Business theme 2
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What is organic growth in a business?
Organic growth is internal. It occurs when a business expands by itself by bringing out new products or entering new markets.
What is inorganic growth in a business?
Inorganic growth is external. Growing externally is when a business joins forces with another.
A merger
Where two or more businesses voluntarily agree to join up and work as one business.
A takeover
Where one business buys another and gaining control through buying shares.
What are the methods of organic growth?
Entering new markets, creating new products and developing new technology.
What is a public limited company (PLC)
They are able to raise capital through selling shares on a stock exchange which can be bought and sold by anyone.
Stock exchange
A place where shares in a company or business enterprise are bought and sold.
What is flotation?
Flotation is the process of converting a private company into a public company by issuing shares available for the public.
What are some disadvantages of becoming a PLC?
-More complex accounting and reporting procedures.
-Risk of a potential takeover.
-Increased public and media attention.
-Less privacy around financial performance.
-Greater influence on decision making by external share holders.
What are some advantages of becoming a PLC?
-Ability to raise finance through share capital.
-Limited liability.
-Considered more prestigious and reliable.
-May be able to negotiate better prices with suppliers.
-Greater public awareness of business.
Sale of assets
When a business sells off its unwanted or unused assets to raise funds but the business loses the benefit of owning the assets it sells.
Retained profit
The profit left after all deductions, including dividends, have been made. However profit is not guaranteed.
A dividend
A sum of money paid regularly (typically annually) by a company to its shareholders out of its profits.
Loan capital
Money sourced from financial institutions such as banks, with interest charged on the loan to be repaid.
Share capital
Refers to the funds that a company raises in exchange for issuing an ownership interest in the company in the form of shares. It can put a PLC at risk of being taken over and all share holders are entitled to a share of the profits.
Legislation
The act of making or enacting laws. It can force a business to change its products/services which restricts the businesses operations and opportunities.
Globalisation
Businesses operate internationally and become increasingly interconnected.
How does globalisation affect imports?
Globalisation allows raw products and materials to be imported at lower prices than they would be able to produce in the UK. However importing increases competition from foreign business that sell directly to UK customers.
How does globalisation affect exports?
It opens up new international markets (potential to grow). However international markets are different to operating in the UK which causes problems. They may lack knowledge.
How does globalisation affect location?
It brings opportunities to relocate operations to other countries, lowering labour costs.
Multinationals
Large corporations that have operations in several countries.
Tariffs
A tax on imported goods.
Trade blocs
Created when governments of different countries agree to act together to promote trade among themselves. e.g NAFTA and ASEAN
Subsides
Money given to businesses by the government.
Quotas
Physical limits on imports.
Why are trade barriers imposed?
Protect jobs in domestic industries, protect emerging industries, preventing entry of undesirable goods and raising revenue from tariffs
E-commerce
Enables businesses to access international markets online and they can trade 24 hours a day, also promoting themselves through social media sites.
Trade off
The act of giving up one benefit in order to gain another, greater benefit.
Pressure groups
Organisations that try to make business change their behaviour or operations. They focus on issues like animal rights and workers rights. They can cause bad publicity for business.
How can businesses reduce their impact on the environment?
Recycling, renewable energy, biodegradable packaging, reducing food miles and conserving natural resources.
What is the design mix?
Function, cost and appearance. This can differentiate it from other products.
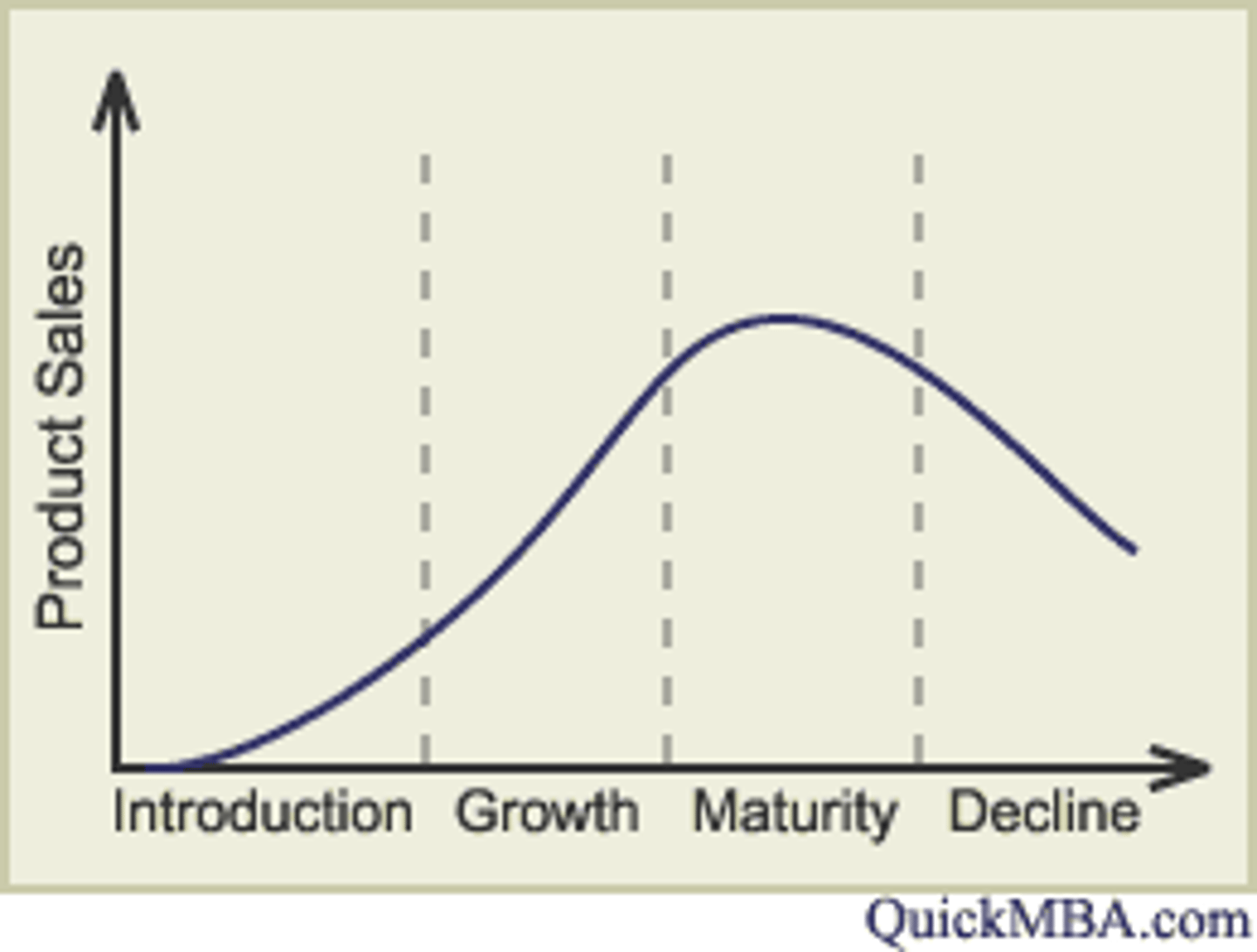
The product life cycle
Intro - product released onto market.
Growth - product is successful, sales increase sharply.
Maturity - sales growth slows, customer loyalty, rivals bring competing products.
Decline - product becomes outdated and sales fall.
Extension strategies
Involves slightly changing the product so it has a fresh appeal to the target market or appeals to a new market segment.
Skimming price
Setting a high price before other competitors come into the market and then lowering the price.
Penetration pricing
Setting a very low price to gain as many sales and then increasing the price once customer loyalty is achieved.
Competitor pricing
Setting a price for a product based on what rival companies are charging for theirs.
Promotional pricing
Temporarily pricing products below the list price to increase short-run sales.
.
Cost plus pricing
Setting a price by adding a fixed amount or percentage to the cost of making a product.
Loss Leader Pricing Strategy
When a business aims to sell high volumes of a product but willing to make a loss.
.
A margin strategy
Involves setting a price that achieves a high profit margin.
A volume strategy
Involves setting a price with a low profit margin, which requires high sales volume in order to be profitable.
Branding
The promotion of a product or service by identifying it with distinct characteristics (usually associated with public perception, quality or effectiveness).
Benefits of sponsorship
Lots of exposure, associated with a good cause.
Benefits of product trials
Encourages customers to use a new product or service they might not usually use.
Benefits of developing a strong brand
Customer instantly recognises brand, positive characteristics associated with brand, customer loyalty, trusting a strong brand, can charge premium prices.
Technology in promotion
Social media, Apps, Targeted advertising and emails. Businesses can reach a wider variety of customers at a lower cost.
Benefits of retailing
Customers have opportunity to browse and try products, help and advice can be provided to customers, point of sale promotion and customers enjoy retail stores.
Etailing
The selling of retail goods on the Internet
Benefits of etailing
Business dont have to rent or own retail space, customers can buy at any time, customers can be accessed all over the world and small business are able to compete.
Job production
Producing a one-off item specially designed for the customer.
Batch production
A manufacturing operation that produces goods in large batches in standard lot sizes.
Flow production
Large-scale production of a standard product, where each operation on a unit is performed continuously one after the other, usually on a production line
Advantages of job production
- Higher prices can be charged as the product is unique and made to customer requirements.
- Products can match exact requirements, which increases customer satisfaction.
- Employees are more motivated as each project is different.
- The business can gain a competitive edge by offering unique products.
Disadvantages of job production
- High wages need to be paid to the highly skilled staff required.
- High costs can push up the price, making it too high, putting customers off who are looking for value for money.
- Expensive tools and machinery may be required, which often lie idle during different jobs
- Lead times can be lengthy meaning customers cannot walk in and purchase the product.
- Materials may need to be ordered for each different job, so the business misses out on bulk buying discounts.
Advantages of batch production
- Batches can be adapted to meet customer requirements.
- Quicker and easier.
- Machinery can be standardised, saving on costs.
- Less need for highly skilled workers so wage costs are lower.
- Materials can be bought in bulk so discounts can be obtained.
Disadvantages of batch production
- If a mistake is used it can ruin an entire batch.
- Employees are demotivated as the tasks are repetitive.
- Small batches can raise the unit cost of each item in the batch.
- High stock levels are required, so overstocking can occur.
- loss of quality.
Productivity
The output per worker. It measures how much each worker produces over time.
Economies of scale
Describes the situation where the average costs of production fall as the volume of production increases.
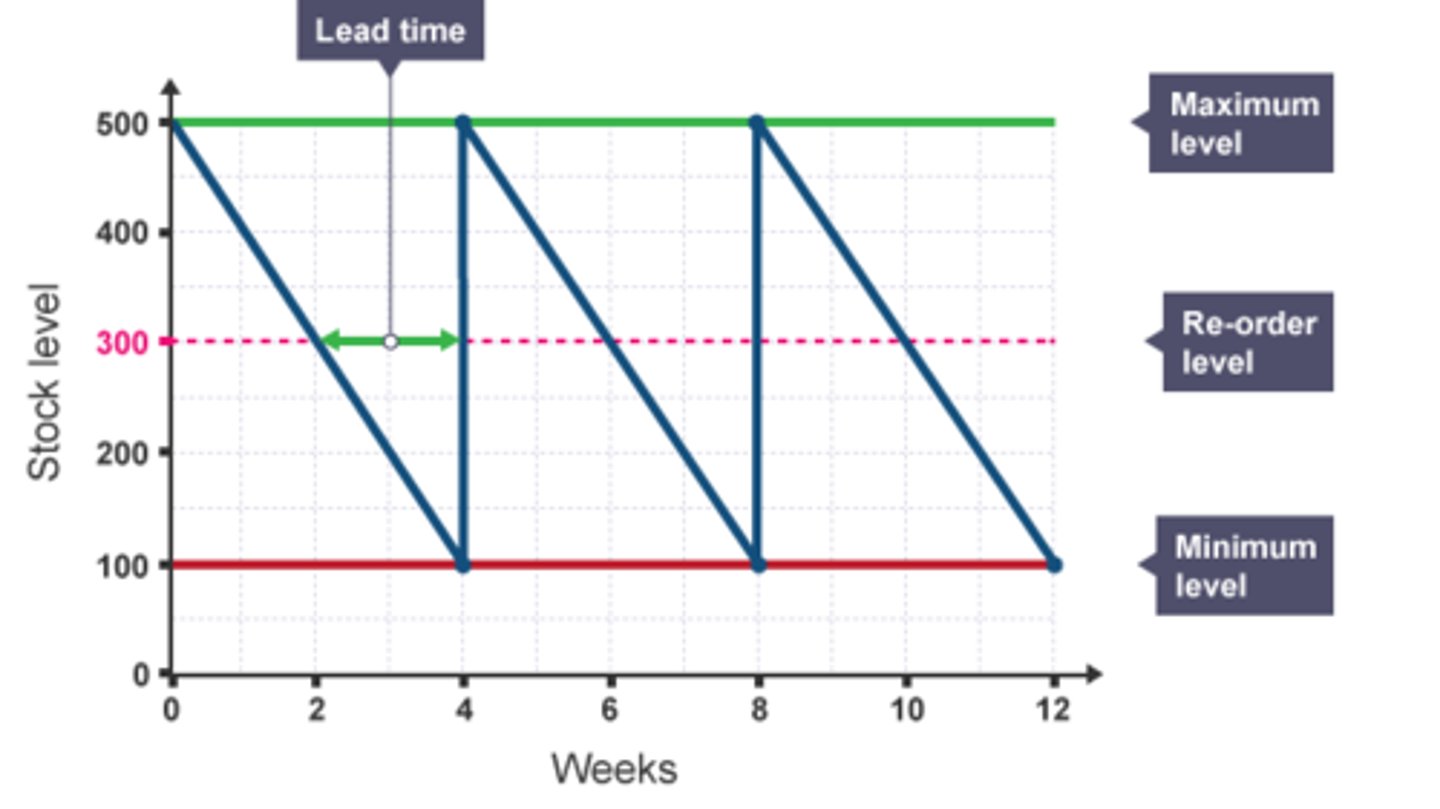
Bar gate stock graphs
Minimum stock level = buffer stock.
Just in time (JIT)
Stock is delivered only when it is needed, so no stock is kept by the business. For this to work the business must have good relationships with suppliers, a well organised system and regular demand for their products.
Just in case (JIC)
The business holds buffer stocks of raw materials/ finished goods just in case there is a problem with deliveries or there is an unexpected surge in demand.
Quality control
Usually at the end to test if a good or service meets customers expectations.
Quality assurance
A method of improving quality standards. This occurs at all stages of production to ensure customer satisfaction is achieved.
Benefits of good quality
- Allows for premium price to be charged.
- Builds a strong brand image.
- Competitive advantage.
- Differentiates the product.
The sales process
A series of steps that a salesperson goes through to help the customer make a satisfying buying decision.
Gross profit
Profit that a business makes on its trading activity before any indirect costs have been deducted.
sales revenue - cost of sales
Net profit
Profit that the business is able to return to shareholders or reinvest back into the business.
gross profit - other expenses and interest.
Gross profit margin
Indicates proportion of sales revenue turned into gross profit.
gross profit/sales revenue x100
Net profit margin
Indicates the proportion of sales revenue turned into net profit.
net profit/sales revenue x100
Average rate of return
Average annual profit / Cost of investment x 100
Average annual profit = total profit/no. of years.
What can quantitative data be used for?
Monitor performance of business, compare performance with competitors, anticipate needs of customers, make business decisions and set aims and objectives.
Hierarchical structure
Has a long chain of command to make the business easier to control and provides opportunities for promotion. It can be costly and slows down communication
Shape of a pyramid
Flat structure
Has fewer levels of management but a wider span of control. It improves business flexibility but lines of authority aren't always clear.
Centralised
Decisions made by senior managers.
Decentralised
Decisions are delegated to regional employees at local stores and branches.
Span of control
The number of subordinates a line manager is responsible for in a business.
Remote working
When people do their work at home rather than in a company office.
Video conferencing
Live conferences over the Internet that includes voice, video, and or text.
Flexible working
Business has more control over its cost and can increase or lower its capacity when needed. Freelance contracts are often used when businesses needs to employ a specialist. However employees might nit be committed to the business is they dont have job security.
Freelance
Self employed workers that usually work for several different clients. Usually no benefits.
Job description
Job title, key duties, salary or wage.
Person specification
Contains a description of characteristics, qualifications and skills that are required to meet the needs of a job description.
CV
A document which describes your qualifications and the jobs you have done, which you send to an employer that you want to work for.
Internal recruitment
The process of seeking employees who are currently within the firm to fill open positions. It is fast and cheaper than external advertising. Employees are motivated.
External recruitment
The process of seeking new employees from outside the firm. There are more potential applicants and new ideas can be brought into the business. Suitable if business wants to expand.
Formal training
Employees attend specific training courses. They may be provided by external companies.
Informal training
Employees learn skills 'on the job', by developing skills and experience from being coached by other employees. It is cheaper and less time consuming.
Performance management
Employees are set targets for the year ahead. Their targets may be linked to pay and rewards.
What can a motivated workforce create?
Hard working and flexible workforce, reduce employee sick leave rates, improve customer service, improve communication within business, retain good employees, increase productivity.
Fringe benefits
Any financial extras beyond the regular pay check, such as health insurance, life insurance, paid vacation and/or retirement.
Piece rate system
A compensation system under which employees are paid a certain amount for each unit of output they produce.
Job rotation
A job enrichment strategy that involves moving employees from one job to another.
Job enrichment
Increasing the number of tasks in a particular job and giving workers the authority and control to make meaningful decisions about their work.
Autonomy
Empowered to make your own decisions.
Job enlargement
Increasing the number of different tasks in a given job by changing the division of labor.
Remuneration
Financial incentives e.g bonus