Year 10 Earth and Space: Bigger than Big
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Light year
the distance light travels in one year
galaxy
a giant group of dust, gas, and stars held together by gravity
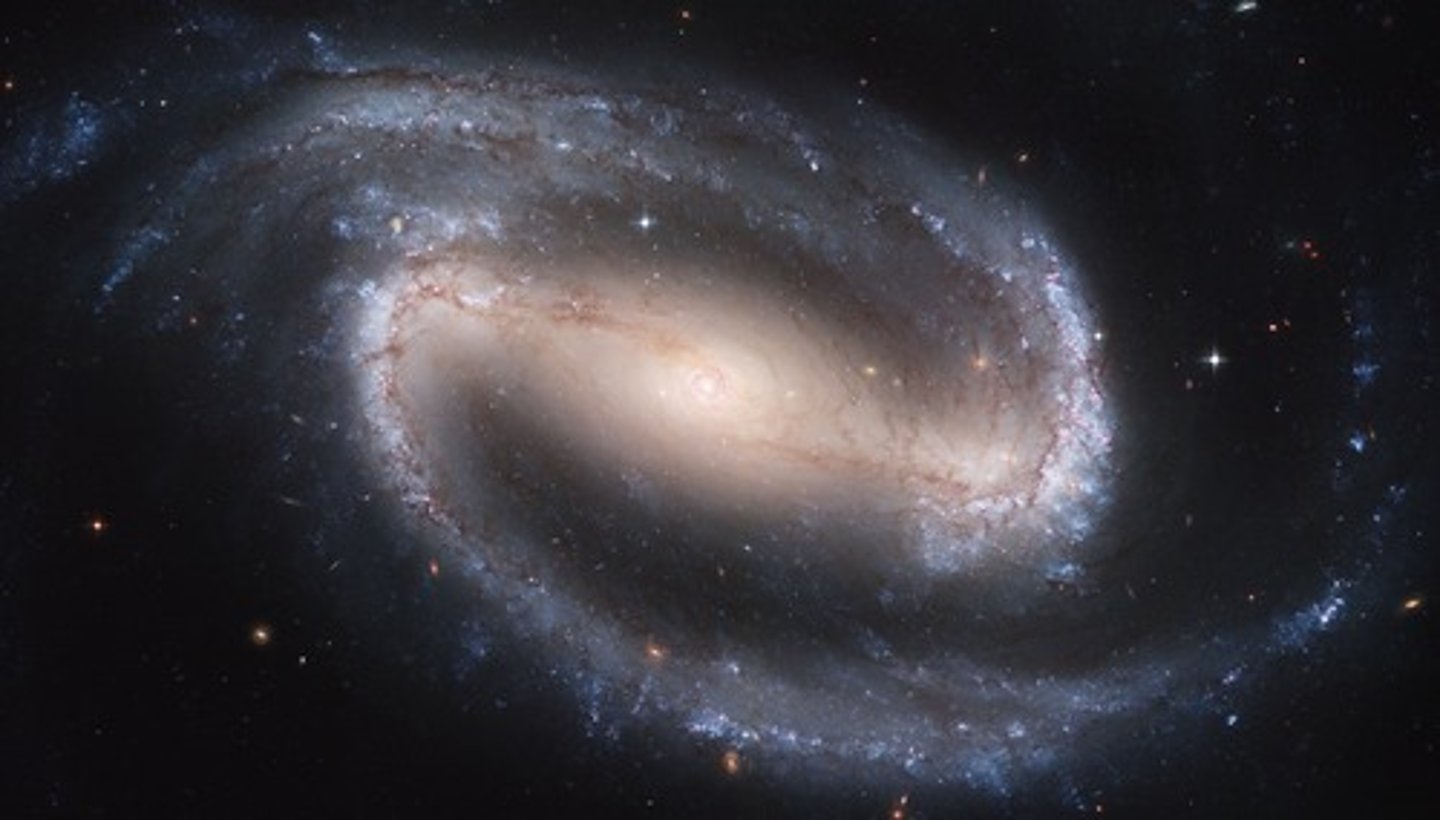

universe
space and all matter in it

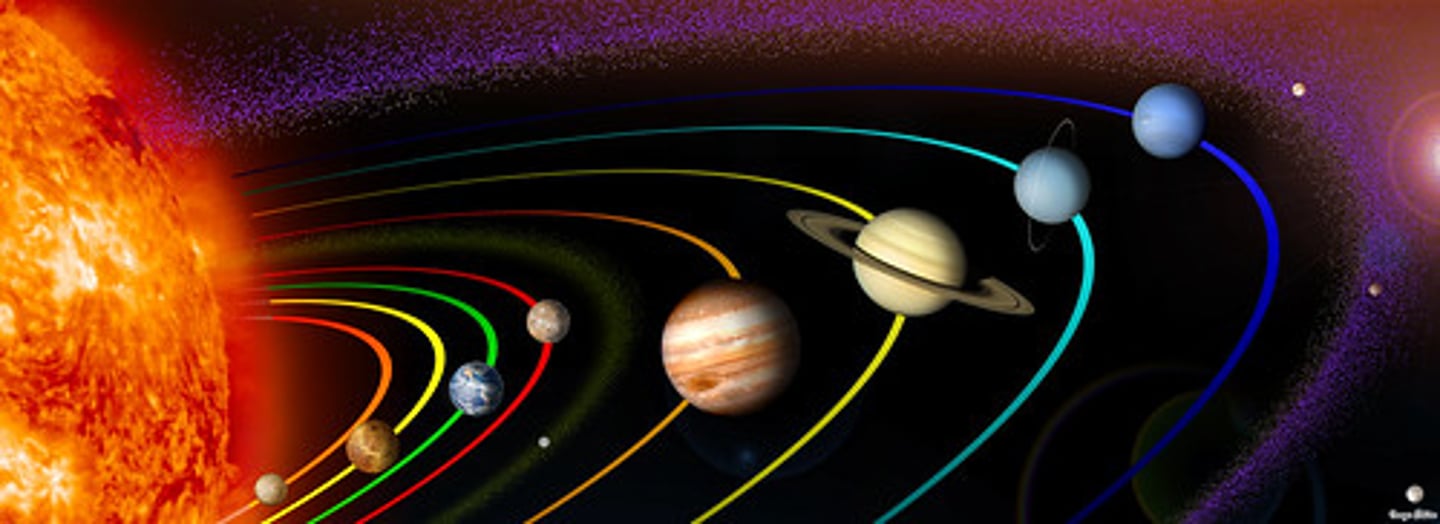
Solar System
a system made up of the Sun, the eight planets and their moons, dwarf planets, and smaller objects
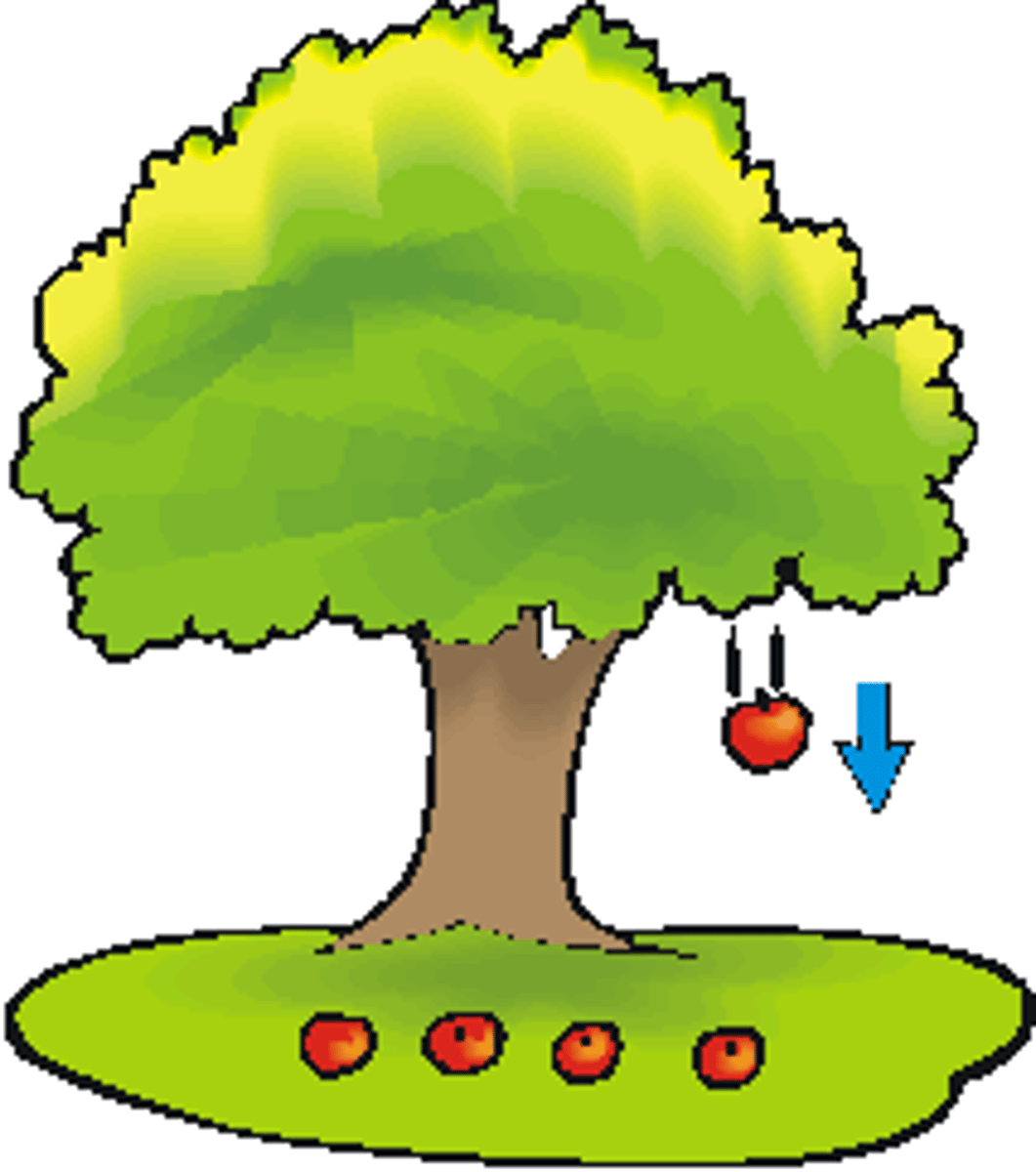
gravity
a force that pulls two objects toward each other
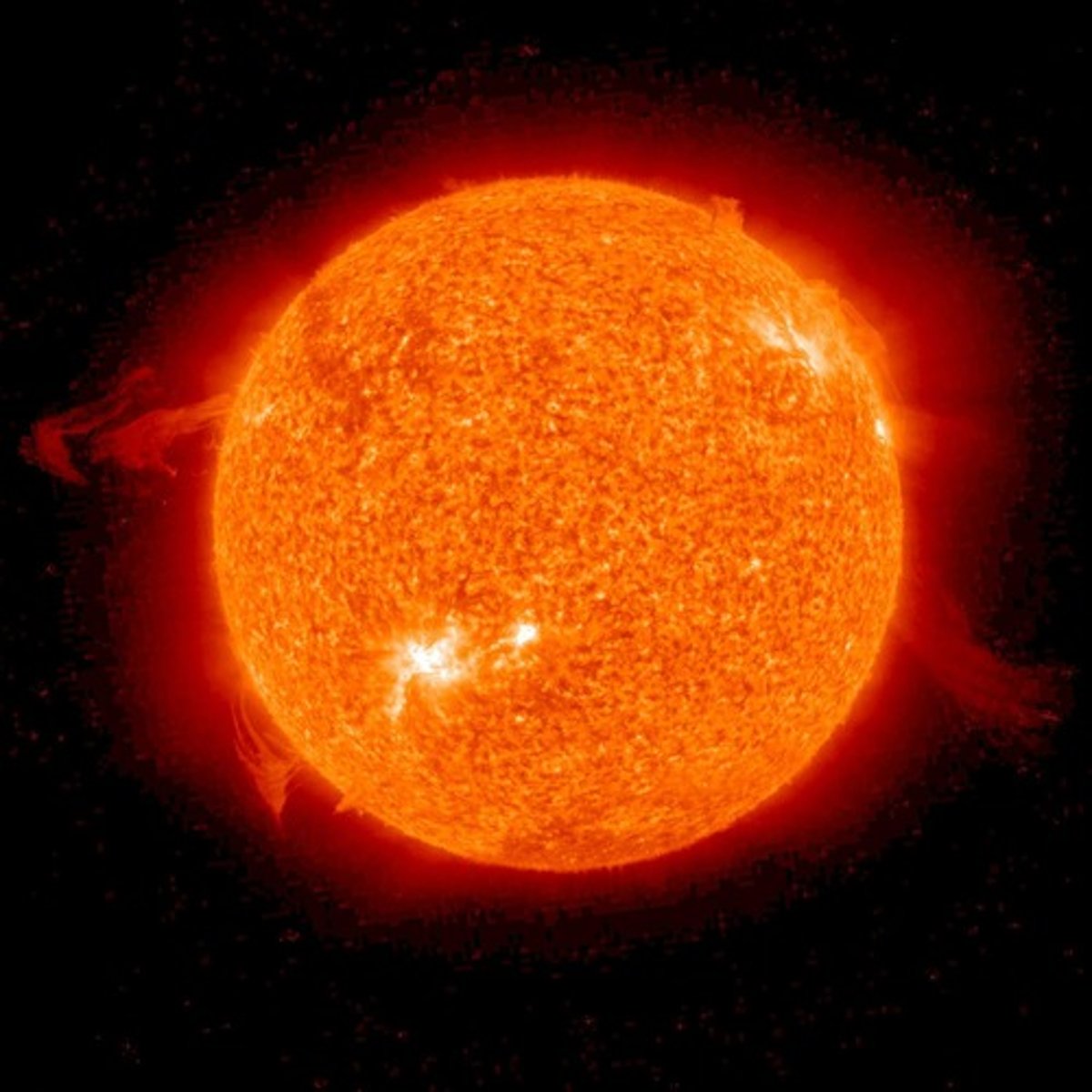
Star
large hot spheres of hydrogen gas powered by nuclear fusion reactions in the core
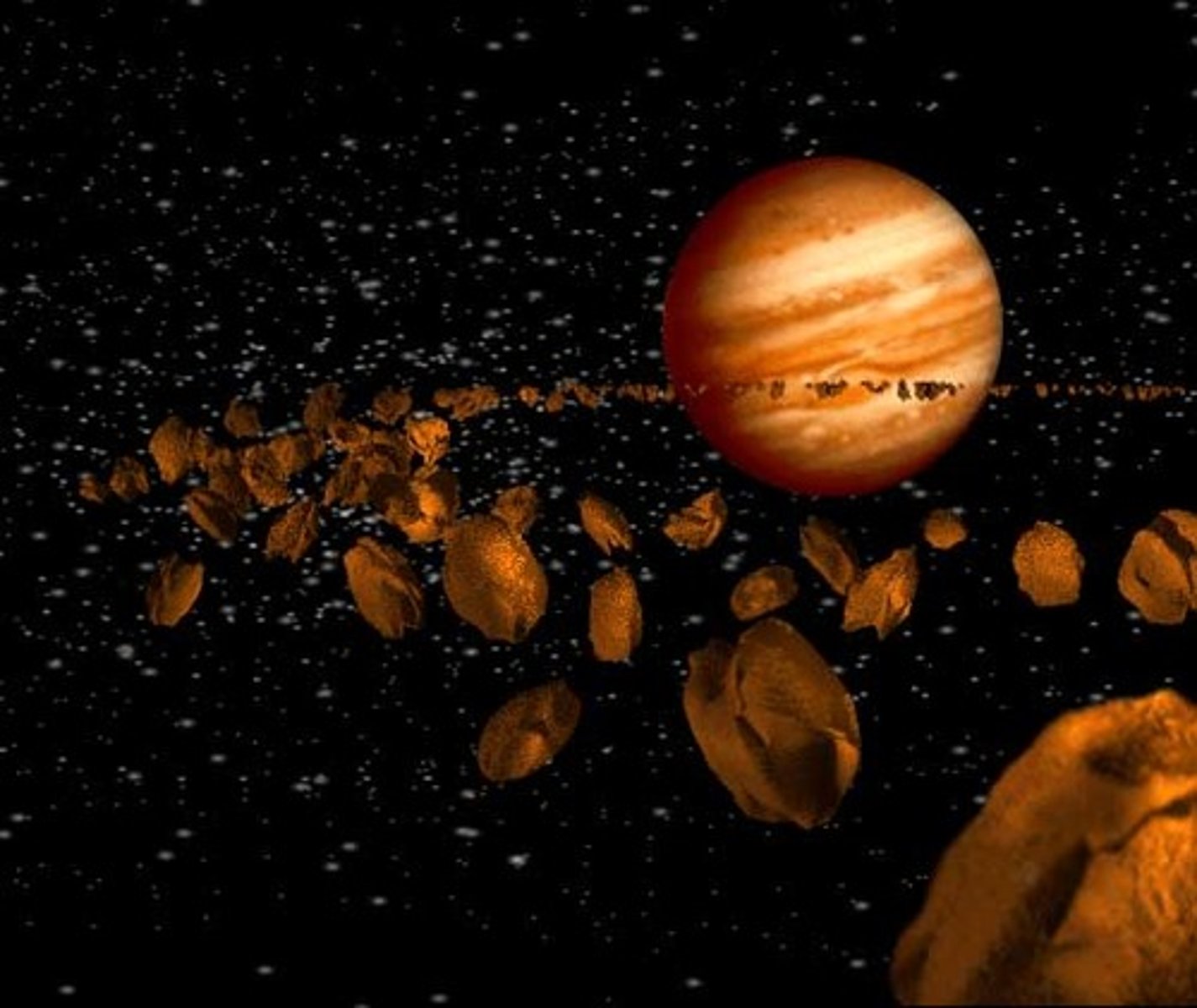
Asteroid belt
an area between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter where most asteroids are located

planet
A large body in space that orbits a star and does not produce light of its own

Moon
an object that orbits a planet or a dwarf planet

outer planet
a planet made up mostly of gases and is called a gas giant
atmosphere
a collection of gases that surround a planet

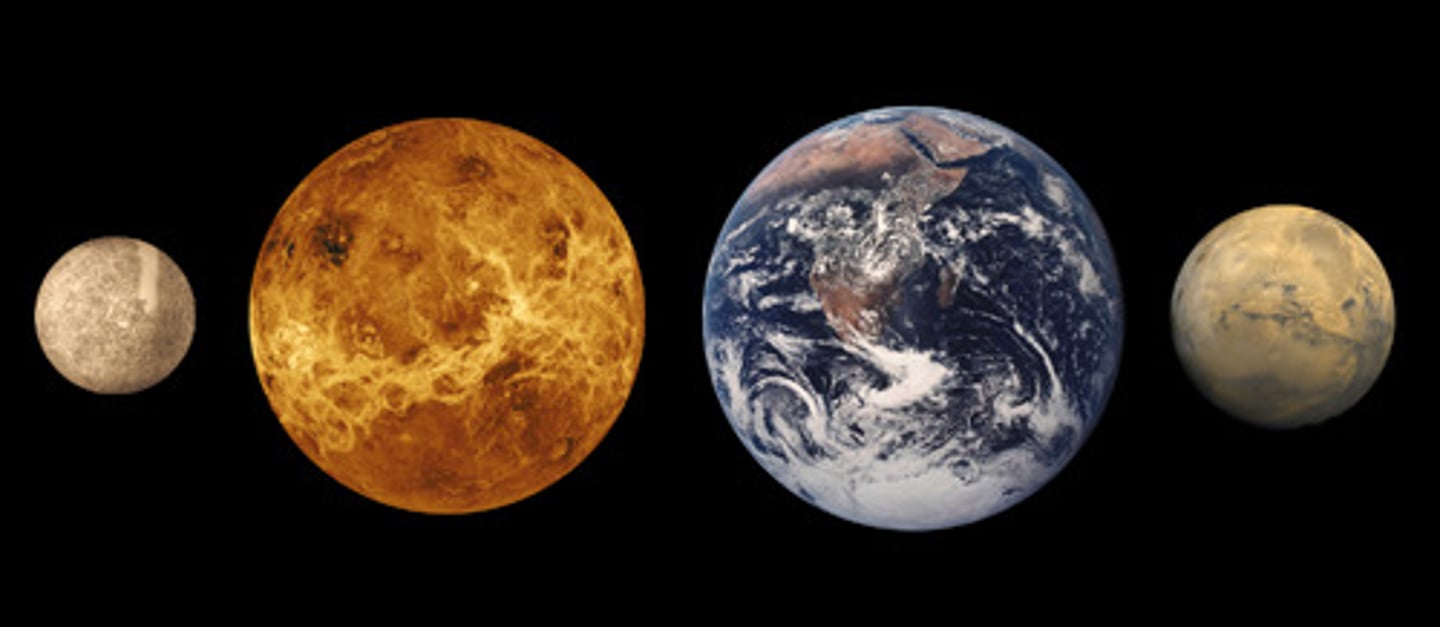
inner planet
a planet made up of rocks or metals with a solid surface

Galaxy
a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held together by gravitational attraction.
Astronomical Unit
The average distance between Earth and the sun, about 150 million kilometers
neutron star
a star that has collapsed under gravity to the point that the electrons and protons have smashed together to form neutrons
Black hole
An object whose gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
White Dwarf
A small, hot, dim star that is the leftover center of an old star
red giant
A star that expands and cools once it runs out of hydrogen fuel
supernova
A gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses and throws its outer layers into space
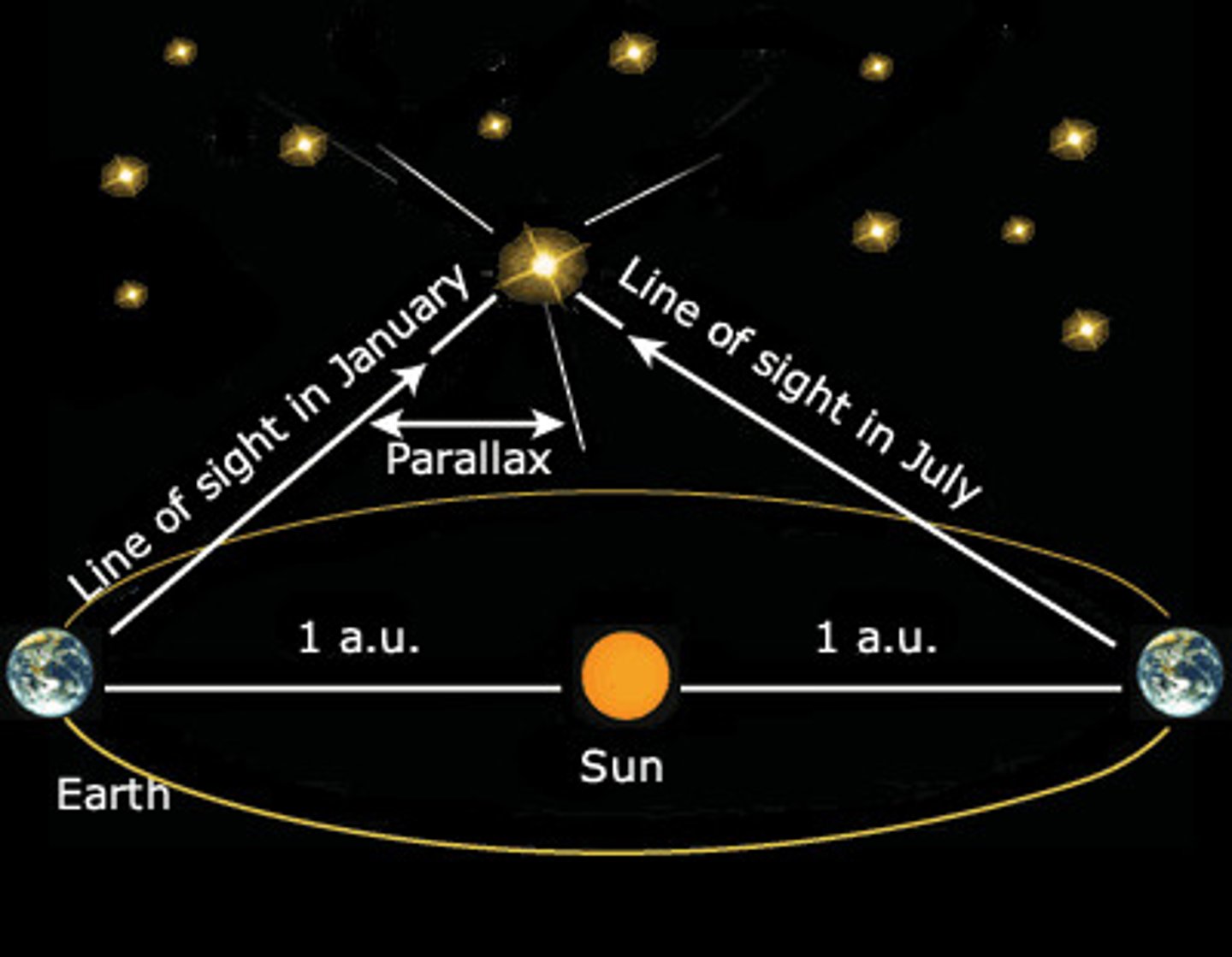
Parallax method
A method for measuring the distances to nearby stars that relies on the fact that a star appears displaced relative to the background of distant stars when viewed from two different positions in space. Satellites orbit outside the Earth's atmosphere can measure distances up to almost 1000 pc in this way.
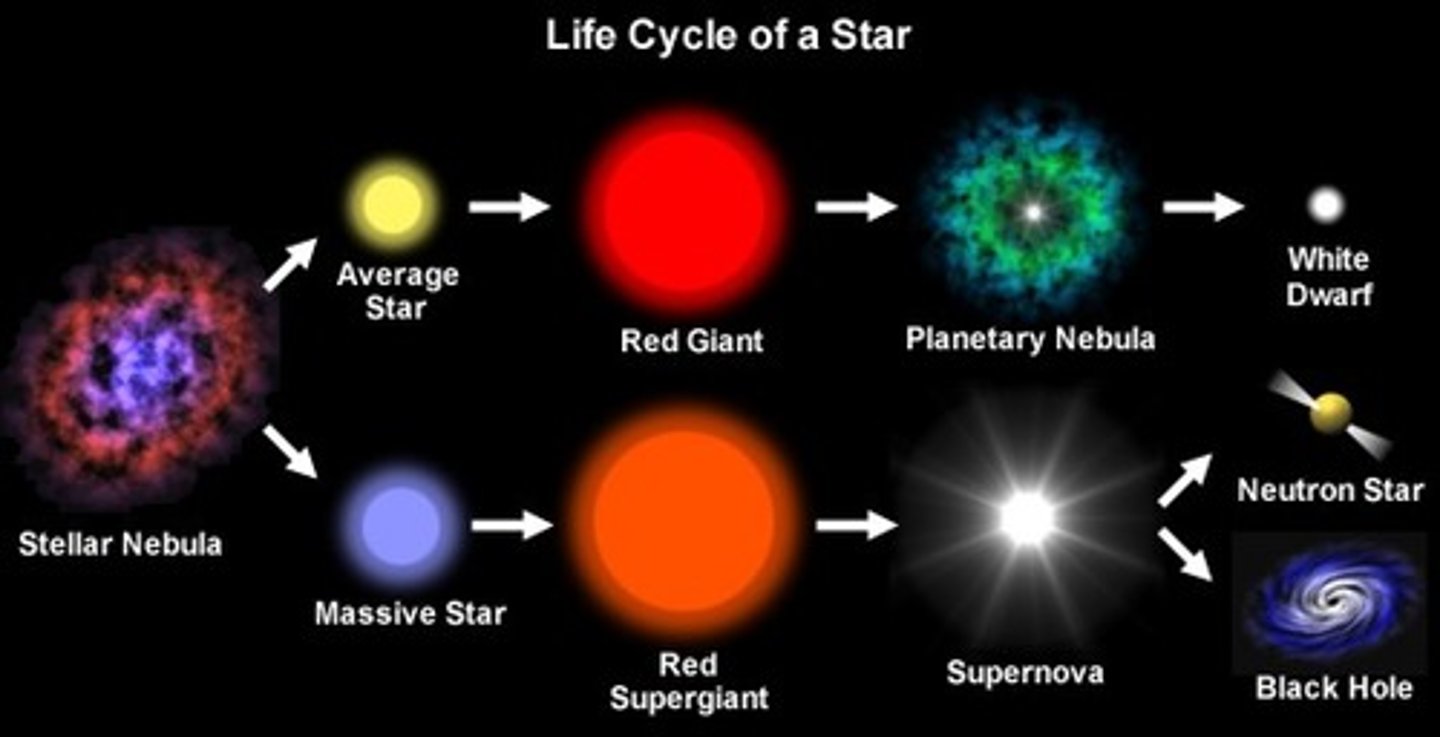
Supernova
A gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses and throws its outer layers into space
Edwin Hubble
Provided evidence on: expansion of the universe; that galaxies exist outside of the milky way;
classification system for galaxies.

radiotelescope
a telescope that picks up sound waves from very distant stars
space telescope
Telescopes in orbit above Earth's atmosphere.
telescope
A device built to observe distant objects by making them appear closer
Infra-red
This has wavelengths that are longer than visible light, and can be felt as heat.
infrared telescope
Telescope designed to detect infrared radiation
Big Bang Theory
Cosmological model that explains the sudden development of the universe through expansion from a hot, dense state.
Steady State Theory
a theory which states that there was no beginning to the universe and that the universe does not change in appearance.
Life cycle of a star
the series of events that occurs in the life of any star
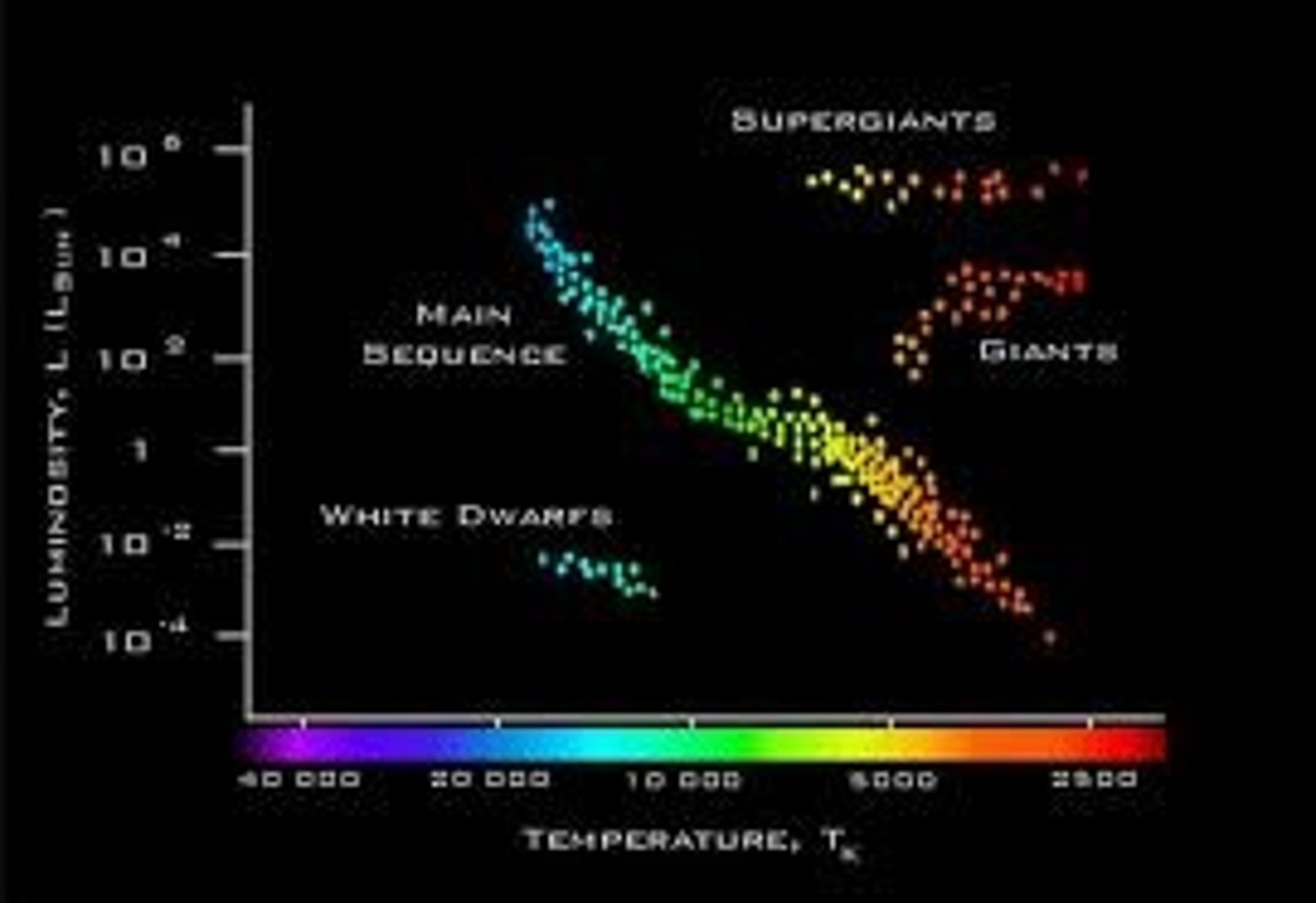
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
organizes the family of stars into a diagram; across bottom is star's temperature and side is star's absolute magnitude; a star's temperature and color depend on how big the star is
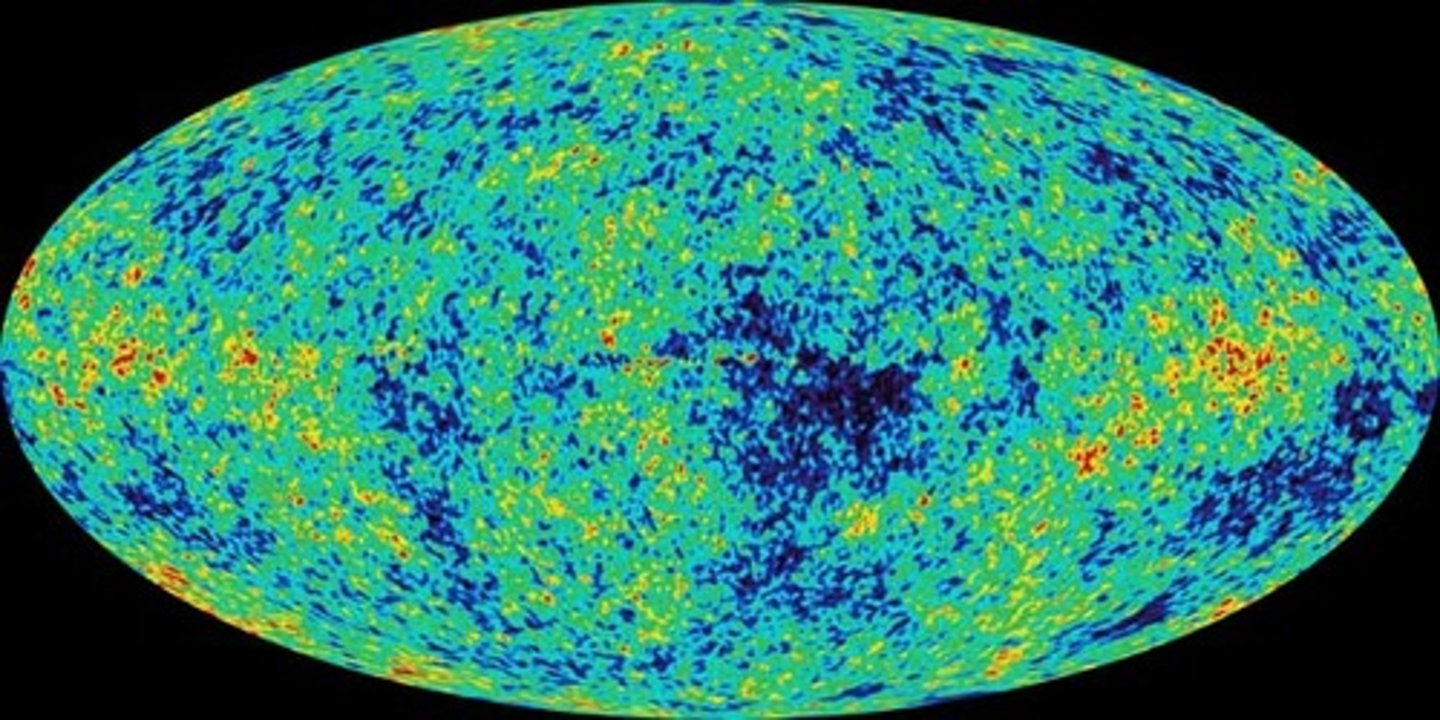
cosmic radiation
Naturally occurring background radiation from outer space.
Evidence for Big Bang Theory
greenhouse effect
warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere
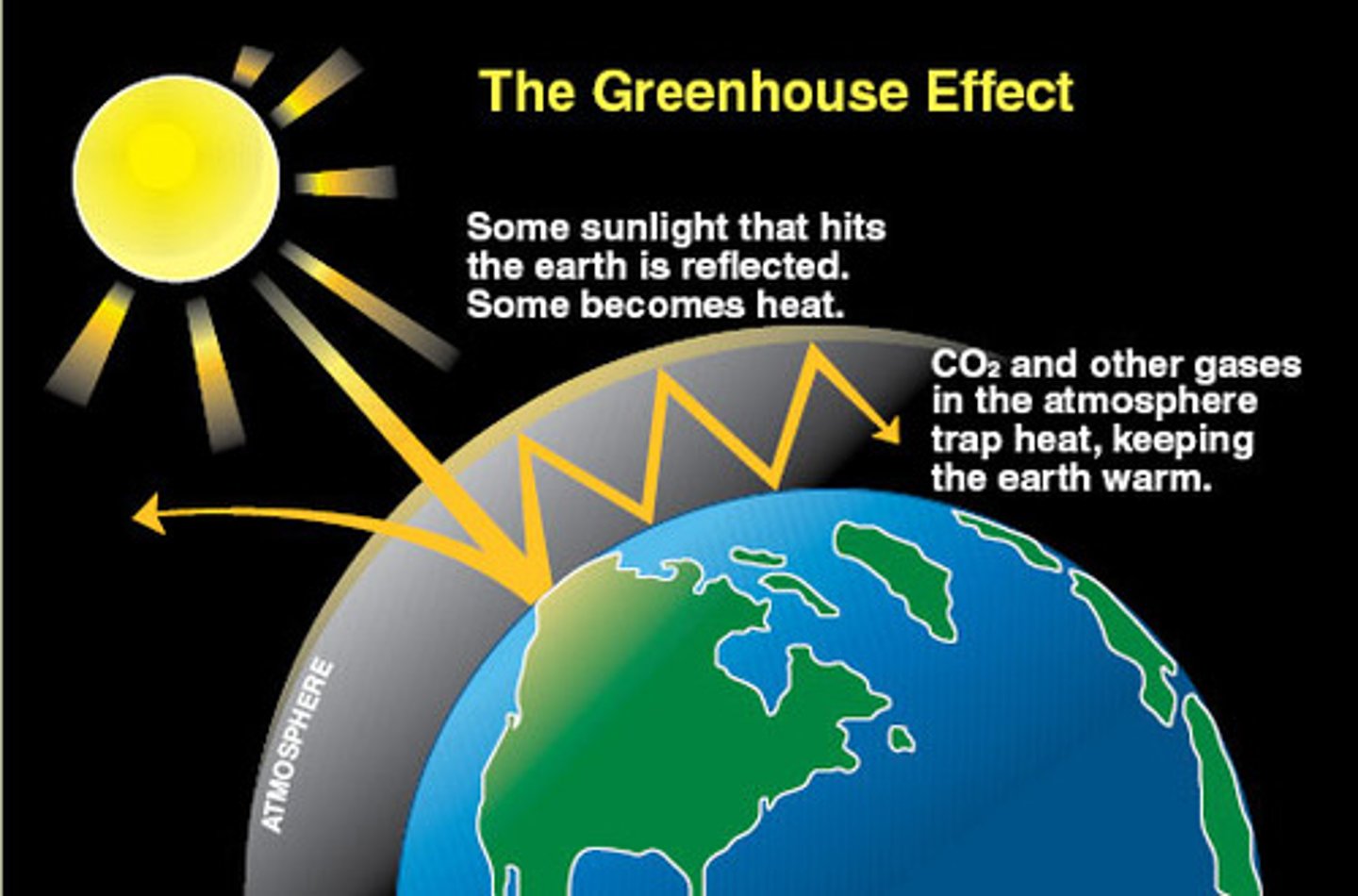
climate change (global warming)
A rise in the average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans. It is caused by increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, resulting from human activities such as deforestation and burning of fossil fuels.

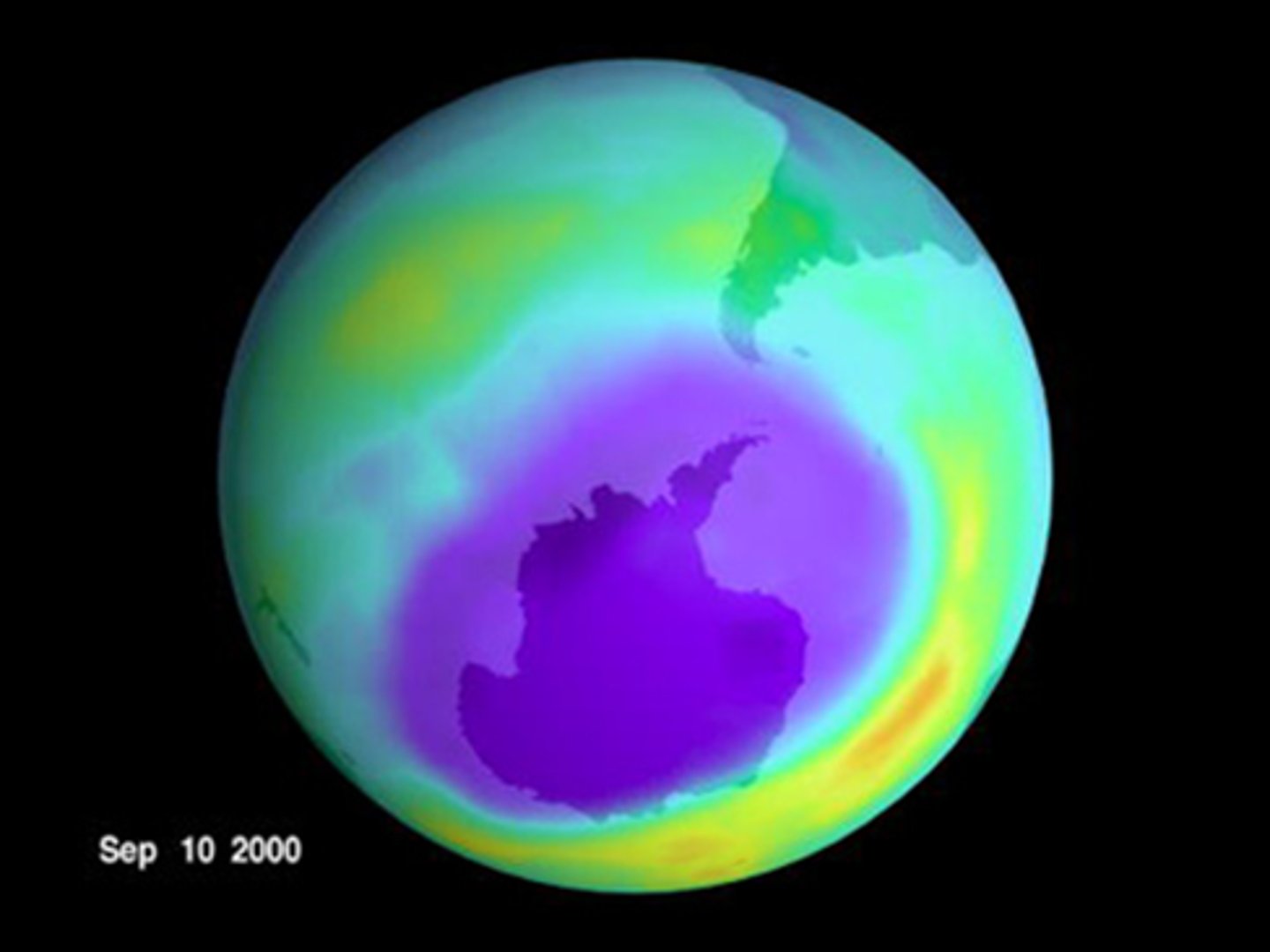
ozone layer depletion
loss of ozone molecules in atmosphere resulting in increase in harmful solar radiation reaching ground level
loss of biodiversity
declining number and variety of the species in an area
rising sea levels
(n) the increased height of the level of seas and oceans

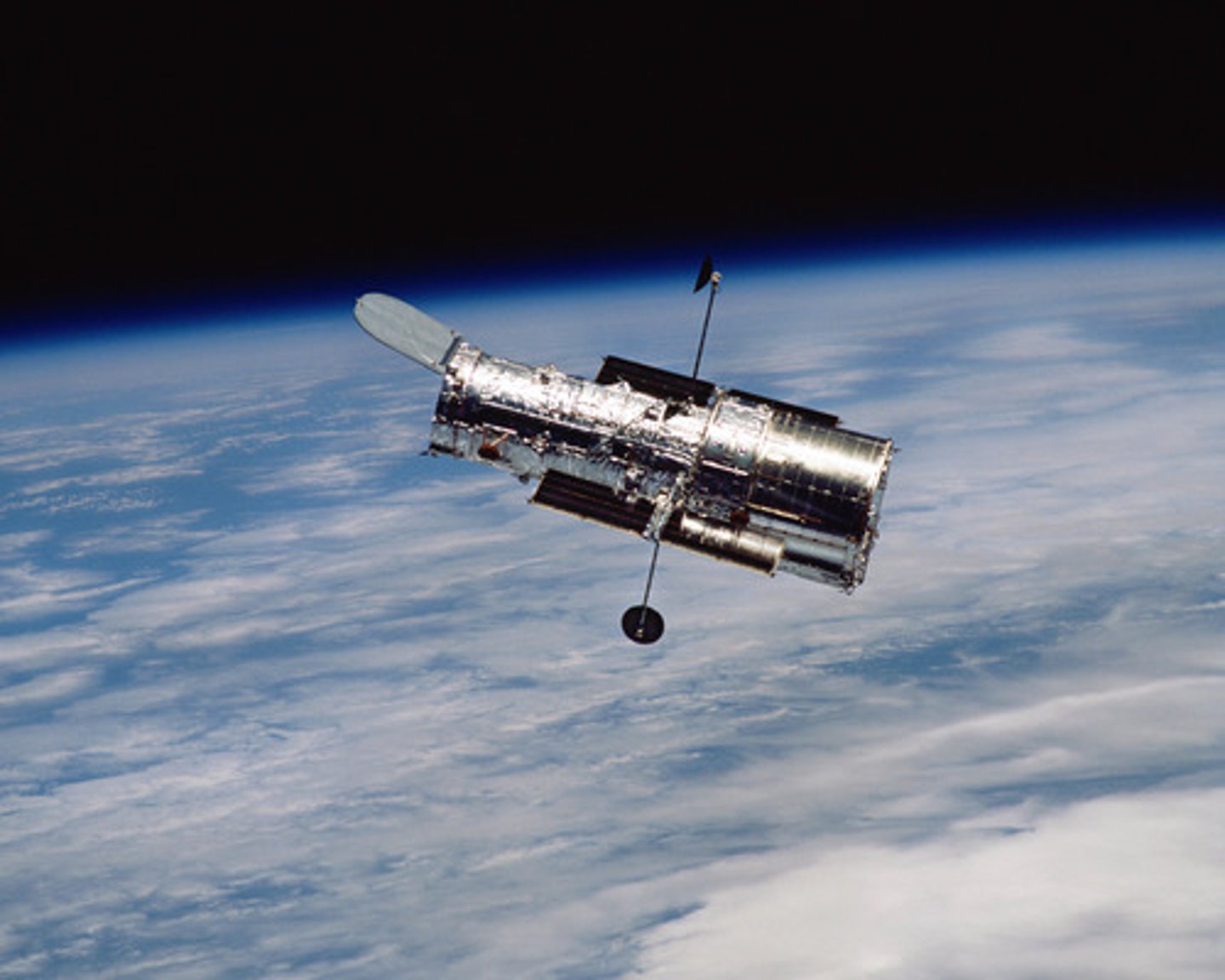
Describe the Hubble Telescope
- Technology - space telescope
- Launched 1990 with regular service updates.
- 515km from Earth
- High clarity images due to being outside of atmospheric particle refraction.
- High level of sensitivity due to being outside of light pollution.
- Detects Ultraviolet, Visible, near-infrared electromagnetic energy waves.
- Hubble deep field has extended aperture (23 days)
- Fine Guidance Sensors keep Hubble focused on a single target area, increasing the clarity of images.

Outline the evidence for the Big Bang Theory that explains the origin of the universe.
1. Data showing galaxies continuing to move further away from each other (Hubble - 1920).
2. Background cosmic radiation (Penzias and Wilson - 1960)
How old is the MIlky Way Galaxy?
13.62 billion years
How many stars are estimated to be in the MIlky Way Galaxy?
100 billion
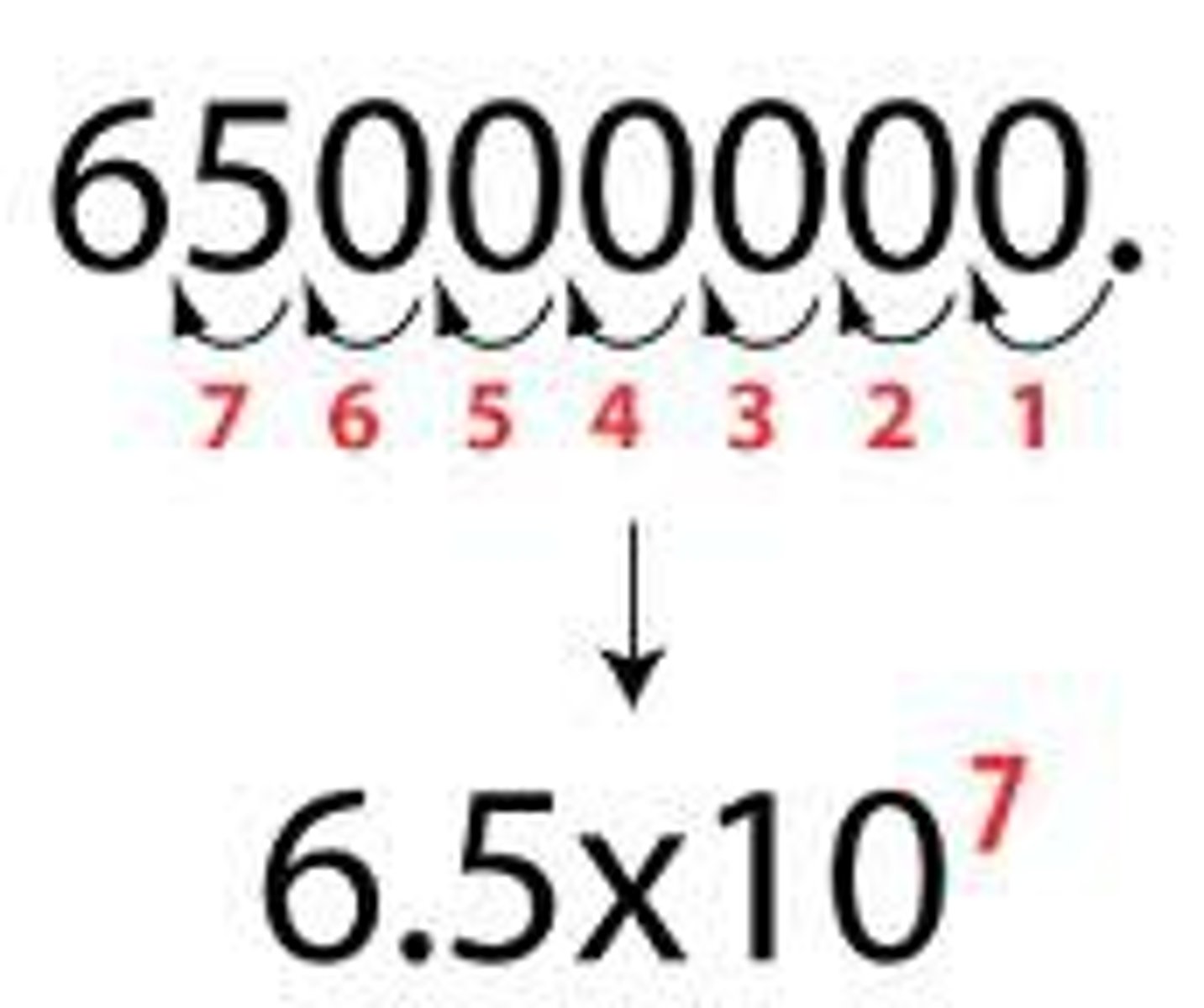
Convert 340 0800 000 to scientific notation
3.4 x 10^8
Why do astrophysicist use the measurement of light years rather than kilometers?
The vast nature of space reduces the need for fine precision units such as the metre. By using Light Years (ly) as a scientific unit, the number of significant numbers is reduced and there is less error in communication.