Comprehensive Guide to Psychoactive Drugs: Names, Routes, and Effects on Brain and Behavior
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Psychopharmacology
Study of the ways drugs affect the nervous system and behavior
Chemical name
Describes a drug's complex molecular structure
Generic name
Name of the drug's active ingredient; often a shortened, simpler version of the chemical name
Brand name
Unique trademarked name given by the manufacturer
Blood Plasma
The liquid component of your blood; contributes to 55% of your blood's total volume
Absorption Rate
The time to reach maximum plasma concentration
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Endothelial cell walls in capillaries in the brain fit together tightly, forming 'tight' junctions
Astrocytes
Supportive cells in the brain that help maintain the blood-brain barrier
BBB-Free Brain Sites
Specialized brain regions where the BBB is weak or absent
Circumventricular Organ (CVO)
Specialized brain regions where the BBB is weak or absent, allowing communication with the blood
Metabolism
The process by which the body breaks down drugs into more water-soluble compounds for easier excretion
Cytochrome p450 enzyme family
Involved in the metabolism of drugs in the liver
Excretion
The process of eliminating metabolized drugs through urine, feces, sweat, breast milk, and exhaled air
Neurotransmission
The process by which neurotransmitters are released, activate receptors, and are removed from the synapse
Agonist
A substance that binds to a receptor and activates it, producing a biological response similar to the natural neurotransmitter
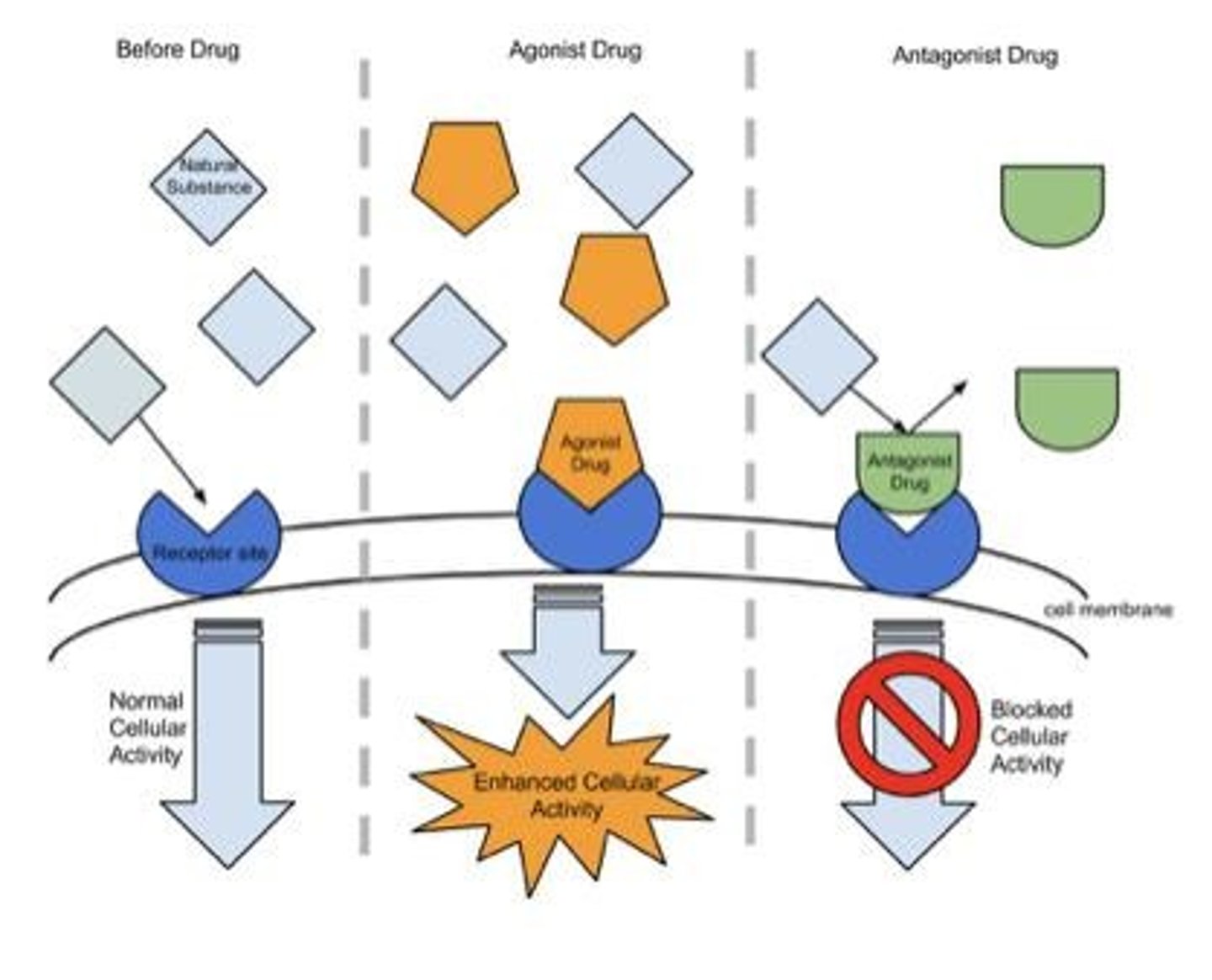
Antagonist
A substance that binds to a receptor but does not activate it, blocking or reducing the effect of the natural neurotransmitter
Competitive binding
Occurs at the neurotransmitter binding site where the drug competes with the neurotransmitter to bind to the receptor
Non-competitive binding
Occurs at an alternate binding site on the same receptor
Direct agonist
A type of competitive binding that directly activates the receptor
Direct antagonist
A type of competitive binding that directly blocks receptor activation
Indirect agonist
A type of non-competitive binding that enhances receptor activation
Indirect antagonist
A type of non-competitive binding that weakens receptor activation
Psychoactive drug
A chemical substance that changes the function of the nervous system and results in alterations of perception, mood, cognition, and behavior
Group 1
Antianxiety Agents and Sedative Hypnotics
Group 2
Antipsychotic Agents
Group 3
Antidepressants
Group 4
Opioid Analgesics
Group 5
Psychotropics
Behavioral Stimulants
A category of psychotropic drugs that enhance behavior.
Psychedelic and Hallucinogen Stimulants
Substances that alter perception and cognition.
General Stimulants
Drugs that increase alertness and energy.
Barbiturates
Indirect agonist of GABA-A receptors with sedative-hypnotic properties.
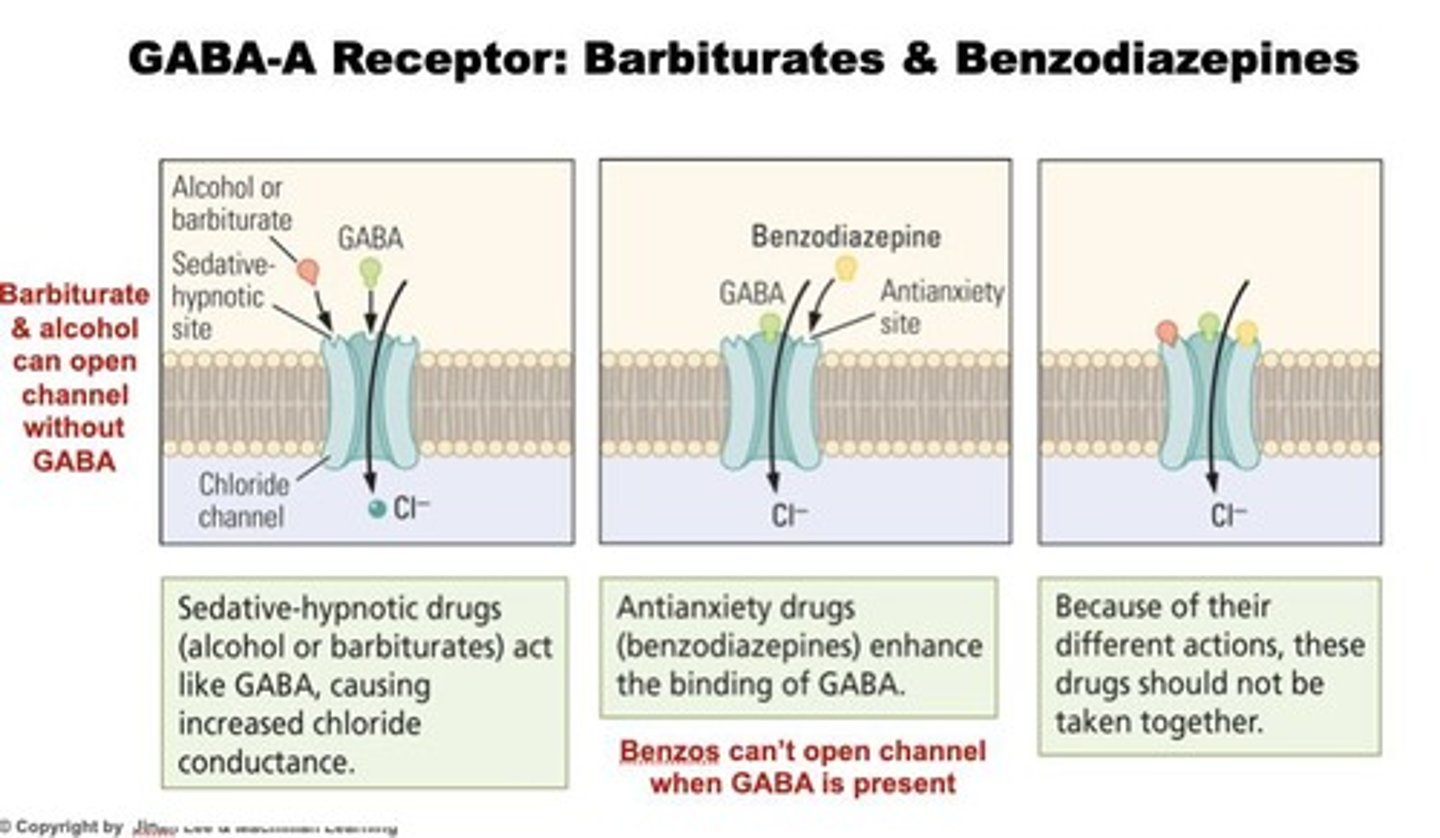
Benzodiazepines
Indirect agonist of GABA-A receptors with anti-anxiety properties.
Ketamine
Used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia or pain management.
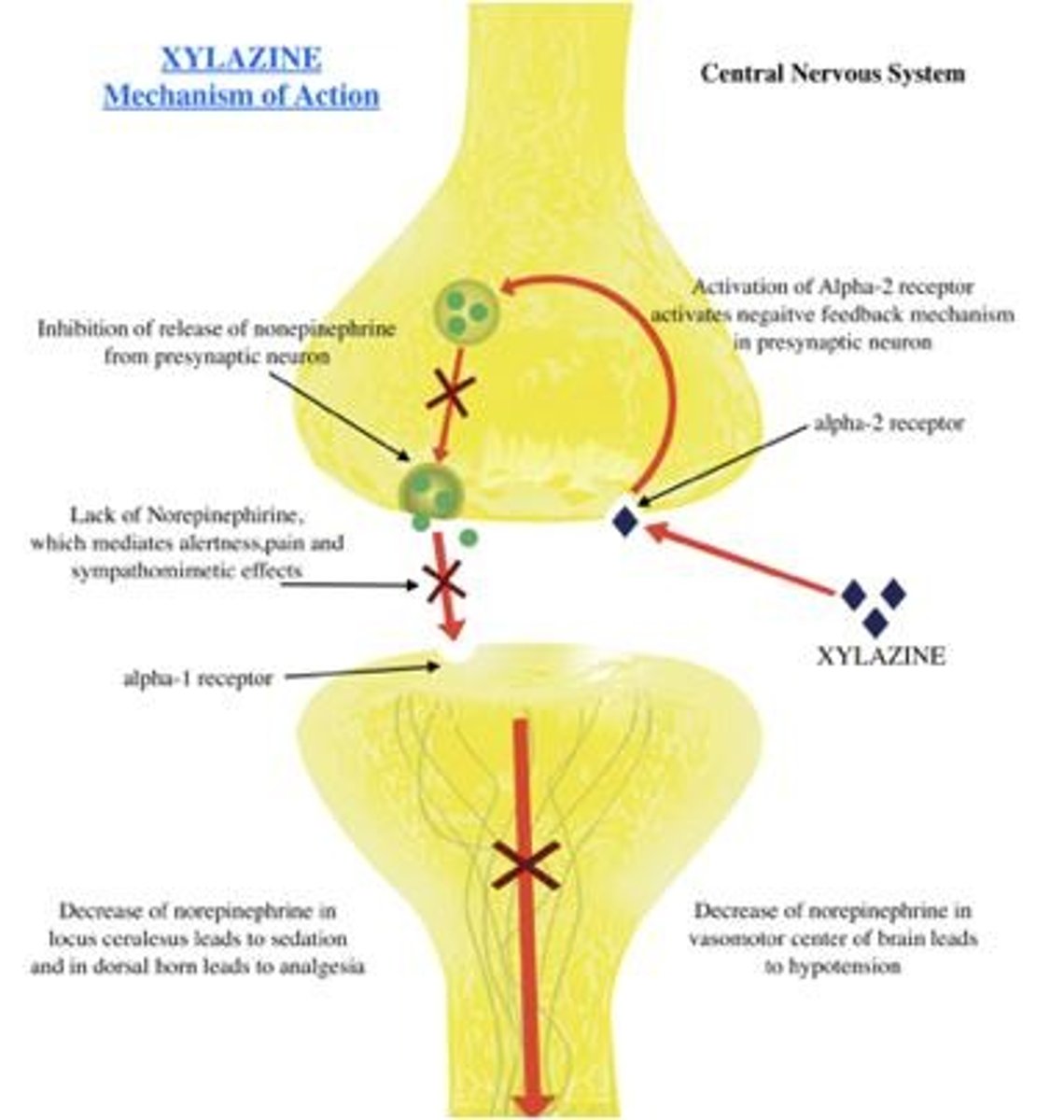
Xylazine
Nn-opiod sedative or tranq used for sedation, anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and analgesia in animals.
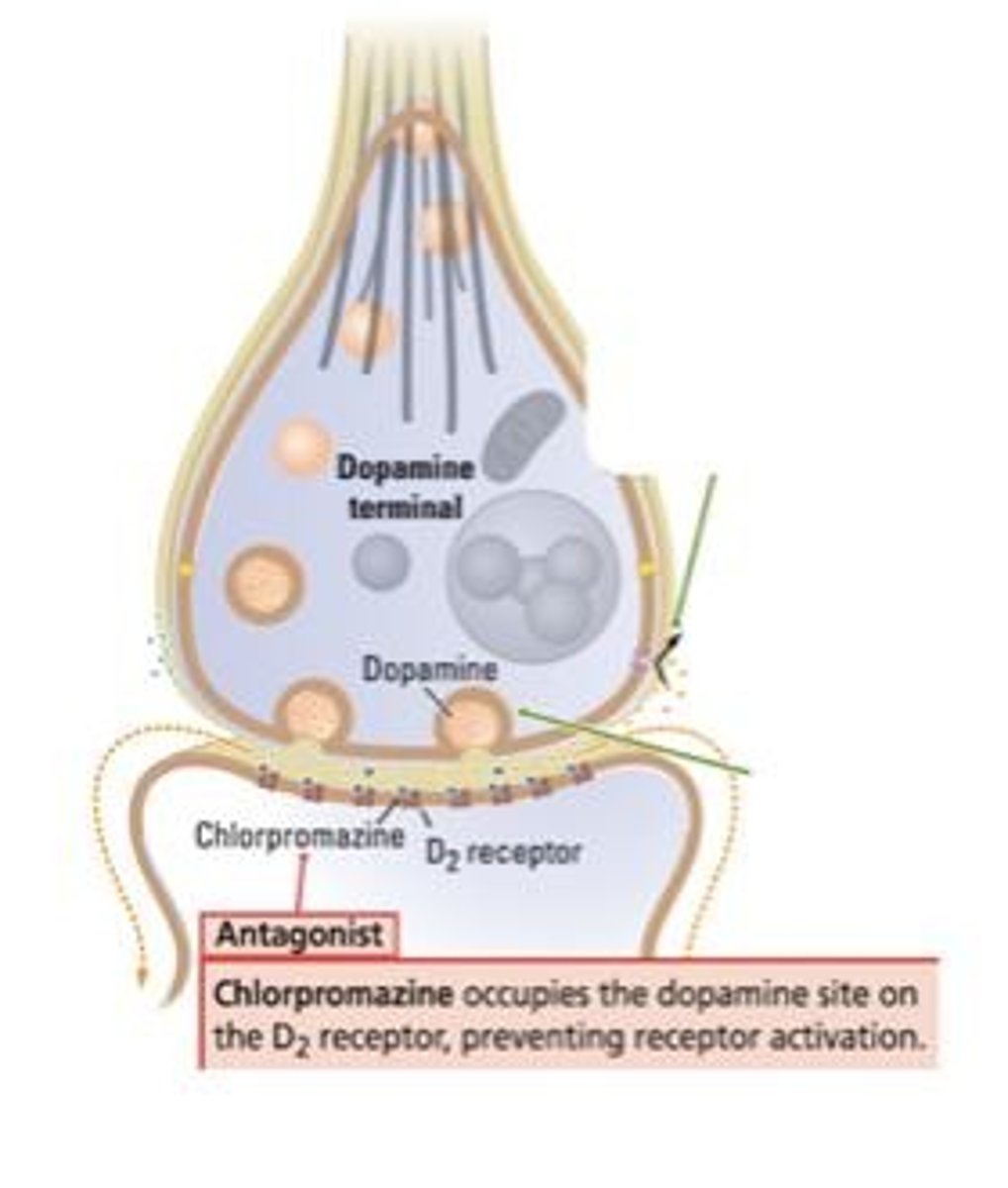
Antipsychotic Agents
Type of psychoactive drugs to treat psychosis.
Psychosis
A mental state characterized by a loss of contact with reality.
First-Generation Antipsychotics
Mainly D2 receptor antagonists that also block noradrenergic, cholinergic, and histamine receptors.
Second-Generation Antipsychotics
D2 and 5-HT2 receptor antagonists that increase selectivity, enhancing effect and lowering side effects.
Antidepressants
A class of drugs used to treat depression and related mood disorders.
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Characterized by prolonged feelings of worthlessness and guilt, general slowing of behavior, and frequent thoughts of suicide.
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Block the monoamine oxidase enzyme responsible for the degradation of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Increase the amount of 5-HT in the brain by inhibiting serotonin uptake.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Increase the amount of 5-HT and norepinephrine by blocking the reuptake system.
Therapeutic lag
The 2-3 weeks period indicating that simply elevating serotonin levels alone will not treat depression.