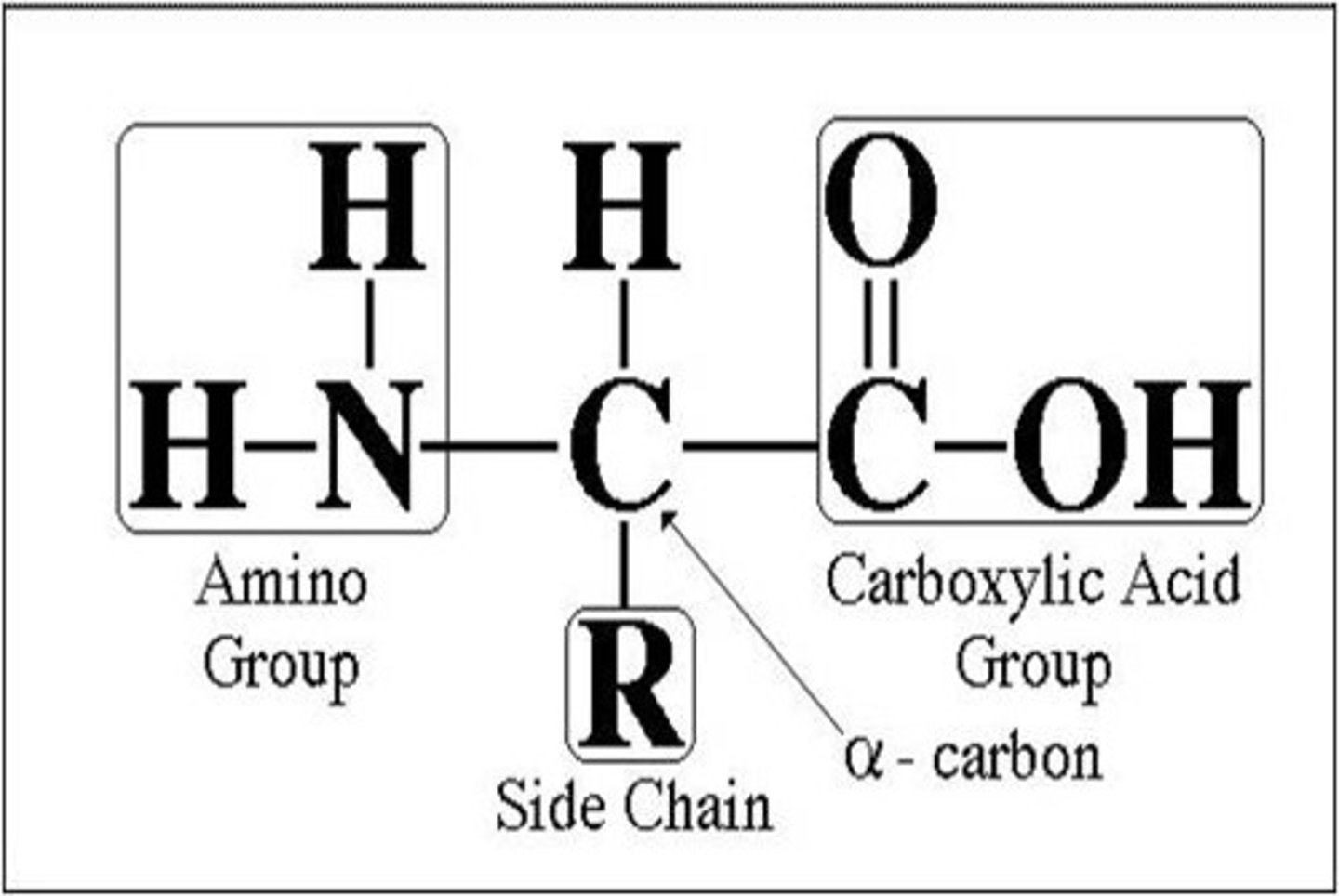
If you put many of these molecules together (by removing water), what larger molecule will they form?
Protein
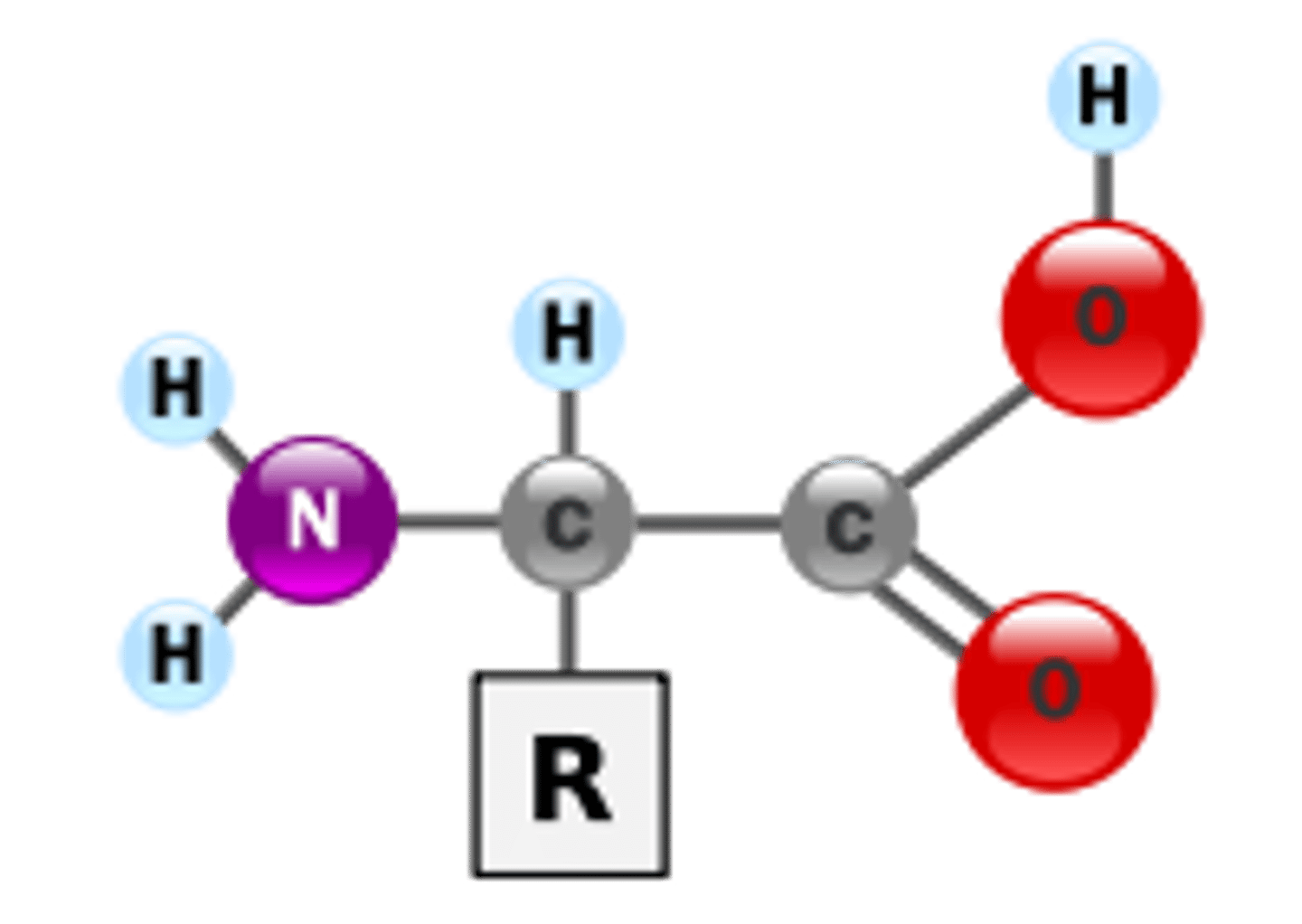
Which group of biomolecules function in building tissues, structure maintenance, and repair?
Protein group
The "meat" you eat (beef, chicken, ham, etc) is actually ___ and therefore, which type of biomolecule?
Muscle; Protein
Proteins that are produced by white blood cells and circulate in your blood stream help to defend your body against foreign invaders. What type of biomolecule are antibodies?
Antibodies
This type of biomolecule is nonpolar; it does not dissolve in water.
Lipid
This lipid has both a polar and non-polar region. It's non-polar regions face the aqueous cytoplasm and extracellular fluid making it an excellent boundary for the cell. This molecule is known as a(n) ___.
Phospholipid
Long-term, back-up energy storage and insulation are the functions of which biomolecule?
Lipids
List 3 types of lipids.
1. Triglycerides (true fats) such as fats, oils, & waxes
2. Phospholipids
3. Steroids
Identify these 2 molecules
Top = Saturated Fatty Acid
Bottom = Unsaturated Fatty Acid
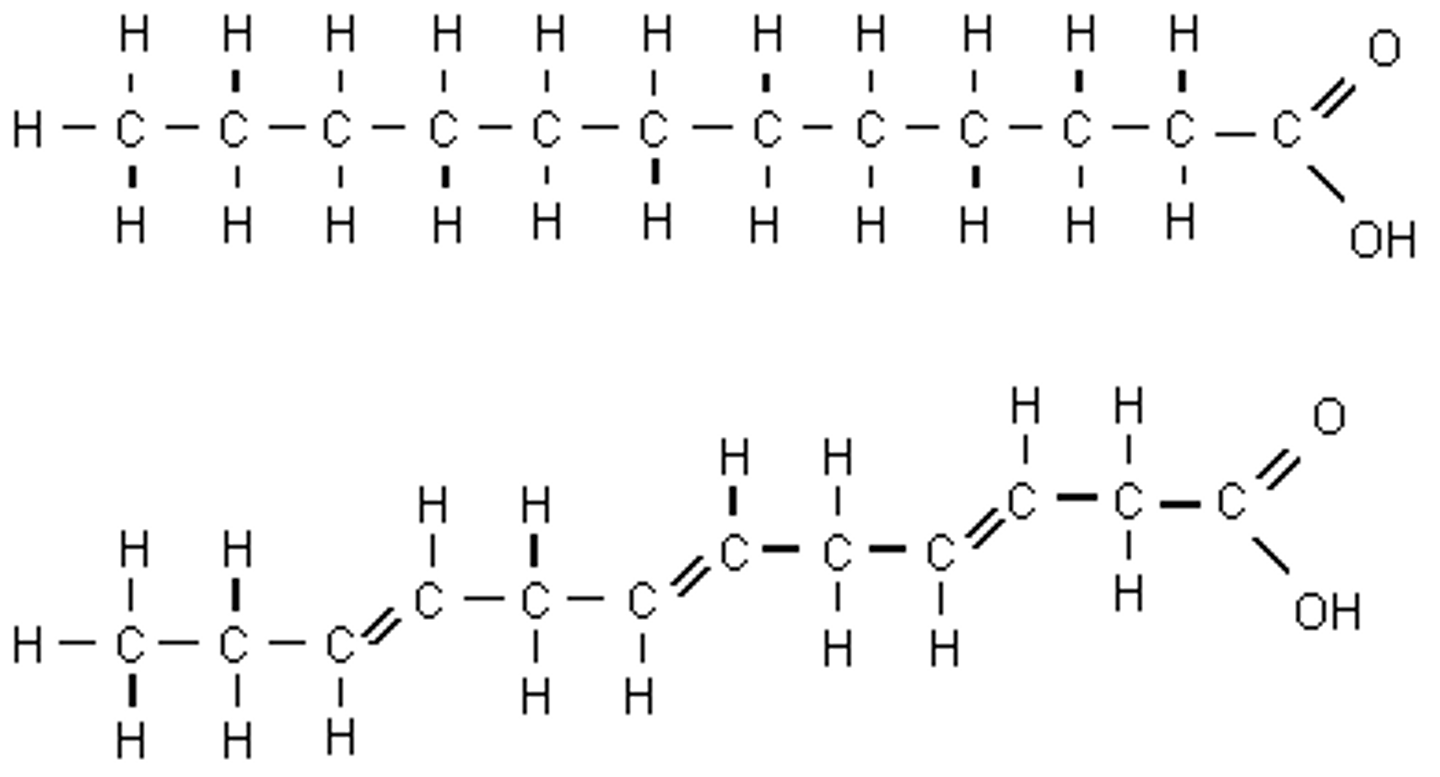
Which of these 2 molecules tends to be liquid at room temperature like a vegetable oil?
Bottom one - unsaturated fatty acid
(*Note - double bonds between some of the carbon atoms)
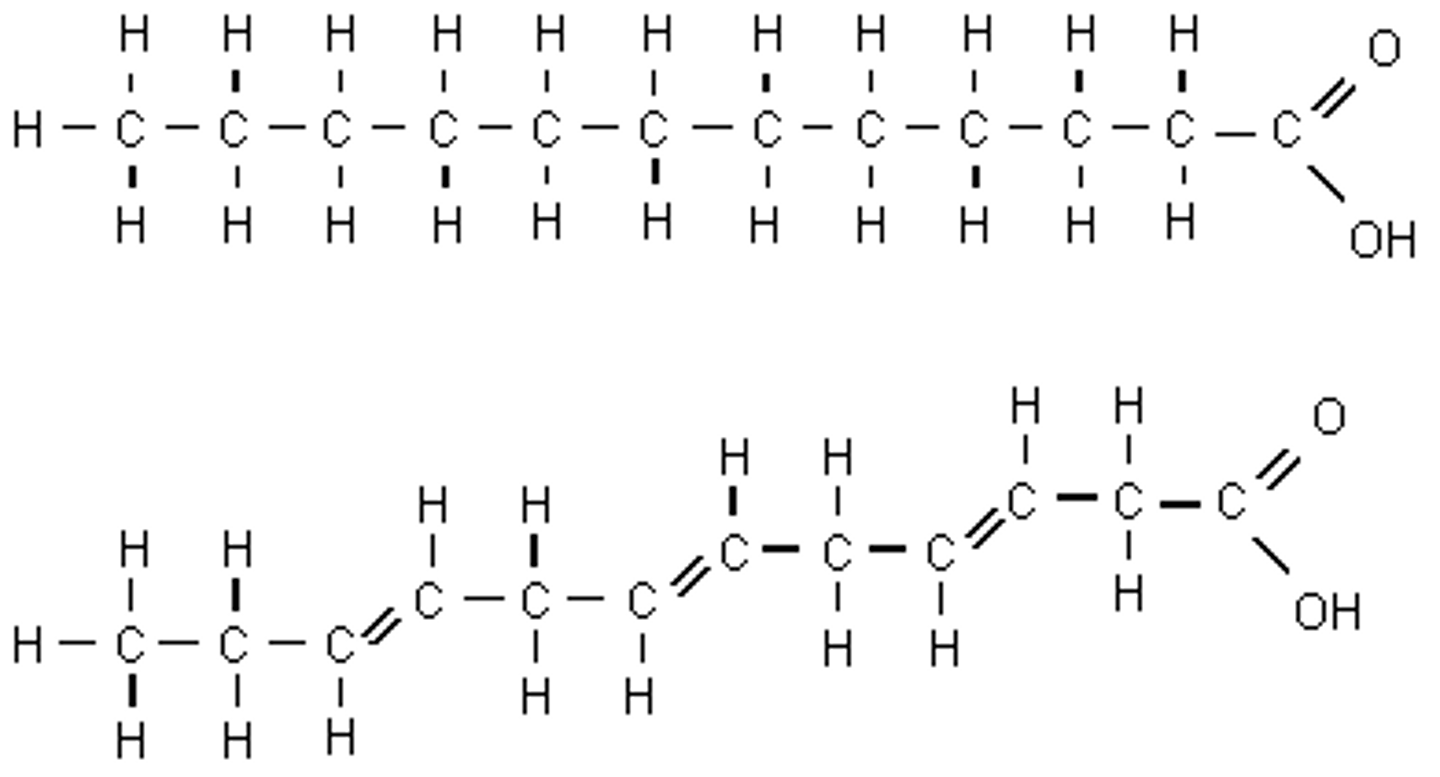
Identify this molecule.
Lipid
(triglyceride= glycerol +fatty acids)
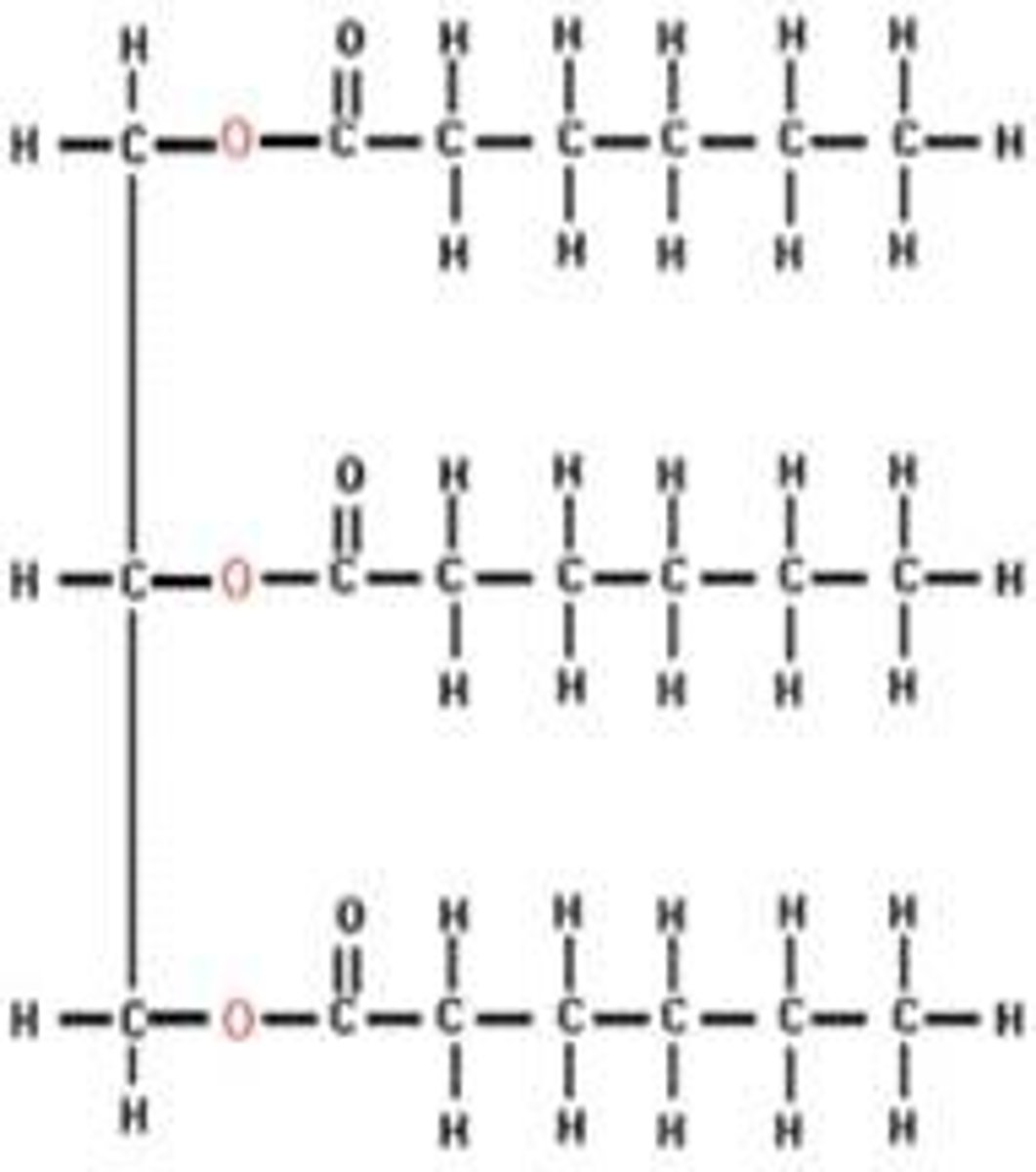
1. Identify
2. Where woud you expect to find this?
1. Phospholipid bilayer
2. Cell membrane
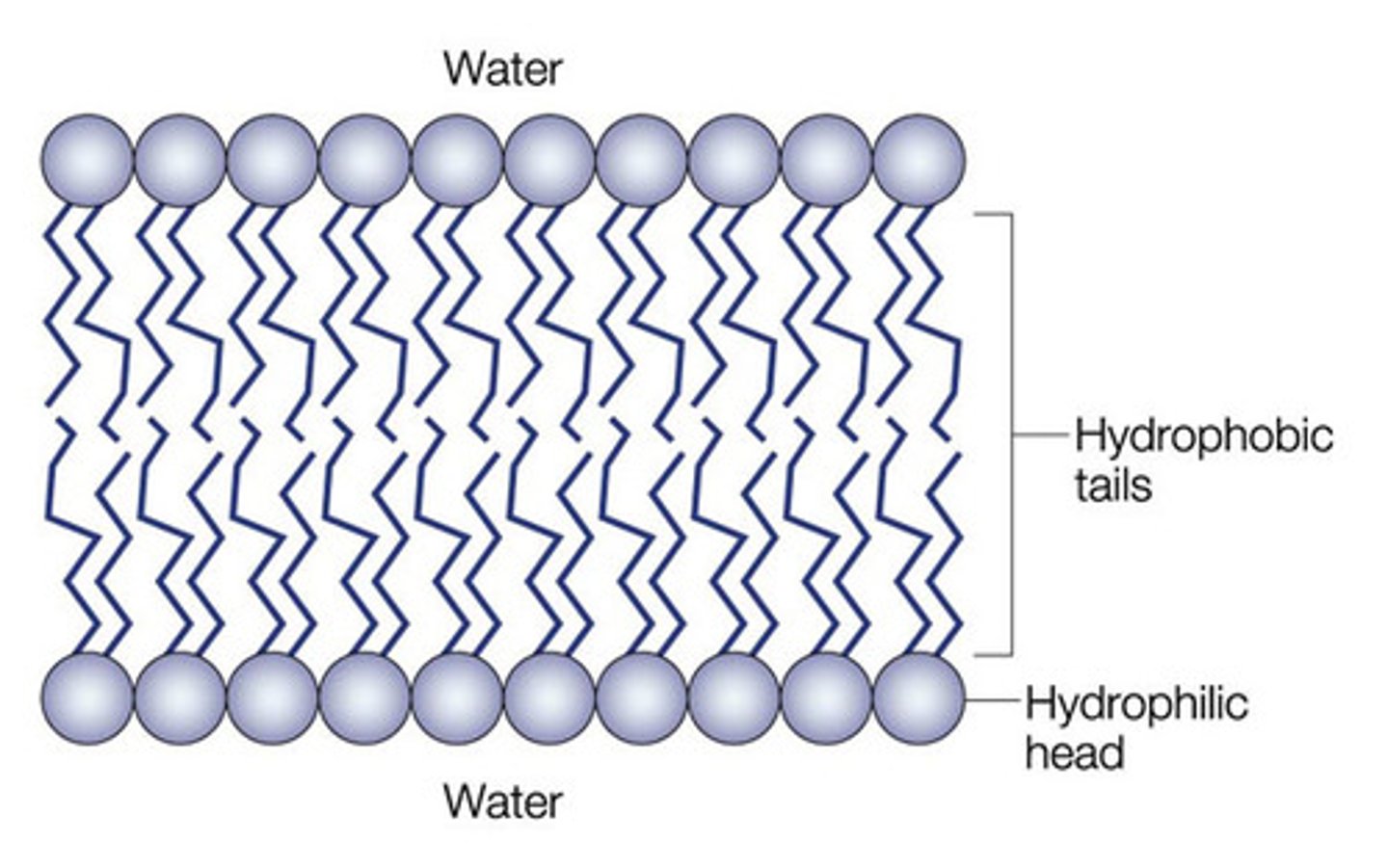
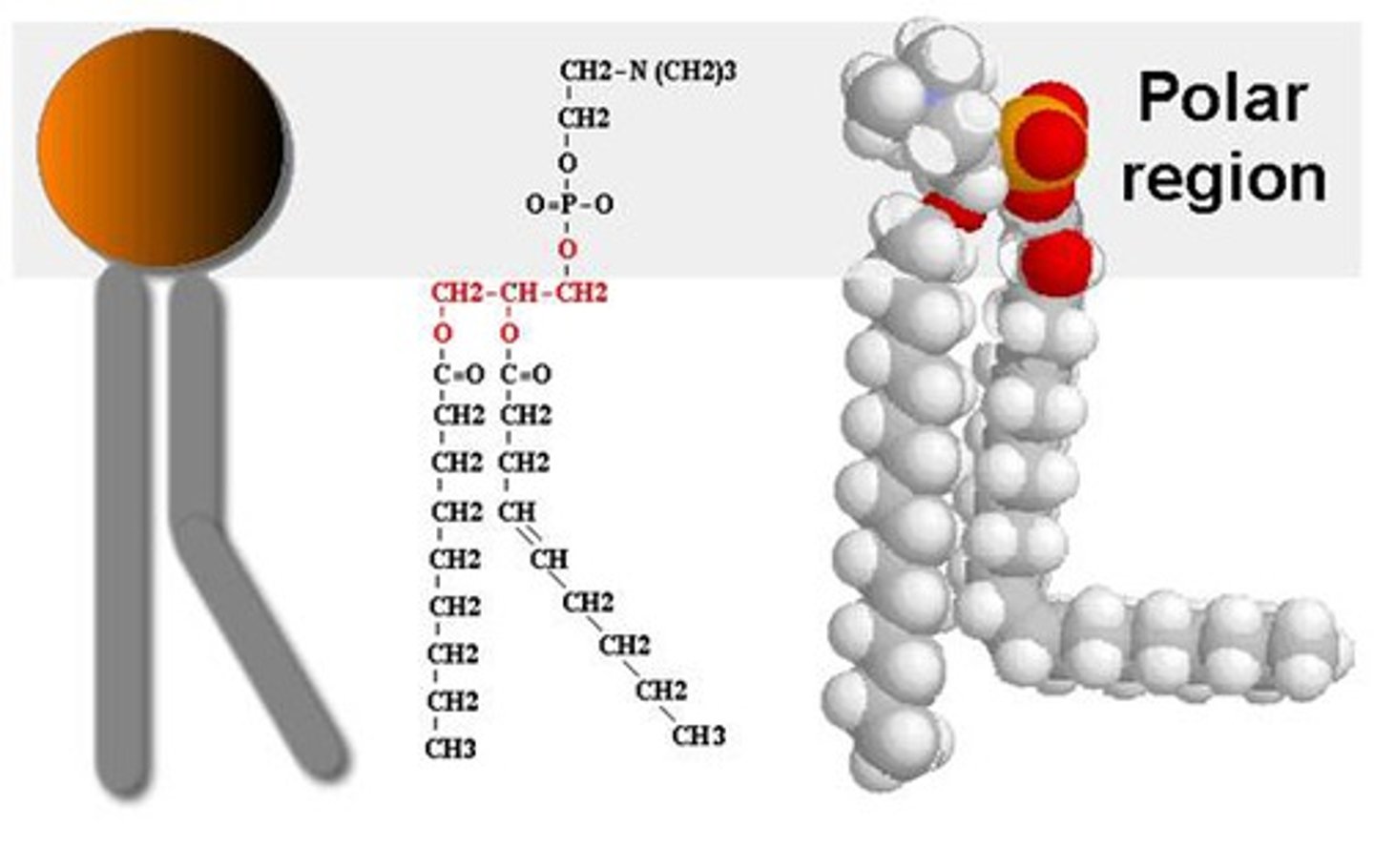
1. Identify this molecule.
2. Where would you expect to find it?
1. Phospholipid
2. Cell membrane (or other membranes) to form bilayer
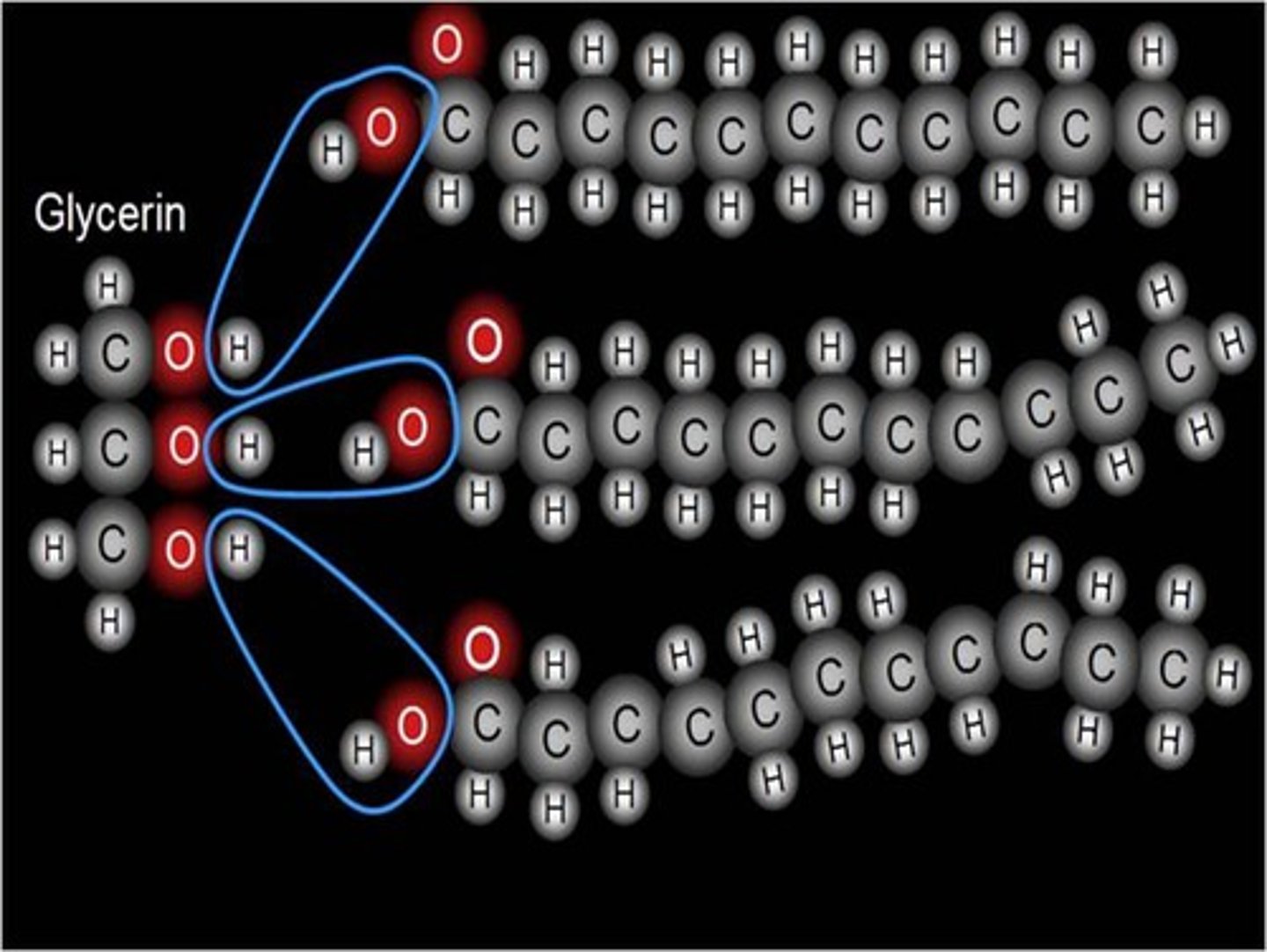
The molecules surrounded by blue circles are removed when this lipid is formed. The process is called_________ ____________.
Dehydration synthesis, a building reaction
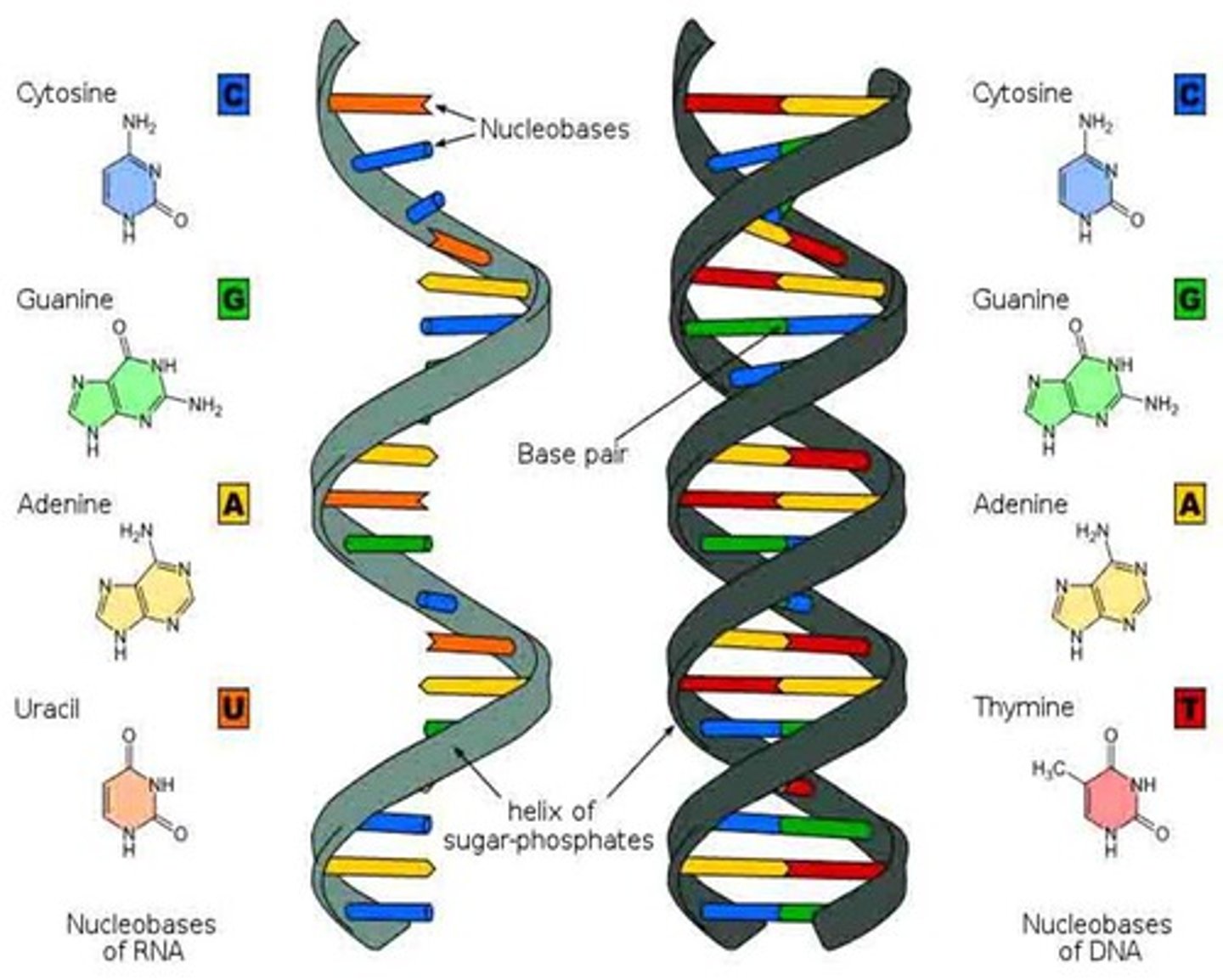
Which molecule is RNA?
The one on the left
(single sided)
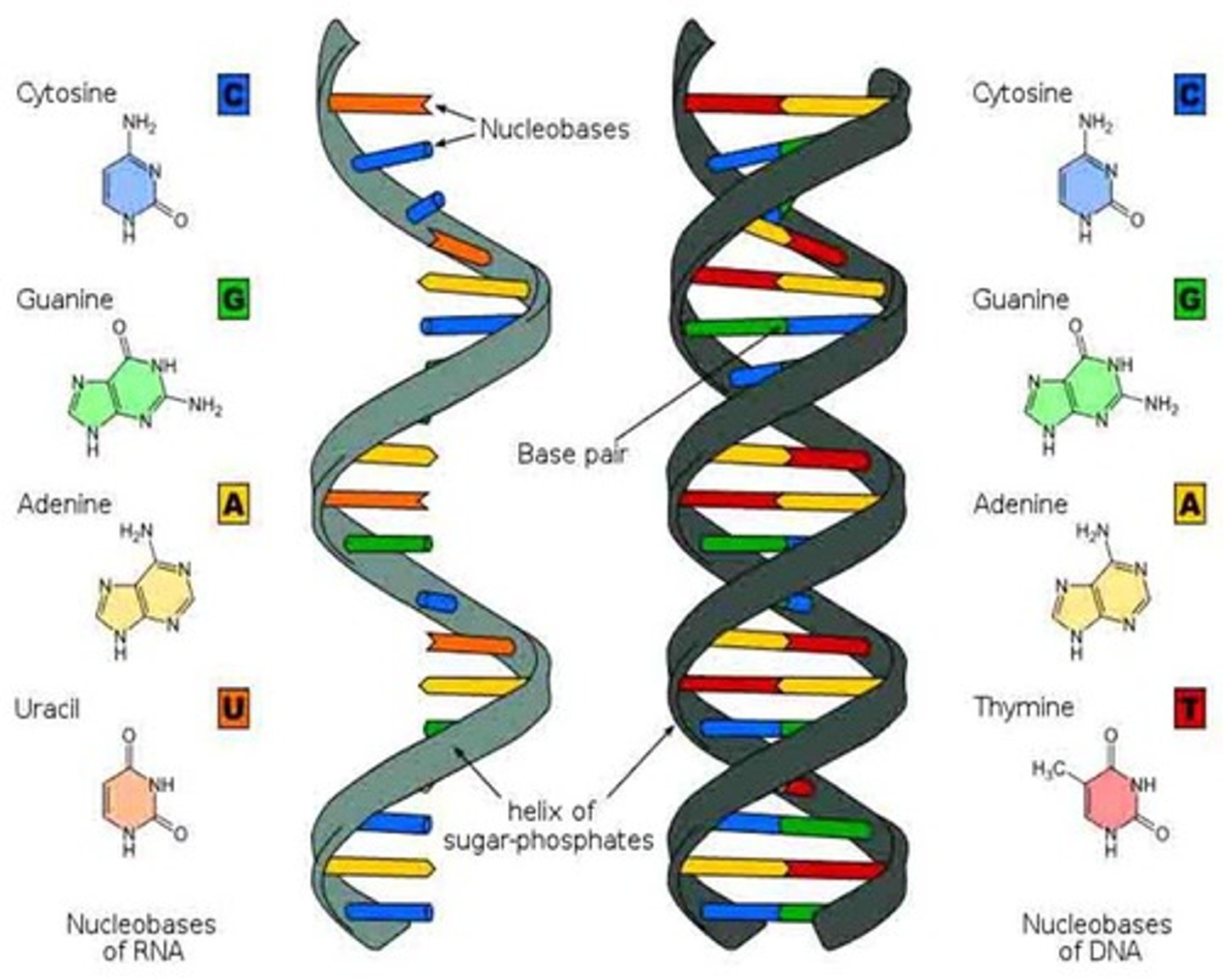
How do you know the molecule on the right is DNA?
1. Double helix
2. Thymine is a nucleotide
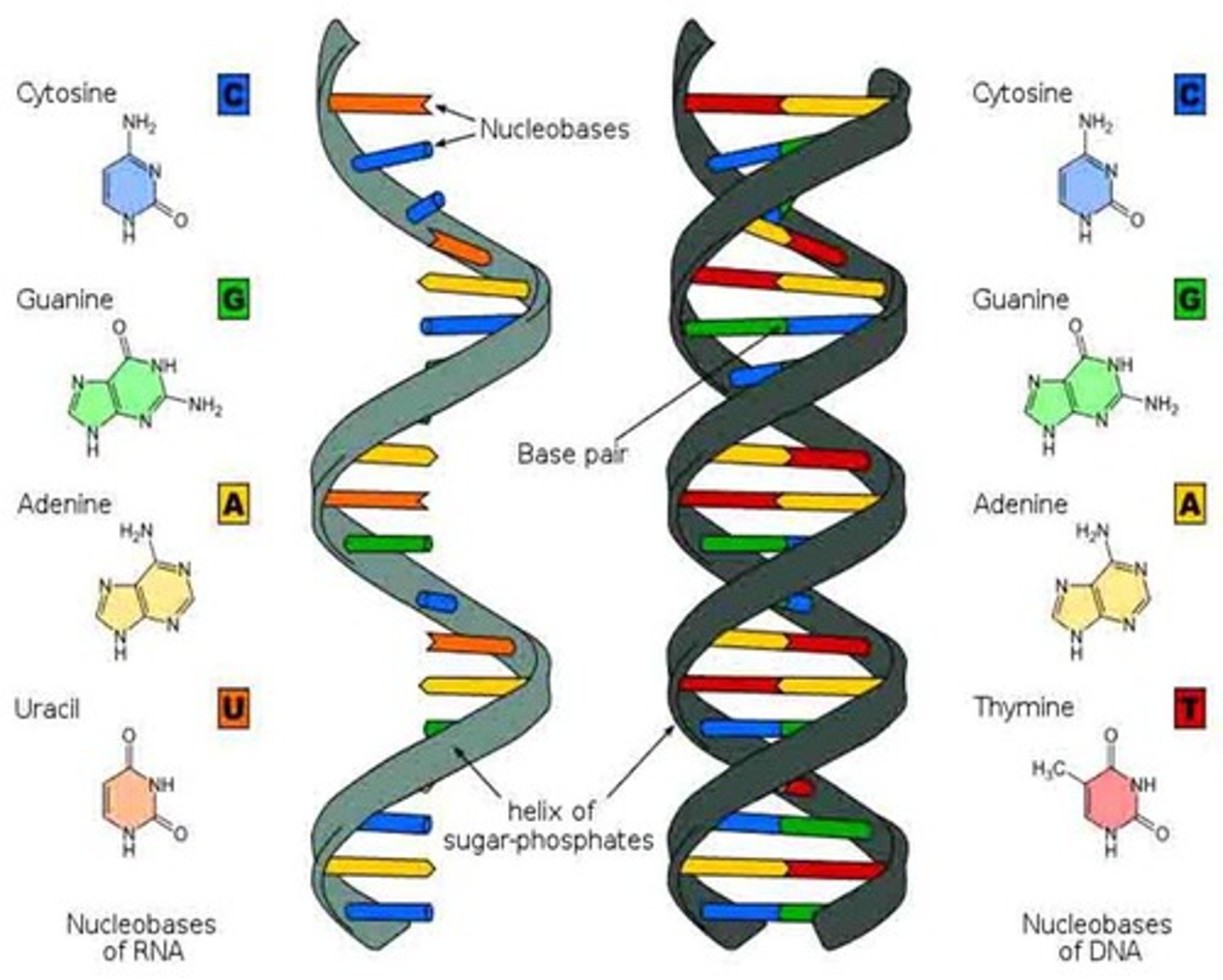
1. What is the sugar in the molecule on the left?
2. What is the sugar in the molecule on the right?
1. Ribose
2. Deoxyribose
These 3 molecules make up a(n) ___ which is a monomer of ___.
nucleotide
nucleic acid
Which nucleic acid functions as the Genetic Code which stores hereditary info?
DNA
Which nucleic acid functions as the instructions for synthesizing proteins?
DNA
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things).
Denature disrupts secondary and tertiary structure, NOT primary structure (peptide bonds)
to make or produce
Synthesis
enzyme
-ase
Polypeptide
Another name for a protein
Peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids to form a protein
Calories per gram for carbs and proteins
4
Calories per gram for lipids
9
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms, humans cannot digest, lack enzymes
Base pairing practice: 5' ATCG 3' of DNA
3' TAGC 5'
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy. Recognize a single stereoisomer (sucrose but not sucralose)