VCE Unit 3 BM AOS 3: Operations Systems
1/69
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Operations management
involves coordinating and organising the activities involved in producing the goods or services that a business sells to customers.
Operations managers aim for productivity and efficiency in their operations process. (i.e., they want to make a good quality product/service for the minimum cost)
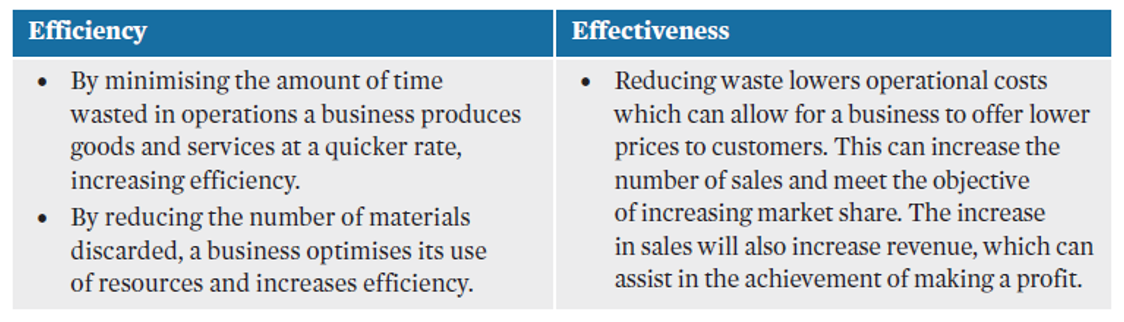
Efficiency
how productively a business uses its resources when producing a good or service.
An operations manager will constantly aim to maximise the productivity of a business’ operations system to improve this concept
Effectiveness
the extent to which a business achieves its stated objectives.
Operations managers can optimise a business’ operations system by selecting the most suitable strategies to lower production costs, improve quality, and reduce wastage
Operations management and business objectives

Inputs
the resources used by a business to produce goods and services.
include, but are not limited to:
•Labour resources e.g., employees
•Raw materials (unprocessed resources) e.g., flour and iron
•Capital resources (physical assets) e.g., equipment and machinery
•Financial resources
•Time
•Utilities e.g., electricity, water, and gas
•Information e.g., information that contributes to the transformation process such as, knowledge of manufacturing
Processes
the actions performed by a business to transform inputs into outputs.
Sometimes referred to as ‘transformation’.
include, but are not limited to:
•Mixing
•Designing
•Baking
•Computing
•Cutting
•Washing
•Assembling
Constructing
outputs
the final goods or services produced as a result of a business’s operations system, that are delivered or provided to customers.
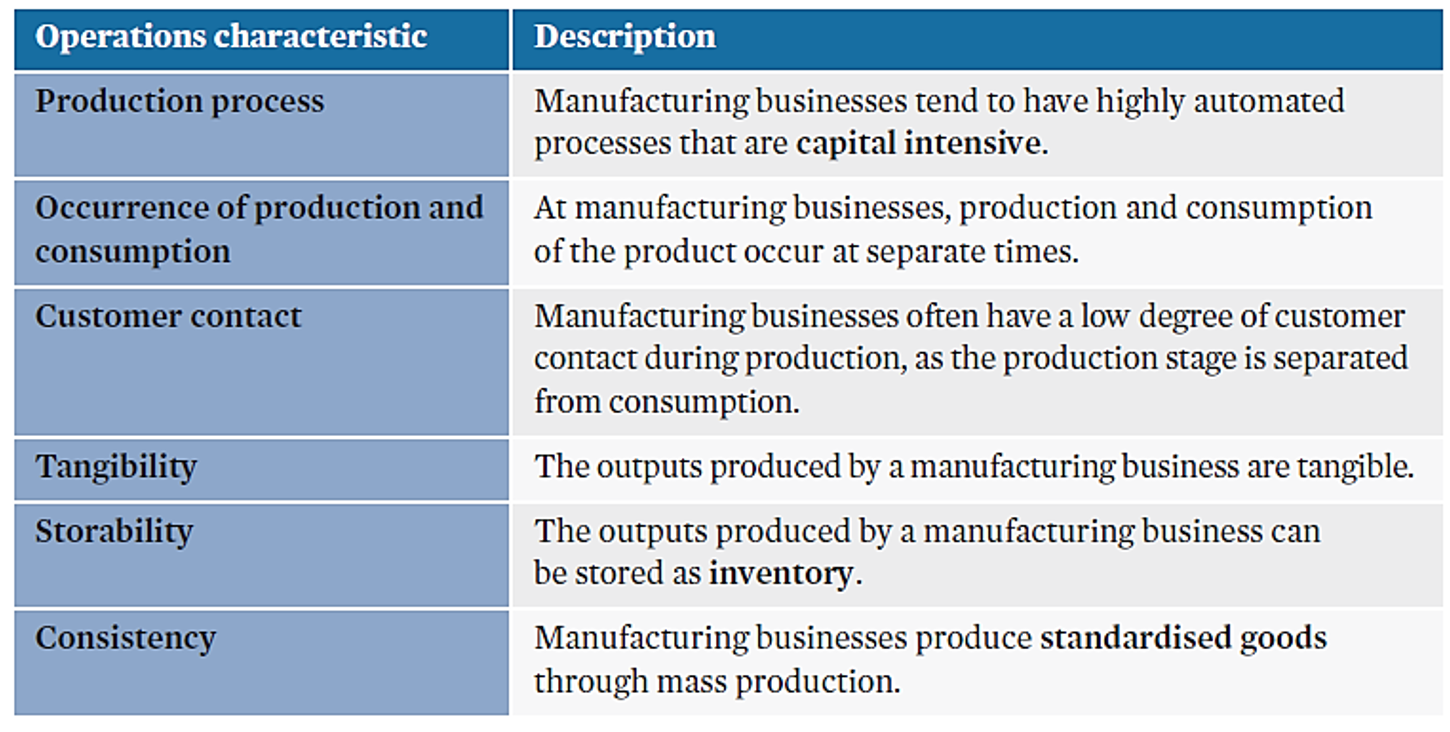
Manufacturing businesses
•businesses that use resources and raw materials to produce a finished physical good.
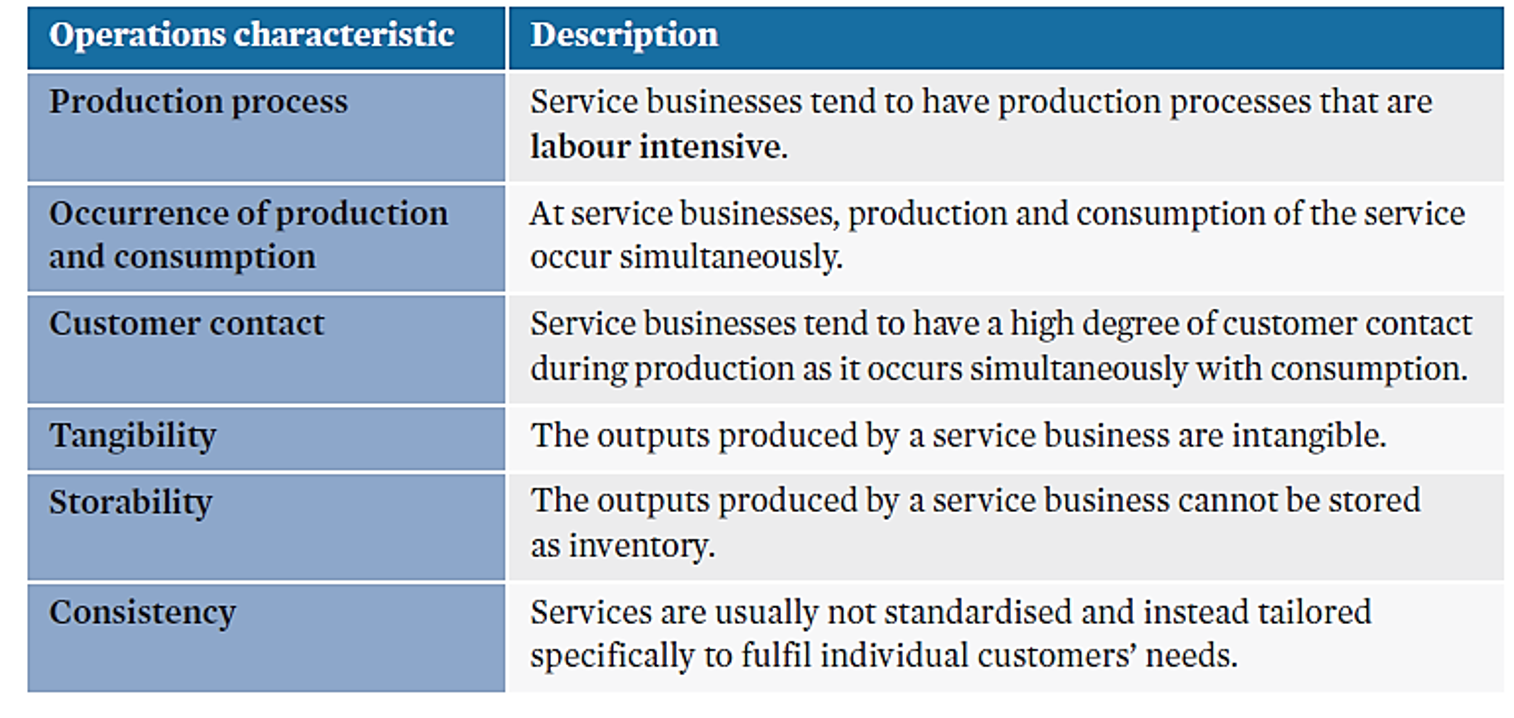
service businesses
businesses that provide intangible products, usually with the use of specialised expertise.
characteristics of manufacturing businesses
characteristics of service businesses
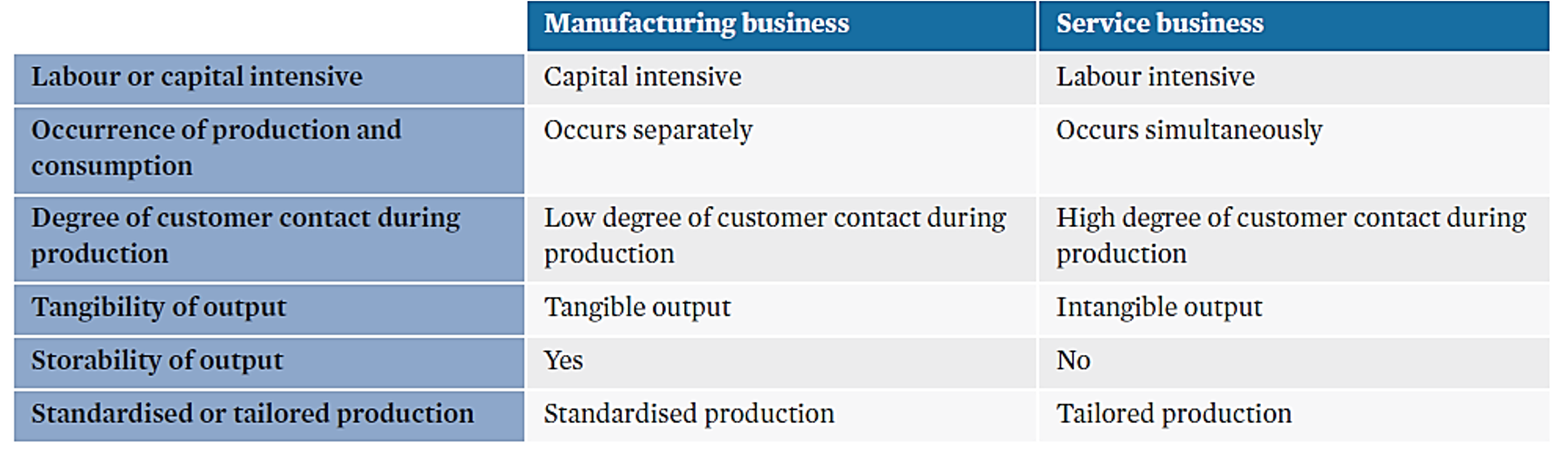
similarities between manufacturing and service businesses
•Both types of businesses aim to optimise their operations to produce high-quality outputs at a low cost of production.
•Both types of businesses have to deal with suppliers during the process of managing operations.
•Both types of businesses can utilise forms of technology in their operations systems.
•Both types of businesses aim to optimise efficiency and effectiveness in their operations.
differences between manufacturing and service businesses
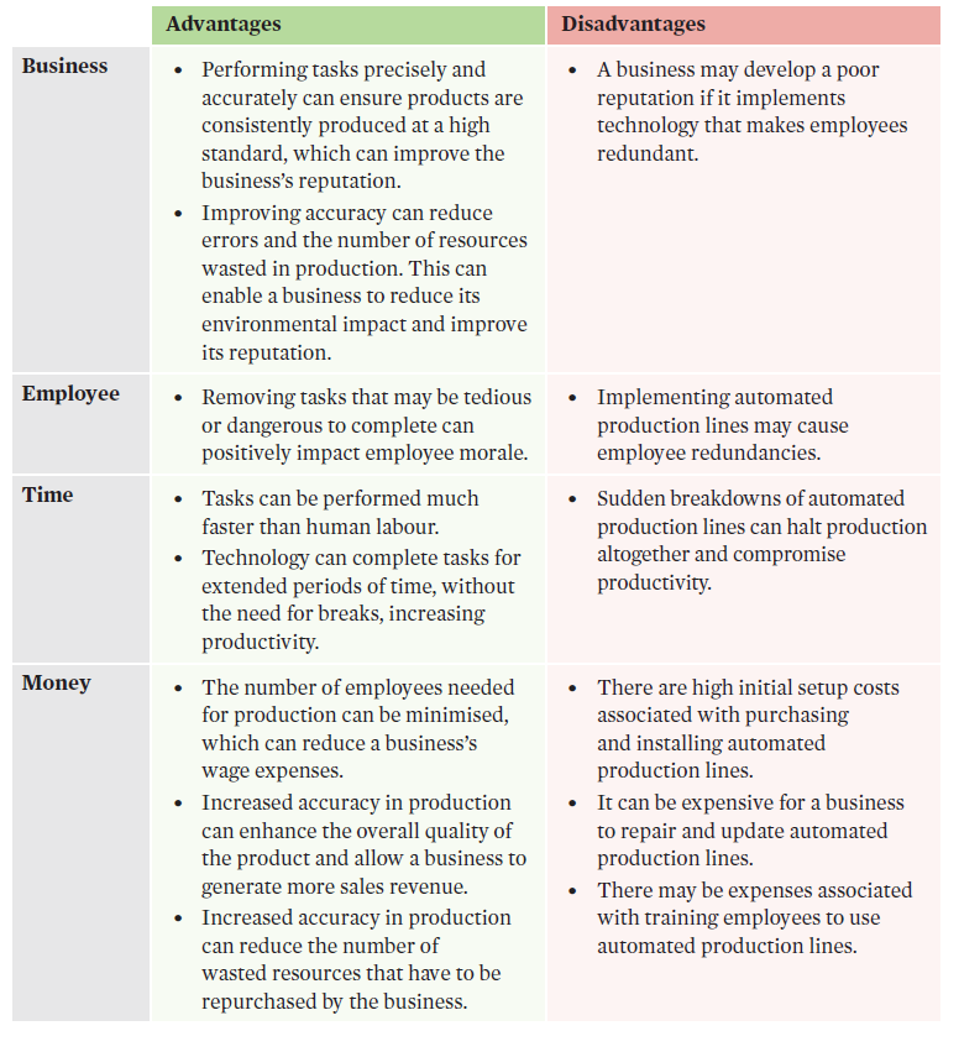
automated production lines
involve machinery and equipment that are arranged in a sequence, and the product is developed as it proceeds through each step.
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
Automated production lines can perform at speeds much faster than humans, reducing the amount of time taken to produce outputs, thus improving productivity. | Automated production lines perform tasks with a high degree of accuracy, which can decrease the number of errors that occur during production. This enhances the overall quality of the final product, which can increase customer satisfaction, sales, and market share. |
evaluation of automated production lines
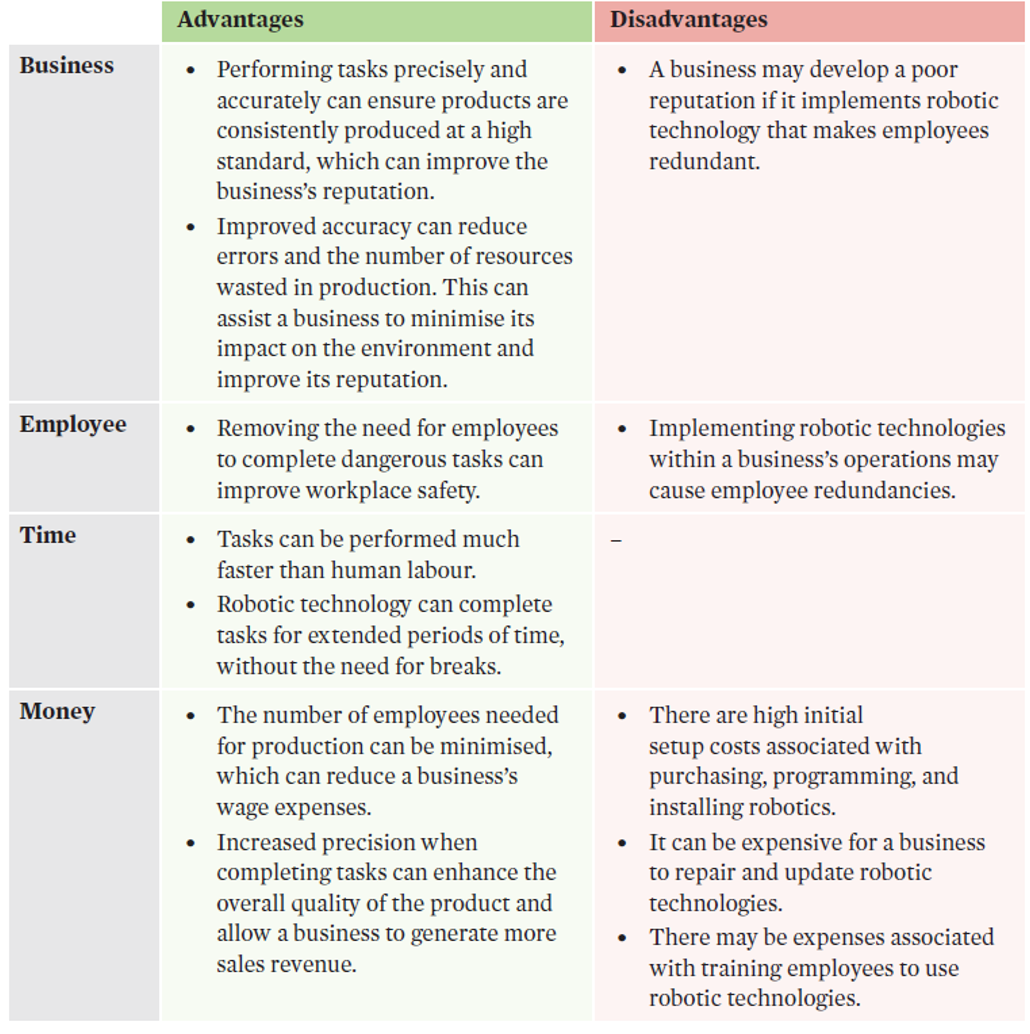
robotics
programmable machines that are capable of performing specified tasks.
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
Robotics can perform specific tasks quickly and with high levels of accuracy. This can reduce the amount of time and resources wasted in production, therefore resources are used more optimally, improving productivity. | Robotics can perform specified tasks quickly with high levels of precision, which can minimise the number of errors that occur during production. This can enhance the overall quality of the final product and increase customer satisfaction, sales, and market share. |
evaluation of robotics
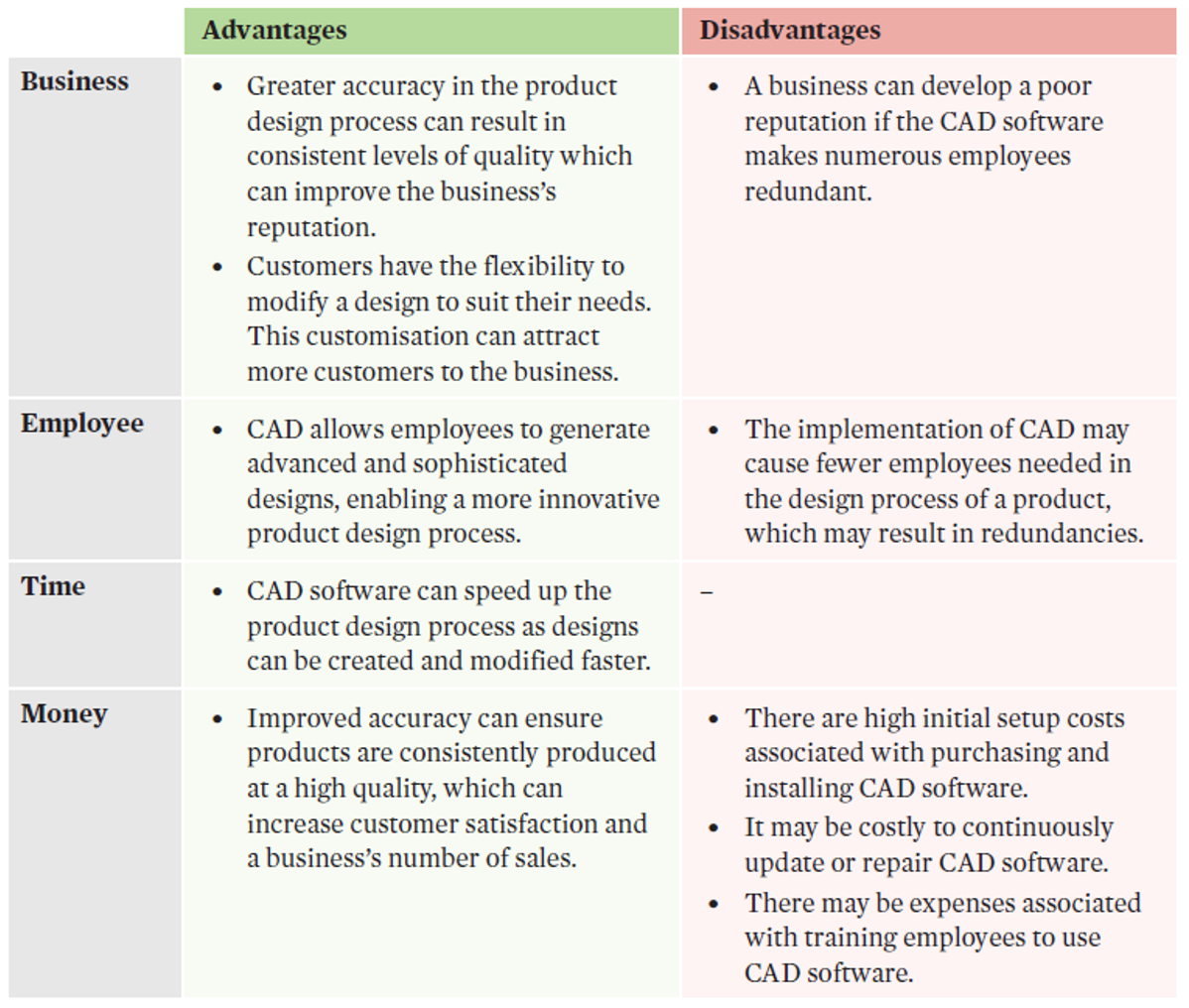
Computer aided design (CAD)
is digital design software that aids the creation, modification, and optimisation of a design and the design process.
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
CAD can reduce the time and labour needed to design a product, allowing resources to be used more optimally and productively. CAD allows the design to be viewed from multiple angles, to ensure all of the design features are met before production. | A business can use CAD to develop various prototypes and choose the best design to produce. Choosing the best option enables the business to manufacture the highest quality design, which can increase customer satisfaction, sales, and market share. |
CAD evaluation
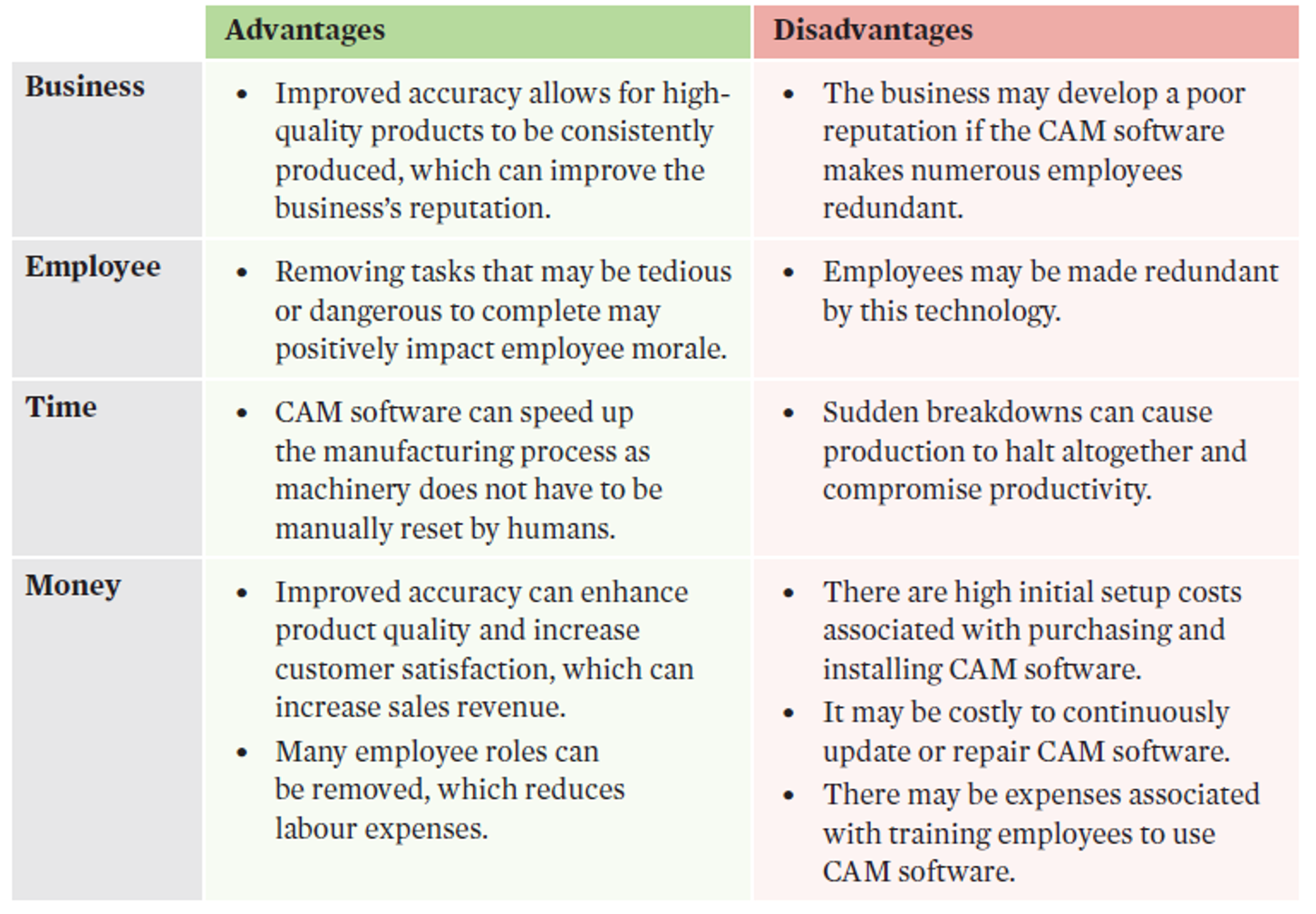
Computer aided manufacturing (CAM)
involve the use of software that controls and directs production processes by coordinating machinery and equipment through a computer.
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
CAM does not require machinery to be manually reset by humans which reduces the amount of time and labour resources used in the production process, thus improving productivity. CAM can follow specific instructions and complete tasks more accurately than humans which can reduce the amount of waste that is generated during production, and therefore optimise a business’s use of resources. | CAM software is able to coordinate tasks so they are performed with a high degree of accuracy, enabling the business to achieve a consistent level of quality, which can increase customer satisfaction, sales, and market share. |
CAM evaluation
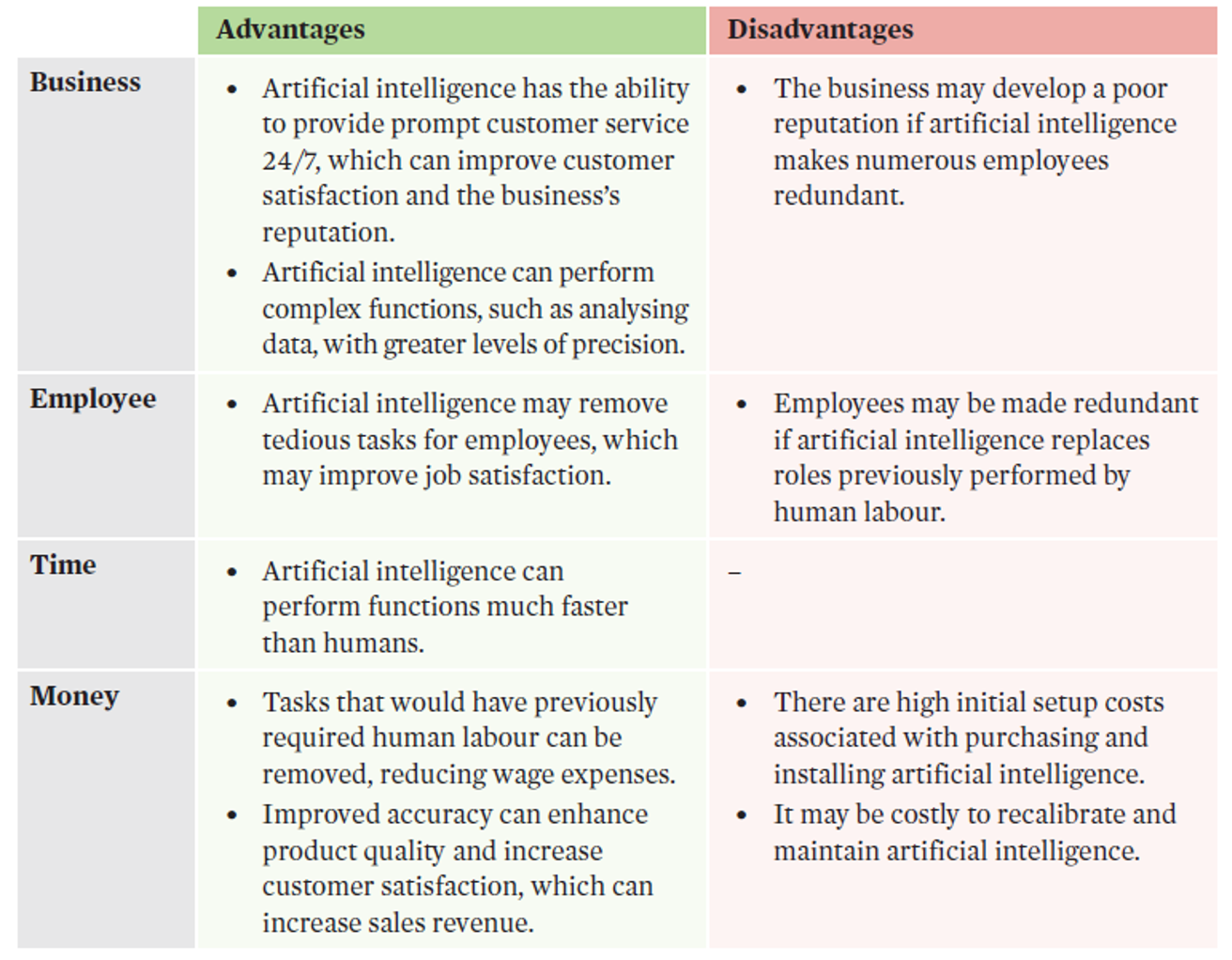
Artificial intelligence (AI)
involves using computerised systems to simulate human intelligence and mimic human behaviour.
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
AI can reduce the time and labour used to complete complex tasks that would usually require human intelligence. This can allow resources to be used more optimally and improve productivity. | AI can perform complex tasks, such as providing timely and high-quality customer assistance. This can improve customer satisfaction levels, and allow for increases in sales and market share. |
AI evaluation
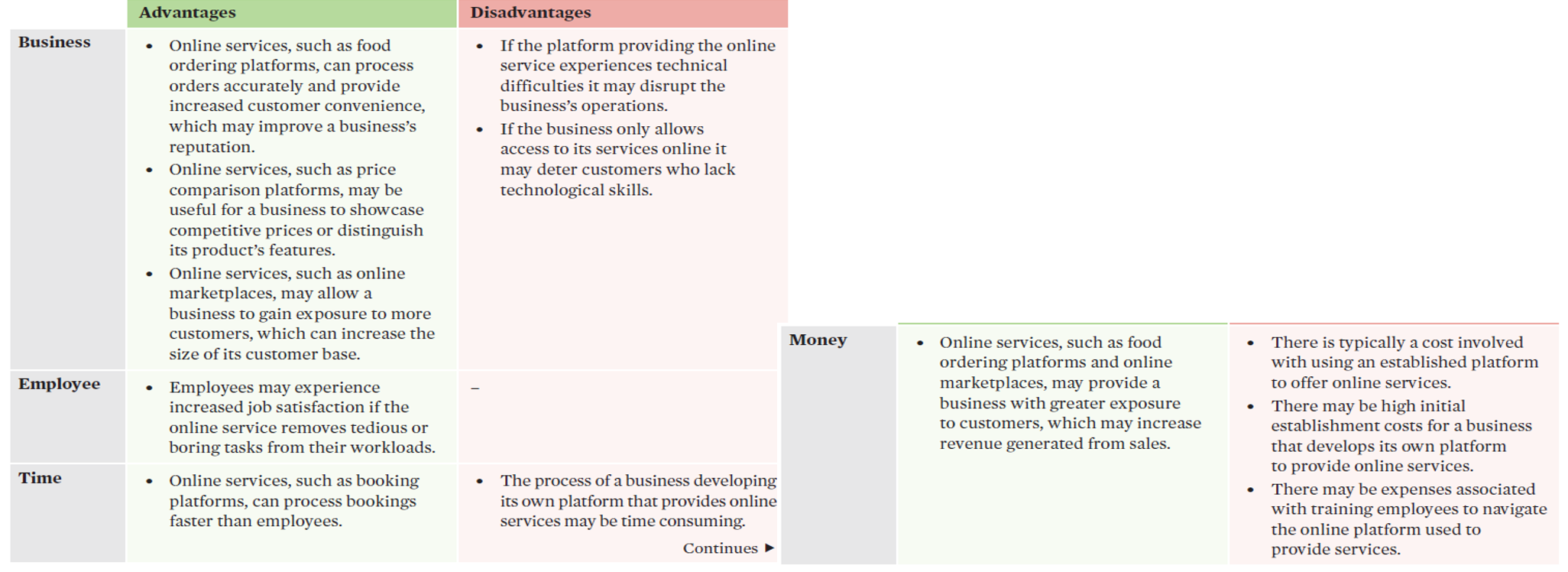
online services
services that are provided via the internet.
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
Online services can remove the need for employees to perform certain tasks and enable labour resources to be used more efficiently. | Implementing online services within an operations system can improve convenience for customers, increasing levels of customer satisfaction, sales, and market share. |
online services evaluation
inventory
the goods and materials held as stock by a business.
materials handling
the physical handling of goods in warehouses and at distribution points.
materials management
materials involves organising and monitoring the delivery, storage, and use of materials required for production.
Improving the management of the materials required for production can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of an operations system.
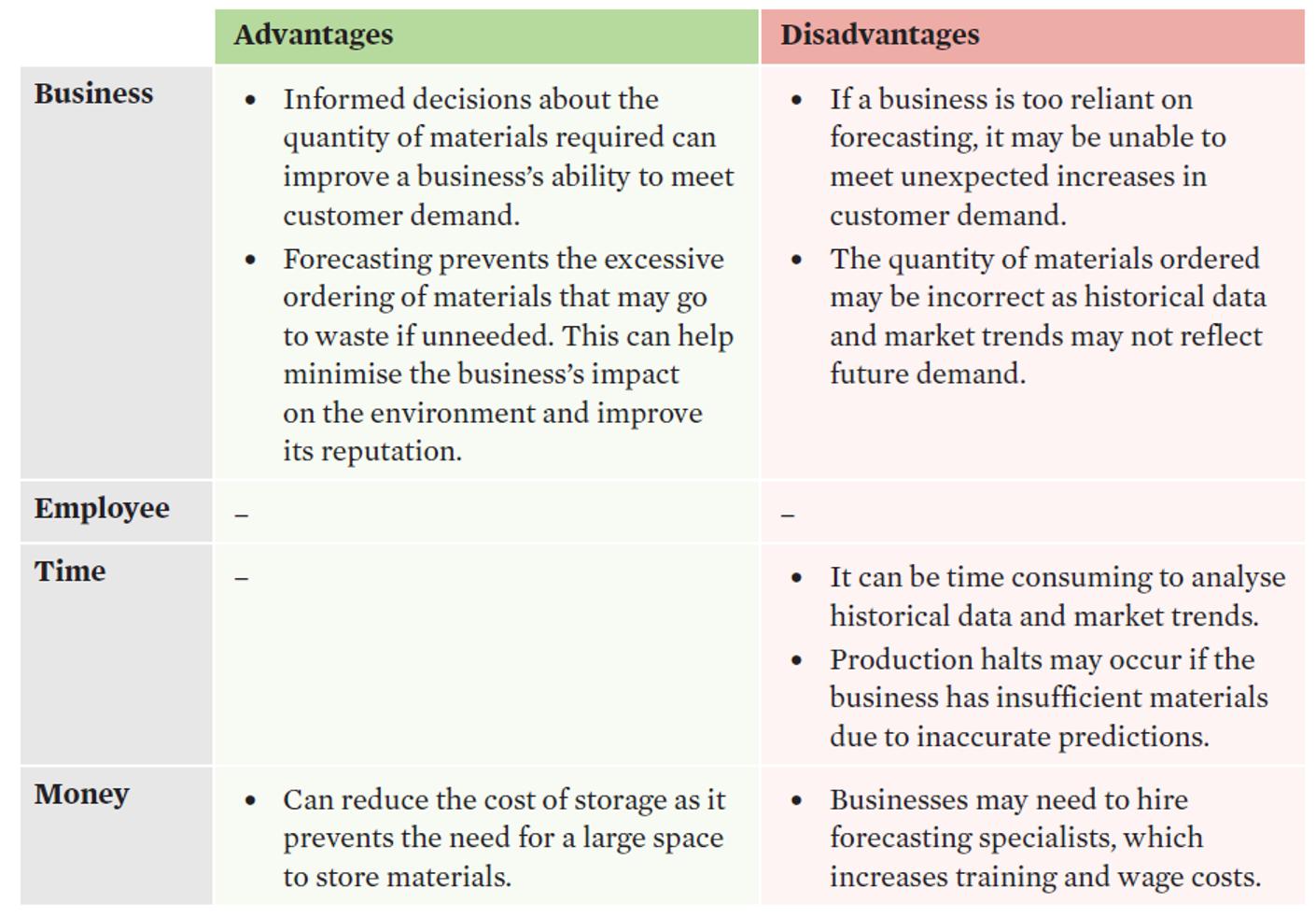
forecasting
•a materials planning tool that predicts customer demand for an upcoming period using past data and market trends.
•assists managers to make informed decisions relating to the quantities of materials needed to meet predicted customer demand therefore, matching supply with demand.
• allows a business to determine what to produce, how to produce it and in what quantity, how much materials it needs and what transport is required.
forecasting evaluation
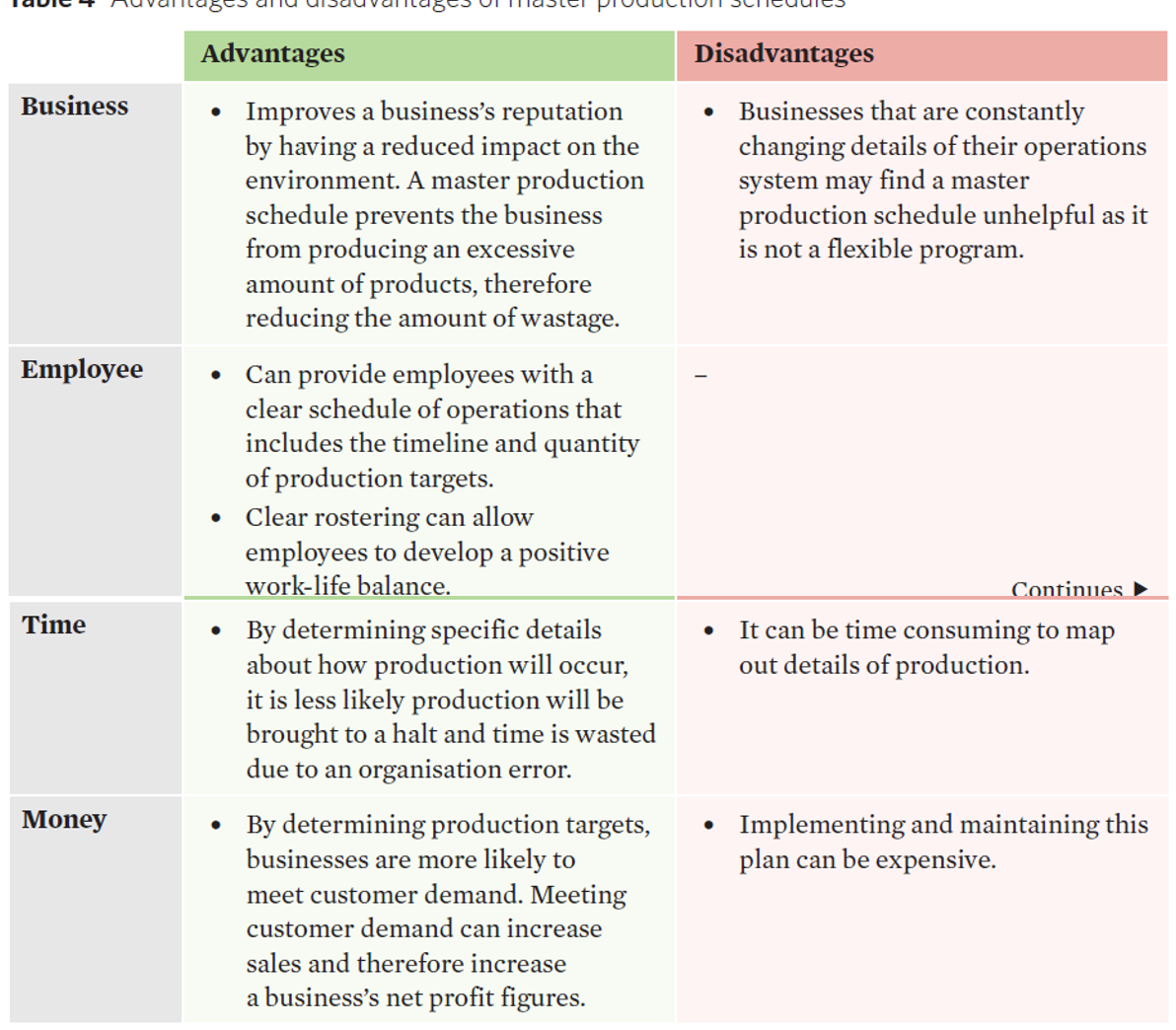
master production schedule (MPS) (materials planning)
•a plan that outlines what a business intends to produce, in specific quantities, within a set period of time.
specifies details such as the location, timing, and quantity of the production of outputs.
•Managers then use this information to help them determine the materials, machinery, and labour required to meet those production targets.
master production schedule evaluation
materials requirement planning (MRP) (materials planning)
•a process that itemises the types and quantities of materials required to meet production targets set out in the master production schedule.
•It must consider:
•Lead times of suppliers
•Exact number of inputs needed
•Amount of stock (inventory) on hand
•Purchasing procedures (Bulk or just in time)
materials requirement planning evaluation

MPS and MPR efficiency and effectiveness
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
Promotes an organised operations system and minimises the number of avoidable errors that occur, such as halts in production, which improves productivity by reducing the number of interruptions and allowing operations to flow smoothly Having the exact materials needed for production reduces the amount of excess stock that expires or becomes damaged in storage which optimises resources by reducing waste. | Ensures there are sufficient materials to meet customer demand. Meeting customer demand helps meet the objective of increasing customer satisfaction and sales. |
inventory control
•ensures that costs are minimised and that the operations system has access to the right amounts of inputs when required.
•Modern businesses use barcoding and computerised stock levels, which minimises loss and theft and provides precise, real-time information.
•A common strategy used is Just in time.
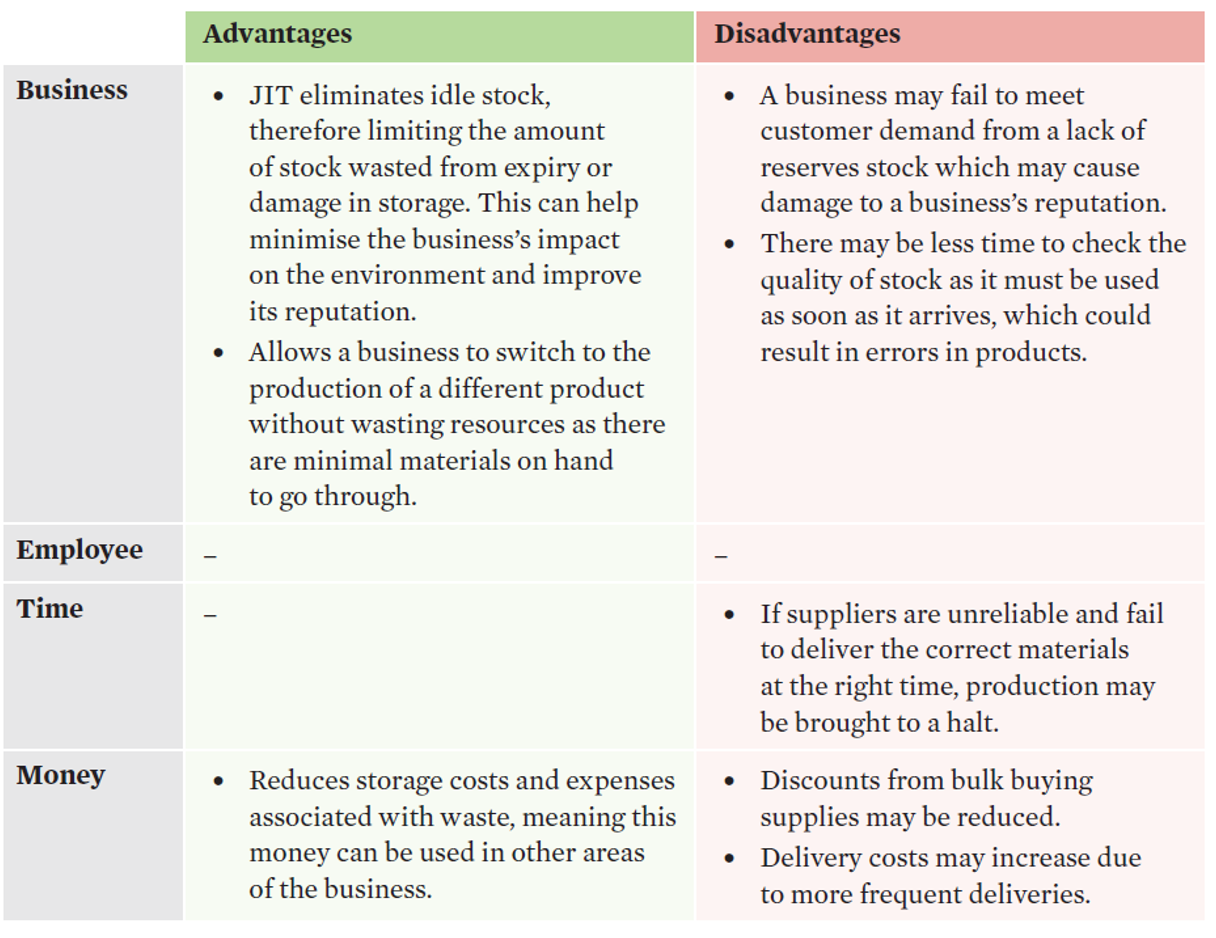
Just in Time (JIT)
an inventory control approach that delivers the correct type and quantity of materials as soon as they are needed for production.
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
Holding minimal stock can free up areas in the workspace that can be utilised to increase production. Minimising the amount of stock held can prevent resources from becoming damaged or expiring, allowing resources to be used optimally. | Costs saved from reducing storage space can be used in other areas of the business, such as sales and marketing, which can meet the objective of increasing sales. A reduction in idle stock can reduce expenses associated with waste which can meet the objective of increased profits. |
Just in time evaluation
Quality
•the degree of excellence of goods or services and their fitness for a stated purpose.
•
•Note: it applies to goods and services.
The question: does the customer get what they wanted/expected?
•When managing ________, a business will hope to:
•minimise waste and defects (therefore improving productivity and efficiency).
•strictly conform to standards.
•reduce variance in final output.
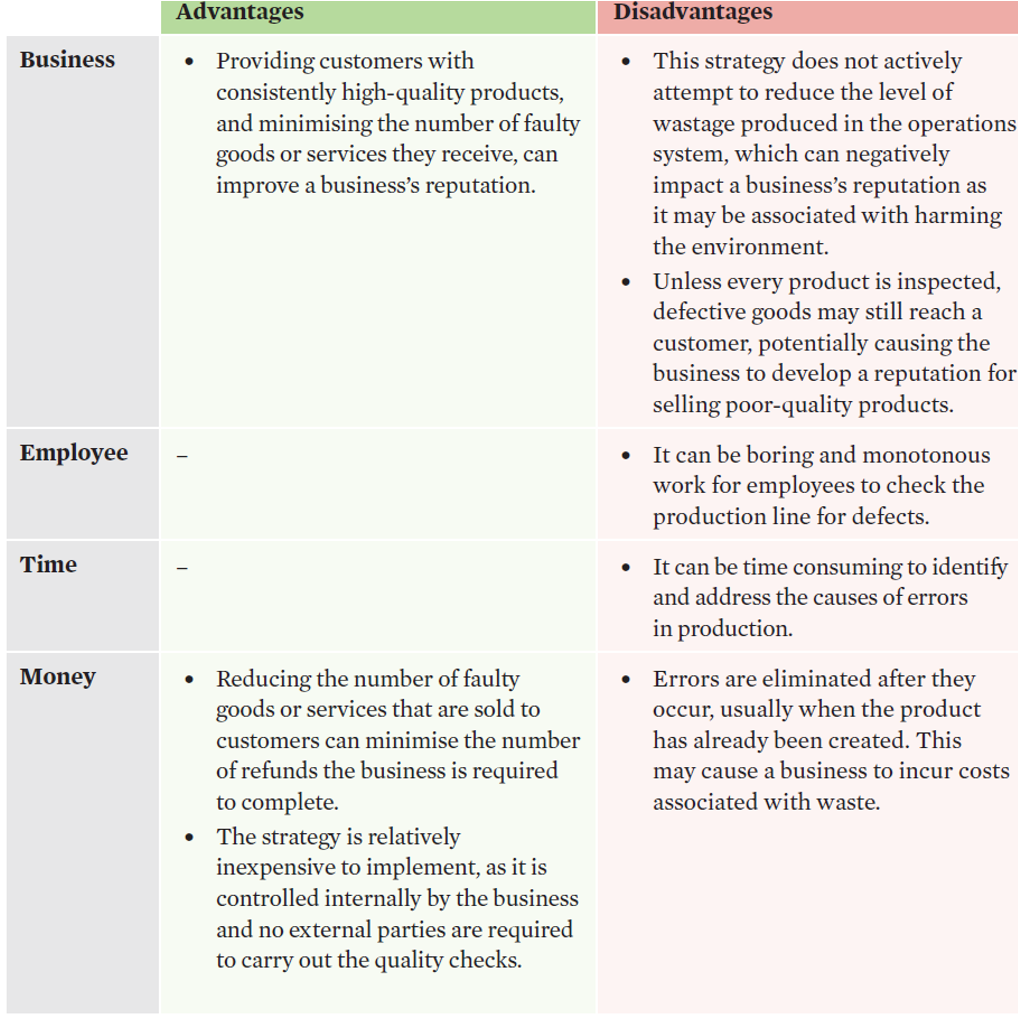
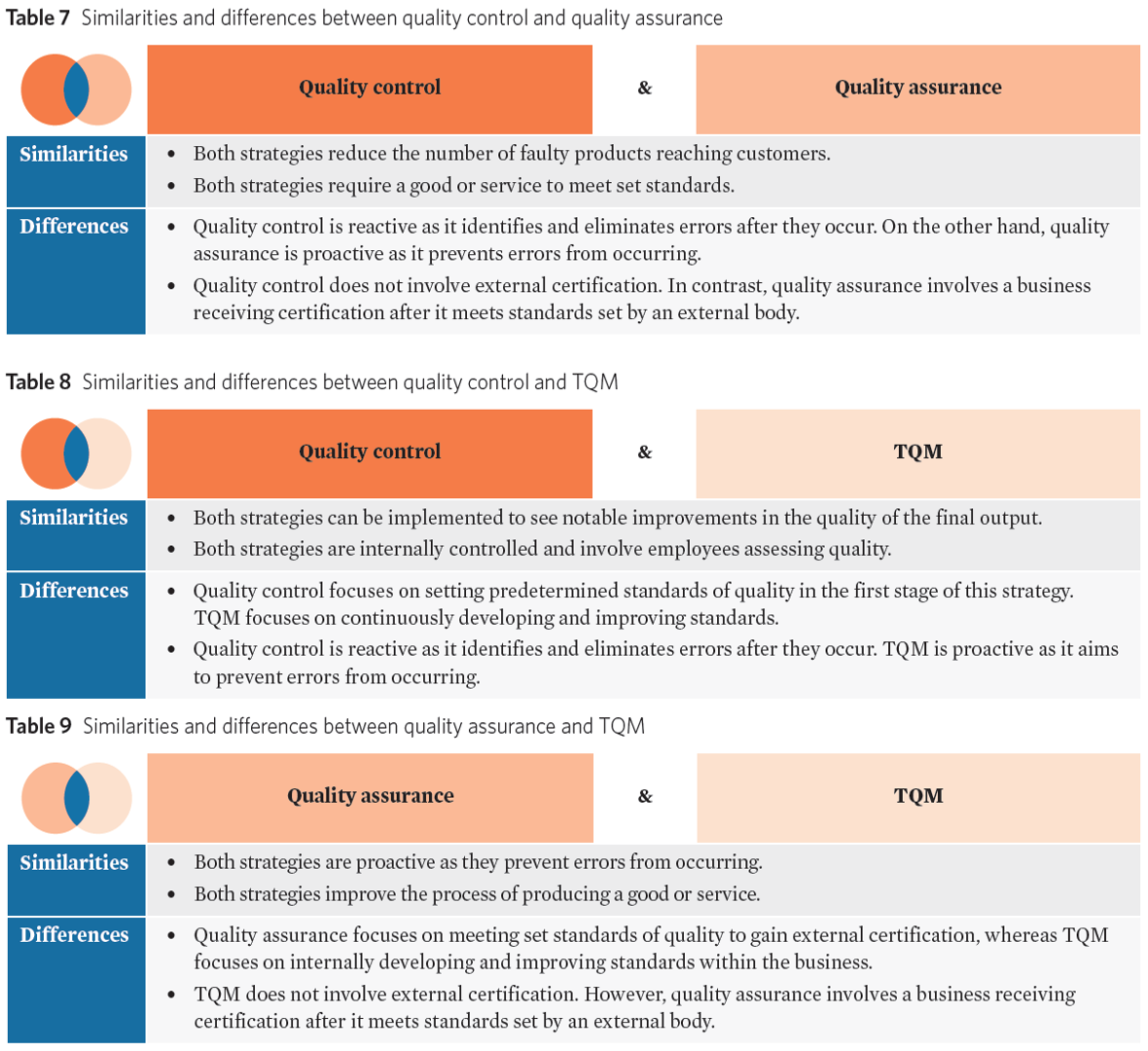
quality control
•the use of inspections at various points in the production process to check for problems and defects.
•Specifications or benchmarks are set before these physical checks are completed.
•It is a reactive form of quality management that aims to minimise the potential losses that could occur from defects and to fix the source of any problems.
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
Identifying and fixing the cause of an error prevents the error from reoccurring, which results in less waste being created during production. Reducing waste allows a business to optimise its use of resources. It also reduces the number of potential errors that could halt production, enabling the operations system to flow continuously without interference and increasing productivity. | Removing defective products prevents customers from receiving faulty goods or services. This can allow a business to meet the objectives of increasing sales and market share. |
quality control steps
1.Standards of quality are established.
2.Inspections are regularly conducted.
3.A good or service is compared against set standards.
4.A good or service is removed if it does not meet the set standards.
5.The cause of the error is fixed to prevent further errors.
quality control evaluation
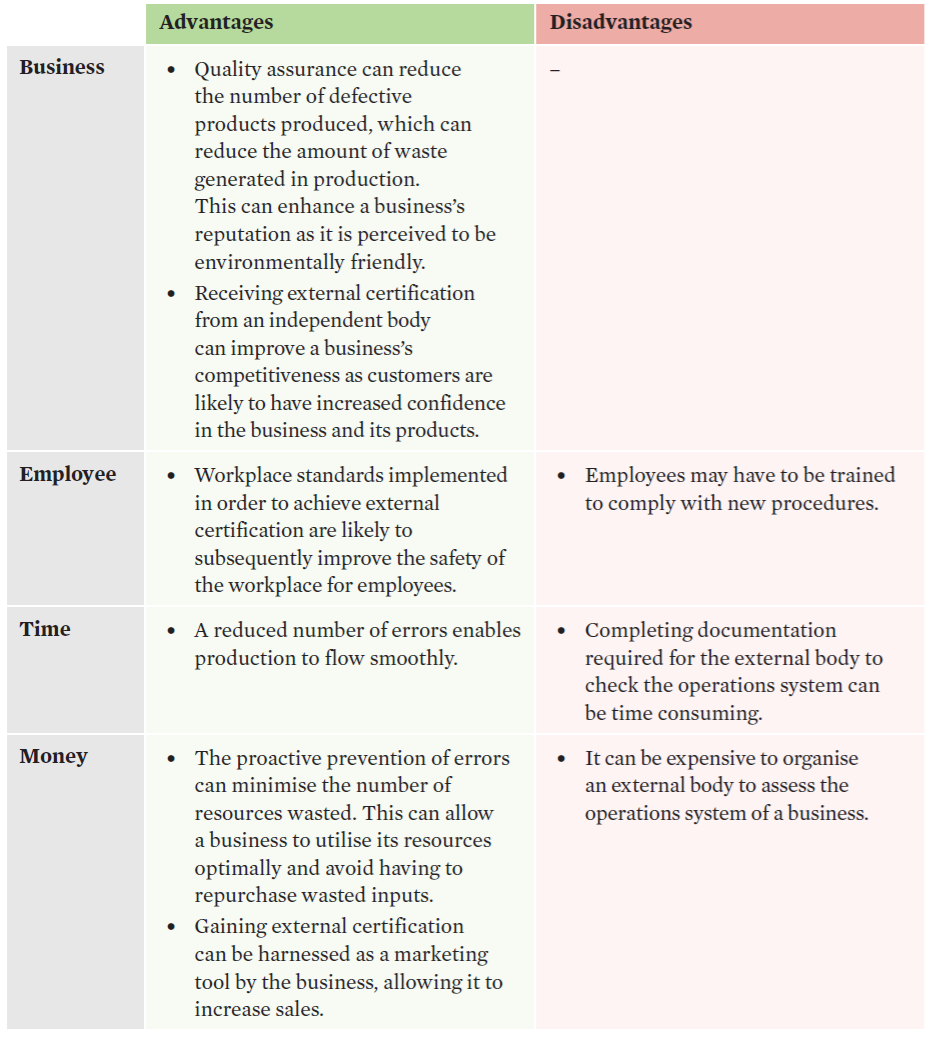
quality assurance
•involves a business achieving a certified standard of quality in its production after an independent body assesses its operations system.
•It is a proactive quality management strategy – it aims to fix problems in the operations process before they occur.•
•These systems can include process checklists, audits and the development of standards.
•ISO 9001 – widely used international standard. A business documents all processes and procedures and has these processes verified by an external body such as the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO).
Efficiency | Effectiveness |
Preventing errors before they occur reduces the number of faulty products produced, reducing a business’s waste. This can allow a business to optimise its use of resources. Preventing errors before they occur can reduce the number of production halts related to addressing the causes of errors. This can promote seamless operations and reduce the amount of time wasted in the production process, improving efficiency as less of the ‘time’ input is required. | Customers are more inclined to purchase from a business with certified quality standards. This can allow a business to increase its sales and meet the objectives of increasing profit and market share. |
quality assurance evaluation
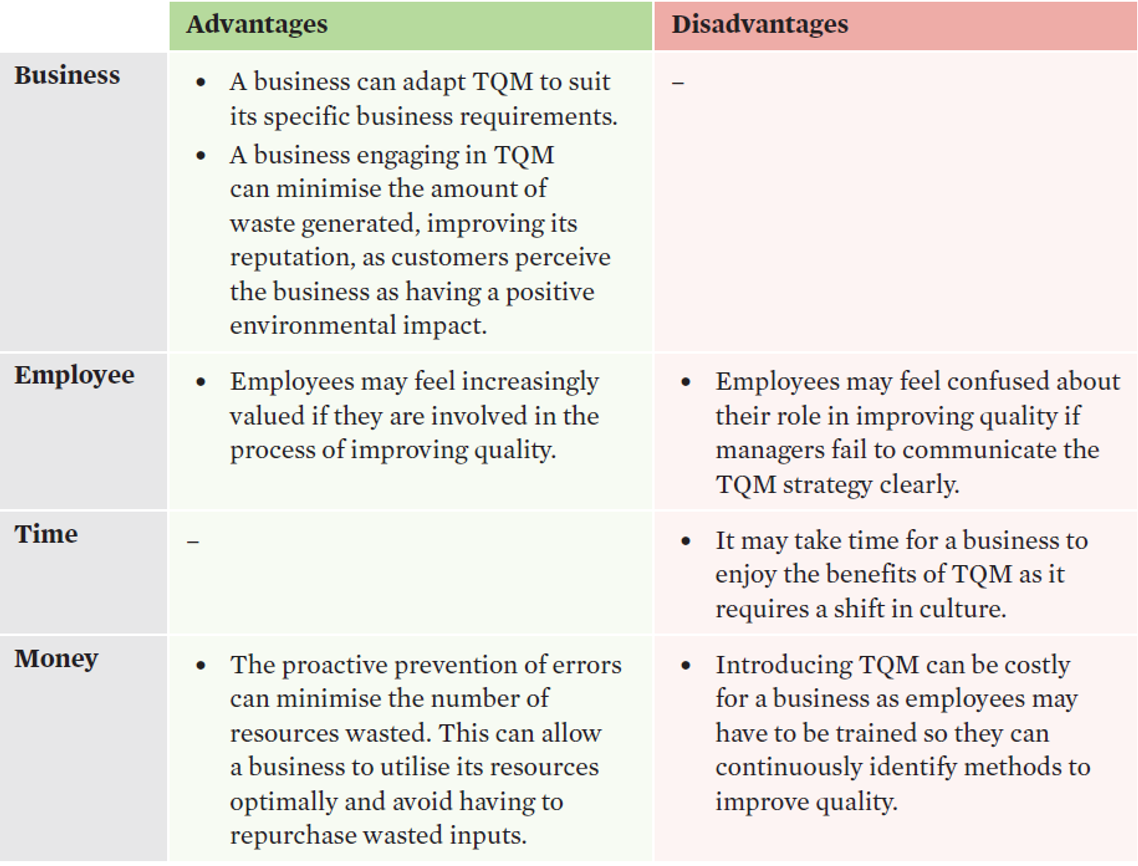
total quality management (TQM)
•a holistic approach whereby all employees are committed to continuously improving the business’ operations system to enhance quality for customers.
•In organisations that use this strategy, quality becomes both a commitment and the responsibility of every employee in the business.
Three pillars
1.Employee Empowerment
•Employees are placed into ‘quality circles’ to improve employee involvement – these teams meet regularly to solve problems related to operations.
2.Continuous improvement
•A process that involves a constant evaluation of, and improvement in, the way things are done in a business.
•organisations strive to keep improving their product or service – there is no ‘final’ level of quality to be reached.
3.Customer focus
•In theory, all employees are accountable to customers, and meeting their needs is the main focus.
TQM evaluation
comparison of quality management strategies
waste minimisation
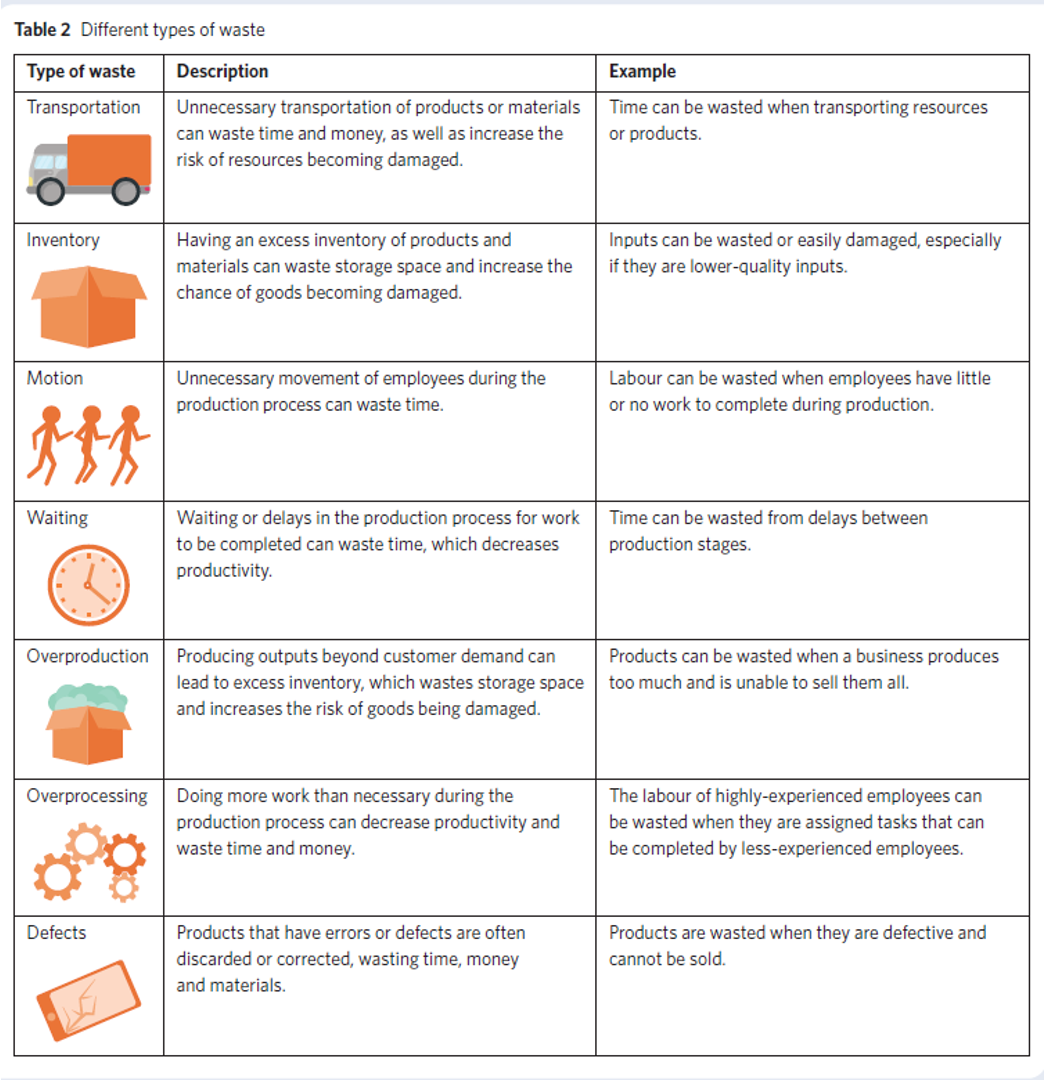
the process of reducing the amount of unused material, time, or labour within a business.
This may include reducing the amount of defective, unused, returned or discarded materials.
Waste minimisation strategies include:
•reducing waste at the source
•redesigning products and packaging
•procurement of materials made from recycled materials
•reusing scrap material
•improving quality control
•exchanging waste with other businesses
•recycling waste materials
TIMWOOD types of waste
reduce
•aims to decrease the amount of resources, labour, or time discarded during production.
•E.g. review and select the optimal transport routes for the distribution of products. This will reduce the amount of time and fuel wasted.
reuse
•aims to make use of items which would have otherwise been discarded.
•E.g. reusing storage items such as, cardboard boxes or plastic containers which can save on costs for the business.
recycle
•aims to transform items which would have otherwise been discarded.
•E.g. recycling plastic by transforming them into other plastic products such as, table and chairs.
Lean management
the process of systematically reducing waste in all areas of a business’ operations system to improve efficiency and effectiveness whilst simultaneously improving quality and therefore, customer value.
•Pull
•One-piece Flow
•Takt
Zero Defects
Pull strategy
•a lean management strategy that involves customers determining the number of products a business should produce for sale.
•For example, a bakery making a birthday cake when it is ordered.
•Whilst the application of pull can reduce a business’ materials wastage, it also enables it to optimise its use of labour resources, leading to increased productivity.
one piece flow strategy
a lean management strategy that involves processing a product individually through a stage of production and passing it onto the next stage of production before processing the next product, continuing this process throughout all stages of production.
This largely relates to eliminating waiting time or idle time.
A business that implements one-piece flow can quickly deliver products to customers as one product moves through each stage of the entire production process without delay.
Takt strategy
•a lean management strategy that involves synchronising the steps of a business’ operations system to meet customer demand.
•This refers to the rate of production needed to meet customer demand.
•Takt time is the average time that passes between production starting on one unit of a product and the start of production of the next unit, in order to meet demand.
•Business that applies takt ensures there is a continuous pace in its operational processes, allowing it to keep up with customer demands. To achieve a continuous pace, the output of one production stage is transferred to the next step in a timely manner.
zero defects strategy
a lean management strategy that involves a business preventing errors from occurring in the operations system by ensuring there is an ongoing attitude of maintaining a high standard of quality for the final output.
When a business finds a defect in its operations system, production is halted so that the error is not passed on to the next stage of the production process.
The business then identifies and fixes the error to prevent any further defects from occurring in the future.
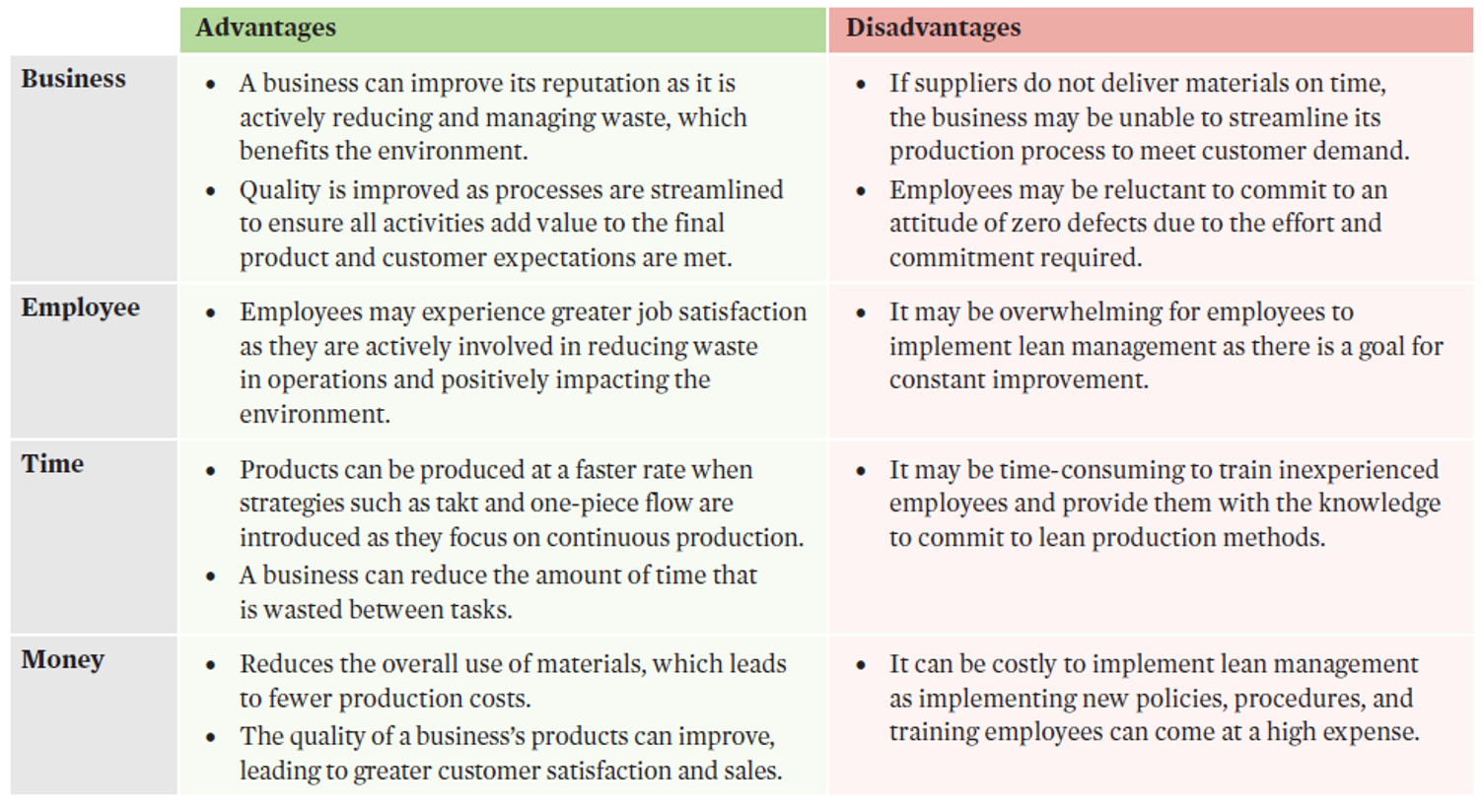
lean management and efficiency and effectiveness
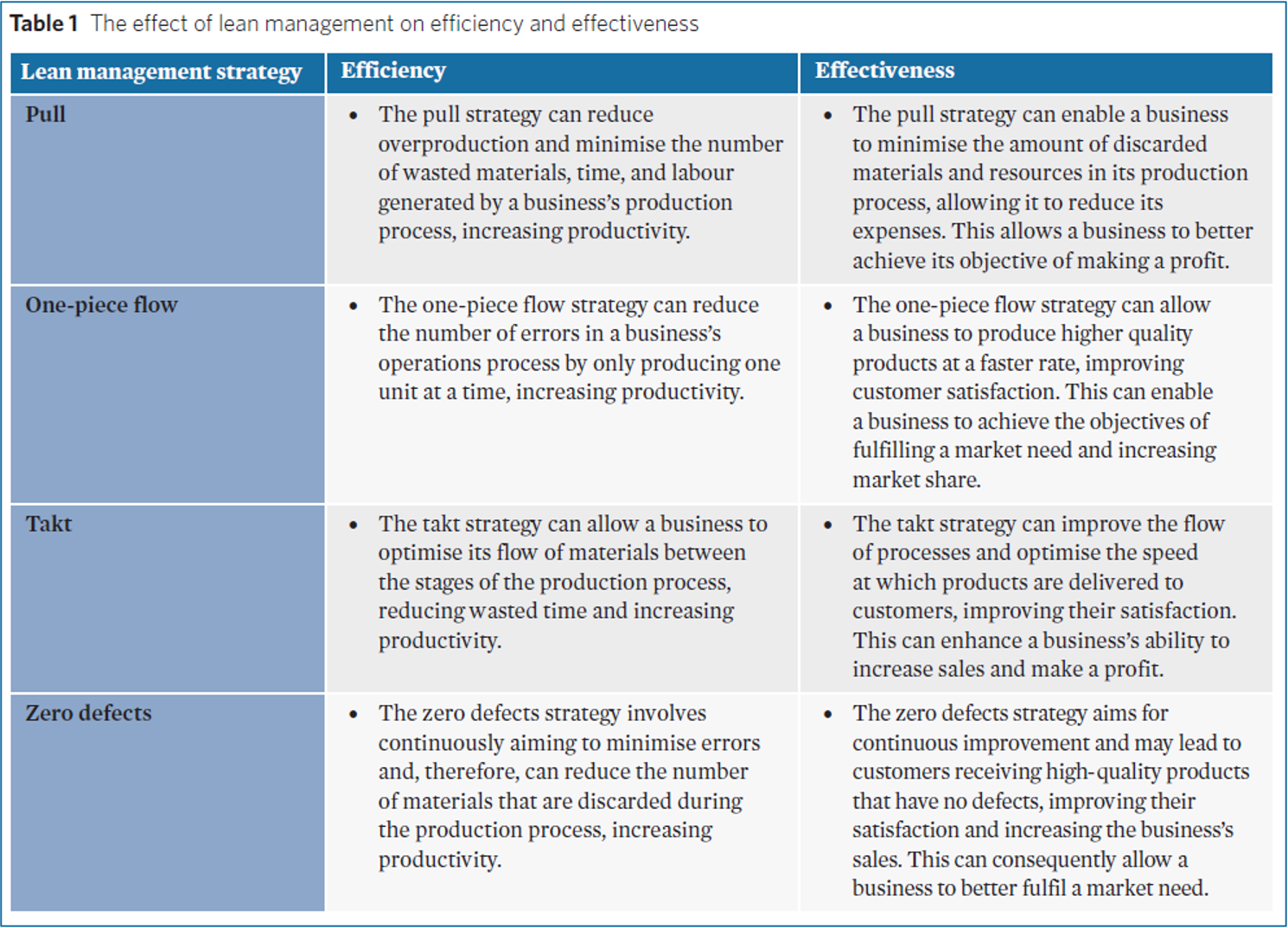
Lean management evaluation
corporate social responsibility (CSR)
•the ethical conduct of a business beyond legal obligations, and the consideration of social, economic, and environmental impacts when making business decisions.
•When managing an operations system, a business can choose the quickest and cheapest methods of producing its goods in order to increase profitability.
•However, a business that utilises the most cost-effective practices may negatively affect the general community and the environment.
•To ensure it is operating in an ethical manner, it is important for a business to address CSR considerations, such as the environmental sustainability of its inputs and the amount of waste generated in its processes and production of its outputs.
CSR considerations for inputs
•When sourcing materials and resources from suppliers, a manager should consider how the business can improve the environmental sustainability of its inputs.
•Strategies that a manager can implement to demonstrate CSR considerations relating to the environmental sustainability of inputs include:
•Sourcing inputs locally, rather than from overseas suppliers, to reduce transport emissions and minimise the business’ carbon footprint.
•Sourcing inputs from suppliers that use environmentally-sustainable methods when extracting and harvesting natural resources.
•Implementing operations strategies, such as forecasting and just in time, to reduce the risk of over-ordering inputs that may later be discarded due to expiry or damage.
•Purchasing energy-efficient machinery for production.
Installing reusable, renewable, and/or clean energy sources in the business.
CSR considerations for processes
•By implementing processes that are socially responsible, a business can reduce waste and enhance its overall reputation, therefore improving both efficiency and effectiveness.
•Strategies that can minimise the amount of waste generated from processes include:
•Using technology that performs tasks in a precise and consistent manner to reduce the number of defective products discarded in production.
•Developing methods to capture and recycle unused or excess input materials, allowing them to be reused in the operations system.
•Implementing operations strategies, such as Just in Time and lean management, to reduce the number of materials being unnecessarily wasted.
•Disposing of any harmful waste that cannot be treated, in a responsible and safe manner.
•Developing policies that promote the efficient use of energy in the workplace, such as switching off all machinery and lights after use.
•Training employees on how to minimise waste when executing production tasks.
CSR considerations for outputs
•One of the most important CSR considerations is that any output produced by a business’ operations system creates minimal waste and environmental damage without impacting quality.
•Strategies that a business can implement to minimise the amount of waste generated from its outputs include:
•Developing an alternative product that is more environmentally friendly than the business’s current good or service.
•Creating products that have recyclable or biodegradable elements at the end of their lifecycle.
•Eliminating as much plastic as possible in the packaging and creation of the final product.
•Delivering products to retailers in bulk to reduce the business’s carbon emissions from transportation.
•Offering customers incentives for returning the product at the end of its life cycle so that it can be properly recycled or reused.
Providing clear labelling on a product about appropriate methods of disposal.
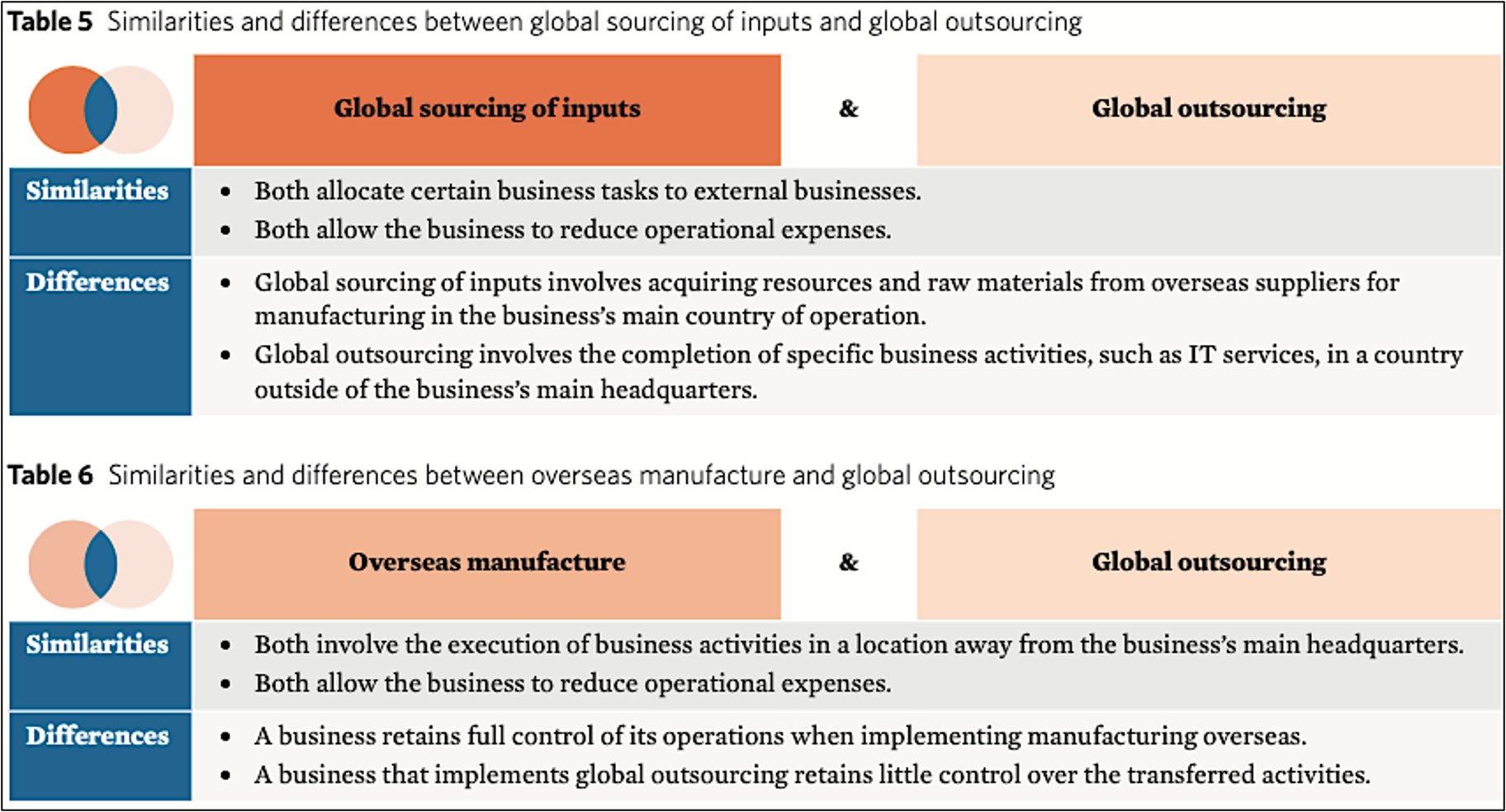
global sourcing of inputs
the practice of seeking the most cost-efficient materials and other inputs, including from countries overseas.
This may be beneficial to a business as they exploit efficiencies such as low-cost skilled labour, low-cost raw materials, lower taxes, lower tariffs due to free trade agreements.
When choosing to source its inputs globally, a business should consider several factors that may affect its expenses and reputation, including:
•Price of materials and resources
•Delivery costs between different countries
•Environmental impact used by suppliers to extract inputs
•Supplier’s treatment of workers e.g., pay, working conditions, whether they operate in an ethical and socially-responsible manner
Government regulations i.e., tariffs and quotas
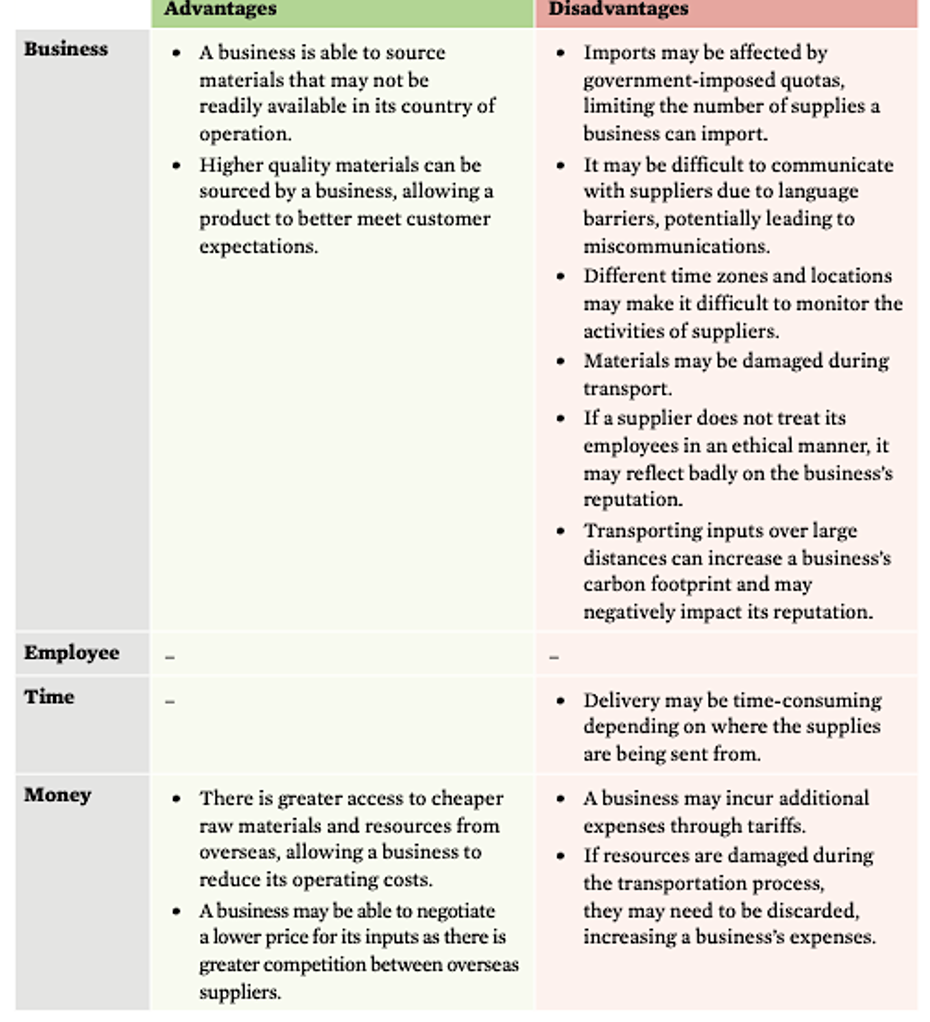
global sourcing of inputs evaluation
overseas manufacture
involves a business producing goods or services outside of the country where its headquarters are located.
This is also known as offshoring.
Businesses must carefully choose where to manufacture, considering areas such as; political stability, costs, ease of getting the product to market more quickly, production costs and delivery time.
Many businesses choose to manufacture overseas to reduce labour, overhead and component costs, but keep R&D, design and short-run manufacturing in Australia.
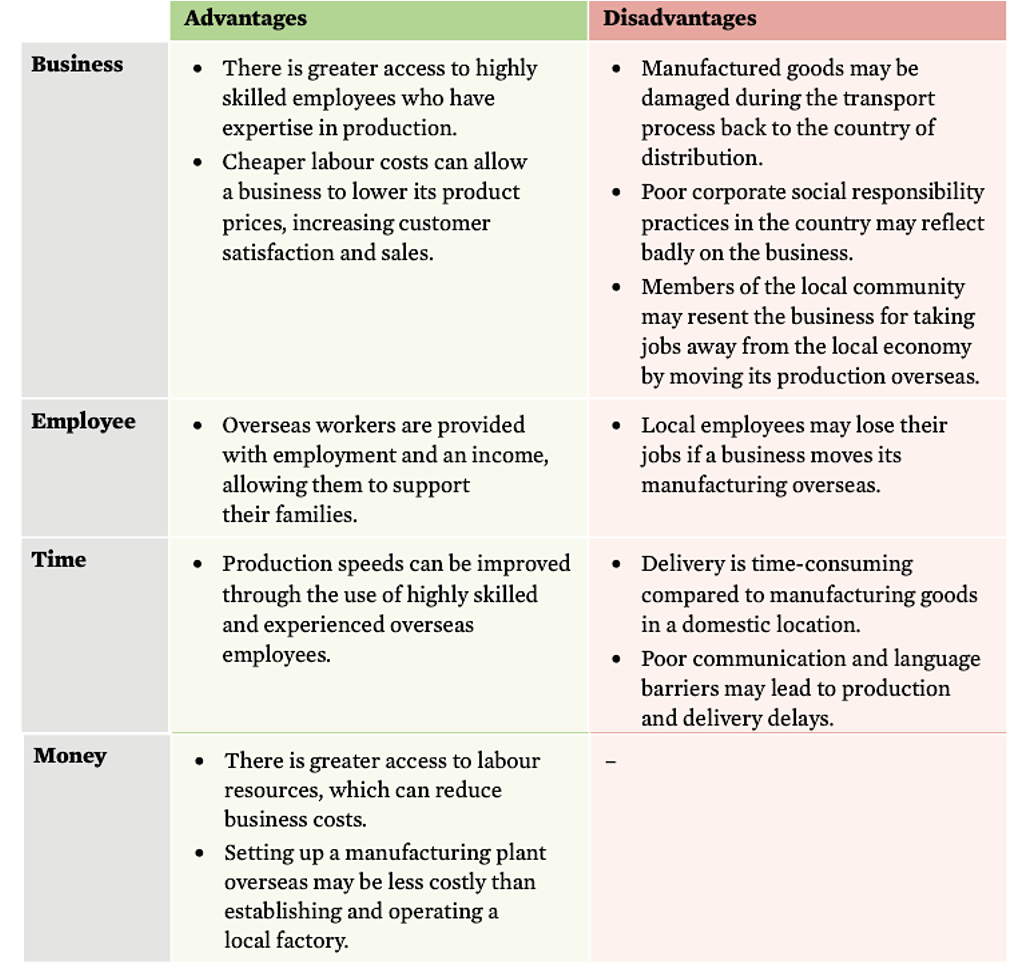
overseas manufacture evaluation
global outsourcing
•involves transferring specific business activities to an external business in an overseas country.
•Generally, businesses outsource areas that are not part of their core business. E.g., QANTAS outsources its IT to several businesses overseas.
•Global outsourcing means the business operations can be contracted out to countries all over the world.
•Many people disapprove of sending tasks overseas because of the negative impact on local employment and local suppliers.
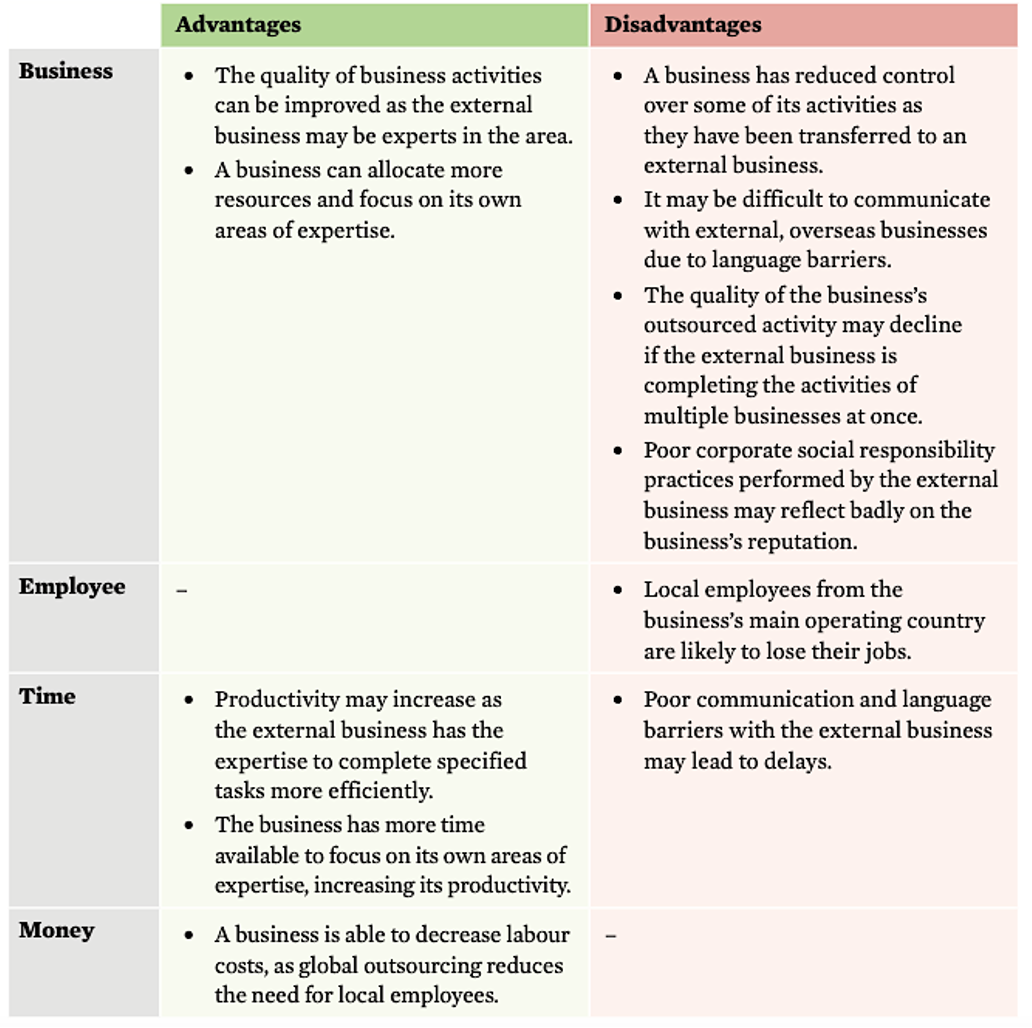
global outsourcing evaluation
comparison of global considerations