Science Summative - Atoms
5.0(2)Studied by 21 people
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:05 PM on 12/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
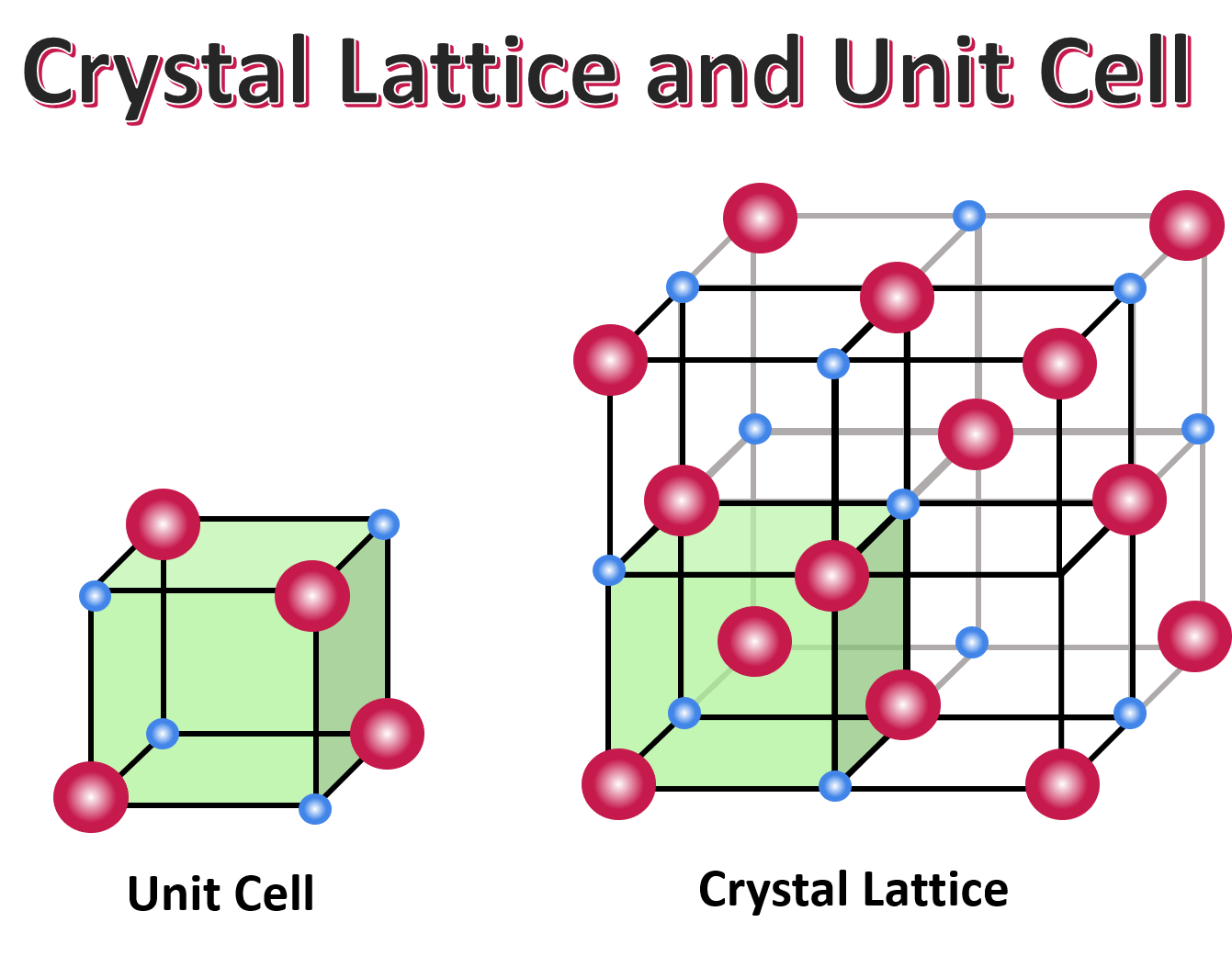
What is a unit cell in a crystal lattice?
The smallest building block of a crystal and the repeating block of a crystal
2
New cards
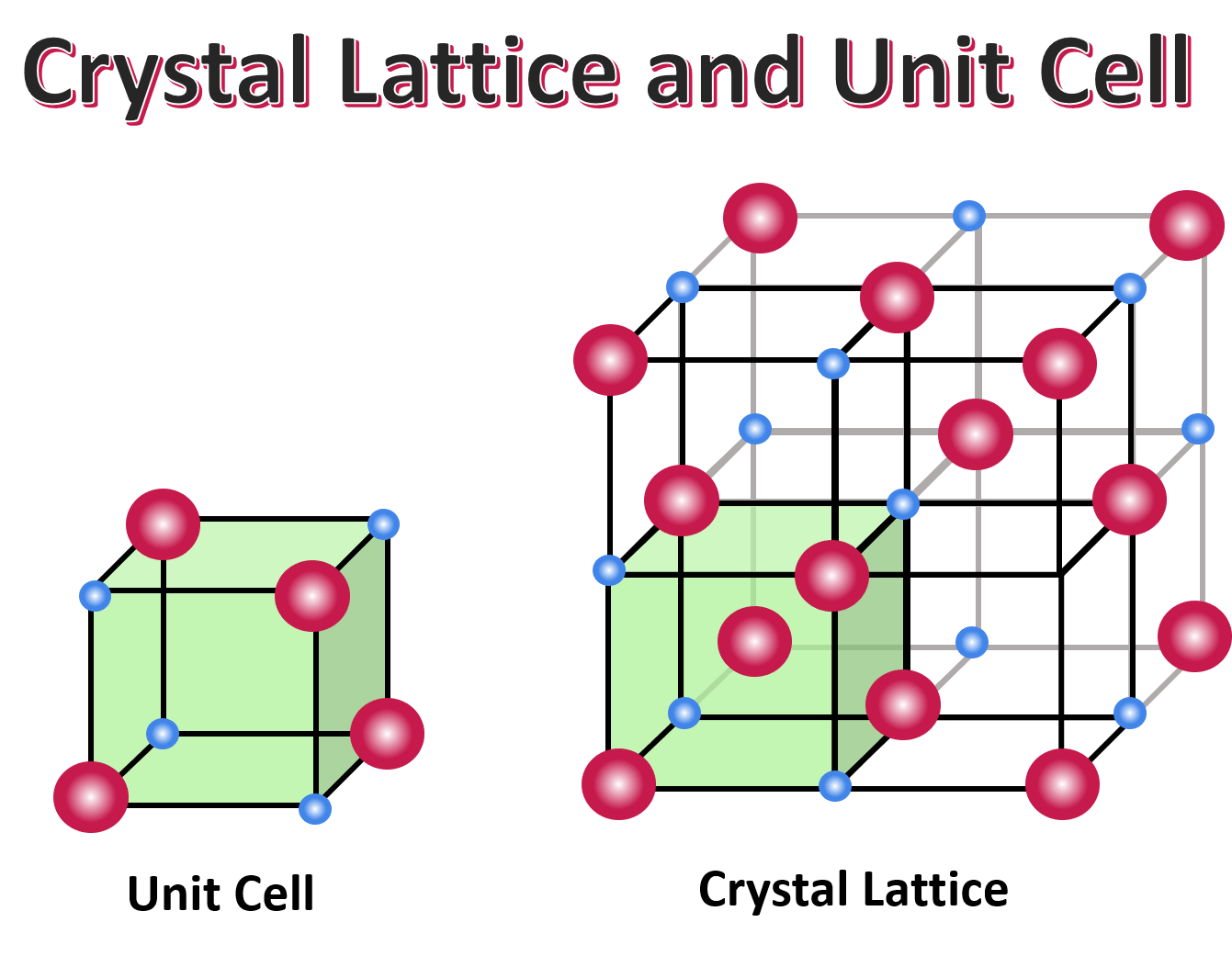
What is a crystal lattice?
The overall shape or structure of a crystal
3
New cards
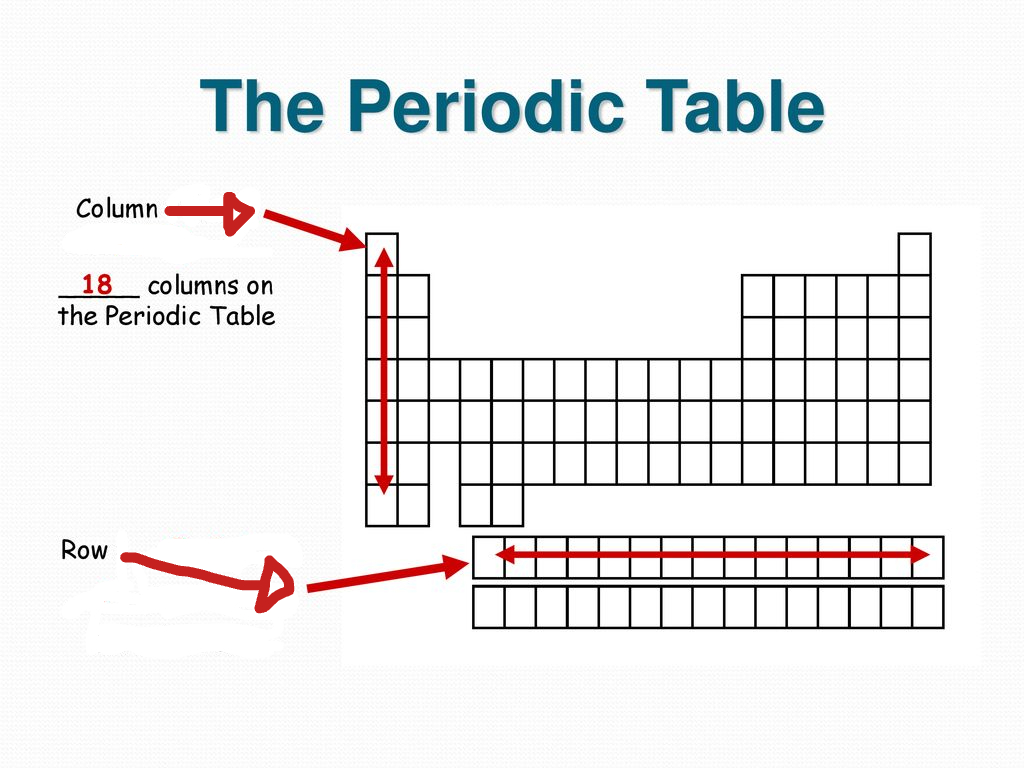
What are columns called in the periodic table?
Groups or families
4
New cards
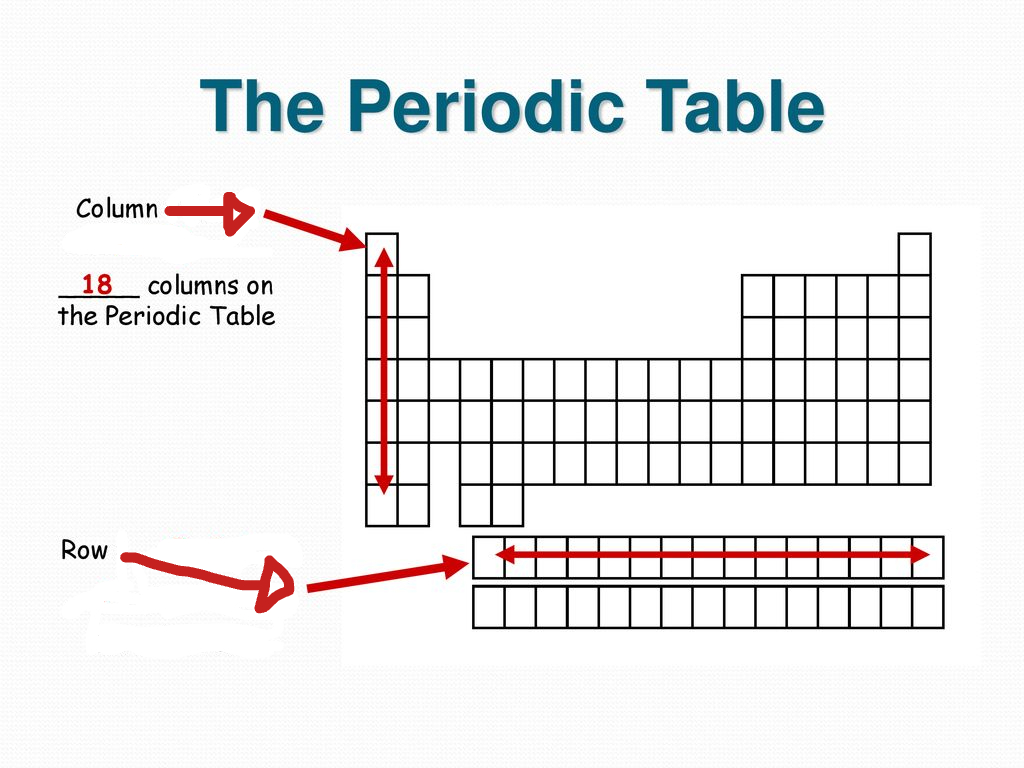
What are rows called in the periodic table?
Periods
5
New cards
How are elements arranged in the periodic table?
in order of increasing atomic number
6
New cards
How are elements placed in groups in the periodic table?
Based on the number of valence electrons.
7
New cards
How can you tell the number of electrons in any atom?
The atomic number
8
New cards
How can you tell the number of valence electrons in any atom?
It is the atoms main group number. Ex: Oxygen is in group 16, it has 6 valence electrons. Calcium is in group 2, it has 2 valence electrons.
9
New cards
Which subatomic particles make up an atom’s mass?
Protons and Neutrons
10
New cards
What are the two main ways how atoms chemically bond?
Ionically and Covalently
11
New cards
Covaliant bond
When only non-metals share electrons
12
New cards
Ionic bond
When metals and non-metals transfer electrons
13
New cards
Why do atoms chemically bond?
To have a full outer shell, or to be stable
14
New cards
Which subatomic particle is responsible for chemical bonding?
Electrons
15
New cards
Where are protons located?
The nucleus
16
New cards
Where are neutrons located?
The Nucleus
17
New cards
Where are electrons located?
The electron cloud
18
New cards
Why are elements in groups 18 non-reactive?
They all have full outer shells
19
New cards
What are the three subatomic particles that make up an atom?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
20
New cards
What charge does a proton have?
Positive
21
New cards
What charge does a neutron have?
No charge
22
New cards
What charge does an electron have?
Negative
23
New cards
What is the mass of a proton?
1 amu (atomic mass unit)
24
New cards
What is the mass of a neutron?
1 amu (atomic mass unit)
25
New cards
What is the mass of a electron?
0 amu (atomic mass unit)
26
New cards
How does the term “opposites attract” apply to ionic bonding?
Atoms give away electrons in ionic bonding. One atom becomes positive (more protons) and the other negative (more electrons). The opposites need to attract to complete the compound.
27
New cards
What does the dark staircase line do?
Separates metals from non-metals
28
New cards
Where are metals located on the periodic table?
On the left
29
New cards
Where are non-metals located on the periodic table?
On the right
30
New cards

What is the ratio of apples to oranges?
6:3
31
New cards

What is the ratio of pears to apples and oranges?
3:9
32
New cards
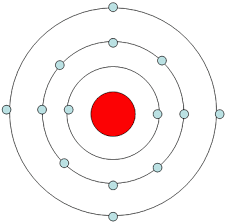
How many valence electrons are in this atom represented by a bohr model?
4
33
New cards
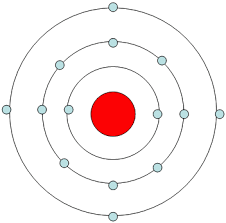
How many protons are in this atom represented by a bohr model?
14
34
New cards

What is the arrow pointing to?
The atomic number
35
New cards
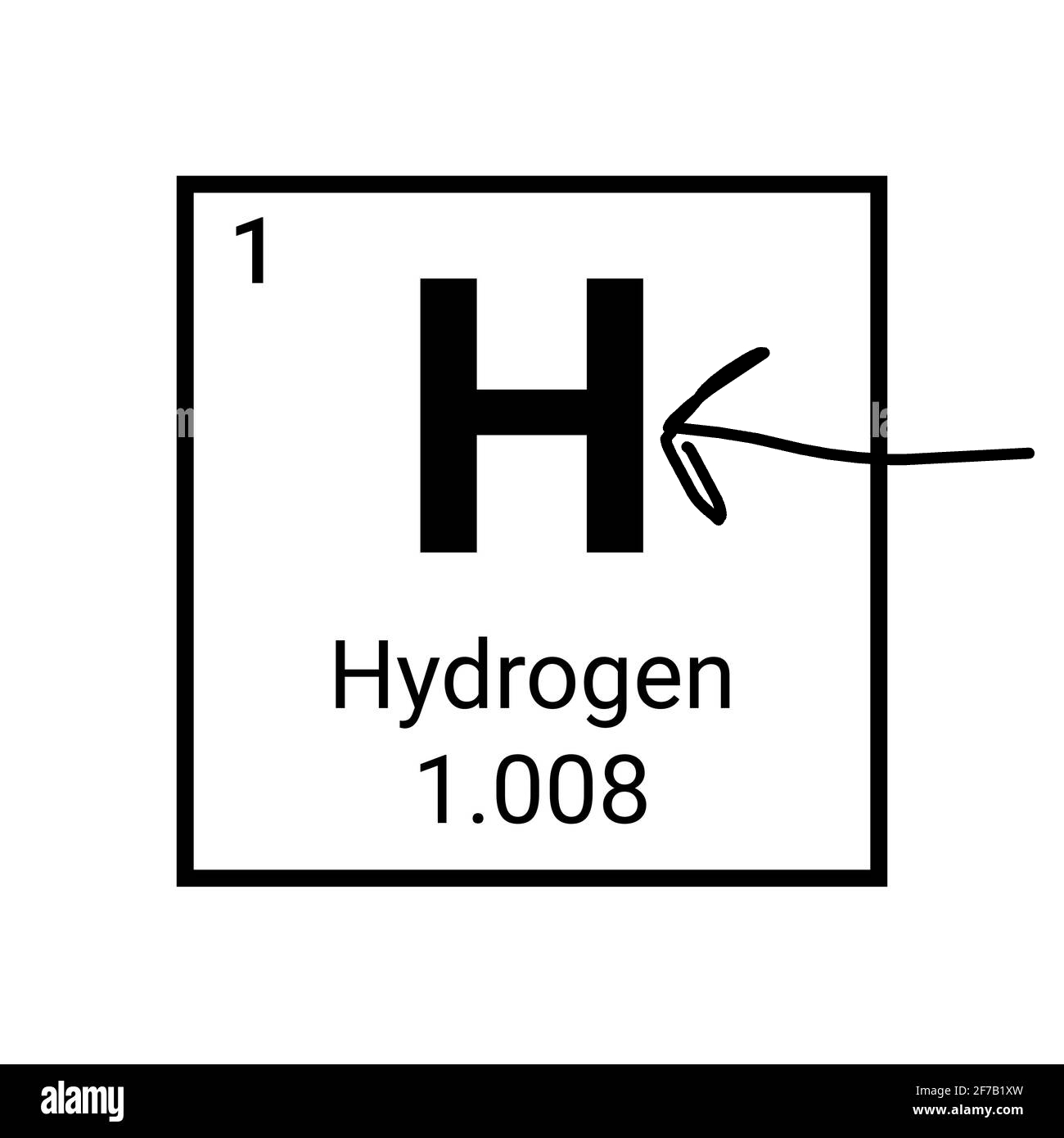
What is the arrow pointing to?
The element symbol
36
New cards
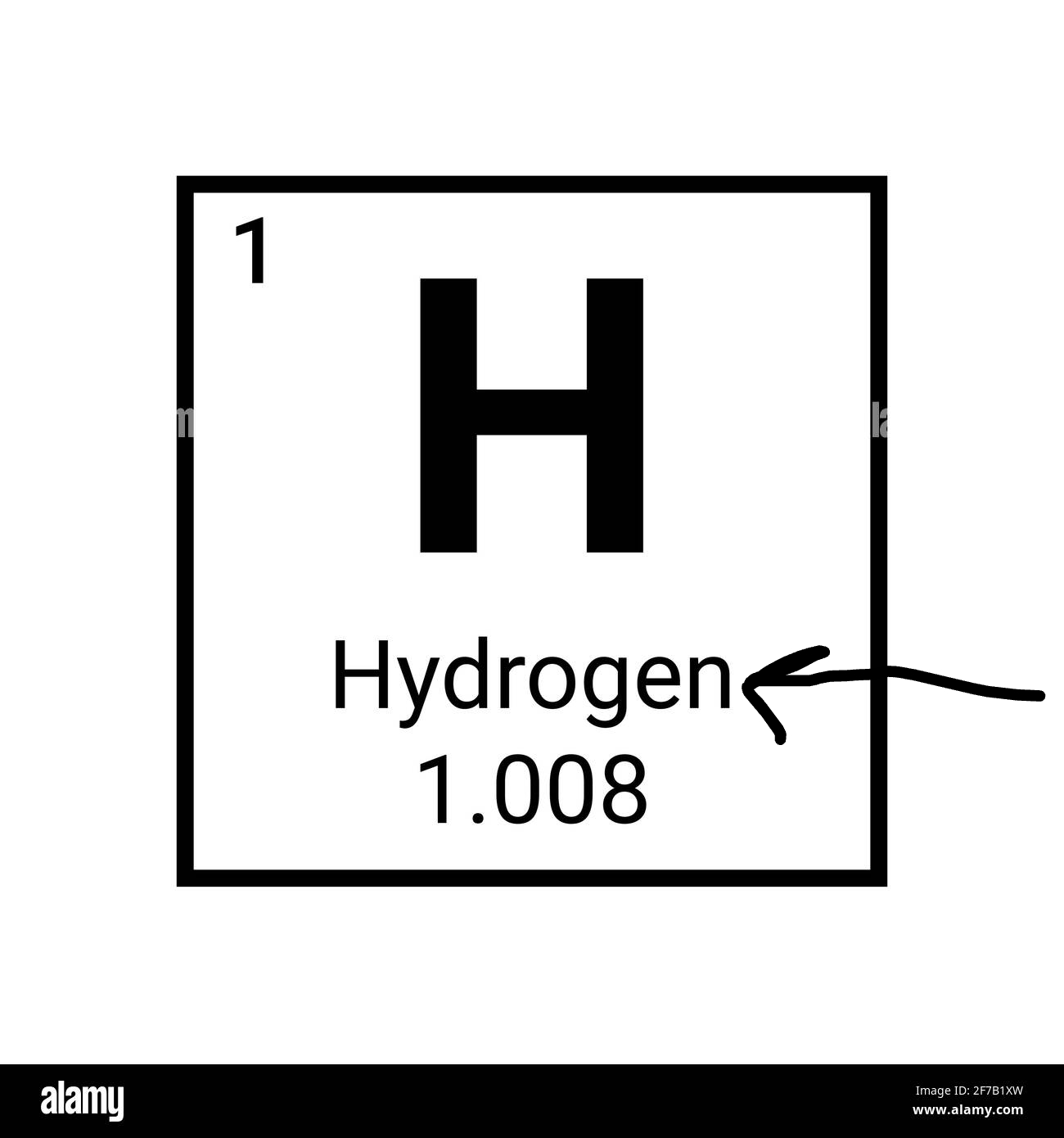
What is the arrow pointing to?
The element name
37
New cards
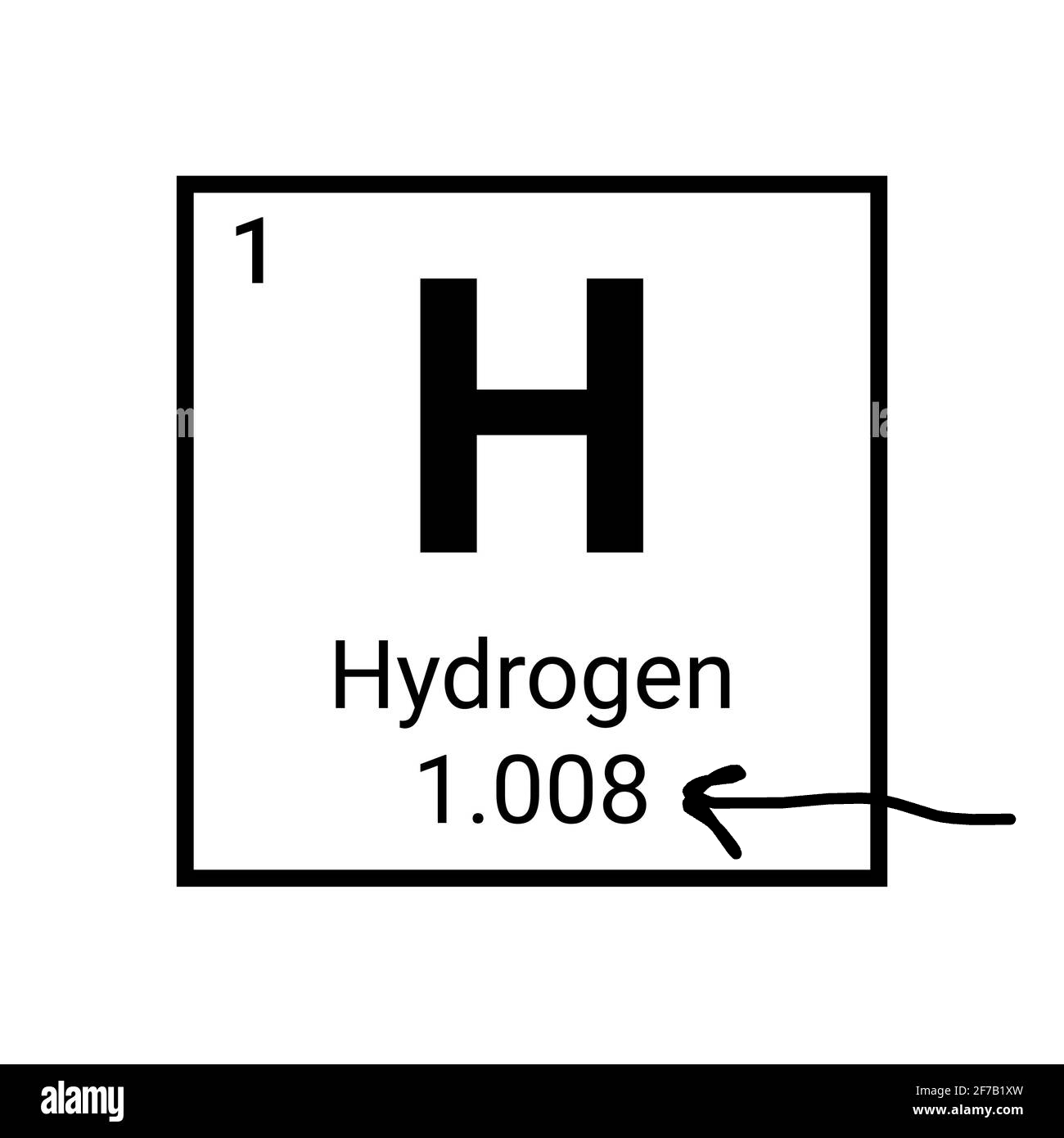
What is the arrow pointing to?
The atomic mass
38
New cards

What kind of bond is this?
A single bond
39
New cards
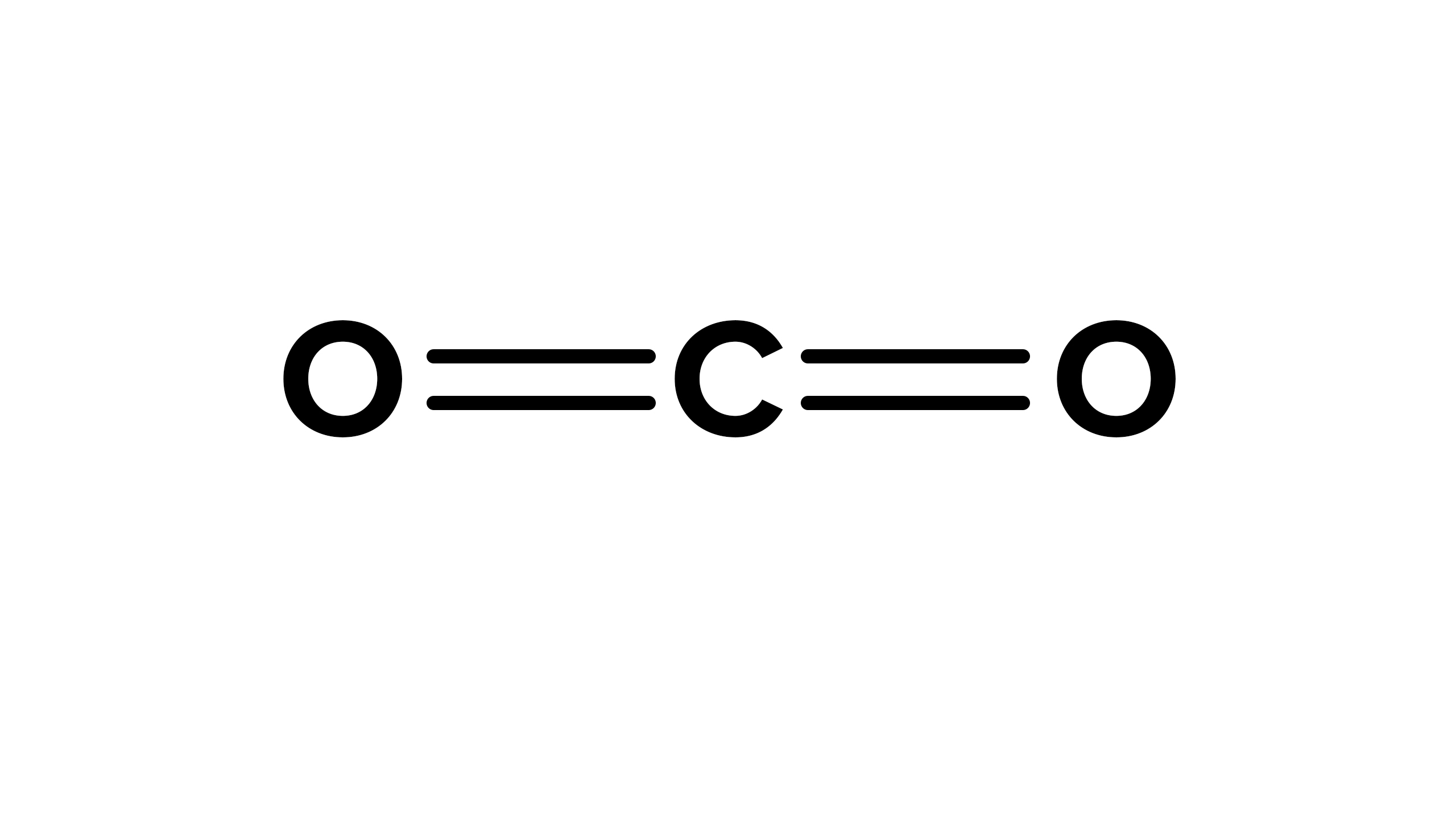
What kind of bond is this?
A double bond
40
New cards
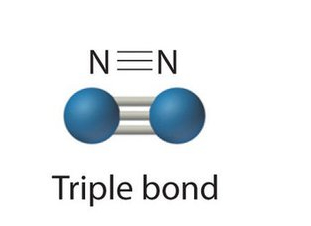
What kind of bond is this?
A triple bond
41
New cards
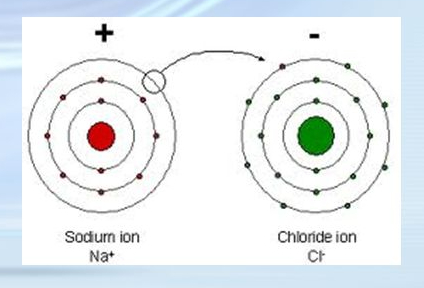
What kind of chemical bond is this?
Ionic
42
New cards
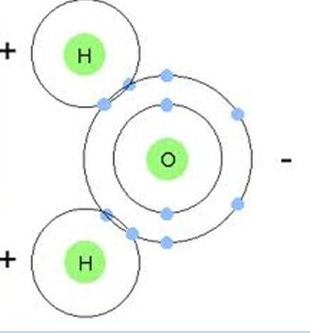
What kind of chemical bond is this?
Covalent
43
New cards

How many valence electrons are in the elements shown by this dot diagram?
3
44
New cards
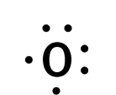
How many valence electrons are in the elements shown by this dot diagram?
6