NMAT Chem
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Density
Mass per unit volume
Specific gravity
Can be used to determine if object will sink or float
Intensive property
Properties that does not depend on the amount of matter in a substance; value doesn’t change no matter how many or few
Boiling point
Intensive property; temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor
Extensive property
Properties that depend on the amount of matter in a substance
Chemical property
Properties that are determined without changing the identity of the substance; dependent on the composition
Solubility
Maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a particular solvent under specific conditions; often expressed as a ratio or other measures of concentration
Unsaturated
Contains less solute than the solvent is capable of dissolving under the given conditions; amount dissolved is less than maximum
Saturated
Contains the maximum quantity of solute that is normally possible at a given temperature; not all will be dissolved
Supersaturated
Contains more solute than normally expected for a saturated solution; amount of solute is more than maximum; can only be achieved if you alter or lower the solubility
Molarity
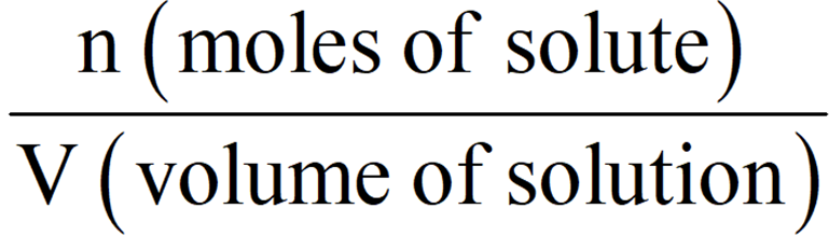
Protons
Positively charged sub-atomic particle with a mass of 1.67×10-27 kg
Neutrons
Neutral charge and has a mass of 1.67×10-27 kg
Electrons
Negatively charged particles with a mass of 9.11×10-31 kg that is considered to be negligible; not in nucleus; lightest mass
Atomic number
Equal to the number of protons
Mass number
Equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons
Charge
Equal to the difference between number of protons and the number of electrons
Atomic weight
Weighted average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of that particular element
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element but have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons, thus different mass number
Isotones
Elements with the same number of neutrons
Isobars
Atomic species having the same mass number but different atomic number
Isoelectronic
Elements having the same number of electrons
Metals
Gives electrons; highly conductive for heat and electricity
Nonmetals
Receives electrons; poor conductors; high electronegativities and ionization energies
Aufbau principle
Electrons occupy lowest energy orbitals and builds up
Hund’s rule
Electrons occupy empty orbitals before doubling
Ionic bonds
Transfer of electrons
Covalent bonds
Sharing of electrons
Dipole-dipole & Hydrogen bonding
Strongest electrostatic interactions
Ideal gas equation
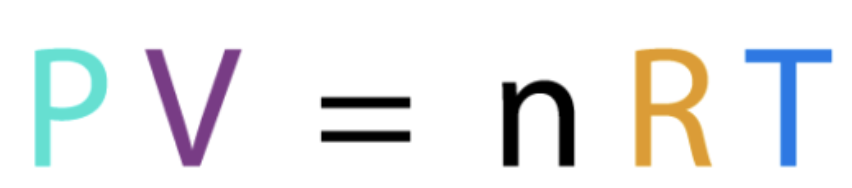
Synthesis
Two or more elements or compounds combine to make a more complex substance
Decomposition
Compounds break down into simpler substances
Single replacement
Occurs when one element replaces another in a compound
Double replacement
Occurs when different atoms in two different compounds trade places
Oxidation
Loss of electrons
Reduction
Gain of electrons
Limiting reagent
Reactant that is first to be totally consumed halting further reactions
Excess reagent
Reactant that is left when the limiting reagent is consumed
Enthalpy
Total energy of an object or system
Endothermic
Reactions require addition of energy; product has higher enthalpy than reactant
Exothermic
Reactions require removal of energy; product has a lower enthalpy than reactant
Spontaneous reactions
Reactions that require a very small activation energy and can start without external interference
Le chatelier’s principle
When an equilibrium system is subjected to a change in temperature, pressure, or concentration of a reacting species, the system responds by attaining a new equilibrium that partially offsets the impact of the change
Arrhenius acid
H+ producer
Arrhenius base
OH- producer
Brønsted-lowry acid
H+ donor
Brønsted-lowry base
H+ acceptor
Lewis acid
Electron-pair acceptor
Lewis base
Electron-pair donor
Acids
Sour in taste; corrosive to most metals
Bases
Bitter in taste; slippery to the touch
Titrant
Substance with known concentration to be added
Analyte
Substance whose unknown concentration is to be determined
Indicator
Substance that changes property under certain conditions to signal when to stop adding the titrant
Equivalence point
Added titrant neutralizes the analyte
End point
Point when the pH changes the color of the indicator