Zebrafish Biomedical Hatchery Exam Questions
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are the 5 freedoms?
Freedom from hunger and thirst
Freedom from discomfort
Freedom from pain, injury or disease
Freedom to express normal behaviour
Freedom from fears and disease
3 R’s of Animal Research:
replacement, reduction, refinement
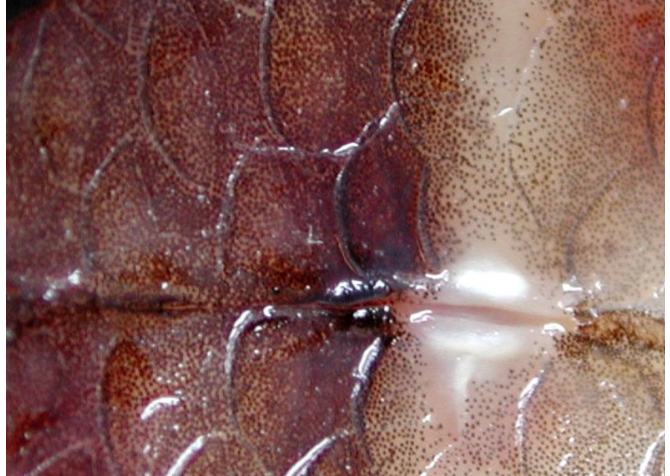

Cycloid scales (zebra fish)

Ctenoid
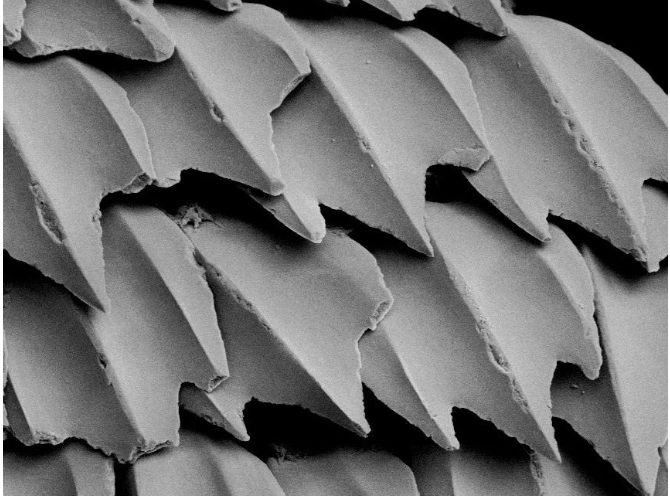
Placoid scales
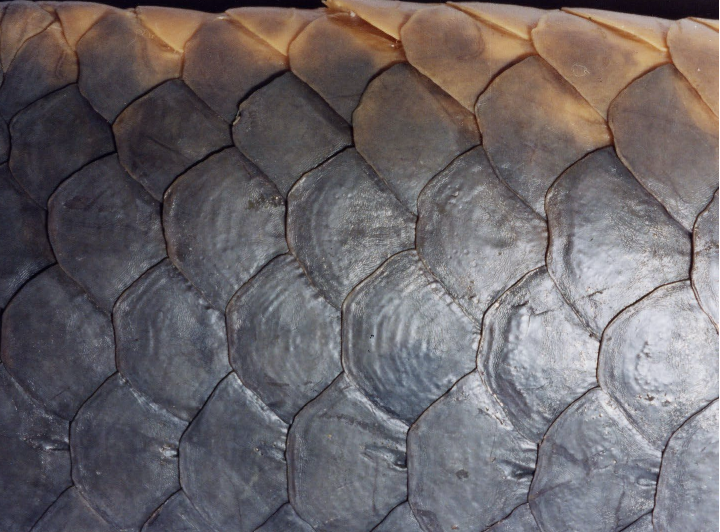

Cosmoid scales

Ganoid scales
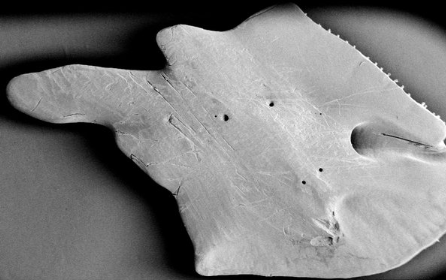
Ganoid scales
Turbitity
water clarity vs. light penetration
The limit for unionized ammonia for salmonids is…
0.125
Oddity effect:
Fish that look different are more likely to be targeted by predators
Shoal:
Group of fish staying together but they do their own thing. (swimming opposite directions)
School:
A shoal that swim in a synchronized way is a….
DPF means?
Days post fertilization
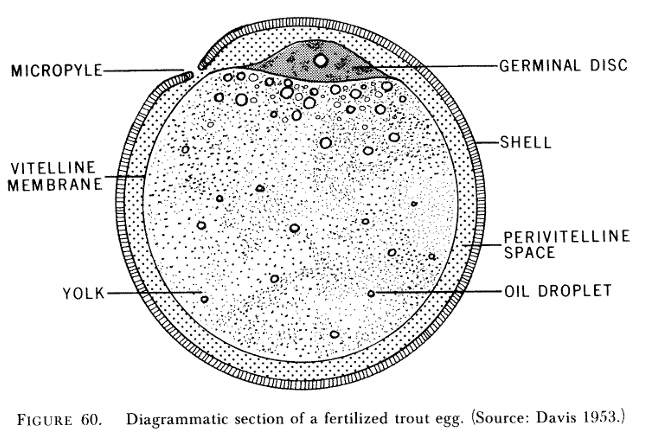
How many ways can sperm enter a rainbow trout egg?
1
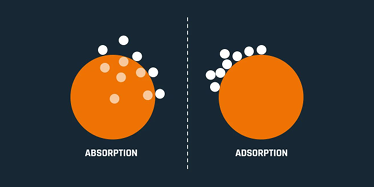
What is the difference between adsorption and absorption?
•Absorption involves molecules being drawn into the material's structure
•Adsorption involves molecules adhering to the surface.
What is the purpose of a treatment?
To reduce the population of disease agents to a level where the fish immune system can handle it. Basically it helps the fish cure itself
Prophylactic:
prevents outbreaks of disease before signs observed
Therapeutic:
After signs of disease are shown
Fin erosion:
anything not related to disease that causes deformed fins. (aggersion, fin rubbing)
Fin Rot:
disease related that causes deformed fins
What is a good spawning time for zebra fish?
Monsoon season
How often can zebrafish reproduce?
Every few days
How many eggs per spawn?
hundreds of eggs per spawn (200-300)
What makes a zebrafish a good research fish?
easier egg visibility, shell removal is simple, affordable, reproduce rapidly, and grow 30x faster than human embryos (70% similar to humans)

How can you tell the difference between male and female?
Males: torpedo-shaped, skinny, golden stripes, pinkish hue, orange colouration on anal fin, tubercles
Females: bulbous (round), silver stripes, white belly and yellow tint to fins
How to get more males or females?
Males: Low DO, high levels of cortisol during differentiation
Females: Low density, abundant food,
What type of research are zebrafish known for?
cancer and genetic studies
what are the strains of zebrafish?
AB: common lab strain, easy to breed- few mutations
TU: genome reference strain - has behavior and immune deficiencies
WIK: Wild caught from India
SJA: inbred AB line, uniform genetics
Glo fish: fluorescent - used for gene assessment and marking
When do zebrafish start feeding? and what type?
through the water column, Zebrafish begin feeding a few days after swim-up, once the yolk sac is absorbed, and they require zooplankton such as rotifers and brine shrimp
Do zebrafish swim up?
Yes
What are the 3 types of zebrafish housing?
Centralized system (one water reservoir w racks)
distributed systems: multiple reservoirs serving different racks
Stand Alone Systems: Each rack has its own filtration and reservoir
What makes a distributed system unique?
it has more than 1 filter
What would you do if you get chlorine in your system?
prevent, get rid of chloramine with sulfur (since it doesn’t gas off)
Ethical Euthanasia
loss of equilibrium (anesthetic)
method that ensures brain death (pithing)
Types of anesthia
MS-222 (Tricaine): Most common vet-approved anesthetic with rapid recovery but is acidic and may need buffering.
Eugenol (Clove Oil / Aqui-S): Requires a lower dose than MS-222 and causes less stress but recovery takes longer and approval varies.
Benzocaine: Similar to MS-222 with slightly longer recovery but is less water-soluble and more stressful for zebrafish.
Metomidate (Aqua-Calm): Used to reduce handling stress, induces anesthesia quickly but has long recovery and causes muscle twitching.
Lidocaine: Provides rapid induction and recovery for surgery but has a very small safety margin.
Propofol: Very fast and short-acting anesthetic that must be used within 30 minutes because it is not fully water-soluble.
Gradual Cooling (Hypothermia): Lowers zebrafish to ~10°C for temporary anesthesia but is unsafe for long durations or surgical procedures
Preferred habitat for zebra fish
slow moving or stagnant water, highly adaptable depths of 1-5cm
Egg and embryo…
develop rapidly (within 2 days they swim up)
Spine deformities
Platyspondly - football
Lordosis - up/down
Kyphosis - humpback
scoliosis
Microsporidians
Pseudoloma neurophilia- Infects brain, spinal cord, nerves; can affect muscle, kidney, and ovaries.
Pleistophora hyphessobryconis- infects muscle tissue heavily.
Dinoflagellate — Piscinoodinium pillulare (“Velvet”): Yellow/velvet-looking coating; infects skin + gills.
Ciliate — Ichthyophthirius (Ich / White Spot):Causes white spots, mucus, flashing, lethargy.
Myxozoa — Myxidium streisingeri:Usually low impact; found in kidney tubules.
Nematode — Pseudocapillaria tomentosa: Long white intestinal worms; chronic mortality and emaciation.
Zebrafish embryos hatch within
4 days of fertilization
The yolk sac of Zebrafish is completely absorbed after
7 days after hatch
The temperature range ZF can handle is
6-38
Average life span of a Zebrafish is
4 years
Why are Zebrafish so popular for research? List 4
1. Embryology – we share 70% of genes with zebra fish and embryos grow 30 times faster
2. They have practical advantages such as they are small and affordable, reproduce often, and gene manipulation is simple
3. Rapid development – organs for within 2 days. Life cycle in general is quick
4. External fertilization allows us to actually observe and manipulate
Adding cold water to your ZF housing unit could induce spawning
true