Risk Management Test 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is the life insurance benchmark for adequate coverage?
12-18 x gross annual pay (must be at least 10x)
What is the purpose of the life insurance benchmark?
To estimate how much coverage is needed to replace income and provide security for dependents
What is the free-look period
A 30-day window (in most states) allowing the cancellation of a life insurance policy for a full refund.
What is a grace period?
Typically 31 days after a missed premium where coverage remains active. If death occurs, the benefit is still paid minus the premium that is owed.
what is the greatest danger of a variable life insurance policy
You could die when the market is low, reducing the policy's cash value and death benefit
How long does an insurance policy have to rescind a policy due to misrepresentation?
Two years from the issue date
What can an insurer do if misrepresentation is found after the rescission period?
They can adjust the benefit and premiums based on the corrected information
Why do beneficiary designations override wills?
Beneficiary designations are the operation of law or titling
What is a Section 1035 exchange
A provision in the U.S. tax code that allows an individual to swap an existing life insurance policy or annuity for a new "like-kind" policy without triggering a taxable event on any gains
What determines the taxability of disability benefits
Whoever pays the premium. If it is paid with after-tax dollars, the benefits are tax-free. If it is paid with pre-tax or employer dollars, the benefits are taxable
What is the elimination period in disability insurance
The waiting period before benefits begin which is typically 90 days
why does paying attention to small details like elimination periods matter
they affect the cost of premiums and when benefits begin, influencing overall protection
what type of life insurance is best for a 30 year old single female
Term Life insurance because:
Affordable premiums: At age 30, she’s young and healthy, so term life rates are very low compared to permanent policies. She can get a large amount of coverage for a small monthly payment.
Covers key financial risks: Term life can protect against specific short- to medium-term obligations—like paying off student loans, a mortgage, or supporting dependents if she has them later—without overpaying for lifelong coverage she may not need yet.
Flexibility: If her life situation changes (marriage, kids, home purchase), she can renew or convert the policy later to permanent insurance.
Simple structure: Term life is straightforward—coverage lasts for a set period (e.g., 20 or 30 years), and only pays if death occurs during that term. There’s no cash value or investment component to manage.
What are the five laws of gold
1. Gold comes gladly to those who save
2. Gold labors diligently for the wise owner
3. Gold clings to the cautious owner
4. Gold slips away from the man who invests it in unfamiliar ventures
5. Gold flees the man who chases impossible earnings
Gold comes gladly to those who save
Save at least 10%
Gold labors diligently for the wise owner
Invest wisely
Gold clings to the cautious owner
Protect wealth
Gold slips away from the man who invests it in unfamiliar ventures
Avoid risky adventures
Gold flees the man who chases impossible earnings
Don't seek unrealistic returns
Start Thy Purse to Fattening
Save at least one-tenth of all you earn. For every ten coins you bring in, put one aside for the future.
Control Thy Expenditures
Live below your means and create a budget to ensure you have money for necessities, enjoyments, and worthwhile desires without overspending. Avoid lifestyle inflation, where expenses rise with income.
Make Thy Gold Multiply
Put your savings to work by investing them so that they generate more wealth for you.
Guard Thy Treasures from Loss
Only invest in ventures where your principal is safe, can be reclaimed, and will yield a fair return. Consult with wise and experienced men for advice.
Make of Thy Dwelling a Profitable Investment
Own your own home as a profitable asset.
Insure a Future Income
Provide in advance for your old age and the needs of your family.
Increase Thy Ability to Earn
Cultivate your own skills and knowledge to become more valuable. Invest in yourself through study and practice to improve your performance and earning potential
What type of insurance is used for business buy/sell agreements and why?
The best type of insurance for a business buy/sell agreement is life insurance. It provides the funds needed for surviving owners or the company to buy out the deceased or disabled owner’s interest, ensuring a smooth transition of ownership, financial stability, and fair compensation to all parties.
What is the purpose of life insurance
To provide income replacement, cover debts, and support dependents upon the insured's death
What are the main parties to a life insurance contract
Policy owner (who controls the policy), the insured (the person whose life is covered), and the beneficiary
What factors affect life insurance underwriting
age
gender
health
lifestyle
occupation
medical history
driving record
tobacco use
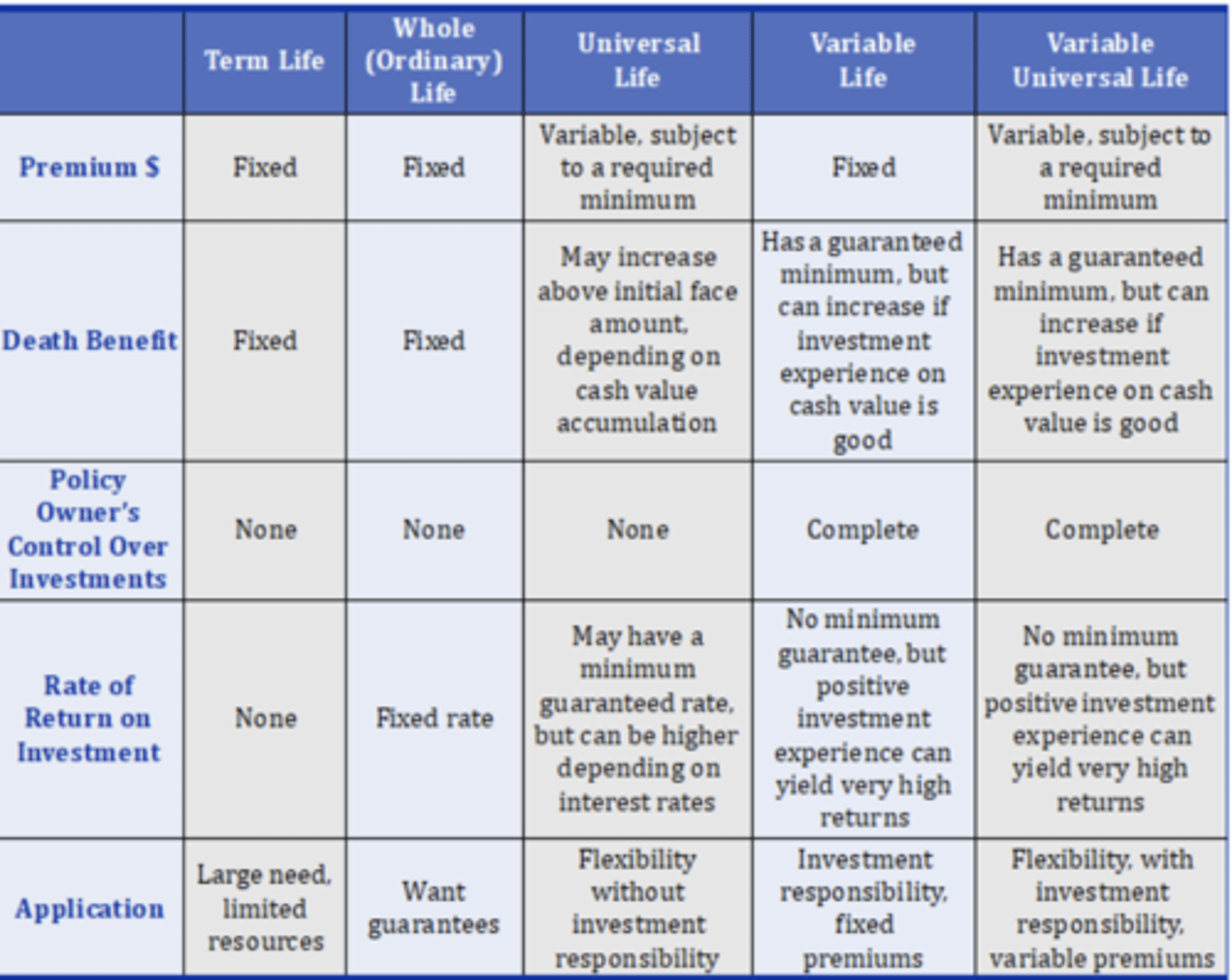
What are the three main types of life insurance
Term
Whole
Universal Life
What are the advantages of term life
Low cost, high coverage per dollar, and flexibility to convert to permanent insurance
What are the disadvantages of term life
No cash value, temporary coverage, and rising premiums with age
What are the advantages of whole life insurance
Lifetime protection, fixed premiums, cash value growth, and tax deferred savings
what are the disadvantages of whole life insurance
high cost, inflexible premiums, and limited investment return
What are the advantages of universal life insurance
flexible premiums, adjustable death benefits, and tax-deferred cash value growth
What are the disadvantages of universal life insurance
Higher cost and possible policy lapse if target premiums are not met
What are life insurance nonforfeiture options
cash surrender value, reduced paid-up insurance, and extended term insurance
what are common riders in life insurance
waiver of premium, double indemnity, guaranteed insurability, and long-term care riders
Double indemnity
an insurance provision that pays out double the policy's face value if the insured person dies accidentally
What is the purpose of the incontestability clause
It prevents the insurer from voiding the policy after two years due to misstatement, except for fraud
What is the difference in free look v. grace period
Free look = refund period after purchase
Grace period = covered protection after mispayment
What is group term life insurance
Employer provided life insurance under one master contract, often with up to $50,000 tax free benefit
What is the tax rule for an employer-paid group term life over $50,000?
The excess coverage is taxable to the employee based on IRS Table I rates
What is a modified endowment contract (MEC)
A life policy funded too quickly (fails 7-pay test); withdrawals taxed as income and penalized before age 59.5
What is the 7-pay test
It limits the total amount of premiums you can pay into the policy during the first seven years. If you pay more than the limit, the policy fails the test and can be reclassified as a MEC, which can lead to unfavorable tax treatment on withdrawals and loans
what is key person insurance
Insurance owned by a business to protect against financial loss if a vital employee dies
What are the main types of buy/sell agreements
Entity (stock redemption), cross-purchase, and wait-and-see agreements
What is the typical benefit level for disability income insurance
60-70% of gross income
What is the difference between short-term and long-term disability insurance
Short term lasts up to 2 years.
Long term can last to age 65 or a lifetime
What are common exclusions in disability insurance
war
self-inflicted injuries
work-related injuries (due to worker's comp)
criminal acts
intoxication
pre-existing conditions
what are residual benefits in disability insurance
Partial benefits are paid when returning to work with reduced income
what is the cost of living adjustment (COLA) rider
it increases the benefits based on changes in the consumer price index (CPI)
what are the future and automatic increase riders
Future increase = optional benefit growth with income
Automatic increase = yearly benefit raised by %
What are the main provisions of a life insurance policy
Grace period
Incontestability
Misstatement of age/gender
Assignment
Suicide clause
Reinstatement
Policy loans
What is the purpose of split-dollar life insurance
The employer and employee share the costs. The employer is reimbursed, and the remainder goes to the employee's beneficiary
What is the tax-free benefit rule
Life insurance proceeds are excluded from taxable income if paid due to death
What is the taxation rule for policy loans
They aren't taxable while the policy is in force, but reduce the death benefit if unpaid
What is the human life value approach?
Calculates insurance need based on:
(Future Income - Personal Expenses - Taxes) / (Work-Life Expectancy)
What is the needs approach
Estimates family's cash needs after death:
Final expenses, debt, income replacement, retirement for spouse
What is the capitalized earnings approach
Determines the lump sum needed so investment returns can generate the desired income perpetually
What are the dividend options for participating policies
cash
reduced premium
paid-up additions
interest accumulation
one-year term
What are surrender charges
Fees recouping insurer costs when a policy is surrendered early
What is the difference between preferred, standard, and underwriting classes
Preferred = low risk
Standard = average risk
Table-rated = higher risk with premium surcharges (A=25%, B=50%, C=75%)