History and Future of Telescopes: From Hubble to Webb
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Hans Lippershey
First inventor of the telescope, patented in 1608.

Refracting Telescope
Uses lenses to bend light for magnification.
Galileo Galilei
First to use telescope for astronomy in 1609.

Keplerian Telescope
Features convex lenses for improved magnification.
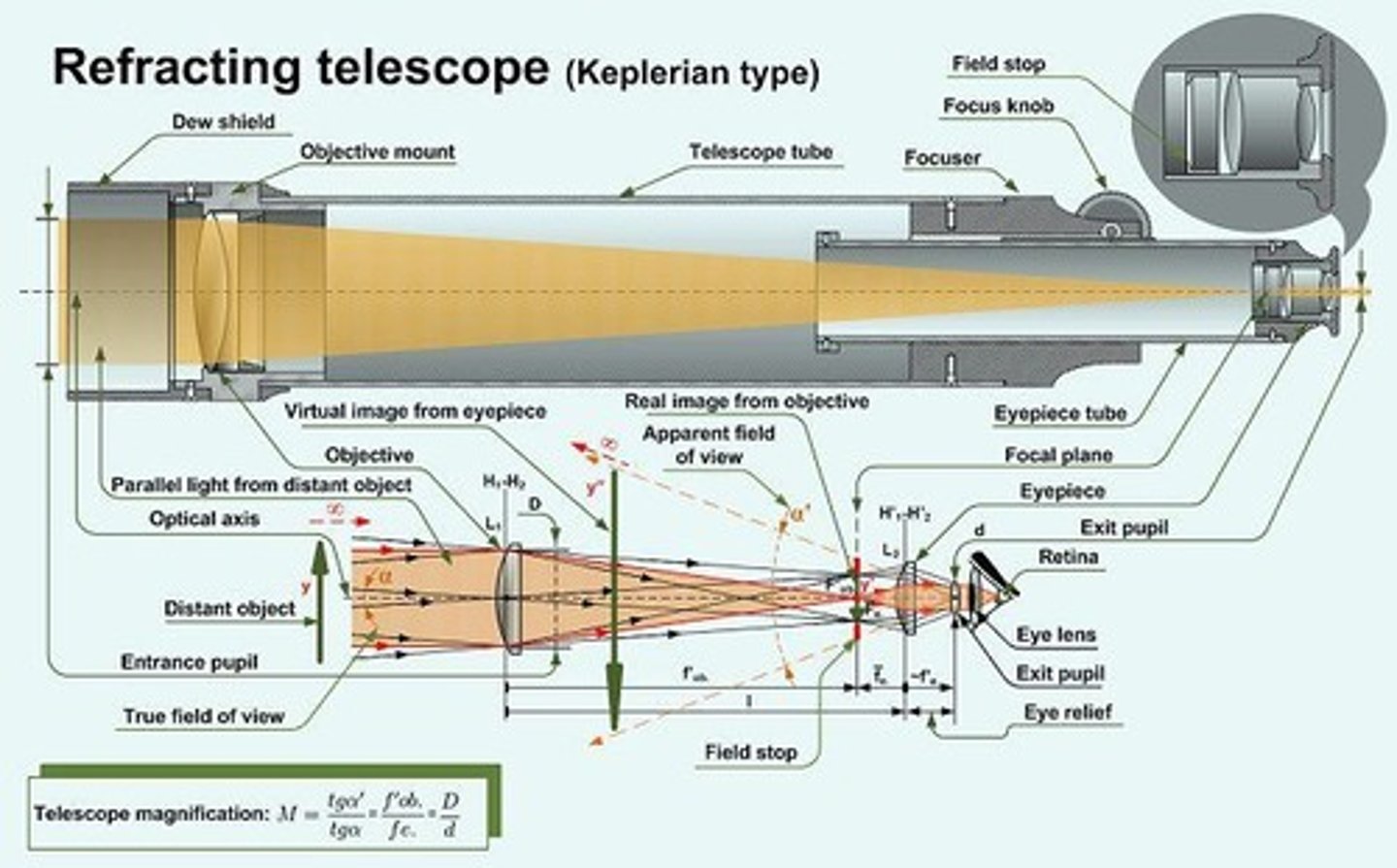
Johannes Kepler
Developed Keplerian telescope design in 1611.
Isaac Newton
Built first usable reflecting telescope in 1668.
Reflecting Telescope
Uses mirrors to gather and focus light.
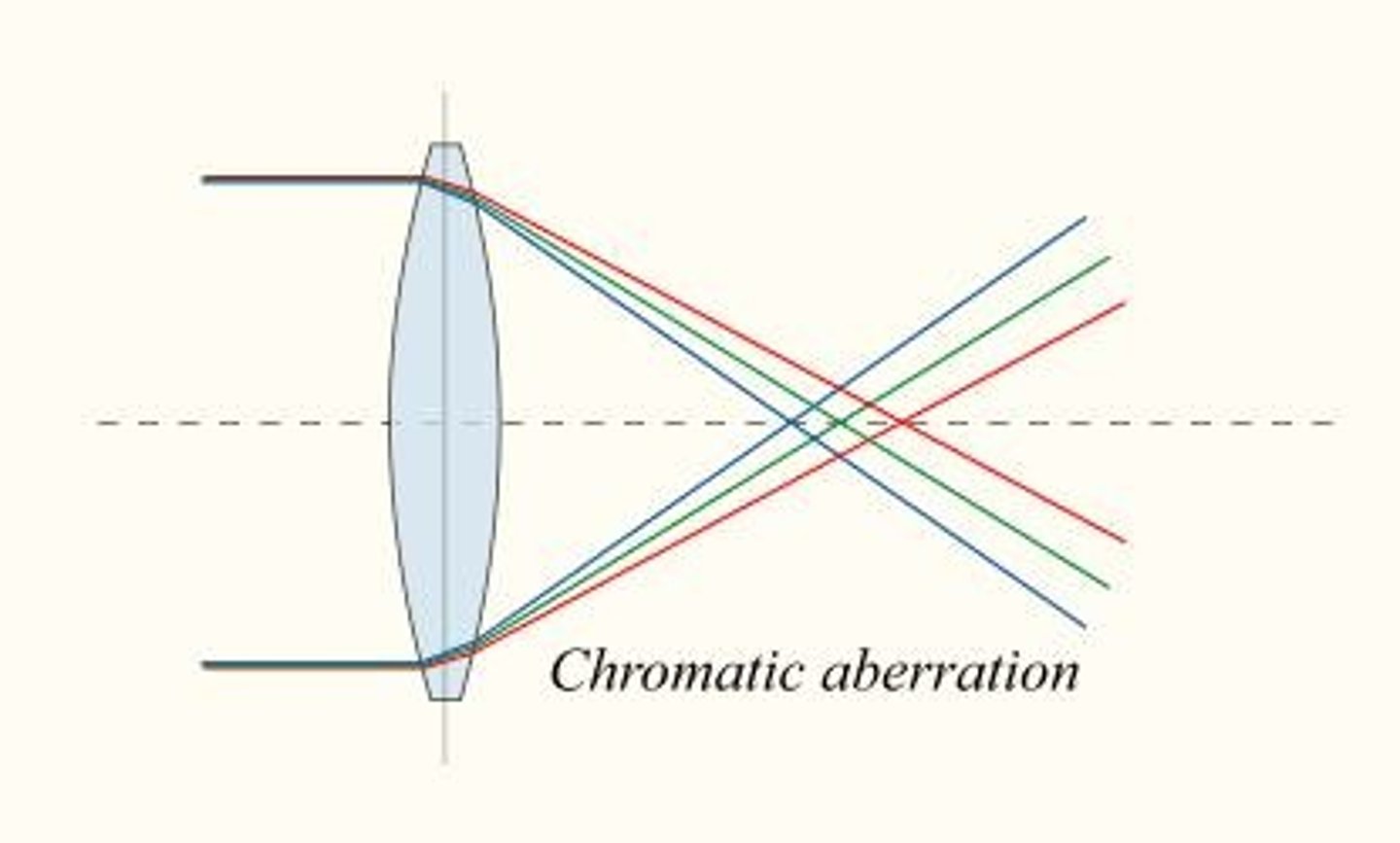
Chromatic Aberration
Distortion from lens failing to focus all colors.
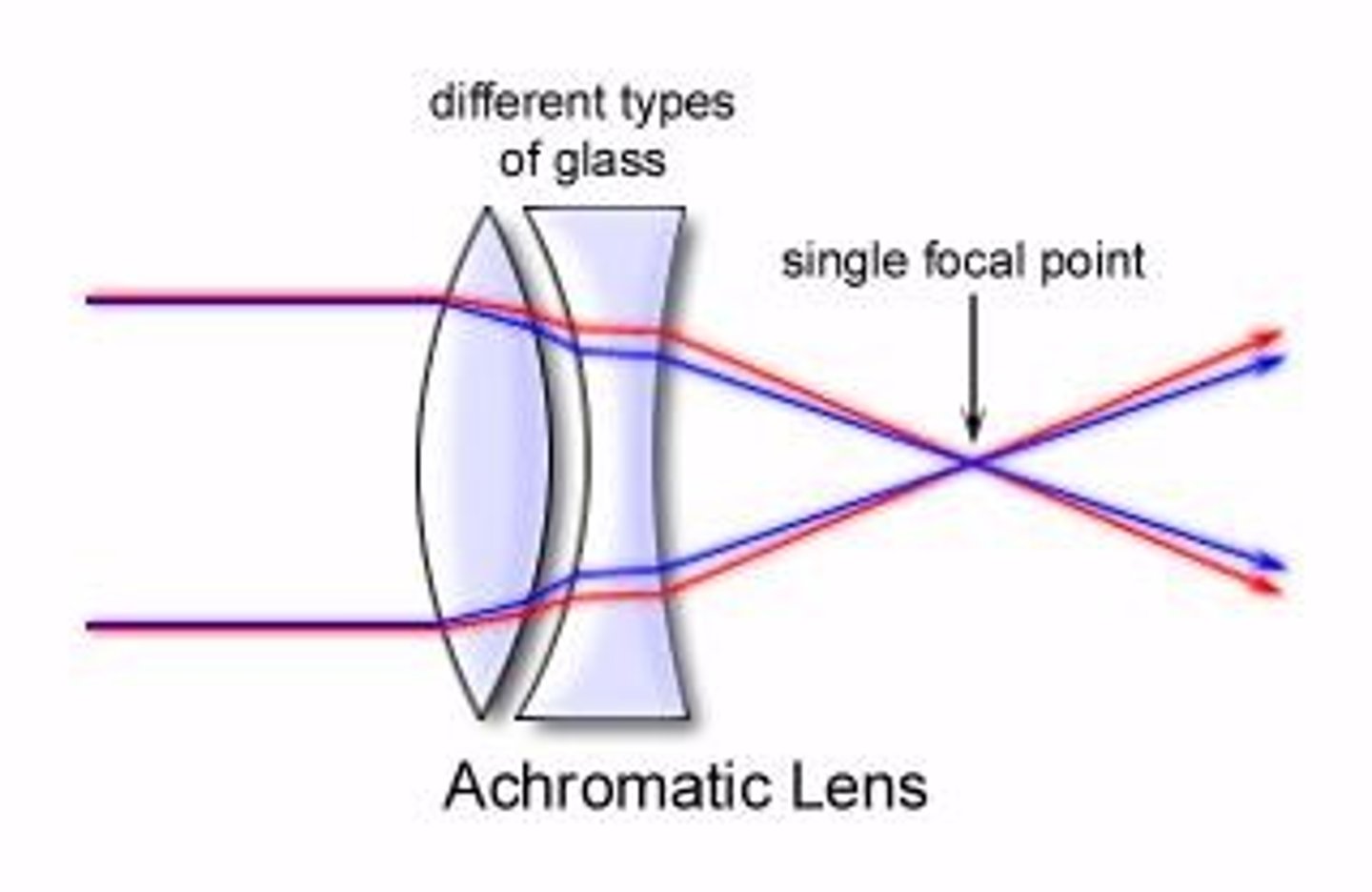
Achromatic Lens
Reduces chromatic aberration using multiple glass types.
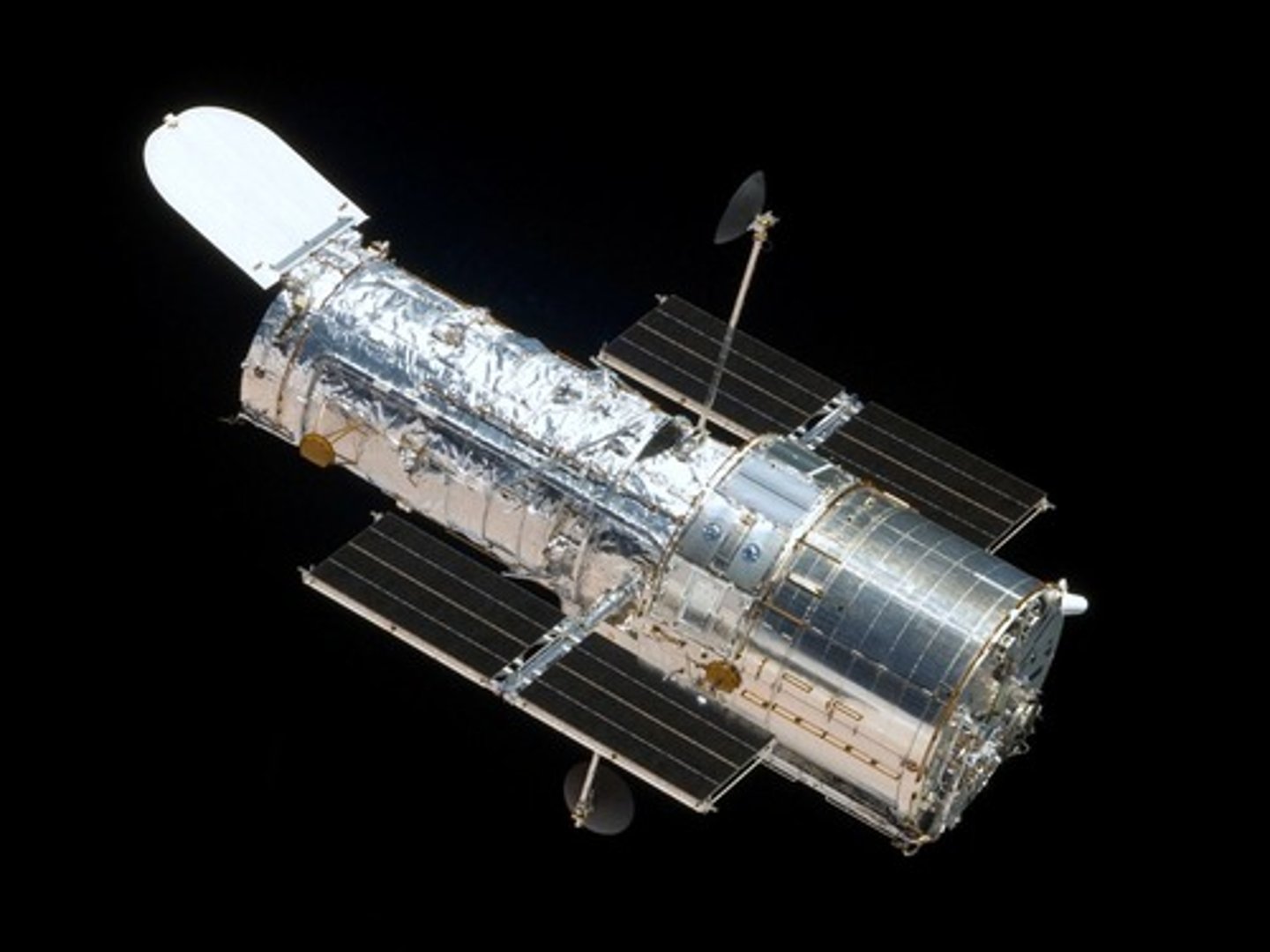
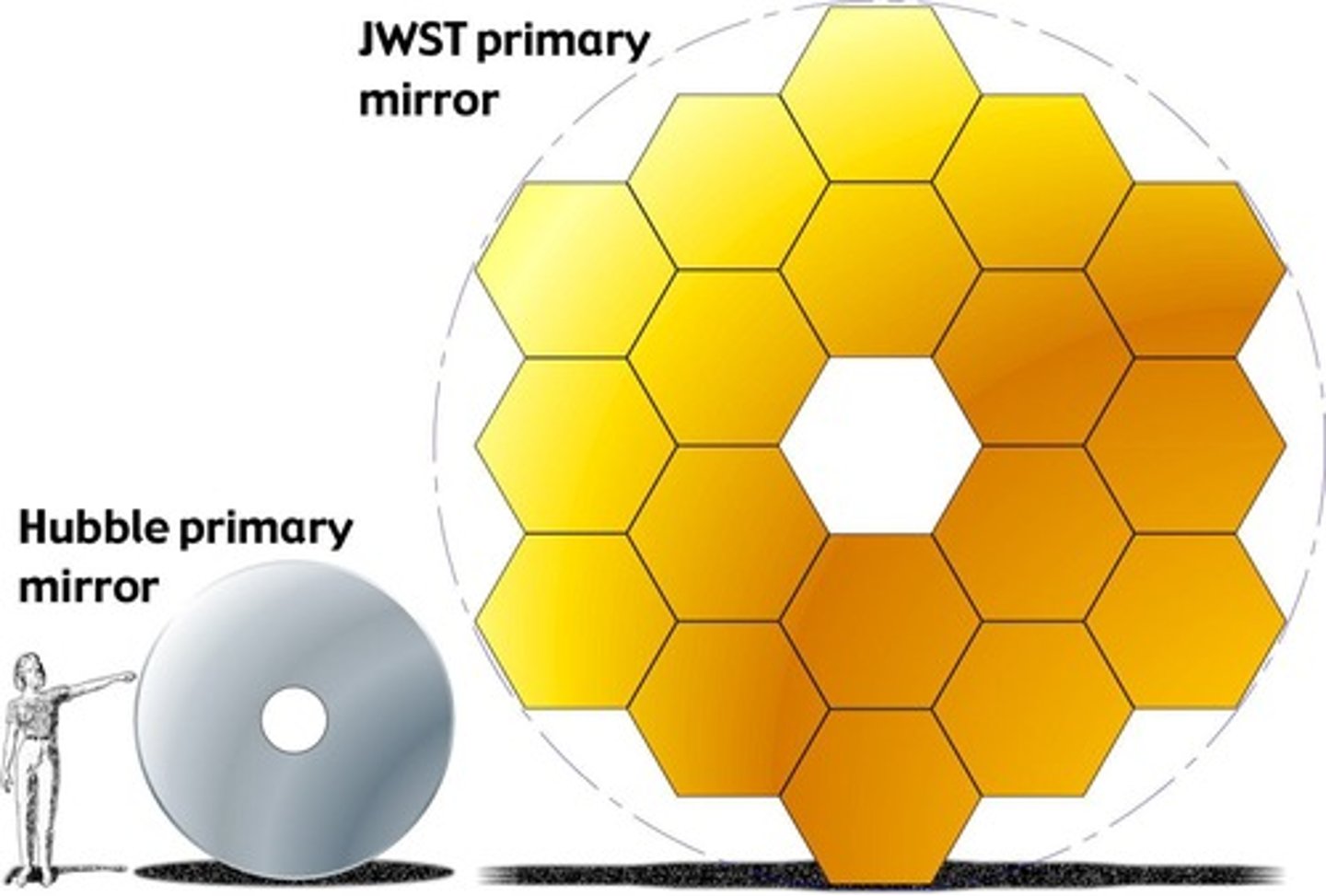
Hubble Space Telescope
Launched in 1990, orbits Earth at 380 miles.

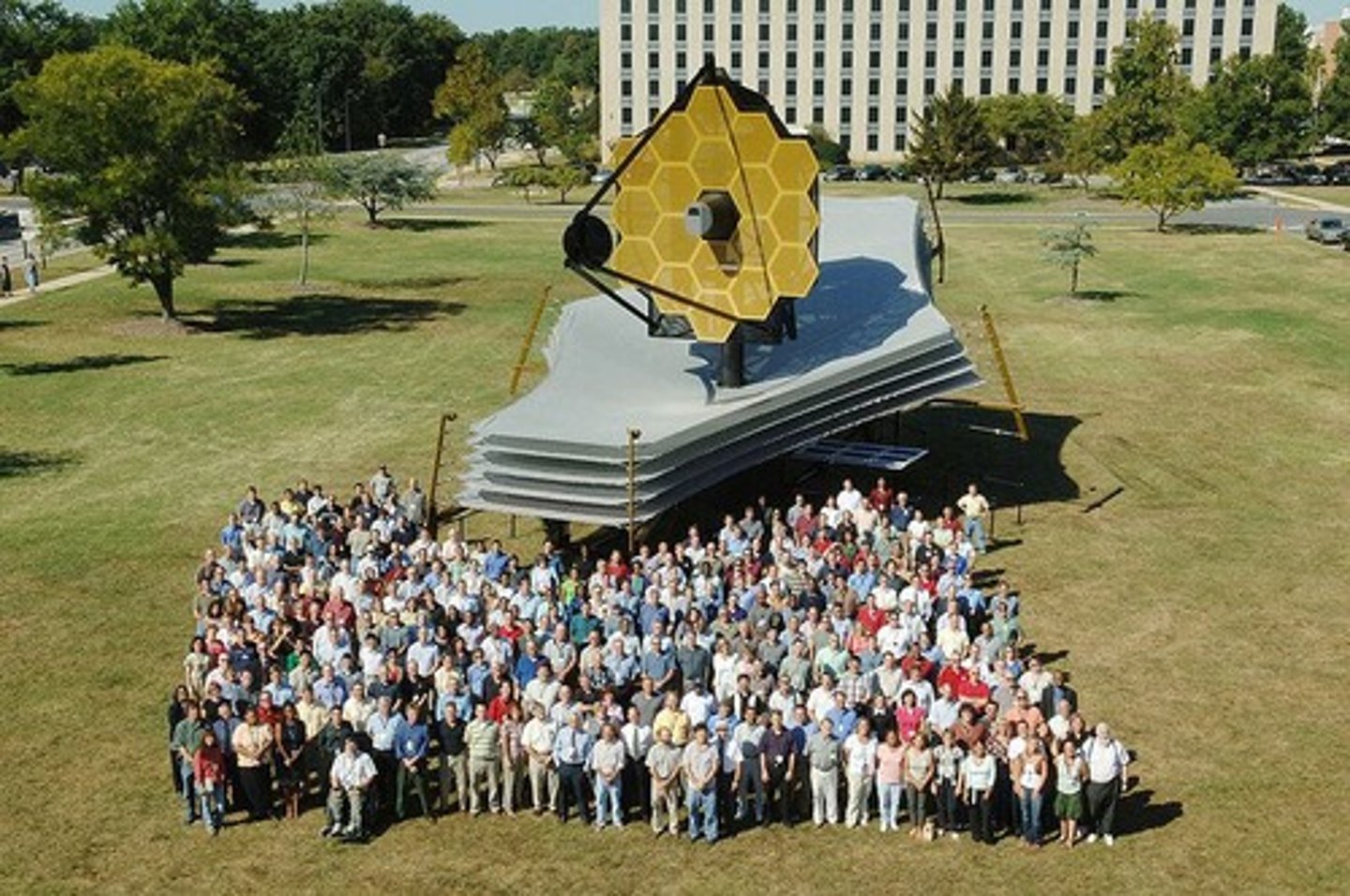
James Webb Space Telescope
Space-based observatory optimized for infrared wavelengths.

Infrared Wavelengths
Longer wavelengths allowing deeper space observation.
Lyman Spitzer
Introduced concept of space observatories in the 1940s.
NASA and ESA
Collaborated to design Hubble Space Telescope.
Mission Lifetime
Webb aims for over 10 years operational life.
L2 Point
Webb's operational location, 1.5 million km from Earth.
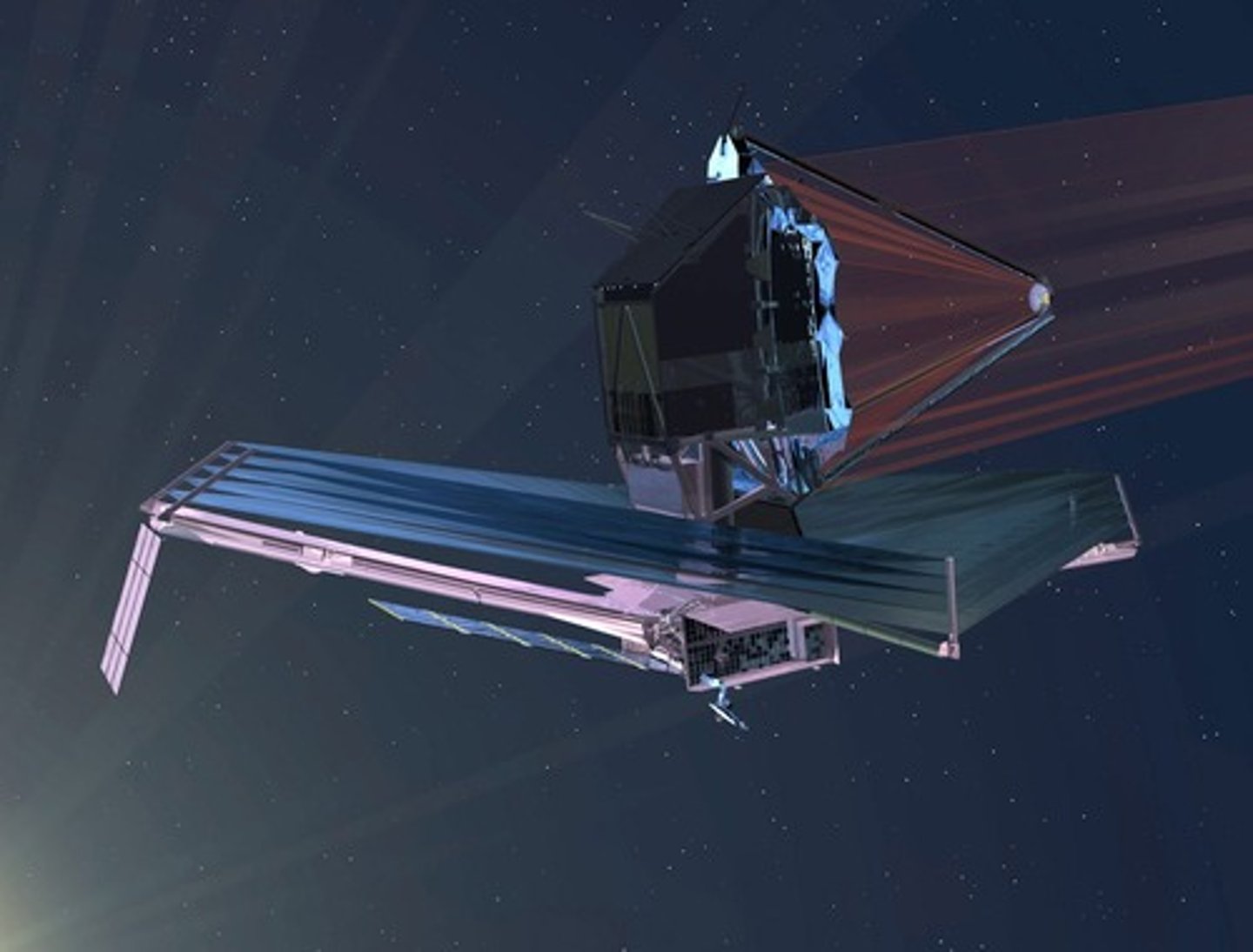
Primary Mirror Size
Webb's mirror is 6.5 meters in diameter.
Sunshade Size
Webb's sunshade is roughly tennis court-sized.

Communication System
Uses high frequency radio for data transmission.
Deep Space Network
Receives signals from Webb for data processing.
Cooling Requirement
Webb operates below 50 Kelvin for infrared observations.
Servicing Challenges
Webb is too far for current servicing missions.
Mass of Webb
Approximately 6,500 kg, half of Hubble's mass.
Light Collecting Area
Webb has 7 times Hubble's light-gathering capacity.
Astronomical Observations
Focus on faint, distant objects in infrared.
Commissioning Period
Lasts 6 months post-launch for system checks.
First Galaxies
Webb aims to observe early universe galaxy formation.
Dust Clouds
Webb studies star and planet formation in dust.